Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Cation-π interactions enabled water-stable perovskite X-ray flat mini-panel imager
Cation-π interactions enabled water-stable perovskite X-ray flat mini-panel imager
The water stability of perovskites remains challenging due to their intrinsic ionic nature. Here, the authors present water stable perovskite X-ray imager driven by strong cation-π interactions between organic cations and a complete release of microstrain during dimension transformation process.
- Wanting Pan
- , Yuhong He
- & Haotong Wei
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrashort vertical-channel MoS2 transistor using a self-aligned contact
Ultrashort vertical-channel MoS2 transistor using a self-aligned contact
The simultaneous scaling down of the channel length and gate length of 2D transistors remains challenging. Here, the authors report a self-alignment process to fabricate vertical MoS2 transistors with sub-1 nm gate length and sub−50 nm channel length, exhibiting on-off ratios over 105 and on-state currents of 250 μA/μm at 4 V bias.
- Liting Liu
- , Yang Chen
- & Yuan Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Purely self-rectifying memristor-based passive crossbar array for artificial neural network accelerators
Purely self-rectifying memristor-based passive crossbar array for artificial neural network accelerators
Designing memristor-integrated passive crossbar arrays to accelerate artificial neural networks with high reliability remains a challenge. Here, the authors propose a self-rectifying resistive switching device incorporated into a crossbar array with a density of 1 kb whose operational performance is assessed in terms of defected-cell proportion, reading margin, and selection functionality.
- Kanghyeok Jeon
- , Jin Joo Ryu
- & Gun Hwan Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Octopus-inspired deception and signaling systems from an exceptionally-stable acene variant
Octopus-inspired deception and signaling systems from an exceptionally-stable acene variant
The design of multifunctional platforms with tunable spectroscopic and fluorescent properties that span the ultraviolet, visible, and near-infrared spectral regions remains challenging. Here, the authors report an actuator-type system that leverages a readily-prepared, easily-processable, and exceptionally-stable nonacene-like molecule to achieve multiple complementary dynamic operating modes.
- Preeta Pratakshya
- , Chengyi Xu
- & Alon A. Gorodetsky
-
Article
| Open Access A broad-spectrum gas sensor based on correlated two-dimensional electron gas
A broad-spectrum gas sensor based on correlated two-dimensional electron gas
Gas sensors typically detect only few specific gases; the authors show a broad-spectrum sensor based on correlated 2-dimensional electron gas (C-2DEG), which detects various gases quantitatively and measures partial pressures, through a purely physical mechanism.
- Yuhao Hong
- , Long Wei
- & Zhaoliang Liao
-
Article
| Open Access Physics-aware differentiable design of magnetically actuated kirigami for shape morphing
Physics-aware differentiable design of magnetically actuated kirigami for shape morphing
A differentiable design framework that integrates both geometrical and magnetomechanical analyses to inversely program the shape morphing in magnetically actuated kirigami is proposed, achieving intricate shapes and multistate transitions.
- Liwei Wang
- , Yilong Chang
- & Wei Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Full hardware implementation of neuromorphic visual system based on multimodal optoelectronic resistive memory arrays for versatile image processing
Full hardware implementation of neuromorphic visual system based on multimodal optoelectronic resistive memory arrays for versatile image processing
In-sensor and near-sensor computing are emerging as the next-generation computing paradigm, for high-density and low-power sensory processing. Here, the authors report a fully hardware-implemented artificial visual system for versatile image processing based on multimodal-multifunctional optoelectronic resistive memory devices with optical and electrical resistive switching modes.
- Guangdong Zhou
- , Jie Li
- & Shukai Duan
-
Article
| Open Access Extendable piezo/ferroelectricity in nonstoichiometric 2D transition metal dichalcogenides
Extendable piezo/ferroelectricity in nonstoichiometric 2D transition metal dichalcogenides
Nonstoichiometric transition metal dichalcogenides break symmetry, enabling piezo/ferroelectric effects. Here, the authors propose an approach to integrate these properties with diverse 2D materials, advancing multifunctional materials and devices.
- Yi Hu
- , Lukas Rogée
- & Shu Ping Lau
-
Article
| Open Access Ground-state electron transfer in all-polymer donor:acceptor blends enables aqueous processing of water-insoluble conjugated polymers
Ground-state electron transfer in all-polymer donor:acceptor blends enables aqueous processing of water-insoluble conjugated polymers
Chemical approaches to improve aqueous dispersions of conjugated polymers are limited by the feasibility of modifying the backbone or lead to poor performance. Here, Liu et al. show that ground-state electron transfer in donor:acceptor blends aids aqueous dispersion, for high conductivity and solubility.
- Tiefeng Liu
- , Johanna Heimonen
- & Simone Fabiano
-
Article
| Open Access Ultra-narrow inhomogeneous spectral distribution of telecom-wavelength vanadium centres in isotopically-enriched silicon carbide
Ultra-narrow inhomogeneous spectral distribution of telecom-wavelength vanadium centres in isotopically-enriched silicon carbide
Several solid-state defect platforms have been proposed for application as a spin-photon interface in quantum communication networks. Here the authors report spin-selective optical transitions and narrow inhomogeneous spectral distribution of V centers in isotopically-enriched SiC emitting in the telecom O-band.
- Pasquale Cilibrizzi
- , Muhammad Junaid Arshad
- & Cristian Bonato
-
Article
| Open Access Highly stretchable polymer semiconductor thin films with multi-modal energy dissipation and high relative stretchability
Highly stretchable polymer semiconductor thin films with multi-modal energy dissipation and high relative stretchability
Stretchable polymer semiconductors with high mechanical and electrical properties are challenging to develop. Wu et al. show that reversible molecular ordering under strain important for performance optimization and relative stretchability can be used to compare the relative strain tolerance of materials.
- Hung-Chin Wu
- , Shayla Nikzad
- & Zhenan Bao
-
Article
| Open Access Record high room temperature resistance switching in ferroelectric-gated Mott transistors unlocked by interfacial charge engineering
Record high room temperature resistance switching in ferroelectric-gated Mott transistors unlocked by interfacial charge engineering
Ferroelectric transistors are promising building blocks for developing energy-efficient memory and logic applications. Here, the authors report a record high 300 K resistance on-off ratio achieved in ferroelectric-gated Mott transistors by exploiting a charge transfer layer to tailor the channel carrier density and mitigate the ferroelectric depolarization effect.
- Yifei Hao
- , Xuegang Chen
- & Xia Hong
-
Article
| Open Access Unconventional polarization fatigue in van der Waals layered ferroelectric ionic conductor CuInP2S6
Unconventional polarization fatigue in van der Waals layered ferroelectric ionic conductor CuInP2S6
The authors find unconventional fatigue characteristics, involving dramatic morphological changes and anomalous polarization enhancement in van der Waals layered ferroelectric CuInP2S6, due to a synergic effect of ionic conduction and surface oxidation.
- Ziwen Zhou
- , Shun Wang
- & Lu You
-
Article
| Open Access Micro- and nanofabrication of dynamic hydrogels with multichannel information
Micro- and nanofabrication of dynamic hydrogels with multichannel information
Responsive hydrogels containing multichannel information have potential in miniature devices, but their fabrication can be challenging. Here, the authors report the creation of hydrogel materials with each pixel containing three-channel information for printing of distinct images in one location.
- Mingchao Zhang
- , Yohan Lee
- & Metin Sitti
-
Article
| Open Access Measuring gas discharge in contact electrification
Measuring gas discharge in contact electrification
Contact electrification triggers gas breakdown. Using Coulomb force to estimate voltage, this work provides experimental evidence for the Paschen curves that govern such discharge.
- Hongcheng Tao
- & James Gibert
-
Article
| Open Access Direct identification of interfacial degradation in blue OLEDs using nanoscale chemical depth profiling
Direct identification of interfacial degradation in blue OLEDs using nanoscale chemical depth profiling
Understanding the degradation mechanism of organic light-emitting diodes is essential to improve device performance and stability. Here, authors present a high-resolution diagnostic method to obtain molecular information with 7-nm depth resolution and analyse devices at different degradation levels.
- Gustavo F. Trindade
- , Soohwan Sul
- & Ian S. Gilmore
-
Article
| Open Access Ultraflexible, cost-effective and scalable polymer-based phase change composites via chemical cross-linking for wearable thermal management
Ultraflexible, cost-effective and scalable polymer-based phase change composites via chemical cross-linking for wearable thermal management
Jing et al. report a cost-effective chemical cross-linking method for synthesizing ultraflexible polymer-based phase change composites with 3D crosslinked networks and further demonstrate portable applications for wearable thermal management.
- Yaoge Jing
- , Zhengchuang Zhao
- & Tingxian Li
-
Article
| Open Access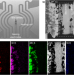 Operando analysis of a solid oxide fuel cell by environmental transmission electron microscopy
Operando analysis of a solid oxide fuel cell by environmental transmission electron microscopy
By contacting a solid oxide fuel cell to a microelectromechanical system inside an environmental electron microscope, the authors establish links between environmental conditions (gas atmosphere, temperature), cell voltage and atomic-scale structure.
- Q. Jeangros
- , M. Bugnet
- & M. Duchamp
-
Article
| Open Access High-performance van der Waals antiferroelectric CuCrP2S6-based memristors
High-performance van der Waals antiferroelectric CuCrP2S6-based memristors
Layered thio- and seleno-phosphate ferroelectrics show promise for next-generation memory but have thermal stability issues. Using the electric field-driven phase transition in antiferroelectric CuCrP2S6, the authors introduce a robust memristor, emphasizing the potential of van der Waals antiferroelectrics in advanced neuromorphic computing.
- Yinchang Ma
- , Yuan Yan
- & Xixiang Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Peculiar transient behaviors of organic electrochemical transistors governed by ion injection directionality
Peculiar transient behaviors of organic electrochemical transistors governed by ion injection directionality
Few studies have investigated the structural properties of organic mixed ionic-electronic conductors in relation to the transient device characteristics. Here, Kim et al. show that backbone-dependent molecular orientation affects ion injection directionality, which determines ion mobility and transient response.
- Ji Hwan Kim
- , Roman Halaksa
- & Myung-Han Yoon
-
Article
| Open Access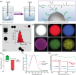 3D-printed liquid metal polymer composites as NIR-responsive 4D printing soft robot
3D-printed liquid metal polymer composites as NIR-responsive 4D printing soft robot
“The combination of stimuli responsive nanomaterials and 3D printing leads interesting applications in the fields of soft robots and actuators. Here, the authors present a 3D printing approach for the fabrication of liquid metal nanoparticles-polymer composites acting as light controlled soft robots which can lift weights, grasp and release items”.
- Liwen Zhang
- , Xumin Huang
- & Ruirui Qiao
-
Article
| Open Access Functional Janus structured liquids and aerogels
Functional Janus structured liquids and aerogels
A combination of functional nanoparticles and liquid streaming can be used to generate structures for the fabrication of soft functional materials. In this study, authors demonstrate the creation of Janus-structured liquids with anisotropic and programmable distributions of nanoparticles by utilizing interfacial assembly and jamming of nanoparticles at the liquid-liquid interface.
- Ahmadreza Ghaffarkhah
- , Seyyed Alireza Hashemi
- & Mohammad Arjmand
-
Article
| Open Access Universal selective transfer printing via micro-vacuum force
Universal selective transfer printing via micro-vacuum force
Transfer printing of inorganic semiconductors is essential for high-performance flexible electronics. Here, Park et al. report the micro-vacuum assisted selective transfer to integrate inorganic thin-film semiconductors on unusual substrates.
- Sang Hyun Park
- , Tae Jin Kim
- & Keon Jae Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Tough soldering for stretchable electronics by small-molecule modulated interfacial assemblies
Tough soldering for stretchable electronics by small-molecule modulated interfacial assemblies
“The interface mismatch of soft substrates and rigid silicon-based microelectronics frequently causes failures of integrated circuits. Here, the authors develop a stretchable solder based on liquid metal-polymer composites which enables seamless integration of electronic components with soft substrates, showcasing high conductivity and stretchability”.
- Liqing Ai
- , Weikang Lin
- & Xi Yao
-
Article
| Open Access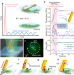 Autonomous nanorobots with powerful thrust under dry solid-contact conditions by photothermal shock
Autonomous nanorobots with powerful thrust under dry solid-contact conditions by photothermal shock
Optically trapping objects, marked by Nobel Prizes in 1997 and 2018 for applications in vacuum and liquids, remains challenging on solid surfaces. Here, the authors demonstrate a breakthrough by using photothermal-shock tweezers and explore nano-conventional robot applications
- Zhaoqi Gu
- , Runlin Zhu
- & Fuxing Gu
-
Article
| Open Access An ultrasmall organic synapse for neuromorphic computing
An ultrasmall organic synapse for neuromorphic computing
Designing high performance organic neuromorphic devices remains a challenge. Here, Liu et al. report the development of an organic synapse based on a semicrystalline polymer PBFCL10 with device dimension of 50 nm and integration size of 1 Kb and a mixed‐signal neuromorphic hardware system based on the organic neuromatrix and FPGA controller for decision‐making tasks.
- Shuzhi Liu
- , Jianmin Zeng
- & Gang Liu
-
Article
| Open Access High speed underwater hydrogel robots with programmable motions powered by light
High speed underwater hydrogel robots with programmable motions powered by light
Underwater soft robots made of stimuli-responsive shape-changing hydrogels generally present low actuation speed which is limited by the water diffusion between hydrogels and their surrounding environment. Here, the authors develop dynamic hydrogel robots with a fast and switchable actuation based on a thermally driven chain conformation change after mechanical programming.
- Chujun Ni
- , Di Chen
- & Qian Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access A robust and tunable Luttinger liquid in correlated edge of transition-metal second-order topological insulator Ta2Pd3Te5
A robust and tunable Luttinger liquid in correlated edge of transition-metal second-order topological insulator Ta2Pd3Te5
The interplay of electronic correlations and topology has been a forefront topic in condensed matter physics. Wang et al. present evidence of a correlated topological edge state supporting the Luttinger liquid behaviour in the candidate quadrupole topological insulator Ta2Pd3Te5.
- Anqi Wang
- , Yupeng Li
- & Jie Shen
-
Article
| Open Access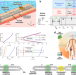 Amphibious epidermal area networks for uninterrupted wireless data and power transfer
Amphibious epidermal area networks for uninterrupted wireless data and power transfer
Body area networks represent a wearable technology suitable for applications like virtual reality and health monitoring. Here, the study presents a wireless battery-free channel that works reliably in harsh environments, including underwater. It utilizes stretchable magneto-inductive metamaterials to enable uninterrupted communication.
- Amirhossein Hajiaghajani
- , Patrick Rwei
- & Peter Tseng
-
Article
| Open Access Critical role of electrons in the short lifetime of blue OLEDs
Critical role of electrons in the short lifetime of blue OLEDs
Designing robust blue organic light-emitting diodes is a long-standing challenge in the display industry. Here, the authors show that electron-induced degradation reactions play a more critical role in the short lifetime of devices with iridium-based emitters under real operational conditions.
- Jaewook Kim
- , Joonghyuk Kim
- & Woo Youn Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Lead-free Zr-doped ceria ceramics with low permittivity displaying giant electrostriction
Lead-free Zr-doped ceria ceramics with low permittivity displaying giant electrostriction
Electrostrictors are materials that develop mechanical strain proportional to the square of the applied electric field. Here authors report. Zr-doped-Ceria as a new lead-free electrostrictive material with a similar electrostriction coefficient to the best electrostrictor material currently in use.
- Maxim Varenik
- , Boyuan Xu
- & Igor Lubomirsky
-
Article
| Open Access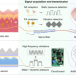 A robotic sensory system with high spatiotemporal resolution for texture recognition
A robotic sensory system with high spatiotemporal resolution for texture recognition
Artificial sensory systems are typically limited by their performance and response to static and dynamic stimuli. Here, Bai et al. propose an iontronic slip-sensor, which responds to both static pressure and high-frequency vibrations up to 400 Hz, achieving high spatiotemporal resolution for texture recognition.
- Ningning Bai
- , Yiheng Xue
- & Chuan Fei Guo
-
Article
| Open Access Direct observation of intrinsic room-temperature ferroelectricity in 2D layered CuCrP2S6
Direct observation of intrinsic room-temperature ferroelectricity in 2D layered CuCrP2S6
CuCrP2S6 is a potential candidate for realizing low-dimensional multiferroicity. Here, authors report direct observation of robust out-of-plane ferroelectricity in the two-dimensional van der Waals layered CuCrP2S6 at room temperature down to 2.6 nm and study its origin from an atomic perspective. (299 in total)
- Weng Fu Io
- , Sin -Yi Pang
- & Jianhua Hao
-
Article
| Open Access Electrocatalytic on-site oxygenation for transplanted cell-based-therapies
Electrocatalytic on-site oxygenation for transplanted cell-based-therapies
Oxygen is the most limiting factor in cell transplantation. Here, the authors present an on-site oxygen production platform for implantable cell therapeutics via electrocatalytic water electrolysis, demonstrating the maintenance of high cell loading in hypoxic incubation and a rat model.
- Inkyu Lee
- , Abhijith Surendran
- & Tzahi Cohen-Karni
-
Article
| Open Access Fabrication of robust and cost-efficient Hoffmann-type MOF sensors for room temperature ammonia detection
Fabrication of robust and cost-efficient Hoffmann-type MOF sensors for room temperature ammonia detection
Developing fast-responsive NH3 sensors at room temperature is challenging. Here the authors developed robust Hoffmann-type MOF based NH3 sensors with a low detection limit (25 ppb) and quick response (5 s). The sensors exhibit high NH3 selectivity, stability, and easy recovery.
- Sa Wang
- , Yu Fu
- & Zhenjie Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access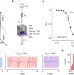 Probabilistic computing with NbOx metal-insulator transition-based self-oscillatory pbit
Probabilistic computing with NbOx metal-insulator transition-based self-oscillatory pbit
Probabilistic computing has recently emerged as a promising energy-based computing system for solving non-deterministic polynomial-time-hard (NP-hard) problems. Here the authors develop a novel pbit unit, using NbOx volatile memristor, in which a self-clocking oscillator harnesses noise-induced metal-insulator transition, enabling high-performance probabilistic computing.
- Hakseung Rhee
- , Gwangmin Kim
- & Kyung Min Kim
-
Article
| Open Access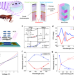 Circular polarization-resolved ultraviolet photonic artificial synapse based on chiral perovskite
Circular polarization-resolved ultraviolet photonic artificial synapse based on chiral perovskite
Circularly polarized light adds a unique dimension to optical information processing and communication. Here, the authors present a development of a photonic artificial synapse device using chiral perovskite hybrid materials and carbon nanotubes. The heterostructure exhibits efficient synaptic and neuromorphic behaviors, enabling accurate recognition of circularly polarized images.
- Qi Liu
- , Qi Wei
- & Mingjie Li
-
Article
| Open Access An artificially-intelligent cornea with tactile sensation enables sensory expansion and interaction
An artificially-intelligent cornea with tactile sensation enables sensory expansion and interaction
Existing artificial corneas can assume partial functions of the human cornea, but sense reconstruction remains a challenge. Qu et al. develop an artificially-intelligent cornea with tactile sensation that enables sensory expansion and interaction.
- Shangda Qu
- , Lin Sun
- & Wentao Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Interface-type tunable oxygen ion dynamics for physical reservoir computing
Interface-type tunable oxygen ion dynamics for physical reservoir computing
Physical reservoirs that contain intrinsic nonlinear dynamic processes could serve as next-generation dynamic computing systems. Here, Liu et al. introduced an interface-type transistor based on oxygen ion dynamics to perform reservoir computing.
- Zhuohui Liu
- , Qinghua Zhang
- & Chen Ge
-
Article
| Open Access Printed sustainable elastomeric conductor for soft electronics
Printed sustainable elastomeric conductor for soft electronics
Printed stretchable electronics with sustainable elastomers are typically limited by their electro-mechanical performances. Herein, Lv et al. report a sustainable vegetable oil-based polyurethane-enabled printed conductor with high performance enabled by the porous binder and sintering of silver flakes.
- Jian Lv
- , Gurunathan Thangavel
- & Pooi See Lee
-
Article
| Open Access The ultra-thin, minimally invasive surface electrode array NeuroWeb for probing neural activity
The ultra-thin, minimally invasive surface electrode array NeuroWeb for probing neural activity
Minimal invasiveness and robust signal detection are required in neural probes. Here, the authors develop NeuroWeb, an ultra-thin, minimally invasive surface electrode array. In vivo electrophysiological and optogenetic experiments show single-unit activity of neurons with high signal-to-noise ratio.
- Jung Min Lee
- , Young-Woo Pyo
- & Hong-Gyu Park
-
Article
| Open Access Negative capacitors and inductors enabling wideband waveguide metatronics
Negative capacitors and inductors enabling wideband waveguide metatronics
The authors showcase a method to design negative lumped elements by engineering the effective permittivity within the waveguide, which enables realizations of wideband waveguide metatronics and promises performance enhancement in various fields.
- Xu Qin
- , Pengyu Fu
- & Yue Li
-
Article
| Open Access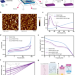 Azobenzene-based optoelectronic transistors for neurohybrid building blocks
Azobenzene-based optoelectronic transistors for neurohybrid building blocks
Designing efficient optoelectronic synaptic devices with advanced light responsive multimodal platforms remains a challenge. Here, the authors report on an organic optoelectronic neuromorphic platform that is based on conductive polymers and light-sensitive molecules that can be used to imitate the retina including visual pathways and typical memory processes of neurons.
- Federica Corrado
- , Ugo Bruno
- & Francesca Santoro
-
Article
| Open Access Reconfigurable self-assembly of photocatalytic magnetic microrobots for water purification
Reconfigurable self-assembly of photocatalytic magnetic microrobots for water purification
Microrobot collectives promise new functions beyond individuals’ capability. Here, nature-inspired reconfigurable self-assembly of microrobots was created, driven by their photocatalytic and magnetic properties, showing potential application in water purification.
- Mario Urso
- , Martina Ussia
- & Martin Pumera
-
Article
| Open Access Organic photodiodes with bias-switchable photomultiplication and photovoltaic modes
Organic photodiodes with bias-switchable photomultiplication and photovoltaic modes
Preparation of photodiodes with photomultiplication/photovoltaic two operating modes is promising but challenging. Here, the authors report a bias-switchable dual-mode organic photodiode by adopting traps and blocking layer, achieving detectivity of 1012 Jones and fast response speed in both modes.
- Qingxia Liu
- , Lingfeng Li
- & Yadong Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access A super liquid-repellent hierarchical porous membrane for enhanced membrane distillation
A super liquid-repellent hierarchical porous membrane for enhanced membrane distillation
Membrane distillation is an emerging desalination technology to obtain freshwater from saline based on low-grade energy. Here the authors report on novel superhydrophobic hierarchical porous membranes with enhanced distillation flux suitable for desalination or wastewater treatment.
- Youmin Hou
- , Prexa Shah
- & Hans-Jürgen Butt
-
Article
| Open Access Realistic prediction and engineering of high-Q modes to implement stable Fano resonances in acoustic devices
Realistic prediction and engineering of high-Q modes to implement stable Fano resonances in acoustic devices
The authors demonstrate that laser Doppler vibrometer measurements are a powerful tool for predicting the maximum pressure enhancement of high-Q modes. The results presented enable future applications of acoustic BICs by filling the missing data gap on field enhancement.
- Felix Kronowetter
- , Marcus Maeder
- & Steffen Marburg
-
Article
| Open Access Rheological engineering of perovskite suspension toward high-resolution X-ray flat-panel detector
Rheological engineering of perovskite suspension toward high-resolution X-ray flat-panel detector
The film uniformity is essential to the fixed pattern noise (FPN) and resolution of X-ray detectors. Here the authors demonstrate the rheological engineering of the perovskite suspension to achieve low FPN of 1.39% and high resolution of 0.51 lp/pix.
- Zihao Song
- , Xinyuan Du
- & Jiang Tang
-
Article
| Open Access Programming actuation onset of a liquid crystalline elastomer via isomerization of network topology
Programming actuation onset of a liquid crystalline elastomer via isomerization of network topology
Tuning actuation temperatures of liquid crystalline elastomers can help control actuation behaviour, but normally cannot be altered following the synthesis of the material. Here, the authors report the development of an elastomer with varying actuation temperature depending on the conditions.
- Guancong Chen
- , Haijun Feng
- & Qian Zhao

 Compact and wideband nanoacoustic pass-band filters for future 5G and 6G cellular radios
Compact and wideband nanoacoustic pass-band filters for future 5G and 6G cellular radios