Featured
-
-
-
Article |
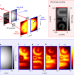 Polarization entanglement-enabled quantum holography
Polarization entanglement-enabled quantum holography
By exploiting polarization entanglement between photons, quantum holography can circumvent the need for first-order coherence that is vital to classical holography.
- Hugo Defienne
- , Bienvenu Ndagano
- & Daniele Faccio
-
Article
| Open Access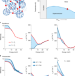 Evidence for metastable photo-induced superconductivity in K3C60
Evidence for metastable photo-induced superconductivity in K3C60
Evidence for light-induced superconductivity in K3C60 was limited to optical methods due to the short lifetime of the phase. Extending the lifetime from picoseconds to nanoseconds now allows measurement of its negligible electrical resistance.
- M. Budden
- , T. Gebert
- & A. Cavalleri
-
News & Views |
 Got the quantum jitters
Got the quantum jitters
Among the many reasons a signal may deviate from perfect periodicity, quantum-limited jitter is arguably the most fundamental. A clever experiment has now stripped away technical noise to unveil quantum-limited jitter of ultrafast soliton frequency combs.
- Miro Erkintalo
-
Letter |
 Quantum diffusion of microcavity solitons
Quantum diffusion of microcavity solitons
Quantum jitter fundamentally limits the performance of microresonator frequency combs. The timing jitter of the solitons that generate the comb spectra is analysed, reaching the quantum limit and establishing fundamental limits for soliton microcombs.
- Chengying Bao
- , Myoung-Gyun Suh
- & Kerry J. Vahala
-
Letter |
 Maximum information states for coherent scattering measurements
Maximum information states for coherent scattering measurements
Wavefront shaping can reduce uncertainties due to measurement noise through disordered media—key to many imaging applications. Optimal precision can be achieved using light fields that are eigenstates of an operator related to the medium’s scattering matrix.
- Dorian Bouchet
- , Stefan Rotter
- & Allard P. Mosk
-
Article |
 Clocking Auger electrons
Clocking Auger electrons
Self-referenced attosecond streaking enables in situ measurements of Auger emission in atomic neon excited by femtosecond pulses from an X-ray free-electron laser with subfemtosecond time resolution and despite the jitter inherent to X-ray free-electron lasers.
- D. C. Haynes
- , M. Wurzer
- & A. L. Cavalieri
-
-
Article |
 Zero-refractive-index materials and topological photonics
Zero-refractive-index materials and topological photonics
A general approach to derive direction-dependent complex refractive indices close to zero produces infinite families of time-reversible and infinite families of time-irreversible electromagnetic materials, without invoking the concept of topology.
- S. A. R. Horsley
- & M. Woolley
-
-
News & Views |
 Clock comparison using black holes
Clock comparison using black holes
Observing accreting black holes in the early Universe allows precise comparison of clocks over intercontinental distances on Earth. This is achieved with a novel observation strategy using the next generation of very long baseline interferometry systems.
- Rüdiger Haas
-
Letter |
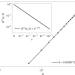 The Heisenberg limit for laser coherence
The Heisenberg limit for laser coherence
The coherence of a close-to-ideal laser beam can be quadratically better than what was believed to be the quantum limit. This new Heisenberg limit could be attained with circuit quantum electrodynamics.
- Travis J. Baker
- , Seyed N. Saadatmand
- & Howard M. Wiseman
-
Article |
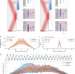 Resonant phase-matching between a light wave and a free-electron wavefunction
Resonant phase-matching between a light wave and a free-electron wavefunction
Energy–momentum phase-matching enables strong interactions between free electrons and light waves. As a result, the wavefunction of the electron exhibits a comb structure, which was observed using photon-induced near-field electron microscopy.
- Raphael Dahan
- , Saar Nehemia
- & Ido Kaminer
-
Article |
 Intercontinental comparison of optical atomic clocks through very long baseline interferometry
Intercontinental comparison of optical atomic clocks through very long baseline interferometry
Very long baseline interferometry is used to compare two optical clocks located in Japan and Italy through the observation of extragalactic radio sources. This approach overcomes limitations of the performance of satellite transfer techniques.
- Marco Pizzocaro
- , Mamoru Sekido
- & Tetsuya Ido
-
-
Article |
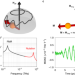 Inertial spin dynamics in ferromagnets
Inertial spin dynamics in ferromagnets
Inertial dynamics are observed in a ferromagnet. Specifically, a nutation is seen on top of the usual spin precession that has a lifetime on the order of 10 picoseconds.
- Kumar Neeraj
- , Nilesh Awari
- & Stefano Bonetti
-
News & Views |
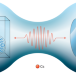 An odd couple
An odd couple
An atomic spin oscillator coupled to a mechanical membrane resonator forms an effective negative-mass oscillator. Entanglement in this hybrid quantum system is created by a backaction-evading position measurement, despite the macroscopic separation.
- Brian D’Urso
- & James Millen
-
-
Article |
 Braiding photonic topological zero modes
Braiding photonic topological zero modes
The non-zero geometric phase acquired by the braiding of vortex modes in photonic waveguide lattices demonstrates their potential to serve as a platform for the study of both Abelian and non-Abelian braiding in bosonic systems.
- Jiho Noh
- , Thomas Schuster
- & Mikael C. Rechtsman
-
Letter |
 Excitons bound by photon exchange
Excitons bound by photon exchange
Electrons and holes in doped quantum wells cannot form bound states from usual Coulomb interaction. However, when the system is embedded in a cavity, the exchange of photons provides an effective attraction, leading to the creation of bound excitons.
- Erika Cortese
- , Ngoc-Linh Tran
- & Simone De Liberato
-
-
Article |
 Unscrambling entanglement through a complex medium
Unscrambling entanglement through a complex medium
Higher-dimensional entanglement between two photons can be preserved for a photon passing through a complex medium by applying an appropriate scrambling operation on the entangled partner that does not enter the complex medium.
- Natalia Herrera Valencia
- , Suraj Goel
- & Mehul Malik
-
Article |
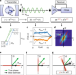 Implementation of a canonical phase measurement with quantum feedback
Implementation of a canonical phase measurement with quantum feedback
An adaptive heterodyne technique with a Josephson parametric amplifier detector allows a high-precision single-shot canonical phase measurement on a one-photon wave packet, complementing near-ideal measurements of photon number or field amplitude.
- Leigh S. Martin
- , William P. Livingston
- & Irfan Siddiqi
-
News & Views |
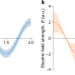 Squeezing hots up
Squeezing hots up
Squeezed light is useful for metrology and quantum information. An optomechanical squeezed light source that works at room temperature will facilitate the technological applications of quantum light.
- André Xuereb
-
Letter |
 Origin of strong-field-induced low-order harmonic generation in amorphous quartz
Origin of strong-field-induced low-order harmonic generation in amorphous quartz
Strong-field-induced nonlinearities from the injection of electrons into the conduction band contribute to harmonic generation in amorphous quartz. Close to the damage threshold, they dominate over intraband and interband contributions.
- P. Jürgens
- , B. Liewehr
- & A. Mermillod-Blondin
-
News & Views |
 Ring a ring o’ pulses
Ring a ring o’ pulses
Quantum cascade lasers are bright and compact semiconductor lasers that emit light in the mid- to far-infrared spectral region. The use of a closed ring cavity has now set them on the path towards ultrafast pulses.
- Johann Riemensberger
-
Letter |
 Error-corrected gates on an encoded qubit
Error-corrected gates on an encoded qubit
Error-corrected quantum gates that can tolerate dominant errors during the execution of quantum operations have been demonstrated. Substantial improvement of the gate fidelity sheds light on fault-tolerant universal quantum computation.
- Philip Reinhold
- , Serge Rosenblum
- & Robert J. Schoelkopf
-
Letter |
 Repulsive photons in a quantum nonlinear medium
Repulsive photons in a quantum nonlinear medium
- Sergio H. Cantu
- , Aditya V. Venkatramani
- & Vladan Vuletić
-
Letter |
 Towards satellite-based quantum-secure time transfer
Towards satellite-based quantum-secure time transfer
Transmitting the time signal and generating the secure key with the same carrier photon improves the security of a satellite-based quantum-secure time transfer protocol, which uses two-way quantum key distribution.
- Hui Dai
- , Qi Shen
- & Jian-Wei Pan
-
Measure for Measure |
 With a fine-tooth comb
With a fine-tooth comb
The tool of choice to measure optical frequencies with extremely high precision is the optical frequency comb. Camille-Sophie Brès explains what makes this technique so powerful.
- Camille-Sophie Brès
-
Letter |
 A quantum network node with crossed optical fibre cavities
A quantum network node with crossed optical fibre cavities
A passive, heralded and high-fidelity quantum memory network node has been realized, which connects simultaneously to two quantum channels provided by orthogonally aligned optical fibre cavities coupled with a single atom.
- Manuel Brekenfeld
- , Dominik Niemietz
- & Gerhard Rempe
-
Article |
 Quantum metasurfaces with atom arrays
Quantum metasurfaces with atom arrays
A kind of quantum metasurface made of an atom array is proposed, providing the possibility to control both spatiotemporal and quantum properties of transmitted and reflected light.
- R. Bekenstein
- , I. Pikovski
- & M. D. Lukin
-
Article |
 Non-Hermitian bulk–boundary correspondence in quantum dynamics
Non-Hermitian bulk–boundary correspondence in quantum dynamics
Measurements of non-Hermitian photon dynamics show boundary-localized bulk eigenstates given by the non-Hermitian skin effect. A fundamental revision of the bulk–boundary correspondence in open systems is required to understand the underlying physics.
- Lei Xiao
- , Tianshu Deng
- & Peng Xue
-
Article |
 Revealing the missing dimension at an exceptional point
Revealing the missing dimension at an exceptional point
The modes of the radiation field generated from an emitter are usually determined by the eigenstates of the surrounding environment. However, this scenario breaks down in a non-Hermitian system, at the spectral degeneracy known as an exceptional point.
- Hua-Zhou Chen
- , Tuo Liu
- & Ren-Min Ma
-
-
News & Views |
 On-chip tunnel management
On-chip tunnel management
Speed is of the essence when it comes to signal processing, but electronic switching times have reached a limit. Optically controlled tunnel currents across a nanoscale plasmonic gap could considerably accelerate future nanoelectronic devices.
- Olga Smirnova
-
Article |
 Symmetry-breaking-induced plasmonic exceptional points and nanoscale sensing
Symmetry-breaking-induced plasmonic exceptional points and nanoscale sensing
The hybridized modes of an asymmetric plasmonic dimer show avoided crossing of both the real and imaginary parts. This can lead to plasmonic exceptional points, which are used for biosensing with very high sensitivity.
- Jun-Hee Park
- , Abdoulaye Ndao
- & Boubacar Kanté
-
News & Views |
 Mode-locking dissected
Mode-locking dissected
Despite the wide use of mode-locked lasers, no general theory for mode-locking exists. An attractor dissection approach provides some intuitive understanding of the complex dynamics in one type of mode-locking.
- F. Ömer Ilday
-
Letter |
 Strong optical coupling through superfluid Brillouin lasing
Strong optical coupling through superfluid Brillouin lasing
Light-induced deformations in a film of superfluid helium covering an optical microresonator can greatly enhance Brillouin interactions, enabling strong coupling between counter-propagating modes as well as Brillouin lasing.
- Xin He
- , Glen I. Harris
- & Warwick P. Bowen
-
Article |
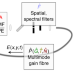 Mechanisms of spatiotemporal mode-locking
Mechanisms of spatiotemporal mode-locking
Mode-locking of lasers can be understood as self-organization, and the three-dimensional case of spatiotemporal mode-locking can described using attractor dissection theory, which helps develop an intuition for this complex case.
- Logan G. Wright
- , Pavel Sidorenko
- & Frank W. Wise
-
-
Article |
 Variational quantum unsampling on a quantum photonic processor
Variational quantum unsampling on a quantum photonic processor
The variational quantum unsampling protocol provides a way to realize verification and inference of near-term quantum circuit outputs. This protocol is then experimentally verified on a quantum photonic processor.
- Jacques Carolan
- , Masoud Mohseni
- & Dirk Englund
-
Article |
 Electromagnetically induced transparency at a chiral exceptional point
Electromagnetically induced transparency at a chiral exceptional point
The optical analogue of electromagnetically induced transparency and absorption can be modulated by chiral optical states at an exceptional point, which is shown in a system of indirectly coupled microresonators.
- Changqing Wang
- , Xuefeng Jiang
- & Lan Yang
-
-
Letter |
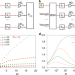 Distributed quantum sensing in a continuous-variable entangled network
Distributed quantum sensing in a continuous-variable entangled network
Experiments demonstrate quantum phase sensing with a four-mode entangled state, reaching a measurement precision that is beyond what can be achieved by separate individual probes.
- Xueshi Guo
- , Casper R. Breum
- & Ulrik L. Andersen
-
-
-
Letter |
 Impact of the Langdon effect on crossed-beam energy transfer
Impact of the Langdon effect on crossed-beam energy transfer
In inertial confinement fusion experiments, the effect of the overlapping laser beams on the plasma is predicted to lead to a distortion of the electron distribution function, which has now been observed in experiments.
- David Turnbull
- , Arnaud Colaïtis
- & Dustin H. Froula
-
Letter |
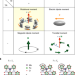 Observation of a ferro-rotational order coupled with second-order nonlinear optical fields
Observation of a ferro-rotational order coupled with second-order nonlinear optical fields
The authors use optical spectroscopy to show that RbFe(MoO4)2 hosts a ferro-rotational phase. This is the final form of ferroic order to be observed.
- Wencan Jin
- , Elizabeth Drueke
- & Liuyan Zhao

 Probing bulk topological invariants using leaky photonic lattices
Probing bulk topological invariants using leaky photonic lattices Light captured in flight
Light captured in flight Bigger is better
Bigger is better Perovskite fever
Perovskite fever Photonic crystal maze
Photonic crystal maze Tamed by topology
Tamed by topology