Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access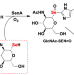 Substrate binding and catalytic mechanism of the Se-glycosyltransferase SenB in the biosynthesis of selenoneine
Substrate binding and catalytic mechanism of the Se-glycosyltransferase SenB in the biosynthesis of selenoneine
SenB is a Se-glycosyltransferase in the microbial biosynthesis pathway of selenoneine. Here, the authors perform the structure-function investigation, providing mechanistic insights into a two-step catalytic reaction of SenB.
- Wei Huang
- , Jun Song
- & Feng Long
-
Perspective
| Open Access Annexins—a family of proteins with distinctive tastes for cell signaling and membrane dynamics
Annexins—a family of proteins with distinctive tastes for cell signaling and membrane dynamics
Annexins are calcium-regulated membrane binding proteins with an array of cellular activities. Here, Gerke et al. describe recent research highlighting the many functions of annexins and provide a view on directions for the future.
- Volker Gerke
- , Felicity N. E. Gavins
- & Ursula Rescher
-
Article
| Open Access Pro-ferroptotic signaling promotes arterial aging via vascular smooth muscle cell senescence
Pro-ferroptotic signaling promotes arterial aging via vascular smooth muscle cell senescence
Ferroptosis is a novel form of regulated cell death associated with lipid oxidation. Here, the authors demonstrate that the proferroptosis signal is activated and drives vascular aging by inducing senescence in vascular smooth muscle cells.
- Di-Yang Sun
- , Wen-Bin Wu
- & Pei Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Monovalent metal ion binding promotes the first transesterification reaction in the spliceosome
Monovalent metal ion binding promotes the first transesterification reaction in the spliceosome
Hybrid QM/MM molecular dynamics simulations reveal that the kinetics and thermodynamics of the first splicing step are regulated by a K+ ion that facilitates optimal positioning of reactive moieties.
- Jana Aupič
- , Jure Borišek
- & Alessandra Magistrato
-
Article
| Open Access The vacuolar iron transporter mediates iron detoxification in Toxoplasma gondii
The vacuolar iron transporter mediates iron detoxification in Toxoplasma gondii
Iron is essential to cells, however without correct storage can lead to cell damage. Aghabi et al. show that the vacuolar iron transporter (VIT) is required for iron storage in the parasite Toxoplasma gondii. They find VIT protects against iron toxicity and has a role in parasite virulence.
- Dana Aghabi
- , Megan Sloan
- & Clare R. Harding
-
Article
| Open Access Ratiometric measurement of MAM Ca2+ dynamics using a modified CalfluxVTN
Ratiometric measurement of MAM Ca2+ dynamics using a modified CalfluxVTN
MAM Ca2+ dynamics play an important role in diverse biological processes, but directly and specifically measuring Ca2+ concentrations in this region is technically challenging. Here the authors report a MAM-specific BRET-based Ca2+ indicator called MAM-Calflux, which works as both a Ca2+ indicator and a structural marker due to its ratiometric nature.
- Eunbyul Cho
- , Youngsik Woo
- & Sang Ki Park
-
Article
| Open Access Excessive copper impairs intrahepatocyte trafficking and secretion of selenoprotein P
Excessive copper impairs intrahepatocyte trafficking and secretion of selenoprotein P
Selenium and copper are two essential trace elements whose homeostasis and distribution is regulated by hepatic release of selenoprotein P (SELENOP) and ceruloplasmin, respectively. Here, the authors show that excessive copper results in hepatic SELENOP accumulation in the trans Golgi which might limit the selenium transport to peripheral organs.
- Maria Schwarz
- , Caroline E. Meyer
- & Anna P. Kipp
-
Article
| Open Access Microbiota-assisted iron uptake promotes immune tolerance in the intestine
Microbiota-assisted iron uptake promotes immune tolerance in the intestine
Iron deficiencies are a common non intestinal symptom seen in patients with irritable bowel disease. Here the authors show an associative link between microbiota assisted uptake of nutrients including iron and the promotion of immune tolerance in the intestine.
- Lizhen Zhu
- , Geng Li
- & Xing Chang
-
Article
| Open Access Pulcherriminic acid modulates iron availability and protects against oxidative stress during microbial interactions
Pulcherriminic acid modulates iron availability and protects against oxidative stress during microbial interactions
Microbes often produce molecules (termed siderophores) that bind iron and then are taken up using specific receptors for iron acquisition. Here, the authors show that a compound produced by Bacillus subtilis plays a more complex role, by modulating iron availability and conferring protection against oxidative stress during inter-species competition.
- Vincent Charron-Lamoureux
- , Lounès Haroune
- & Pascale B. Beauregard
-
Article
| Open Access LncRNA modulates Hippo-YAP signaling to reprogram iron metabolism
LncRNA modulates Hippo-YAP signaling to reprogram iron metabolism
Iron metabolism dysregulation is associated with various diseases including cancer. Here, the authors show that one iron-triggered lncRNA LncRIM regulates cellular iron metabolism effectively by wiring up the Hippo-YAP signaling pathway and promotes breast cancer development.
- Xin-yu He
- , Xiao Fan
- & Aifu Lin
-
Article
| Open Access Mitochondrial ATP synthase as a direct molecular target of chromium(III) to ameliorate hyperglycaemia stress
Mitochondrial ATP synthase as a direct molecular target of chromium(III) to ameliorate hyperglycaemia stress
Despite common use as a diabetes mellitus supplement, chromium(III)’s pharmacological effects remain unknown. We identified the Cr(III)-proteome in cells with a metalloproteomic approach and uncovered ATP synthase as a vital target to relieve hyperglycaemia stress.
- Haibo Wang
- , Ligang Hu
- & Hongzhe Sun
-
Article
| Open Access Structural insights into the elevator-type transport mechanism of a bacterial ZIP metal transporter
Structural insights into the elevator-type transport mechanism of a bacterial ZIP metal transporter
The ZIP family (SLC39A) is involved in transition metal homeostasis. Here, authors use integrated approaches to conclude that the ZIP from Bordetella bronchiseptica (BbZIP) utilizes the elevator-type transport mechanism to achieve alternating access.
- Yao Zhang
- , Yuhan Jiang
- & Jian Hu
-
Article
| Open Access Uptake mechanism of iron-phytosiderophore from the soil based on the structure of yellow stripe transporter
Uptake mechanism of iron-phytosiderophore from the soil based on the structure of yellow stripe transporter
Iron is an essential mineral in plant physiology. YS1 transporter imports iron–phytosiderophore complex (Fe(III)–DMA) from the soil. Here, the authors describe the cryo-EM structures of barley YS1 in complex with substrate, and a synthetic substrate analog.
- Atsushi Yamagata
- , Yoshiko Murata
- & Mikako Shirouzu
-
Article
| Open Access Design and directed evolution of noncanonical β-stereoselective metalloglycosidases
Design and directed evolution of noncanonical β-stereoselective metalloglycosidases
Metallohydrolases are ubiquitous enzymes. Here the authors show the design and biochemical characterisation of metalloglycosidase by constructing a hydrolytically active Zn-binding site within a barrel-shaped outer membrane protein OmpF.
- Woo Jae Jeong
- & Woon Ju Song
-
Article
| Open Access Intramyocardial hemorrhage drives fatty degeneration of infarcted myocardium
Intramyocardial hemorrhage drives fatty degeneration of infarcted myocardium
It is unclear why hemorrhagic myocardial infarctions (hMI) are destined for adverse outcomes. Here, the authors show that hMI drives fatty degeneration of infarct territories and contributes to adverse remodeling of the heart, which can be mitigated via timely depletion of iron within the hMI zone.
- Ivan Cokic
- , Shing Fai Chan
- & Rohan Dharmakumar
-
Article
| Open Access Manganese-driven CoQ deficiency
Manganese-driven CoQ deficiency
Across phylae, excess manganese disrupts energy metabolism by unclear mechanisms. Here, Diessl et al. report that failure of mitochondrial bioenergetics upon manganese overload is due to mismetallation of a diiron enzyme crucial for CoQ biosynthesis
- Jutta Diessl
- , Jens Berndtsson
- & Sabrina Büttner
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis of ion uptake in copper-transporting P1B-type ATPases
Structural basis of ion uptake in copper-transporting P1B-type ATPases
P1B-type ATPases export excess transition metals from cells. Here, the authors report a molecular structure of CopA, a coppertransporting P1B-ATPase from A. fulgidus, in an inward-facing E1 conformation.
- Nina Salustros
- , Christina Grønberg
- & Pontus Gourdon
-
Article
| Open Access Coordination of metal center biogenesis in human cytochrome c oxidase
Coordination of metal center biogenesis in human cytochrome c oxidase
Mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase is a heme aa3-copper oxygen reductase. Here, authors report that metal center-specific metallochaperones form dynamic assemblies to control heme a biosynthesis and coordinate copper transfer to the copper sites.
- Eva Nývltová
- , Jonathan V. Dietz
- & Antoni Barrientos
-
Article
| Open Access Design principles for site-selective hydroxylation by a Rieske oxygenase
Design principles for site-selective hydroxylation by a Rieske oxygenase
SxtT and GxtA are Rieske oxygenases that are involved in paralytic shellfish toxin biosynthesis and catalyze monohydroxylation reactions at different positions on the toxin scaffold. Here, the authors present crystal structures of SxtT and GxtA with the native substrates β-saxitoxinol and saxitoxin as well as a Xenon-pressurized structure of GxtA, which reveal a substrate access tunnel to the active site. Through structure-based mutagenesis studies the authors identify six residues in three different protein regions that determine the substrate specificity and site selectivity of SxtT and GxtA. These findings will aid the rational engineering of other Rieske oxygenases.
- Jianxin Liu
- , Jiayi Tian
- & Jennifer Bridwell-Rabb
-
Article
| Open Access Siderophore-mediated zinc acquisition enhances enterobacterial colonization of the inflamed gut
Siderophore-mediated zinc acquisition enhances enterobacterial colonization of the inflamed gut
Zinc is an essential cofactor for bacterial metabolism. Here, the authors show that the probiotic bacterium Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 utilizes the siderophore yersiniabactin as a zincophore, allowing the microbe to grow in zinc-limited media and to thrive in the inflamed gut.
- Judith Behnsen
- , Hui Zhi
- & Manuela Raffatellu
-
Article
| Open Access Cryo-EM structure of the sodium-driven chloride/bicarbonate exchanger NDCBE
Cryo-EM structure of the sodium-driven chloride/bicarbonate exchanger NDCBE
The mechanisms involved in SLC4-mediated ion transport are still under debate. Here, the authors present a cryoEM structure of the Sodium-driven Chloride/Bicarbonate Exchanger NDCBE, which - together with computational modeling and mutagenesis - reveals molecular determinants of ion transport by SLC4.
- Weiguang Wang
- , Kirill Tsirulnikov
- & Ira Kurtz
-
Article
| Open Access Crystal structure of an archaeal CorB magnesium transporter
Crystal structure of an archaeal CorB magnesium transporter
CNNM/CorB proteins are a conserved family of membrane proteins associated with Mg2+ transport. Here, structures of an archaeal CorB protein in apo state and with Mg2+-ATP bound and accompanying biophysical experiments suggest direct Mg2+ transport by CorB proteins.
- Yu Seby Chen
- , Guennadi Kozlov
- & Kalle Gehring
-
Article
| Open Access Efficient long-range conduction in cable bacteria through nickel protein wires
Efficient long-range conduction in cable bacteria through nickel protein wires
Filamentous cable bacteria conduct electrical currents over centimeter distances through fibers embedded in their cell envelope. Here, Boschker et al. show that the fibers consist of a conductive core containing nickel proteins that is surrounded by an insulating protein shell.
- Henricus T. S. Boschker
- , Perran L. M. Cook
- & Filip J. R. Meysman
-
Article
| Open Access Multi-target mode of action of silver against Staphylococcus aureus endows it with capability to combat antibiotic resistance
Multi-target mode of action of silver against Staphylococcus aureus endows it with capability to combat antibiotic resistance
Silver (Ag) has been used as an antimicrobial agent since a long time, but its molecular mechanism of action was not elucidated due to technical challenges. Here, the authors develop a mass spectrometric approach to identify the Ag-proteome in Staphylococcus aureus, and capture a molecular snapshot of the dynamic bactericidal mode of action of Ag through targeting multiple biological pathways.
- Haibo Wang
- , Minji Wang
- & Hongzhe Sun
-
Article
| Open Access Development of a mugineic acid family phytosiderophore analog as an iron fertilizer
Development of a mugineic acid family phytosiderophore analog as an iron fertilizer
Iron is an essential plant nutrient that is poorly bioavailable in alkaline soils, resulting in reduced agricultural productivity. Here, the authors report the synthesis of stable and cheap iron-chelator, proline-2’-deoxymugineic acid (PDMA), and demonstrate its utility as potential fertilizer.
- Motofumi Suzuki
- , Atsumi Urabe
- & Kosuke Namba
-
Article
| Open Access Calculating metalation in cells reveals CobW acquires CoII for vitamin B12 biosynthesis while related proteins prefer ZnII
Calculating metalation in cells reveals CobW acquires CoII for vitamin B12 biosynthesis while related proteins prefer ZnII
The connection between metal binding to proteins and availabilities of different metals in cells has been unclear. Here, the authors report a metalation-calculator that takes into account competition between metals and their variable accessibility, and thereby elucidate in vivo metal occupancies of three different proteins, CobW, YeiR and YjiA.
- Tessa R. Young
- , Maria Alessandra Martini
- & Nigel J. Robinson
-
Article
| Open Access Seesaw conformations of Npl4 in the human p97 complex and the inhibitory mechanism of a disulfiram derivative
Seesaw conformations of Npl4 in the human p97 complex and the inhibitory mechanism of a disulfiram derivative
The human AAA+protein p97 plays an important role in cellular protein homeostasis. Here, the authors use cryo-EM to obtain further insights into how p97 interacts with its co-factor Npl4 and they observe three distinct conformational states of Npl4 in complex with human p97, which suggests that a seesaw motion is essential for the unfolding activity of the p97 complex.
- Man Pan
- , Qingyun Zheng
- & Minglei Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Heme biosynthesis depends on previously unrecognized acquisition of iron-sulfur cofactors in human amino-levulinic acid dehydratase
Heme biosynthesis depends on previously unrecognized acquisition of iron-sulfur cofactors in human amino-levulinic acid dehydratase
Heme biosynthesis depends on iron-sulfur (Fe-S) cluster biogenesis but the molecular connection between these pathways is not fully understood. Here, the authors show that the heme biosynthesis enzyme ALAD contains an Fe-S cluster, disruption of which reduces ALAD activity and heme production in human cells.
- Gang Liu
- , Debangsu Sil
- & Tracey Ann Rouault
-
Article
| Open Access Light-driven formation of manganese oxide by today’s photosystem II supports evolutionarily ancient manganese-oxidizing photosynthesis
Light-driven formation of manganese oxide by today’s photosystem II supports evolutionarily ancient manganese-oxidizing photosynthesis
Photosynthetic formation of manganese (Mn) oxides from dissolved Mn ions was proposed to occur in ancestral photosystems before oxygenic photosynthesis evolved. Here, the authors provide evidence for this hypothesis by showing that photosystem II devoid of the Mn cluster oxidises Mn ions leading to formation of Mn-oxide nanoparticles.
- Petko Chernev
- , Sophie Fischer
- & Holger Dau
-
Article
| Open Access Resensitizing carbapenem- and colistin-resistant bacteria to antibiotics using auranofin
Resensitizing carbapenem- and colistin-resistant bacteria to antibiotics using auranofin
Multi-drug resistant pathogens remain a serious public health threat. Here, Sun and colleagues identify a role for auranofin, which is normally used as a drug for rheumatoid arthritis, for reversing antibiotic resistance to carbapenem and colistin.
- Hongzhe Sun
- , Qi Zhang
- & Hongyan Li
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular basis for the distinct functions of redox-active and FeS-transfering glutaredoxins
Molecular basis for the distinct functions of redox-active and FeS-transfering glutaredoxins
Glutaredoxins are a family of essential enzymes divided into two major classes with either a CGFS or a CxxC active site, of which only the latter exhibits oxidoreductase activity. Here the authors address the structural basis for the functional difference between the two classes of glutaredoxins.
- Daniel Trnka
- , Anna D. Engelke
- & Christopher Horst Lillig
-
Article
| Open Access An evolutionary path to altered cofactor specificity in a metalloenzyme
An evolutionary path to altered cofactor specificity in a metalloenzyme
Many metalloenzymes are highly specific for their cognate metal ion but the molecular principles underlying this specificity often remain unclear. Here, the authors characterize the structural and biochemical basis for the different metal specificity of two evolutionarily related superoxide dismutases.
- Anna Barwinska-Sendra
- , Yuritzi M. Garcia
- & Kevin J. Waldron
-
Article
| Open Access Metal ions and sugar puckering balance single-molecule kinetic heterogeneity in RNA and DNA tertiary contacts
Metal ions and sugar puckering balance single-molecule kinetic heterogeneity in RNA and DNA tertiary contacts
Mobile group II introns function as ribozymes to splice and reinsert themselves into DNA, thereby colonizing new genomic regions. Here the authors use single-molecule FRET and molecular dynamics simulations to reveal a structural link between metal ion induced kinetic heterogeneity and the sugar puckers at the exon-intron binding interface.
- Fabio D. Steffen
- , Mokrane Khier
- & Roland K. O. Sigel
-
Article
| Open Access A secreted metal-binding protein protects necrotrophic phytopathogens from reactive oxygen species
A secreted metal-binding protein protects necrotrophic phytopathogens from reactive oxygen species
The authors identify a family of iron-binding proteins that is present in phytopathogenic bacteria, fungi and oomycetes. Some of these proteins are secreted, bind metals, protect the pathogen from H2O2-induced death, and are involved in plant infection.
- Lulu Liu
- , Virginie Gueguen-Chaignon
- & Guy Condemine
-
Article
| Open Access Physiologically relevant reconstitution of iron-sulfur cluster biosynthesis uncovers persulfide-processing functions of ferredoxin-2 and frataxin
Physiologically relevant reconstitution of iron-sulfur cluster biosynthesis uncovers persulfide-processing functions of ferredoxin-2 and frataxin
The mechanism of iron-sulfur (Fe-S) cluster biosynthesis is not fully understood. Here, the authors develop a physiologically relevant in vitro model of Fe-S cluster assembly, allowing them to elucidate the sequence of Fe-S cluster synthesis along with the respective roles of ferredoxin-2 and frataxin.
- Sylvain Gervason
- , Djabir Larkem
- & Benoit D’Autréaux
-
Article
| Open Access Involvement of cigarette smoke-induced epithelial cell ferroptosis in COPD pathogenesis
Involvement of cigarette smoke-induced epithelial cell ferroptosis in COPD pathogenesis
Altered iron homeostasis resulting in excessive oxidative stress has been implicated in smoke-induced lung diseases. Here the authors show that ferroptosis of lung epithelial cells, potentially resulting from excessive ferritinophagy, is involved in the pathogenesis of COPD.
- Masahiro Yoshida
- , Shunsuke Minagawa
- & Kazuyoshi Kuwano
-
Article
| Open Access Importance of potassium ions for ribosome structure and function revealed by long-wavelength X-ray diffraction
Importance of potassium ions for ribosome structure and function revealed by long-wavelength X-ray diffraction
Metal ions play essential roles in myriads of biological processes, from catalytic co-factors to supporting protein and nucleic acid structures. Here the authors use long-wavelength X-ray diffraction to locate hundreds of potassium ions taking part in the formation of rRNA tertiary structure, mediating rRNA–protein interactions and supporting ribosomal protein structures and function.
- Alexey Rozov
- , Iskander Khusainov
- & Gulnara Yusupova
-
Article
| Open Access A Ca2+-regulated deAMPylation switch in human and bacterial FIC proteins
A Ca2+-regulated deAMPylation switch in human and bacterial FIC proteins
In many AMPylating FIC proteins a structurally conserved glutamate represses AMPylation. Here, the authors show that this glutamate supports deAMPylation in Enterococcus faecalis FIC (EfFIC), and that EfFIC switches from AMPylation to deAMPylation by binding Ca2+ at distinct sites.
- Simon Veyron
- , Giulia Oliva
- & Jacqueline Cherfils
-
Article
| Open Access Sensing intracellular calcium ions using a manganese-based MRI contrast agent
Sensing intracellular calcium ions using a manganese-based MRI contrast agent
There are only few MRI-compatible calcium reporters and they are limited to measuring extracellular calcium levels. Here the authors develop and validate a cell-permeable, manganese-based paramagnetic MRI contrast agent that enables monitoring intracellular calcium signals in vivo in the rat brain.
- Ali Barandov
- , Benjamin B. Bartelle
- & Alan Jasanoff
-
Article
| Open Access Calcium is an essential cofactor for metal efflux by the ferroportin transporter family
Calcium is an essential cofactor for metal efflux by the ferroportin transporter family
Ferroportin (Fpn) is essential for mammalian iron homeostasis as it exports iron from cells into blood circulation, but the molecular mechanisms of Fpn-mediated iron transport remain obscure. Here the authors use biophysical approaches to reveal that Ca2+ is a required cofactor for Fpn transport activity.
- Chandrika N. Deshpande
- , T. Alex Ruwe
- & Mika Jormakka
-
Article
| Open Access Magnesium uptake by connecting fluid-phase endocytosis to an intracellular inorganic cation filter
Magnesium uptake by connecting fluid-phase endocytosis to an intracellular inorganic cation filter
Metal bioavailability is frequently limited by sequestering agents which makes them inaccessible to cells. Here the authors show that cells can increase Mg2+ uptake via fluid phase endocytosis and accumulate this metal in their vacuole loaded with polyphosphate, and later can be exported to the cytosol.
- Sandra H. Klompmaker
- , Kid Kohl
- & Andreas Mayer
-
Article
| Open Access Structure and functional dynamics of the mitochondrial Fe/S cluster synthesis complex
Structure and functional dynamics of the mitochondrial Fe/S cluster synthesis complex
Fe/S clusters are synthesized by the mitochondrial iron-sulfur cluster assembly (ISC) machinery. Here the authors combine crystallography and small angle X-ray scattering measurements to structurally characterize the core ISC complex and give functional insights into eukaryotic Fe/S cluster synthesis.
- Michal T. Boniecki
- , Sven A. Freibert
- & Miroslaw Cygler
-
Article
| Open Access Hepcidin is regulated by promoter-associated histone acetylation and HDAC3
Hepcidin is regulated by promoter-associated histone acetylation and HDAC3
Hepcidin controls systemic iron levels by inhibiting intestinal iron absorption and iron recycling. Here, Pasricha et al. demonstrate that the hepcidin-chromatin locus displays HDAC3-mediated reversible epigenetic modifications during both erythropoiesis and iron deficiency.
- Sant-Rayn Pasricha
- , Pei Jin Lim
- & Hal Drakesmith
-
Article
| Open Access Biological iron-sulfur storage in a thioferrate-protein nanoparticle
Biological iron-sulfur storage in a thioferrate-protein nanoparticle
The biosynthesis of iron-sulfur clusters in anaerobic organisms has not been extensively investigated. Here, the authors identify and characterize a multi-subunit protein that stores iron and sulfur in thioferrate for the assembly of the clusters inPyrococcus furiosus.
- Brian J. Vaccaro
- , Sonya M. Clarkson
- & Michael W. W. Adams
-
Article
| Open Access Essential role of FBXL5-mediated cellular iron homeostasis in maintenance of hematopoietic stem cells
Essential role of FBXL5-mediated cellular iron homeostasis in maintenance of hematopoietic stem cells
The iron-regulated F-box protein FBXL5 regulates iron homeostasis by mediating the degradation of iron regulatory protein 2 (IRP2). Here the authors show that FBXL5 and its regulation of IRP2 are required for HSC self-renewal and reconstitution capability.
- Yoshiharu Muto
- , Masaaki Nishiyama
- & Keiichi I. Nakayama
-
Article
| Open Access ISCA1 is essential for mitochondrial Fe4S4 biogenesis in vivo
ISCA1 is essential for mitochondrial Fe4S4 biogenesis in vivo
The mitochondrial proteins ISCA1 and ISCA2 form a complex that is involved in the biogenesis of Fe–S clusters. Here the authors report that ISCA1 and ISCA2 interact differently with proteins of the Fe–S machinery and that under certain conditions, ISCA2 seems dispensable for Fe–S biogenesis.
- Lena Kristina Beilschmidt
- , Sandrine Ollagnier de Choudens
- & Alain Martelli
-
Article
| Open Access Structural and mechanistic basis of proton-coupled metal ion transport in the SLC11/NRAMP family
Structural and mechanistic basis of proton-coupled metal ion transport in the SLC11/NRAMP family
Cellular uptake of transition metal ions is mediated by members of the SLC11/NRAMP family. Here the authors determine the structural and functional properties of EcoDMT, a bacterial SLC11 transporter, gathering molecular insight into its transport mechanism and proton coupling process.
- Ines A. Ehrnstorfer
- , Cristina Manatschal
- & Raimund Dutzler
-
Article
| Open Access Disposal of iron by a mutant form of lipocalin 2
Disposal of iron by a mutant form of lipocalin 2
Iron overload can be either hereditary or acquired via transfusions, and current treatments include the use of iron chelators that have adverse effects in some patients. Here the authors modify siderocalin to enhance iron excretion in urine, and demonstrate therapeutic efficacy in iron overload mouse models.
- Jonathan Barasch
- , Maria Hollmen
- & Andong Qiu
-
Article
| Open Access Calcium-controlled conformational choreography in the N-terminal half of adseverin
Calcium-controlled conformational choreography in the N-terminal half of adseverin
The calcium-regulated gelsolin family of actin-binding proteins includes adseverin. Here, the authors report the X-ray crystal structure of the N-terminal portion of adseverin and use small-angle scattering and molecular dynamics simulations to examine the calcium-dependent function of this protein.
- Sakesit Chumnarnsilpa
- , Robert C. Robinson
- & Cedric Leyrat

 Mechanism and structural dynamics of sulfur transfer during de novo [2Fe-2S] cluster assembly on ISCU2
Mechanism and structural dynamics of sulfur transfer during de novo [2Fe-2S] cluster assembly on ISCU2