Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access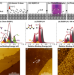 EUV-induced hydrogen desorption as a step towards large-scale silicon quantum device patterning
EUV-induced hydrogen desorption as a step towards large-scale silicon quantum device patterning
Scanning tunnelling microscopy-based H desorption lithography is used for atomic-scale patterning of quantum devices in Si, but its time-consuming nature hinders scalability. Here the authors report H desorption from Si(001):H surface using extreme-UV light and explore implications for patterning.
- Procopios Constantinou
- , Taylor J. Z. Stock
- & Steven R. Schofield
-
Article
| Open Access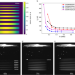 Deconvolution volumetric additive manufacturing
Deconvolution volumetric additive manufacturing
Volumetric additive manufacturing generally suffers from systematic undercuring of fine features, which limits its application range. Here, authors develop a model to predict print time variation with feature size and propose a deconvolution method, enabling precise fabrication of intricate structures.
- Antony Orth
- , Daniel Webber
- & Chantal Paquet
-
Article
| Open Access Direct laser writing of 3D electrodes on flexible substrates
Direct laser writing of 3D electrodes on flexible substrates
This report describes a 3D microelectrode array integrated on a thin-film flexible cable using traditional thin-film processing techniques and direct laser writing of 3D structures at micron resolution via two-photon lithography for neural recording.
- Morgan A. Brown
- , Kara M. Zappitelli
- & Timothy J. Gardner
-
Article
| Open Access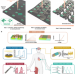 High-speed, scanned laser structuring of multi-layered eco/bioresorbable materials for advanced electronic systems
High-speed, scanned laser structuring of multi-layered eco/bioresorbable materials for advanced electronic systems
Designing and manufacturing eco/bioresorbable electronic systems remains a challenge. The authors introduce a picosecond-pulsed laser-based scheme that exploits controlled patterning, thinning, and/or cutting to manipulate multilayers of eco/bioresorbable materials for a wide range of advanced electronic systems.
- Quansan Yang
- , Ziying Hu
- & John A. Rogers
-
Article
| Open Access Sub-wavelength patterned pulse laser lithography for efficient fabrication of large-area metasurfaces
Sub-wavelength patterned pulse laser lithography for efficient fabrication of large-area metasurfaces
Fabrication of metasurfaces with nanoscale structures is inefficient for large areas. Here, the authors introduce patterned pulse laser lithography for creating structured arrays with sub-wavelength feature on large-area thin films under ambient conditions.
- Lingyu Huang
- , Kang Xu
- & Shaolin Xu
-
Article
| Open Access An achromatic X-ray lens
An achromatic X-ray lens
X-ray diffractive and refractive optical elements suffer from chromatic aberrations, limiting high-resolution X-ray microscopes mainly to bright synchrotron sources. Here, the authors experimentally realise an achromatic X-ray lens by combing a focusing diffractive Fresnel zone plate and a defocusing refractive lens.
- Adam Kubec
- , Marie-Christine Zdora
- & Christian David
-
Article
| Open Access Direct-laser writing for subnanometer focusing and single-molecule imaging
Direct-laser writing for subnanometer focusing and single-molecule imaging
Focus-locking improves localization precision in single-molecule microscopy, but fiducials are often deposited at random and provide limited 3D compensation. Here, the authors fabricate 3D optical fiducials with nanometer accuracy by two-photon direct laser writing, and demonstrate isotropic 3D focus locking.
- Simao Coelho
- , Jongho Baek
- & Katharina Gaus
-
Article
| Open Access High-resolution light field prints by nanoscale 3D printing
High-resolution light field prints by nanoscale 3D printing
Light field prints displaying 3D information often appear pixelated due to limited resolution and misalignment between lenses and colour pixels. Here, the authors present a one-step process via two-photon polymerization lithography to fabricate light field prints with high spatial and angular resolution.
- John You En Chan
- , Qifeng Ruan
- & Joel K. W. Yang
-
Article
| Open Access A universal method for depositing patterned materials in situ
A universal method for depositing patterned materials in situ
Complexity and harsh working conditions pose limitations for fabrication of patterned materials. Here the authors report a single-step method for in situ deposition of materials that is based on semiconductor nanoparticle assisted photon-induced chemical reduction and optical trapping.
- Yifan Chen
- , Siu Fai Hung
- & Sen Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Near-field sub-diffraction photolithography with an elastomeric photomask
Near-field sub-diffraction photolithography with an elastomeric photomask
Photolithography is an established microfabrication technique but commonly uses costly shortwavelength light sources to achieve high resolution. Here the authors use metal patterns embedded in a flexible elastomer photomask with mechanical robustness for generation of subdiffraction patterns as a cost effective near-field optical printing approach.
- Sangyoon Paik
- , Gwangmook Kim
- & Wooyoung Shim
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrafast multi-focus 3-D nano-fabrication based on two-photon polymerization
Ultrafast multi-focus 3-D nano-fabrication based on two-photon polymerization
Two photon polymerization (TPP) allows nanofabrication of three dimensional objects with complex geometries, but is considered to be slow with a limited fabrication rate. Here the authors present a TPP technique based on a digital mirror device scanner which allows for fast parallel nanofabrication with improved precision and flexibility.
- Qiang Geng
- , Dien Wang
- & Shih-Chi Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Cascaded collimator for atomic beams traveling in planar silicon devices
Cascaded collimator for atomic beams traveling in planar silicon devices
Bringing atomic beam technology to the chip scale is challenging due to the long distance required to filter the velocity distribution. Here, the authors report an engineering strategy for on-chip filtering of the velocity profile of atomic beams by fabricating planar, etched microchannel arrays.
- Chao Li
- , Xiao Chai
- & C. Raman
-
Article
| Open Access Integrating temporal and spatial control of electronic transitions for bright multiphoton upconversion
Integrating temporal and spatial control of electronic transitions for bright multiphoton upconversion
Here, the authors control concentration quenching in a stoichiometric Er3+ compound using a core−shell nanostructured host and an integrated optical waveguide circuit excitation platform. The efficient telecom to ultraviolet upconversion allows for exploration of photonic applications involving upconversion nanomaterials.
- Tianying Sun
- , Yuhua Li
- & Feng Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Highly indistinguishable photons from deterministic quantum-dot microlenses utilizing three-dimensional in situ electron-beam lithography
Highly indistinguishable photons from deterministic quantum-dot microlenses utilizing three-dimensional in situ electron-beam lithography
Single indistinguishable photon sources with high flux rates and purity are needed in quantum communications. Here, Gschreyet al. use three-dimensional electron-beam lithography to pattern deterministic quantum-dot microlenses and demonstrate enhanced photon-extraction efficiency and photon indistinguishability.
- M. Gschrey
- , A. Thoma
- & S. Reitzenstein
-
Article |
 Seeded growth of highly crystalline molybdenum disulphide monolayers at controlled locations
Seeded growth of highly crystalline molybdenum disulphide monolayers at controlled locations
Although synthesis of high-quality MoS2 has been demonstrated, growth of monolayer MoS2at controlled locations is highly desirable for applications. Here, the authors introduce a method where patterned seeds of molybdenum source material are used to grow isolated flakes at predetermined locations.
- Gang Hee Han
- , Nicholas J. Kybert
- & A. T. Charlie Johnson
-
Article
| Open Access Dip-pen patterning of poly(9,9-dioctylfluorene) chain-conformation-based nano-photonic elements
Dip-pen patterning of poly(9,9-dioctylfluorene) chain-conformation-based nano-photonic elements
The optoelectronic properties of semiconducting polymers are controlled by altering chemical structure and/or inter-chain order. Perevedentsev et al. propose a nanopatterning approach whereby the geometry of polymer chain segments is modified to engineer metamaterial structures for visible light.
- Aleksandr Perevedentsev
- , Yannick Sonnefraud
- & Donal D. C. Bradley
-
Article |
 High-resolution nanotransfer printing applicable to diverse surfaces via interface-targeted adhesion switching
High-resolution nanotransfer printing applicable to diverse surfaces via interface-targeted adhesion switching
There is an ongoing need for high resolution, versatile and simplistic nanoscale lithography and transfer. Here the authors report a solvent-assisted nanotransfer printing route, which allows for the easy release of 8–20 nm scale features on to a range of substrates.
- Jae Won Jeong
- , Se Ryeun Yang
- & Yeon Sik Jung
-
Article |
 Three-dimensional plasmonic stereoscopic prints in full colour
Three-dimensional plasmonic stereoscopic prints in full colour
Plasmonic nanostructures enable control over the spatial and spectral dependence of scattered light. Here, the authors use pixels formed of nanoellipse or nanosquare dimers to show polarization-dependent full-colour scattering in reflection, and build 3D stereoscopic colour microprints from them.
- Xiao Ming Goh
- , Yihan Zheng
- & Joel K. W. Yang
-
Article |
 Nanomotor lithography
Nanomotor lithography
Miniaturization of devices and machines requires advanced lithographic techniques, whilst the high cost and complexity are the bottlenecks. Li et al.now show an approach for direct, arbitrary nano-patterning using self-propelled nanomotors acting as mobile nanomasks and near-field lenses.
- Jinxing Li
- , Wei Gao
- & Joseph Wang
-
Article |
 Robust and versatile ionic liquid microarrays achieved by microcontact printing
Robust and versatile ionic liquid microarrays achieved by microcontact printing
Ionic liquids are widely used in diverse applications as solvents with high thermal and chemical stability. Gunawan et al.develop a protocol for fabrication of an ionic liquid microdroplet array using a soft lithography technique, and demonstrate its utility as a membrane-free high-performance gas sensor.
- Christian A. Gunawan
- , Mengchen Ge
- & Chuan Zhao
-
Article |
 Laser printing of silicon nanoparticles with resonant optical electric and magnetic responses
Laser printing of silicon nanoparticles with resonant optical electric and magnetic responses
Silicon nanoparticles are of interest for their optical properties, for example, in light scattering. Here, Zywietz et al. achieve the laser printing of silicon nanoparticles on a substrate at predefined positions, and with control over their crystalline phase.
- Urs Zywietz
- , Andrey B. Evlyukhin
- & Boris N. Chichkov
-
Article |
 Two-photon polarization-selective etching of emergent nano-structures on diamond surfaces
Two-photon polarization-selective etching of emergent nano-structures on diamond surfaces
Using light to manipulate matter on scales smaller than its wavelength presents a major challenge. Here, the authors show that two-photon surface excitation of diamond surfaces etches a variety of nano-scale patterns, comprising evidence for carbon ejection via a highly localized photon interaction with the crystal bonds.
- A. Lehmann
- , C. Bradac
- & R. P. Mildren
-
Article
| Open Access Deterministic and electrically tunable bright single-photon source
Deterministic and electrically tunable bright single-photon source
Bright and tunable single-photon sources are essential for future quantum technologies. Here, the authors deterministically couple a quantum dot to a pillar structure that enables application of electric fields to provide a tunable single-photon source with a demonstrated extraction efficiency of 53%.
- A. K. Nowak
- , S. L. Portalupi
- & P. Senellart
-
Article |
 Highly stretchable and transparent nanomesh electrodes made by grain boundary lithography
Highly stretchable and transparent nanomesh electrodes made by grain boundary lithography
One of the key components in stretchable electronics is the electrical conductors, which need to show a low electrical resistance even when strained. Here, by using sacrificial grain boundaries as a fabrication template, Guo and colleagues fabricate highly transparent gold nanomesh electrodes with exceptionally high stretchability.
- Chuan Fei Guo
- , Tianyi Sun
- & Zhifeng Ren
-
Article |
 Atomic layer lithography of wafer-scale nanogap arrays for extreme confinement of electromagnetic waves
Atomic layer lithography of wafer-scale nanogap arrays for extreme confinement of electromagnetic waves
Electromagnetic waves passing through nanogaps can be strongly enhanced, leading to novel physical phenomena. Chen et al. present a new method of atomic layer lithography for patterning uniform arrays of subnanometre gaps in metal films using adhesive tape and show unprecedented field enhancements.
- Xiaoshu Chen
- , Hyeong-Ryeol Park
- & Sang-Hyun Oh
-
Article
| Open Access Three-dimensional deep sub-diffraction optical beam lithography with 9 nm feature size
Three-dimensional deep sub-diffraction optical beam lithography with 9 nm feature size
The fabrication of three-dimensional nanoscale structures is important to nanophotonic applications where light is guided and controlled. The optical beam lithography scheme developed by Gan and colleagues enables the fabrication of three-dimensional structures with feature sizes down to 9 nm.
- Zongsong Gan
- , Yaoyu Cao
- & Min Gu
-
Article |
 Large-scale organic nanowire lithography and electronics
Large-scale organic nanowire lithography and electronics
The high-speed, large-area printing of aligned semiconducting nanowires is vital for practical device applications. Here, the authors use a high-speed printing technique to print semiconducting nanowire arrays onto device substrates with precise nanowire control, and high field-effect mobilities are observed.
- Sung-Yong Min
- , Tae-Sik Kim
- & Tae-Woo Lee
-
Article |
 Bright solid-state sources of indistinguishable single photons
Bright solid-state sources of indistinguishable single photons
For quantum technologies to become widespread and scalable, bright sources of indistinguishable single photons are essential. Through deterministic positioning of quantum dots in pillar cavities, Gazzano et al.present a solid-state single-photon source with brightness as large as 0.65 photons per pulse.
- O. Gazzano
- , S. Michaelis de Vasconcellos
- & P. Senellart
-
Article |
 Non-polydimethylsiloxane devices for oxygen-free flow lithography
Non-polydimethylsiloxane devices for oxygen-free flow lithography
Flow lithography is used to synthesize microparticles but relies on polydimethylsiloxane microchannels for oxygen to permeate and inhibit polymerization near channel interfaces. Now, non-polydimethylsiloxane devices have been developed, which allow oxygen-free lithography, increasing the capabilities of flow lithography.
- Ki Wan Bong
- , Jingjing Xu
- & Patrick S. Doyle

 One-photon three-dimensional printed fused silica glass with sub-micron features
One-photon three-dimensional printed fused silica glass with sub-micron features