News & Views |
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Nonlinearity-induced topological phase transition characterized by the nonlinear Chern number
Nonlinearity-induced topological phase transition characterized by the nonlinear Chern number
Linear topological systems can be characterized using invariants such as the Chern number. This concept can be extended to the nonlinear regime, giving rise to nonlinearity-induced topological phase transitions.
- Kazuki Sone
- , Motohiko Ezawa
- & Takahiro Sagawa
-
Article |
 Multiphoton electron emission with non-classical light
Multiphoton electron emission with non-classical light
Photoemission experiments demonstrate that the photon number statistics of the exciting light can be imprinted on the emitted electrons, allowing the controlled generation of classical or non-classical electron number statistics of free electrons.
- Jonas Heimerl
- , Alexander Mikhaylov
- & Peter Hommelhoff
-
Article |
 Topological temporally mode-locked laser
Topological temporally mode-locked laser
Mode locking, which is a common technique to produce short laser pulses, is demonstrated in a topological laser.
- Christian R. Leefmans
- , Midya Parto
- & Alireza Marandi
-
Article |
 Terahertz field-induced nonlinear coupling of two magnon modes in an antiferromagnet
Terahertz field-induced nonlinear coupling of two magnon modes in an antiferromagnet
Magnons—quanta of spin waves—have potential applications in signal processing technology. But it is challenging to obtain coupling between different magnons. Now a study achieves this by demonstrating nonlinear magnon mixing in an antiferromagnet.
- Zhuquan Zhang
- , Frank Y. Gao
- & Keith A. Nelson
-
News & Views |
 Topological phase transitions have never been faster
Topological phase transitions have never been faster
A nonlinear optical approach has now enabled picosecond control of a complex band structure, driving a non-Hermitian topological phase transition across an exceptional-point singularity.
- Jiangbin Gong
- & Ching Hua Lee
-
Article |
 Non-Hermitian topological phase transitions controlled by nonlinearity
Non-Hermitian topological phase transitions controlled by nonlinearity
The phase transition from a topologically trivial state to non-Hermitian conducting edge modes can be controlled by optical nonlinearities, achieving picosecond switching speeds.
- Tianxiang Dai
- , Yutian Ao
- & Jianwei Wang
-
Article
| Open Access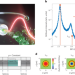 Extreme thermodynamics in nanolitre volumes through stimulated Brillouin–Mandelstam scattering
Extreme thermodynamics in nanolitre volumes through stimulated Brillouin–Mandelstam scattering
Material characterization of liquids in extreme thermodynamic conditions is a challenging technical problem. Brillouin scattering metrology in an optical fibre design with a sealed liquid core now enables spatially resolved temperature and pressure measurements, using carbon disulfide as an example.
- Andreas Geilen
- , Alexandra Popp
- & Birgit Stiller
-
Article |
 Broadband coherent wave control through photonic collisions at time interfaces
Broadband coherent wave control through photonic collisions at time interfaces
Coherent control is an interference technique widely used to control dynamic wave processes. Its analogue in the time domain allows the tailored suppression, enhancement and reshaping of optical pulses, and the mimicking of collisions between them.
- Emanuele Galiffi
- , Gengyu Xu
- & Andrea Alù
-
News & Views |
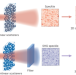 Transmission matrices go nonlinear
Transmission matrices go nonlinear
Measuring the transmission matrix of disordered structures has so far been limited to the domain of linear systems. Now it has been measured for nonlinear disorder, with exciting implications for information capacity.
- Sushil Mujumdar
-
News & Views |
 Of electrons and photons
Of electrons and photons
Multi-colour light fields allow a nonlinear coupling between free electrons and propagating light by stimulated Compton scattering, without the need for near fields to mediate the interaction.
- Niklas Müller
- & Sascha Schäfer
-
Article |
 Nonlinear-optical quantum control of free-electron matter waves
Nonlinear-optical quantum control of free-electron matter waves
Although massive electrons and massless photons are known to interact, their study has so far been confined to the linear regime. Experiments showing two-photon coherent control of a free-electron matter wave now introduce non-linearities.
- Maxim Tsarev
- , Johannes W. Thurner
- & Peter Baum
-
Article |
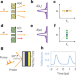 Double-slit time diffraction at optical frequencies
Double-slit time diffraction at optical frequencies
A temporal version of Young’s double-slit experiment shows characteristic interference in the frequency domain when light interacts with time slits produced by ultrafast changes in the refractive index of an epsilon-near-zero material.
- Romain Tirole
- , Stefano Vezzoli
- & Riccardo Sapienza
-
Article
| Open Access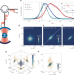 Photon bound state dynamics from a single artificial atom
Photon bound state dynamics from a single artificial atom
Measurements on a single artificial atom—a quantum dot—coupled to an optical cavity show scattering dynamics that depend on the number of photons involved in the light–matter interaction, which is a signature of stimulated emission.
- Natasha Tomm
- , Sahand Mahmoodian
- & Richard J. Warburton
-
Article |
 Observation of temporal reflection and broadband frequency translation at photonic time interfaces
Observation of temporal reflection and broadband frequency translation at photonic time interfaces
Reflection cannot only occur at interfaces in space but also in time. Transmission-line metamaterials support time interfaces at which interference has been observed, forming a temporal version of a Fabry–Pérot cavity.
- Hady Moussa
- , Gengyu Xu
- & Andrea Alù
-
Article |
 Non-equilibrium spectral phase transitions in coupled nonlinear optical resonators
Non-equilibrium spectral phase transitions in coupled nonlinear optical resonators
Dispersive coupling between two optical parametric oscillators induces a first-order phase transition in the system at a critical detuning. This manifests as a discontinuity in the dimer’s spectrum, which may be useful for enhanced sensing.
- Arkadev Roy
- , Rajveer Nehra
- & Alireza Marandi
-
Article |
 Quantized fractional Thouless pumping of solitons
Quantized fractional Thouless pumping of solitons
Interactions between photons arise due to the presence of optical nonlinearities. In topological Thouless pumps, a sufficiently strong nonlinearity leads to soliton transport with a fractionally quantized plateau structure—reminiscent of transport in the fractional quantum Hall effect.
- Marius Jürgensen
- , Sebabrata Mukherjee
- & Mikael C. Rechtsman
-
-
Review Article |
 Physics of highly multimode nonlinear optical systems
Physics of highly multimode nonlinear optical systems
Nonlinearities allow the large number of modes in a multimode fibre to interact and create emergent phenomena. This Review presents the breadth of the high-dimensional nonlinear physics that can be studied in this platform.
- Logan G. Wright
- , Fan O. Wu
- & Frank W. Wise
-
News & Views |
 Quantum underpinnings of an all-photonic switch
Quantum underpinnings of an all-photonic switch
All-optical devices hold promise as a platform for ultralow-power, sub-nanosecond photonic classical and quantum information processing. Measurements of the dynamics of a single photon switch unveil the quantum correlations at the root of its operation.
- Victoria A. Norman
- & Marina Radulaski
-
Letter |
 Dynamical photon–photon interaction mediated by a quantum emitter
Dynamical photon–photon interaction mediated by a quantum emitter
Efficient interactions between two photons is a challenging requirement for quantum information processing. A quantum dot coupled to a waveguide produces strong interactions that can induce photon correlations and reshape two-photon wavepackets.
- Hanna Le Jeannic
- , Alexey Tiranov
- & Peter Lodahl
-
News & Views |
 Topological interface of light
Topological interface of light
Upon combining dissipative and nonlinear effects in a bipartite lattice of cavity polaritons, dissipatively stabilized bulk gap solitons emerge, which create a topological interface.
- Flore K. Kunst
-
Article |
 Gap solitons in a one-dimensional driven-dissipative topological lattice
Gap solitons in a one-dimensional driven-dissipative topological lattice
Drive engineering in optical systems can be used to stabilize new nonlinear phases in topological systems. Dissipatively stabilized gap solitons in a polariton lattice establish drive engineering as a resource for nonlinear topological photonics.
- Nicolas Pernet
- , Philippe St-Jean
- & Jacqueline Bloch
-
Article |
 Direct observations of thermalization to a Rayleigh–Jeans distribution in multimode optical fibres
Direct observations of thermalization to a Rayleigh–Jeans distribution in multimode optical fibres
Optical nonlinearities in multimodal systems lead to a complex behaviour that can be described as a thermalization process, which is expected to lead to a Rayleigh–Jeans distribution. This process has now been observed in graded-index fibres.
- Hamed Pourbeyram
- , Pavel Sidorenko
- & Frank Wise
-
News & Views |
 A controlled cascade interference
A controlled cascade interference
Nonlinear optical effects enable sophisticated functionalities to generate and manipulate light. The precise control of two distinct nonlinear phenomena in a photonic chip can enhance a key optical nonlinearity that makes single-photon sources more efficient.
- Thiago P. Mayer Alegre
- & Gustavo S. Wiederhecker
-
Letter |
 In situ control of effective Kerr nonlinearity with Pockels integrated photonics
In situ control of effective Kerr nonlinearity with Pockels integrated photonics
Many nanophotonic devices rely on optical nonlinearities, which can be indirectly engineered. The quantum interference of different nonlinear pathways directly controls the Kerr nonlinearity without changing the device design.
- Chaohan Cui
- , Liang Zhang
- & Linran Fan
-
Article
| Open Access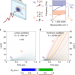 Nonlocal nonlinear phononics
Nonlocal nonlinear phononics
Nonlinear phononics is a method for creating transient structural changes in solids, but its effect is limited to the region of optical excitation. Now, coupling to a propagating polariton allows nonlinear phononics to drive a nonlocal response.
- M. Henstridge
- , M. Först
- & A. Cavalleri
-
Article |
 Riemannian geometry of resonant optical responses
Riemannian geometry of resonant optical responses
The modern understanding of quantum transport relies on geometric concepts such as the Berry phase. The geometric approach has now been extended to the theory of optical transitions.
- Junyeong Ahn
- , Guang-Yu Guo
- & Ashvin Vishwanath
-
News & Views |
 Nonlinear effects get into shape
Nonlinear effects get into shape
Nonlinear optical effects are by default weak but they can be enhanced by sculpting the resulting spectrally periodic pulses from a fibre laser into an optimal shape.
- Thibaut Sylvestre
-
Article |
 Spectrally periodic pulses for enhancement of optical nonlinear effects
Spectrally periodic pulses for enhancement of optical nonlinear effects
The nonlinear optical effects underlying many applications are typically weak, but linear dispersion engineering allows the generation of pulses comprising equidistant frequency components, which enhances the effective nonlinearity.
- Joshua P. Lourdesamy
- , Antoine F. J. Runge
- & C. Martijn de Sterke
-
Article |
 Topological frequency combs and nested temporal solitons
Topological frequency combs and nested temporal solitons
Optical frequency combs are a key technology in precision time keeping, spectroscopy and metrology. A theoretical proposal shows that introducing topological principles into their design makes on-chip combs more efficient and robust against fabrication defects.
- Sunil Mittal
- , Gregory Moille
- & Mohammad Hafezi
-
News & Views |
 Topology puts solitons in the corner
Topology puts solitons in the corner
Nonlinearity and topology are both linked to symmetries, but what happens when the two are combined is not a trivial question. In a nonlinear photonic higher-order topological insulator, solitons localize on the corners together with the topological modes.
- Grazia Salerno
-
Letter
| Open Access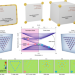 Nonlinear second-order photonic topological insulators
Nonlinear second-order photonic topological insulators
The nonlinear properties of photonic topological insulators remain largely unexplored, as band topology is linked to linear systems. But nonlinear topological corner states and solitons can form in a second-order topological insulator, as shown by experiments.
- Marco S. Kirsch
- , Yiqi Zhang
- & Matthias Heinrich
-
Letter |
 Quantum diffusion of microcavity solitons
Quantum diffusion of microcavity solitons
Quantum jitter fundamentally limits the performance of microresonator frequency combs. The timing jitter of the solitons that generate the comb spectra is analysed, reaching the quantum limit and establishing fundamental limits for soliton microcombs.
- Chengying Bao
- , Myoung-Gyun Suh
- & Kerry J. Vahala
-
Article |
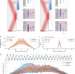 Resonant phase-matching between a light wave and a free-electron wavefunction
Resonant phase-matching between a light wave and a free-electron wavefunction
Energy–momentum phase-matching enables strong interactions between free electrons and light waves. As a result, the wavefunction of the electron exhibits a comb structure, which was observed using photon-induced near-field electron microscopy.
- Raphael Dahan
- , Saar Nehemia
- & Ido Kaminer
-
-
Article |
 Generalized superradiance for producing broadband coherent radiation with transversely modulated arbitrarily diluted bunches
Generalized superradiance for producing broadband coherent radiation with transversely modulated arbitrarily diluted bunches
A new form of superradiance is predicted that ‘in contrast to the standard effect’ arises even for vanishing numbers of particles per wavelength. This finding may enable coherent emission in plasma accelerators.
- J. Vieira
- , M. Pardal
- & R. A. Fonseca
-
Letter |
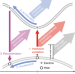 Origin of strong-field-induced low-order harmonic generation in amorphous quartz
Origin of strong-field-induced low-order harmonic generation in amorphous quartz
Strong-field-induced nonlinearities from the injection of electrons into the conduction band contribute to harmonic generation in amorphous quartz. Close to the damage threshold, they dominate over intraband and interband contributions.
- P. Jürgens
- , B. Liewehr
- & A. Mermillod-Blondin
-
Letter |
 Repulsive photons in a quantum nonlinear medium
Repulsive photons in a quantum nonlinear medium
- Sergio H. Cantu
- , Aditya V. Venkatramani
- & Vladan Vuletić
-
Article |
 Mechanisms of spatiotemporal mode-locking
Mechanisms of spatiotemporal mode-locking
Mode-locking of lasers can be understood as self-organization, and the three-dimensional case of spatiotemporal mode-locking can described using attractor dissection theory, which helps develop an intuition for this complex case.
- Logan G. Wright
- , Pavel Sidorenko
- & Frank W. Wise
-
Letter |
 Chip-to-chip quantum teleportation and multi-photon entanglement in silicon
Chip-to-chip quantum teleportation and multi-photon entanglement in silicon
Four single-photon states are generated and entangled on a single micrometre-scale silicon chip, and provide the basis for the demonstration of chip-to-chip quantum teleportation.
- Daniel Llewellyn
- , Yunhong Ding
- & Mark G. Thompson
-
Article |
 Sub-femtosecond electron transport in a nanoscale gap
Sub-femtosecond electron transport in a nanoscale gap
Single-cycle interferometric autocorrelation measurements of electrons tunnelling across the gap of a plasmonic bowtie antenna and quantitative models provide insight into the physical interactions that drive the electron transfer.
- Markus Ludwig
- , Garikoitz Aguirregabiria
- & Daniele Brida
-
-
Letter |
 Impact of the Langdon effect on crossed-beam energy transfer
Impact of the Langdon effect on crossed-beam energy transfer
In inertial confinement fusion experiments, the effect of the overlapping laser beams on the plasma is predicted to lead to a distortion of the electron distribution function, which has now been observed in experiments.
- David Turnbull
- , Arnaud Colaïtis
- & Dustin H. Froula
-
Letter |
 Observation of a ferro-rotational order coupled with second-order nonlinear optical fields
Observation of a ferro-rotational order coupled with second-order nonlinear optical fields
The authors use optical spectroscopy to show that RbFe(MoO4)2 hosts a ferro-rotational phase. This is the final form of ferroic order to be observed.
- Wencan Jin
- , Elizabeth Drueke
- & Liuyan Zhao
-
Article |
 Dynamics of soliton crystals in optical microresonators
Dynamics of soliton crystals in optical microresonators
A dissipative Kerr soliton crystal state is a temporally ordered regular ensemble of soliton pulses within a cavity. Chaotic driving of optical resonators enables the defect-free creation and dynamical characterization of these states.
- Maxim Karpov
- , Martin H. P. Pfeiffer
- & Tobias J. Kippenberg
-
-
Letter |
 High-harmonic generation from an epsilon-near-zero material
High-harmonic generation from an epsilon-near-zero material
High harmonics are generated from a thin film by leveraging the epsilon-near-zero effect. These kinds of harmonic are found to exhibit a pronounced spectral redshift as well as linewidth broadening caused by the time-dependency of this effect.
- Yuanmu Yang
- , Jian Lu
- & Igal Brener
-
Letter |
 A primary radiation standard based on quantum nonlinear optics
A primary radiation standard based on quantum nonlinear optics
Triggered by the fluctuations of the electromagnetic vacuum, parametric down-conversion offers a new primary radiation standard based on quantum nonlinear optics.
- Samuel Lemieux
- , Enno Giese
- & Robert W. Boyd
-
Letter |
 Exchange-driven intravalley mixing of excitons in monolayer transition metal dichalcogenides
Exchange-driven intravalley mixing of excitons in monolayer transition metal dichalcogenides
Two-dimensional electronic spectroscopy experiments and first-principles many-electron calculations demonstrate the quantum mixing of different exciton states in monolayer MoS2. This reveals the many-body effects and dynamics of exciton formation in 2D materials.
- Liang Guo
- , Meng Wu
- & Graham R. Fleming

 Electrons bunch up in quantum light
Electrons bunch up in quantum light Tamed by topology
Tamed by topology