Featured
-
-
Article |
 A chromatin activity-based chemoproteomic approach reveals a transcriptional repressome for gene-specific silencing
A chromatin activity-based chemoproteomic approach reveals a transcriptional repressome for gene-specific silencing
Immune cell pro-inflammatory gene expression is suppressed following prolonged stimulation. Using a chemoproteomic approach, the authors show that methyltransferase G9a forms a protein complex that promotes the transcriptional repressor activity of c-Myc to repress inflammation-induced gene expression.
- Cui Liu
- , Yanbao Yu
- & Xian Chen
-
Article |
 Proteome adaptation in cell reprogramming proceeds via distinct transcriptional networks
Proteome adaptation in cell reprogramming proceeds via distinct transcriptional networks
During somatic cell reprogramming, the cell transits through intermediate states. Here, the authors perform an in-depth quantitative proteomic analysis of the reprogramming of mouse embryonic fibroblasts to induced pluripotent stem cells and observe two waves of proteome reorganisation.
- Marco Benevento
- , Peter D. Tonge
- & Albert J. R. Heck
-
Article |
 MS-GF+ makes progress towards a universal database search tool for proteomics
MS-GF+ makes progress towards a universal database search tool for proteomics
The development of software tools to analyse large mass spectrometry data sets lags behind the increase in diversity of the data. Here the authors develop MS-GF+, a database search tool that outperforms other popular tools in identifying peptides from a variety of data sets.
- Sangtae Kim
- & Pavel A. Pevzner
-
Article
| Open Access Global profiling of co- and post-translationally N-myristoylated proteomes in human cells
Global profiling of co- and post-translationally N-myristoylated proteomes in human cells
Protein N-myristoylation is a ubiquitous modification implicated in the regulation of multiple cellular processes. Here, Thinon et al. report the development of a general method to identify N-myristoylated proteins in human cells and identify over 100 endogenous post- and co-translational substrates of N-myristoyltransferase.
- Emmanuelle Thinon
- , Remigiusz A. Serwa
- & Edward W. Tate
-
Article |
 An optimized optogenetic clustering tool for probing protein interaction and function
An optimized optogenetic clustering tool for probing protein interaction and function
Protein–protein interactions are fundamental to nearly all molecular and cellular processes. Here Taslimi et al.describe a versatile new optogenetic module that can be used to visualize protein–protein interactions, as well as reversibly control them with light with spatiotemporal resolution.
- Amir Taslimi
- , Justin D. Vrana
- & Chandra L. Tucker
-
Article |
 Site-specific mapping and quantification of protein S-sulphenylation in cells
Site-specific mapping and quantification of protein S-sulphenylation in cells
Cysteine S-sulphenylation provides redox regulation of protein functions, but the extent of this post-translational modification in cells is unknown. Here, Yang et al. develop a method to detect hundreds of S-sulphenylation sites in cells, and show that many of them respond to a physiologically relevant redox stimulus.
- Jing Yang
- , Vinayak Gupta
- & Daniel C. Liebler
-
Article
| Open Access Super-resolution imaging and tracking of protein–protein interactions in sub-diffraction cellular space
Super-resolution imaging and tracking of protein–protein interactions in sub-diffraction cellular space
Protein–protein interactions are ubiquitous in cells and these contacts are crucial for a wide number of cellular processes. Here, the authors present a technique for the super-resolution imaging and tracking of protein–protein interactions in cells.
- Zhen Liu
- , Dong Xing
- & Yujie Sun
-
Article |
 A pan-cancer proteomic perspective on The Cancer Genome Atlas
A pan-cancer proteomic perspective on The Cancer Genome Atlas
Analyses of genome and transcriptome data are unable to accurately predict protein levels and function in tumour samples. Here, the authors carry out a comprehensive protein analysis in 3,467 samples from the cancer genome atlas, providing a resource to study the prognostic and therapeutic potential of tumour proteins.
- Rehan Akbani
- , Patrick Kwok Shing Ng
- & Gordon B. Mills
-
Article
| Open Access Protein interaction network of alternatively spliced isoforms from brain links genetic risk factors for autism
Protein interaction network of alternatively spliced isoforms from brain links genetic risk factors for autism
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a complex genetic trait that encompasses a range of neurodevelopmental disorders. Here, the authors clone brain-expressed alternatively-spliced isoforms of ASD risk factors and construct a network of protein interactions that provides further insight into the disease aetiology.
- Roser Corominas
- , Xinping Yang
- & Lilia M. Iakoucheva
-
Article
| Open Access SILAC-based proteomic quantification of chemoattractant-induced cytoskeleton dynamics on a second to minute timescale
SILAC-based proteomic quantification of chemoattractant-induced cytoskeleton dynamics on a second to minute timescale
Actin-dependent motility is driven by the rapid changes in the recruitment of many different structural and regulatory proteins at the cell’s cortex. Sobczyk et al. characterize these changes in the cytoskeletal proteome on a second to minute timescale during chemotactic response in Dictyosteliumusing SILAC-based proteomics.
- Grzegorz J. Sobczyk
- , Jun Wang
- & Cornelis J. Weijer
-
Article
| Open Access Retinoic acid receptor alpha is associated with tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer
Retinoic acid receptor alpha is associated with tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer
Many patients with breast cancer develop resistance to the drug tamoxifen and relapse. Here Johansson et al. identify the nuclear receptor retinoic acid receptor alpha (RARA) as a marker of tamoxifen resistance and show that RARA expression correlates negatively with relapse-free survival of patients.
- Henrik J. Johansson
- , Betzabe C. Sanchez
- & Janne Lehtiö
-
Article |
 Genome-scale proteome quantification by DEEP SEQ mass spectrometry
Genome-scale proteome quantification by DEEP SEQ mass spectrometry
The complexity and dynamic range of mammalian proteomes has stymied comprehensive protein quantification for the past twenty years. Zhou et al. develop DEEP SEQ mass spectrometry and use it to quantify a murine stem cell proteome to a depth equivalent to RNA-seq-based ribosome profiling.
- Feng Zhou
- , Yu Lu
- & Jarrod A. Marto
-
Article |
 Identifying sources of tick blood meals using unidentified tandem mass spectral libraries
Identifying sources of tick blood meals using unidentified tandem mass spectral libraries
The identification of hosts of blood-sucking insects is important for studying ecological factors that affect pathogen distribution. Önder et al. report a proteomics-based methodology for the analysis of blood remnants in ticks that identifies the host species from which the tick has fed up to 6 months earlier.
- Özlem Önder
- , Wenguang Shao
- & Dustin Brisson
-
Article
| Open Access Proteome-wide selected reaction monitoring assays for the human pathogen Streptococcus pyogenes
Proteome-wide selected reaction monitoring assays for the human pathogen Streptococcus pyogenes
Selected reaction monitoring mass spectrometry (SRM-MS) can quantify dynamic changes in protein expression with high sensitivity. Karlsson et al. define optimal detection parameters for 10,412 distinct group A Streptococcus pyogenespeptides, which facilitates proteome-wide SRM-MS studies in this bacterium.
- Christofer Karlsson
- , Lars Malmström
- & Johan Malmström
-
Article |
 Cholesterol modulates cell signaling and protein networking by specifically interacting with PDZ domain-containing scaffold proteins
Cholesterol modulates cell signaling and protein networking by specifically interacting with PDZ domain-containing scaffold proteins
Cholesterol indirectly regulates intracellular signalling by modulating the physical properties of lipid membranes. Sheng et al.now show that many PDZ domains contain a functional cholesterol-binding motif, revealing that cholesterol can also control the localization and function of signalling proteins directly.
- Ren Sheng
- , Yong Chen
- & Wonhwa Cho
-
Article
| Open Access Global kinomic and phospho-proteomic analyses of the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum
Global kinomic and phospho-proteomic analyses of the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum
New approaches are required to combatPlasmodium falciparuminfection. In this proteome-wide study, 1305 phosphorylation sites are identified and 36 kinases are shown to have crucial roles in parasite survival, providing new insights into parasite biology and potential new drug targets for anti-malarial chemotherapy.
- Lev Solyakov
- , Jean Halbert
- & Christian Doerig
-
Article |
 Plasmonic substrates for multiplexed protein microarrays with femtomolar sensitivity and broad dynamic range
Plasmonic substrates for multiplexed protein microarrays with femtomolar sensitivity and broad dynamic range
Protein microarrays are useful both in basic research and also in disease monitoring and diagnosis, but their dynamic range is limited. By using plasmonic gold substrates with near-infrared fluorescent enhancement, Tabakman et al. demonstrate a multiplexed protein array with improved detection limits and dynamic range.
- Scott M. Tabakman
- , Lana Lau
- & Hongjie Dai
-
Article
| Open Access Systems-wide temporal proteomic profiling in glucose-starved Bacillus subtilis
Systems-wide temporal proteomic profiling in glucose-starved Bacillus subtilis
Identifying the transcripts and proteins that fluctuate in response to stimuli provides important information for understanding cell physiology. In this study, 52% of theBacillus subtilispredicted proteome is identified following glucose starvation, revealing further insight into protein dynamics at a global scale.
- Andreas Otto
- , Jörg Bernhardt
- & Dörte Becher
-
Article |
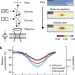 Protein-binding assays in biological liquids using microscale thermophoresis
Protein-binding assays in biological liquids using microscale thermophoresis
Protein interactions in biological environments are expected to differ from the situationin vitro. In this study, a thermophoresis-based technique is described that allows the analysis of protein and small-molecule interactions in biological liquids; the work may allow more efficient drug development.
- Christoph J. Wienken
- , Philipp Baaske
- & Stefan Duhr

 Tumour suppressor TRIM33 targets nuclear β-catenin degradation
Tumour suppressor TRIM33 targets nuclear β-catenin degradation