Featured
-
-
Outlook |
 The RNA and protein landscape that could bring precision medicine to more people
The RNA and protein landscape that could bring precision medicine to more people
The limitations of genomic data have led to a deeper exploration of transcriptomic and proteomic data in cancer.
- Simon Makin
-
Article |
 Ageing hallmarks exhibit organ-specific temporal signatures
Ageing hallmarks exhibit organ-specific temporal signatures
Bulk RNA sequencing of organs and plasma proteomics at different ages across the mouse lifespan is integrated with data from the Tabula Muris Senis, a transcriptomic atlas of ageing mouse tissues, to describe organ-specific changes in gene expression during ageing.
- Nicholas Schaum
- , Benoit Lehallier
- & Tony Wyss-Coray
-
Article |
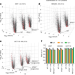 Systematic quantitative analysis of ribosome inventory during nutrient stress
Systematic quantitative analysis of ribosome inventory during nutrient stress
During nutrient stress, ribosomal protein abundance is regulated primarily by translational and non-autophagic degradative mechanisms, but ribosome density per cell is largely maintained by reductions in cell volume and rates of cell division.
- Heeseon An
- , Alban Ordureau
- & J. Wade Harper
-
Article |
 The proteome landscape of the kingdoms of life
The proteome landscape of the kingdoms of life
An advanced proteomics workflow is used to identify 340,000 proteins from 100 taxonomically diverse species, providing a comparative view of proteomes across the evolutionary range.
- Johannes B. Müller
- , Philipp E. Geyer
- & Matthias Mann
-
Article |
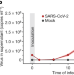 Proteomics of SARS-CoV-2-infected host cells reveals therapy targets
Proteomics of SARS-CoV-2-infected host cells reveals therapy targets
SARS-CoV-2 modulates central cellular pathways, such as translation, splicing, carbon metabolism, proteostasis and nucleic acid metabolism, in human cells; these pathways can be inhibited by small-molecule inhibitors to prevent viral replication in the cells.
- Denisa Bojkova
- , Kevin Klann
- & Christian Münch
-
Article |
 A SARS-CoV-2 protein interaction map reveals targets for drug repurposing
A SARS-CoV-2 protein interaction map reveals targets for drug repurposing
A human–SARS-CoV-2 protein interaction map highlights cellular processes that are hijacked by the virus and that can be targeted by existing drugs, including inhibitors of mRNA translation and predicted regulators of the sigma receptors.
- David E. Gordon
- , Gwendolyn M. Jang
- & Nevan J. Krogan
-
Technology Feature |
 Exposed: cells’ sugary secrets
Exposed: cells’ sugary secrets
Researchers are finally uncovering the truth about glycans — the sugar-based chains that coat cells and decorate many proteins.
- Jyoti Madhusoodanan
-
Article |
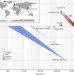 Enamel proteome shows that Gigantopithecus was an early diverging pongine
Enamel proteome shows that Gigantopithecus was an early diverging pongine
The enamel proteome from a 1.9-million-year-old Gigantopithecus tooth shows that the Gigantopithecus and Pongo (orangutan) lineages diverged 12–10 million years ago.
- Frido Welker
- , Jazmín Ramos-Madrigal
- & Enrico Cappellini
-
Article |
 Metabolic regulation of gene expression by histone lactylation
Metabolic regulation of gene expression by histone lactylation
The lactylation of lysine residues on histones in mammalian cells is stimulated by hypoxia and bacterial challenges, and increased histone lactylation induces genes involved in wound healing.
- Di Zhang
- , Zhanyun Tang
- & Yingming Zhao
-
Letter |
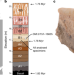 Early Pleistocene enamel proteome from Dmanisi resolves Stephanorhinus phylogeny
Early Pleistocene enamel proteome from Dmanisi resolves Stephanorhinus phylogeny
Palaeoproteomic analysis of dental enamel from an Early Pleistocene Stephanorhinus resolves the phylogeny of Eurasian Rhinocerotidae, by enabling the reconstruction of molecular evolution beyond the limits of ancient DNA preservation.
- Enrico Cappellini
- , Frido Welker
- & Eske Willerslev
-
News Feature |
 Move over, DNA: ancient proteins are starting to reveal humanity’s history
Move over, DNA: ancient proteins are starting to reveal humanity’s history
Proteins dating back more than one million years have been extracted from some fossils, and could help to answer some difficult questions about archaic humans.
- Matthew Warren
-
Editorial |
 The mysterious Denisovans have at last come in from the cold
The mysterious Denisovans have at last come in from the cold
Remains found on the Tibetan Plateau suggest a large hominin adapted to high-altitude life.
-
News |
 Biggest Denisovan fossil yet spills ancient human’s secrets
Biggest Denisovan fossil yet spills ancient human’s secrets
Jawbone from China reveals that the ancient human was widespread across the world — and lived at surprising altitude.
- Matthew Warren
-
Technology Feature |
 Cellular censuses to guide cancer care
Cellular censuses to guide cancer care
In the age of immunotherapy, cancer biologists are relying on a new generation of tools to learn how the interplay between tumours and immune cells shapes the course of disease.
- Michael Eisenstein
-
Letter |
 Proteomics identifies new therapeutic targets of early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma
Proteomics identifies new therapeutic targets of early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma
A subtype of early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma characterized by disrupted cholesterol homeostasis and associated with a poor prognosis responds to treatment with the SOAT1 inhibitor avasimibe in a patient-derived xenograft mouse model.
- Ying Jiang
- , Aihua Sun
- & Zesong Li
-
Letter |
 Subcellular transcriptomes and proteomes of developing axon projections in the cerebral cortex
Subcellular transcriptomes and proteomes of developing axon projections in the cerebral cortex
A subcellular sorting approach enables quantitative analysis of subtypes of growth cones in the brain, and reveals subcellular relationships between local mRNA and local proteomes in developing projection neurons.
- Alexandros Poulopoulos
- , Alexander J. Murphy
- & Jeffrey D. Macklis
-
Research Highlight |
 Prehistoric Europeans feasted on caviar
Prehistoric Europeans feasted on caviar
Pottery fragments hint at how ancient cooks prepared the fishy delicacy.
-
Letter |
 A metabolite-derived protein modification integrates glycolysis with KEAP1–NRF2 signalling
A metabolite-derived protein modification integrates glycolysis with KEAP1–NRF2 signalling
Inhibition of the glycolytic enzyme PGK1 using a small molecular probe reveals a molecular link between glycolysis and the KEAP1–NRF2 signalling cascade.
- Michael J. Bollong
- , Gihoon Lee
- & Raymond E. Moellering
-
Letter |
 An orthogonal proteomic survey uncovers novel Zika virus host factors
An orthogonal proteomic survey uncovers novel Zika virus host factors
Integrative analyses identify host proteins that are modulated by Zika virus at multiple levels and provide a comprehensive framework for the understanding of Zika virus-induced changes to cellular pathways.
- Pietro Scaturro
- , Alexey Stukalov
- & Andreas Pichlmair
-
Letter |
 Cotranslational assembly of protein complexes in eukaryotes revealed by ribosome profiling
Cotranslational assembly of protein complexes in eukaryotes revealed by ribosome profiling
Cotranslational assembly is a prevalent mechanism for the formation of oligomeric complexes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, with one subunit serving as scaffold for the translation of partner subunits.
- Ayala Shiber
- , Kristina Döring
- & Bernd Bukau
-
Letter |
 Quantitative phosphoproteomic analysis of the molecular substrates of sleep need
Quantitative phosphoproteomic analysis of the molecular substrates of sleep need
A subset of synaptic proteins are cumulatively phosphorylated during wakefulness and dephosphorylated during sleep, in accordance with sleep need; this may represent a common mechanism underlying regulation of both synaptic homeostasis and sleep–wake homeostasis.
- Zhiqiang Wang
- , Jing Ma
- & Qinghua Liu
-
Technology Feature |
 Single-cell approaches to immune profiling
Single-cell approaches to immune profiling
Protein- and sequencing-based technologies are helping researchers to profile immune cells ever more deeply.
- Esther Landhuis
-
Technology Feature |
 Protein maps chart the causes of disease
Protein maps chart the causes of disease
Improvements in mapping protein–protein interactions are allowing researchers to deconstruct the delicate mechanics of cells.
- Marissa Fessenden
-
Letter |
 Architecture of the human interactome defines protein communities and disease networks
Architecture of the human interactome defines protein communities and disease networks
Affinity purification–mass spectrometry elucidates protein interaction networks and co-complexes to build, to our knowledge, the largest experimentally derived human protein interaction network so far, termed BioPlex 2.0.
- Edward L. Huttlin
- , Raphael J. Bruckner
- & J. Wade Harper
-
News |
 Living cells bind silicon and carbon for the first time
Living cells bind silicon and carbon for the first time
Modified bacterial enzyme taught to make bonds that evolution avoids.
- Davide Castelvecchi
-
Letter |
 Mechanism of super-assembly of respiratory complexes III and IV
Mechanism of super-assembly of respiratory complexes III and IV
SCAF1 is always required for the interaction between the respiratory chain complexes III and IV, and in animals carrying only the short isoform of SCAF1, the respirasome is absent in most tissues, with the exception of heart and skeletal muscle, where COX7A2 is present instead of SCAF1.
- Sara Cogliati
- , Enrique Calvo
- & José Antonio Enriquez
-
Letter |
 Accessory subunits are integral for assembly and function of human mitochondrial complex I
Accessory subunits are integral for assembly and function of human mitochondrial complex I
Gene-editing technology and large-scale proteomics are used to provide insights into the modular assembly of the human mitochondrial respiratory chain complex I, as well as identifying new assembly factors.
- David A. Stroud
- , Elliot E. Surgenor
- & Michael T. Ryan
-
Article |
 Defining the consequences of genetic variation on a proteome-wide scale
Defining the consequences of genetic variation on a proteome-wide scale
The effect of natural genetic diversity on the proteome is characterized using an outbred mouse model with extensive variation; both transcripts and proteins from mouse livers are quantified to identify a large set of protein quantitative trait loci (pQTL), and mediation analysis identifies causal protein intermediates of distant pQTL.
- Joel M. Chick
- , Steven C. Munger
- & Steven P. Gygi
-
Letter |
 Proteome-wide covalent ligand discovery in native biological systems
Proteome-wide covalent ligand discovery in native biological systems
Small molecules are powerful tools for investigating protein function, and can serve as leads for new therapeutics, but most human proteins lack known small-molecule ligands; here, a quantitative analysis of cysteine-reactive small-molecule fragments screened against thousands of proteins is reported.
- Keriann M. Backus
- , Bruno E. Correia
- & Benjamin F. Cravatt
-
Article |
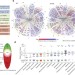 ∆F508 CFTR interactome remodelling promotes rescue of cystic fibrosis
∆F508 CFTR interactome remodelling promotes rescue of cystic fibrosis
A new deep proteomic analysis method is used to identify proteins that interact with wild-type cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) and its mutant version that is the major cause of cystic fibrosis.
- Sandra Pankow
- , Casimir Bamberger
- & John R. Yates III
-
Outlook |
 Proteomics: High-protein research
Proteomics: High-protein research
The effort to catalogue proteins goes deeper in a push to make genetics research deliver practical benefits.
- Neil Savage
-
Outlook |
 Collaborations: Mining the motherlodes
Collaborations: Mining the motherlodes
Collaboration and competition are spurring on major '-omic' projects.
- Katherine Bourzac
-
Article |
 Panorama of ancient metazoan macromolecular complexes
Panorama of ancient metazoan macromolecular complexes
Using biochemical fractionation and mass spectrometry, animal protein complexes are identified from nine species in parallel, and, along with genome sequence information, complex conservation is investigated and over one million protein–protein interactions are predicted in 122 eukaryotes.
- Cuihong Wan
- , Blake Borgeson
- & Andrew Emili
-
Technology Feature |
 A deep look at synaptic dynamics
A deep look at synaptic dynamics
The processes behind neuronal communication have not yet been resolved in detail, but dyes, microscopy and protein analysis are beginning to fill in the gaps.
- Vivien Marx
-
Technology Feature |
 An atlas of expression
An atlas of expression
The first draft of the complete human proteome has been more than a decade in the making. In the process, the effort has also delivered lessons about technology and biology.
- Vivien Marx
-
Article |
 Mass-spectrometry-based draft of the human proteome
Mass-spectrometry-based draft of the human proteome
A mass-spectrometry-based draft of the human proteome and a public database for analysis of proteome data are presented; assembled information is used to estimate the size of the protein-coding genome, to identify organ-specific proteins, proteins predicting drug resistance or sensitivity, and many translated long intergenic non-coding RNAs, and to reveal conserved control of protein abundance.
- Mathias Wilhelm
- , Judith Schlegl
- & Bernhard Kuster
-
Article |
 A draft map of the human proteome
A draft map of the human proteome
A draft map of the human proteome is presented here, accounting for over 80% of the annotated protein-coding genes in humans; some novel protein-coding regions, including translated pseudogenes, non-coding RNAs and upstream open reading frames, are identified.
- Min-Sik Kim
- , Sneha M. Pinto
- & Akhilesh Pandey
-
News |
 Proteins help solve taxonomy riddle
Proteins help solve taxonomy riddle
Proteomic technique proves that 300-year-old Linnaean elephant was wrongly classified.
- Ewen Callaway
-
News |
 Linnaeus's Asian elephant was wrong species
Linnaeus's Asian elephant was wrong species
Molecular sleuths crack 300-year-old mystery over the identity of the Asian elephant type specimen.
- Ewen Callaway
-
Article |
 Temporal regulation of EGF signalling networks by the scaffold protein Shc1
Temporal regulation of EGF signalling networks by the scaffold protein Shc1
The Shc1 scaffold mediates a switch in the signaling output of the epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase over time through recruitment of successive waves of proteins with distinct biological functions.
- Yong Zheng
- , Cunjie Zhang
- & Tony Pawson
-
Letter |
 Variation and genetic control of protein abundance in humans
Variation and genetic control of protein abundance in humans
A large-scale analysis of variation in human protein levels between individuals is performed using mass-spectrometry-based proteomic technology, and a number of protein quantitative trait loci are identified; over 5% of proteins vary by more than 1.5-fold in their expression levels between individuals, and this variation is not always linked to RNA level.
- Linfeng Wu
- , Sophie I. Candille
- & Michael Snyder
-
Letter |
 A complete mass-spectrometric map of the yeast proteome applied to quantitative trait analysis
A complete mass-spectrometric map of the yeast proteome applied to quantitative trait analysis
High-throughput peptide synthesis and mass spectrometry are used to generate a near-complete reference map of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae proteome; two versions of the map (supporting discovery- and hypothesis-driven proteomics) are then applied to a protein-based quantitative trait locus analysis.
- Paola Picotti
- , Mathieu Clément-Ziza
- & Ruedi Aebersold
-
Letter |
 Structure-based prediction of protein–protein interactions on a genome-wide scale
Structure-based prediction of protein–protein interactions on a genome-wide scale
Protein–protein interactions, essential for understanding how a cell functions, are predicted using a new method that combines protein structure with other computationally and experimentally derived clues.
- Qiangfeng Cliff Zhang
- , Donald Petrey
- & Barry Honig
-
Article
| Open Access Architecture of the human regulatory network derived from ENCODE data
Architecture of the human regulatory network derived from ENCODE data
A description is given of the ENCODE consortium’s efforts to examine the principles of human transcriptional regulatory networks; the results are integrated with other genomic information to form a hierarchical meta-network where different levels have distinct properties.
- Mark B. Gerstein
- , Anshul Kundaje
- & Michael Snyder
-
Letter |
 Interaction landscape of membrane-protein complexes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Interaction landscape of membrane-protein complexes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
A survey of 1,590 putative integral, peripheral and lipid-anchored membrane proteins from Saccharomyces cerevisiae reveals unexpected physical associations underlying the membrane biology of eukaryotes and delineates the global topological landscape of the membrane interactome.
- Mohan Babu
- , James Vlasblom
- & Jack F. Greenblatt
-
Letter |
 Tumour micro-environment elicits innate resistance to RAF inhibitors through HGF secretion
Tumour micro-environment elicits innate resistance to RAF inhibitors through HGF secretion
The secretion of hepatocyte growth factor by stromal cells in the tumour micro-environment can make melanoma resistant to RAF inhibitors, through the activation of the MET signalling pathway, but a combination of RAF and MET inhibitors can overcome this resistance.
- Ravid Straussman
- , Teppei Morikawa
- & Todd R. Golub
-
Letter |
 Structure of the nociceptin/orphanin FQ receptor in complex with a peptide mimetic
Structure of the nociceptin/orphanin FQ receptor in complex with a peptide mimetic
The crystal structure of the human nociceptin/orphanin FQ peptide receptor in complex with the peptide mimetic antagonist compound-24 is determined, with potential importance for the development of new therapeutic agents.
- Aaron A. Thompson
- , Wei Liu
- & Raymond C. Stevens
-
Review Article |
 Engineering the third wave of biocatalysis
Engineering the third wave of biocatalysis
Over the past ten years, protein engineering has established biocatalysis as a practical and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional forms of catalysis both in the laboratory and in industry.
- U. T. Bornscheuer
- , G. W. Huisman
- & K. Robins
-
Technology Feature |
 The interaction map
The interaction map
As increasing numbers of protein–protein interactions are identified, researchers are finding ways to interrogate these data and understand the interactions in a relevant context.
- Monya Baker

 Splicing factor YBX1 mediates persistence of JAK2-mutated neoplasms
Splicing factor YBX1 mediates persistence of JAK2-mutated neoplasms