Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Endothelial cells regulate alveolar morphogenesis by constructing basement membranes acting as a scaffold for myofibroblasts
Endothelial cells regulate alveolar morphogenesis by constructing basement membranes acting as a scaffold for myofibroblasts
During alveologenesis myofibroblasts contractions at terminal sacs produce alveoli in the lungs. Here they show that endothelial cells promote myofibroblast-driven alveologenesis by forming basement membranes via Rap1-induced integrin β1 activation.
- Haruko Watanabe-Takano
- , Katsuhiro Kato
- & Shigetomo Fukuhara
-
Article
| Open Access LFA-1 nanoclusters integrate TCR stimulation strength to tune T-cell cytotoxic activity
LFA-1 nanoclusters integrate TCR stimulation strength to tune T-cell cytotoxic activity
CD8+ T cell activation involves cooperation between the T cell receptor and the integrin LFA-1. Here authors show how LFA-1 nanoclusters participate in the calibration of TCR stimulation strength and activation of cytotoxic function in CD8+ T cells.
- Claire Lacouture
- , Beatriz Chaves
- & Loïc Dupré
-
Article
| Open Access De novo design of highly selective miniprotein inhibitors of integrins αvβ6 and αvβ8
De novo design of highly selective miniprotein inhibitors of integrins αvβ6 and αvβ8
Roy et al. describe a generalized method for computationally designing miniproteins selective for a single integrin heterodimer and conformational state. The designed αvβ6 inhibitor remains monomeric and maintains biological activity following aerosolization and shows excellent efficacy in bleomycin induced lung fibrosis.
- Anindya Roy
- , Lei Shi
- & David Baker
-
Article
| Open Access Integrin β3 directly inhibits the Gα13-p115RhoGEF interaction to regulate G protein signaling and platelet exocytosis
Integrin β3 directly inhibits the Gα13-p115RhoGEF interaction to regulate G protein signaling and platelet exocytosis
Zhang et al. show that the adhesion receptor integrin β3 directly inhibits G protein mediated RhoA activation and granule secretion. A peptide mimicking this effect selectively inhibits platelet secretion but not integrin-mediated platelet adhesion.
- Yaping Zhang
- , Xiaojuan Zhao
- & Xiaoping Du
-
Article
| Open Access Cryo-EM structures of full-length integrin αIIbβ3 in native lipids
Cryo-EM structures of full-length integrin αIIbβ3 in native lipids
The structural basis of integrin signaling in health and disease is not fully understood. Here, the authors determine the cryoEM structure of full-length platelet integrin αIIbβ3 in its apo and eptifibatide-bound conformations in a native membrane environment.
- Brian D. Adair
- , Jian-Ping Xiong
- & M. Amin Arnaout
-
Article
| Open Access In mitosis integrins reduce adhesion to extracellular matrix and strengthen adhesion to adjacent cells
In mitosis integrins reduce adhesion to extracellular matrix and strengthen adhesion to adjacent cells
Adopting a round cell morphology before mitosis is crucial. Here, the authors show that in mitosis integrins binding to ligands do not engage the actomyosin cortex, which curbs cell-extracellular matrix adhesion, though β1 integrins are rewired to synergize with cadherins in mitotic cell-cell adhesion.
- Maximilian Huber
- , Javier Casares-Arias
- & Nico Strohmeyer
-
Article
| Open Access Antigen discrimination by T cells relies on size-constrained microvillar contact
Antigen discrimination by T cells relies on size-constrained microvillar contact
T cells can use TCR on microvilli to interact with peptide-MHC (pMHC) complexes on antigen presenting cells. Here the authors characterise how T cells use microvilli to interrogate reconstituted membranes for pMHC complexes and how this is regulated by a balance between glycoproteins/glycocalyces that reduce detection, and the small adhesion protein CD2, which enhances detection.
- Edward Jenkins
- , Markus Körbel
- & David Klenerman
-
Article
| Open Access Specificity of TGF-β1 signal designated by LRRC33 and integrin αVβ8
Specificity of TGF-β1 signal designated by LRRC33 and integrin αVβ8
Microenvironment localization and activation of L-TGF-β1 determine its specific function. Here, the authors elucidated the underlying mechanisms of specific presentation of L-TGF-β1 on the surface of myeloid lineage cells designated by LRRC33, and its activation by integrin αVβ8.
- Zelin Duan
- , Xuezhen Lin
- & Zhe Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanically active integrins target lytic secretion at the immune synapse to facilitate cellular cytotoxicity
Mechanically active integrins target lytic secretion at the immune synapse to facilitate cellular cytotoxicity
Cytotoxic response is mediated by delivery of lytic molecules at the effector cell/target cell junction site, termed the immunological synapse. Here the authors find, using single cell biophysical measurements, that the during this process the αLβ2 integrin, LFA-1, helps focus lytic granule release via talin-dependent, pulling force-mediated spatial guidance.
- Mitchell S. Wang
- , Yuesong Hu
- & Morgan Huse
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanism of integrin activation by talin and its cooperation with kindlin
Mechanism of integrin activation by talin and its cooperation with kindlin
The authors report here that talin and kindlin, the two key integrin binders and activators, are bridged by paxillin to induce microclustering of integrins to potently bind to multivalent extracellular ligand and trigger rapid cell attachment.
- Fan Lu
- , Liang Zhu
- & Jun Qin
-
Article
| Open Access A loss-of-adhesion CRISPR-Cas9 screening platform to identify cell adhesion-regulatory proteins and signaling pathways
A loss-of-adhesion CRISPR-Cas9 screening platform to identify cell adhesion-regulatory proteins and signaling pathways
Targeting integrin-mediated retention of malignant B cells in their protective microenvironment is an efficacious treatment for lymphoma and leukemia. Here, the authors present an unbiased loss-of-adhesion CRISPR screening method, identifying therapeutic targets for these B-cell malignancies.
- Martin F. M. de Rooij
- , Yvonne J. Thus
- & Marcel Spaargaren
-
Article
| Open Access PI3Kγ stimulates a high molecular weight form of myosin light chain kinase to promote myeloid cell adhesion and tumor inflammation
PI3Kγ stimulates a high molecular weight form of myosin light chain kinase to promote myeloid cell adhesion and tumor inflammation
Myeloid cell recruitment during tumor inflammation depends on the VCAM-1 receptor integrin α4β1. Here the authors show that a high molecular weight form of myosin light chain kinase, MLCK210, is required for myeloid cell integrin α4β1 activation and adhesion and that MLCK210 inhibition reduces tumor growth and inflammation in preclinical cancer models.
- Michael C. Schmid
- , Sang Won Kang
- & Judith A. Varner
-
Article
| Open Access Dual clathrin and integrin signaling systems regulate growth factor receptor activation
Dual clathrin and integrin signaling systems regulate growth factor receptor activation
The integration and organization of growth factor signaling, adhesion, and endocytosis is poorly understood. Here the authors use light and electron microscopy to shed light on the role of flat clathrin lattices and cell adhesion in growth factor signaling.
- Marco A. Alfonzo-Méndez
- , Kem A. Sochacki
- & Justin W. Taraska
-
Article
| Open Access Turn-key mapping of cell receptor force orientation and magnitude using a commercial structured illumination microscope
Turn-key mapping of cell receptor force orientation and magnitude using a commercial structured illumination microscope
The authors have recently developed molecular force microscopy (MFM) which uses fluorescence polarisation to measure cell-surface receptor force orientation. Here they show that structured illumination microscopes, which inherently use fluorescence polarisation, can be used for MFM in a turn-key manner.
- Aaron Blanchard
- , J. Dale Combs
- & Khalid Salaita
-
Article
| Open Access Structural mechanism of laminin recognition by integrin
Structural mechanism of laminin recognition by integrin
Recognition of laminin by integrin receptors mediates epithelial cell adhesion to basement membrane. Here, the structures of the α6β1 integrin alone and in complex with three-chain laminin-511 fragment reveal the laminin-integrin interface in molecular detail.
- Takao Arimori
- , Naoyuki Miyazaki
- & Junichi Takagi
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular motion and tridimensional nanoscale localization of kindlin control integrin activation in focal adhesions
Molecular motion and tridimensional nanoscale localization of kindlin control integrin activation in focal adhesions
Focal adhesions (FAs) initiate chemical and mechanical signals involved in cell polarity, migration, proliferation and differentiation. Here, authors combine single protein tracking, super-resolution microscopy and functional assays, which allow correlating the molecular behaviour and 3D nanoscale localization of kindlin with its function in integrin activation inside FAs.
- Thomas Orré
- , Adrien Joly
- & Grégory Giannone
-
Article
| Open Access Mapping the molecular and structural specialization of the skin basement membrane for inter-tissue interactions
Mapping the molecular and structural specialization of the skin basement membrane for inter-tissue interactions
The basement membrane is located at tissue interfaces, but how it mediates distinct inter-tissue interactions is unclear. Here, the authors systematically define the spatial heterogeneity of skin basement membrane composition and show its functional importance in inter-tissue interactions.
- Ko Tsutsui
- , Hiroki Machida
- & Hironobu Fujiwara
-
Article
| Open Access Quantitative single-protein imaging reveals molecular complex formation of integrin, talin, and kindlin during cell adhesion
Quantitative single-protein imaging reveals molecular complex formation of integrin, talin, and kindlin during cell adhesion
Single-molecule localisation microscopy is limited by low labeling and detection efficiencies of the molecular probes. Here the authors report a framework to obtain absolute molecular quantities on a true molecular scale; the data reveal a ternary adhesion complex underlying cell-matrix adhesion.
- Lisa S. Fischer
- , Christoph Klingner
- & Carsten Grashoff
-
Article
| Open Access Diaphanous-related formin mDia2 regulates beta2 integrins to control hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell engraftment
Diaphanous-related formin mDia2 regulates beta2 integrins to control hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell engraftment
Bone marrow engraftment of haematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPCs) requires homing and lodgement to the niche. Here, the authors show that mDia2 is required for HSPC polarization, nuclear MAL, and SRF-induced beta2 integrin expression during transendothelial migration of HSPCs required for engraftment.
- Yang Mei
- , Xu Han
- & Peng Ji
-
Article
| Open Access Rab11b-mediated integrin recycling promotes brain metastatic adaptation and outgrowth
Rab11b-mediated integrin recycling promotes brain metastatic adaptation and outgrowth
Mechanisms governing adaptation of breast cancer to the brain metastatic microenvironment are unclear. Here, the authors use RNA-sequencing and Drosophila screening to identify Rab11b-mediated endosomal recycling as a unique mechanism for adaptation to a challenging metastatic microenvironment, which can be exploited by repurposing statins.
- Erin N. Howe
- , Miranda D. Burnette
- & Siyuan Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Forces during cellular uptake of viruses and nanoparticles at the ventral side
Forces during cellular uptake of viruses and nanoparticles at the ventral side
Many intracellular pathogens mimic extracellular matrix motifs to specifically interact with the host membrane which may influences virus particle uptake. Here authors use single molecule tension sensors to reveal the minimal forces exerted on single virus particles and demonstrate that the uptake forces scale with the adhesion energy.
- Tina Wiegand
- , Marta Fratini
- & Joachim P. Spatz
-
Article
| Open Access General structural features that regulate integrin affinity revealed by atypical αVβ8
General structural features that regulate integrin affinity revealed by atypical αVβ8
The activation mechanism of integrin αVβ8 differs from other integrins. Combining X-ray crystallography, hydrogen deuterium exchange mass spectrometry and mutation, the authors reveal structural features responsible for these differences and provide insights into how typical integrins are regulated.
- Jianchuan Wang
- , Yang Su
- & Timothy A. Springer
-
Article
| Open Access Integrin-linked kinase controls retinal angiogenesis and is linked to Wnt signaling and exudative vitreoretinopathy
Integrin-linked kinase controls retinal angiogenesis and is linked to Wnt signaling and exudative vitreoretinopathy
Integrin-linked kinase (ILK) is an important mediator of integrin signaling. Here Park et al. show that mice with endothelial-specific deletion of Ilk develop vascular defects that resemble familial exudative vitreoretinopathy, and identify mutations in ILK in patients with exudative vitreoretinopathy suggesting a potential role in human pathogenesis.
- Hongryeol Park
- , Hiroyuki Yamamoto
- & Ralf H. Adams
-
Article
| Open Access DNA mechanotechnology reveals that integrin receptors apply pN forces in podosomes on fluid substrates
DNA mechanotechnology reveals that integrin receptors apply pN forces in podosomes on fluid substrates
Podosomes are protrusive structures that coordinate diverse functions related to cell invasion, migration, bone resorption and immune surveillance. Here the authors integrate DNA nanotechnology with FLIM-FRET to demonstrate that podosomes apply pN integrin tensile forces to sense and respond to substrate mechanics.
- Roxanne Glazier
- , Joshua M. Brockman
- & Khalid Salaita
-
Article
| Open Access Thrombospondin-3 augments injury-induced cardiomyopathy by intracellular integrin inhibition and sarcolemmal instability
Thrombospondin-3 augments injury-induced cardiomyopathy by intracellular integrin inhibition and sarcolemmal instability
Thrombospondin 4 has been shown to protect the heart and the skeletal muscle by enhancing matrix secretion and membrane stability thanks to its intracellular function. Here the authors show that thrombospondin 3 exacerbates injury-induced cardiomyopathy and promotes destabilization of the cardiomyocyte membrane by impairing integrin trafficking to the sarcolemma.
- Tobias G. Schips
- , Davy Vanhoutte
- & Jeffery D. Molkentin
-
Article
| Open Access Cis interaction between sialylated FcγRIIA and the αI-domain of Mac-1 limits antibody-mediated neutrophil recruitment
Cis interaction between sialylated FcγRIIA and the αI-domain of Mac-1 limits antibody-mediated neutrophil recruitment
Deposited immune complexes (IC) promote neutrophil recruitment, but the fine tuning of this process is still unclear. Here the authors show that the cis interaction of the IC receptor, FcγRIIA and CD18 integrin, Mac-1, on the neutrophil surface modulates neutrophil adhesion, with FcγRIIA sialylation specifically implicated in this interaction.
- Gurpanna Saggu
- , Koshu Okubo
- & Tanya N. Mayadas
-
Article
| Open Access Cell metabolism regulates integrin mechanosensing via an SLC3A2-dependent sphingolipid biosynthesis pathway
Cell metabolism regulates integrin mechanosensing via an SLC3A2-dependent sphingolipid biosynthesis pathway
Mechanical and metabolic cues contribute to regulate cell and tissue homeostasis but how they are integrated is not known. Here the authors show that the amino acid transporter and integrin coreceptor CD98hc regulates mechanical signaling downstream of integrins indirectly through regulating sphingolipid availability.
- Etienne Boulter
- , Soline Estrach
- & Chloé C. Féral
-
Article
| Open Access Compression force sensing regulates integrin αIIbβ3 adhesive function on diabetic platelets
Compression force sensing regulates integrin αIIbβ3 adhesive function on diabetic platelets
Diabetes is associated with an increased thrombotic response, but the mechanism is unknown. Here the authors demonstrate that compressive force activates integrin αIIbβ3 on discoid diabetic platelets and that platelet aggregates can be eliminated by PI 3-kinase inhibition, but not by anti-thrombotics aspirin or clopidogrel.
- Lining Ju
- , James D. McFadyen
- & Shaun P. Jackson
-
Article
| Open Access MT4-MMP deficiency increases patrolling monocyte recruitment to early lesions and accelerates atherosclerosis
MT4-MMP deficiency increases patrolling monocyte recruitment to early lesions and accelerates atherosclerosis
Matrix metalloproteinases (MMP) are involved in vascular remodeling associated with plaque progression. Little is known about their immune regulatory role in vascular disorders. Here, the authors report that MT4-MMP-deficiency increases the recruitment of patrolling monocytes to early atherosclerotic lesions, which accelerates atherosclerosis.
- Cristina Clemente
- , Cristina Rius
- & Alicia G. Arroyo
-
Article
| Open Access Vps3 and Vps8 control integrin trafficking from early to recycling endosomes and regulate integrin-dependent functions
Vps3 and Vps8 control integrin trafficking from early to recycling endosomes and regulate integrin-dependent functions
The CORVET complex is a multi-subunit complex that regulates fusion between early endosomes. Here the authors show that the CORVET subunits Vps3 and Vps8 also regulate vesicular transport from early to recycling endosomes and are required for recycling integrins to the plasma membrane.
- Caspar T. H. Jonker
- , Romain Galmes
- & Judith Klumperman
-
Article
| Open Access The opposing forces of shear flow and sphingosine-1-phosphate control marginal zone B cell shuttling
The opposing forces of shear flow and sphingosine-1-phosphate control marginal zone B cell shuttling
Marginal zone B (MZB) cells shuttle between the marginal zone and lymphoid follicle to capture and present peripheral blood antigens. Here the authors show that shear force, such as blood flow from the sinus around the follicle, is a directional cue that induces MZB migration on ICAM-1, and that S1P signaling inhibits this directional migration.
- Kerry Tedford
- , Michael Steiner
- & Klaus-Dieter Fischer
-
Article
| Open Access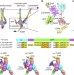 Direction of actin flow dictates integrin LFA-1 orientation during leukocyte migration
Direction of actin flow dictates integrin LFA-1 orientation during leukocyte migration
Integrin αβ heterodimer cell surface receptors mediate adhesive interactions that provide traction for cell migration. Here the authors show that actin flow can orient cell surface integrins during leukocyte migration, suggesting integrin activation by cytoskeletal force.
- Pontus Nordenfelt
- , Travis I. Moore
- & Timothy A. Springer
-
Article
| Open Access Structure of Rap1b bound to talin reveals a pathway for triggering integrin activation
Structure of Rap1b bound to talin reveals a pathway for triggering integrin activation
The transmembrane receptor integrin is activated by talin, but so far it has remained elusive how talin is recruited to the plasma membrane. Here, the authors identify the Rap1-mediated membrane-targeting mechanism for talin, present the Rap1b/talin-F0 structure and show that talin is a direct Rap1b effector.
- Liang Zhu
- , Jun Yang
- & Jun Qin
-
Article
| Open Access Quantitative structural mechanobiology of platelet-driven blood clot contraction
Quantitative structural mechanobiology of platelet-driven blood clot contraction
Blood clot contraction is a cellular (patho)physiological process essential for wound healing, hemostasis, and thrombosis. Here, the authors describe the physical structural mechanism by which platelet filopodia pull “hand-over-hand” on fibrin fibers to compact them into bundled agglomerates.
- Oleg V. Kim
- , Rustem I. Litvinov
- & John W. Weisel
-
Article
| Open Access Novel ecto-tagged integrins reveal their trafficking in live cells
Novel ecto-tagged integrins reveal their trafficking in live cells
Integrins are cell-surface adhesion receptors that are modulated by endo-exocytic trafficking, but existing tools to study this process can interfere with function. Here the authors develop β1 integrins carrying traceable tags in the extracellular domain; a pH-sensitive pHlourin tag or a HaloTag to facilitate dye attachment.
- Clotilde Huet-Calderwood
- , Felix Rivera-Molina
- & David A. Calderwood
-
Article
| Open Access Rules of engagement between αvβ6 integrin and foot-and-mouth disease virus
Rules of engagement between αvβ6 integrin and foot-and-mouth disease virus
Foot-and-mouth disease virus binds αvβ6 integrin, via a conserved RGD motif in the flexible, exposed GH loop of capsid protein VP1, for cell entry. Here Kotechaet al.visualize this interaction with the VP1 GH loop extending away from the viral surface, engaging αvβ6 in an open, active state.
- Abhay Kotecha
- , Quan Wang
- & David I. Stuart
-
Article
| Open Access αV-class integrins exert dual roles on α5β1 integrins to strengthen adhesion to fibronectin
αV-class integrins exert dual roles on α5β1 integrins to strengthen adhesion to fibronectin
Interaction of fibronectin with αv-class and α5β1 integrins results in formation of cell adhesion complexes, but the initial events (<120 s) remain unclear. Here, the authors show that αv-class integrins bind fibronectin faster than α5β1 integrins and subsequently signal to α5ß1 integrins to strengthen the adhesion.
- Mitasha Bharadwaj
- , Nico Strohmeyer
- & Daniel J. Müller
-
Article
| Open Access L-type calcium channels regulate filopodia stability and cancer cell invasion downstream of integrin signalling
L-type calcium channels regulate filopodia stability and cancer cell invasion downstream of integrin signalling
Filopodia have a prominent role in driving cancer cell invasion. Here, the authors show that L-type calcium channels are a druggable target regulating filopodia stability and maturation into focal adhesions in metastatic breast cancer cells.
- Guillaume Jacquemet
- , Habib Baghirov
- & Johanna Ivaska
-
Article
| Open Access PPFIA1 drives active α5β1 integrin recycling and controls fibronectin fibrillogenesis and vascular morphogenesis
PPFIA1 drives active α5β1 integrin recycling and controls fibronectin fibrillogenesis and vascular morphogenesis
During vascular development, fibronectin (FN) is polymerized at the basolateral side of endothelial cells. Here Mana et al. propose a model where PPFIA1 drives recycling of the FN receptor, a5β1 integrin, to the cell surface and enables polar secretion and fibrillogenesis of newly synthesized FN.
- Giulia Mana
- , Fabiana Clapero
- & Donatella Valdembri
-
Article
| Open Access Coordinated integrin activation by actin-dependent force during T-cell migration
Coordinated integrin activation by actin-dependent force during T-cell migration
The role of force in activating integrin cell adhesion receptors is not known. Here the authors develop fluorescent tension sensors for αL and β2 integrins and show that in migrating T cells force is transduced across the β2 integrin, and that this correlates with an active conformational state.
- Pontus Nordenfelt
- , Hunter L. Elliott
- & Timothy A. Springer
-
Article
| Open Access Neutrophil recruitment limited by high-affinity bent β2 integrin binding ligand in cis
Neutrophil recruitment limited by high-affinity bent β2 integrin binding ligand in cis
Integrin β2 attachment regulates inflammation via effects on neutrophil rolling and extravasation through sequential integrin extension then headpiece opening. Here the authors show an alternative open headpiece prior to extension stabilized in cisby ICAM-1 that limits neutrophil adhesion.
- Zhichao Fan
- , Sara McArdle
- & Klaus Ley
-
Article
| Open Access Rational design of a protein that binds integrin αvβ3 outside the ligand binding site
Rational design of a protein that binds integrin αvβ3 outside the ligand binding site
Integrins are transmembrane proteins that have important roles in cell adhesion and signalling. Here the authors design a therapeutic protein that binds integrin αvβ3, has anti-angiogenic activity, and reduces tumour growth in xenograft models, while being seemingly well tolerated.
- Ravi Chakra Turaga
- , Lu Yin
- & Zhi-Ren Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Therapeutic targeting and rapid mobilization of endosteal HSC using a small molecule integrin antagonist
Therapeutic targeting and rapid mobilization of endosteal HSC using a small molecule integrin antagonist
Mobilizing haematopoietic stem cells to the peripheral blood has largely replaced bone marrow transplants as a strategy in the clinic. Here, Cao et al. report the use of an α9β1/α4β1integrin antagonist to induce rapid mobilization of blood stem cells from the bone marrow in a humanized mouse model.
- Benjamin Cao
- , Zhen Zhang
- & Susan K. Nilsson
-
Article
| Open Access αv Integrins combine with LC3 and atg5 to regulate Toll-like receptor signalling in B cells
αv Integrins combine with LC3 and atg5 to regulate Toll-like receptor signalling in B cells
Integrins can regulate antigen-specific and innate immune receptor signalling, thereby affecting immune cell function. Here the authors show that avß3 integrin controls Toll-like receptor (TLR) signalling by regulating its trafficking to limit TLR-mediated B-cell proliferation and antibody production.
- Mridu Acharya
- , Anna Sokolovska
- & Adam Lacy-Hulbert
-
Article
| Open Access A ligand-independent integrin β1 mechanosensory complex guides spindle orientation
A ligand-independent integrin β1 mechanosensory complex guides spindle orientation
During cell division, the orientation of the mitotic spindle is sensitive to forces exerted on the cell cortex. Here Petridou and Skourides show that such cues are sensed by a mechanosensory complex established on force activated integrin β1 independent of ligand binding.
- Nicoletta I. Petridou
- & Paris A. Skourides
-
Article
| Open Access Integrin signalling regulates the expansion of neuroepithelial progenitors and neurogenesis via Wnt7a and Decorin
Integrin signalling regulates the expansion of neuroepithelial progenitors and neurogenesis via Wnt7a and Decorin
The extracellular matrix is suggested to play a role in neurogenesis, but it is unclear what role integrin signalling may play in the developing neuroepithelium. Here, in chick, Long et al. show that expression of constitutively active integrin beta-1 enhances neurogenesis via a novel Wnt7 and decorin pathway.
- K. Long
- , L. Moss
- & C. ffrench-Constant
-
Article
| Open Access Integrin-beta3 clusters recruit clathrin-mediated endocytic machinery in the absence of traction force
Integrin-beta3 clusters recruit clathrin-mediated endocytic machinery in the absence of traction force
Force is known to recruit adaptor proteins to the intracellular tails of integrin extracellular matrix receptors. Here the authors show that matrix force-dependent β3 integrin signals block endocytosis by preventing the recruitment of the clathrin adaptor Dab2.
- Cheng-han Yu
- , Nisha Bte Mohd Rafiq
- & Michael P. Sheetz
-
Article
| Open Access A RIAM/lamellipodin–talin–integrin complex forms the tip of sticky fingers that guide cell migration
A RIAM/lamellipodin–talin–integrin complex forms the tip of sticky fingers that guide cell migration
The leading edge of migrating cells contains activated integrins associated with growing actin filaments that form ‘sticky fingers’ to guide cell migration. Here, the authors detect a complex of MRL proteins, talin and activated integrins in lamellipodia and filopodia in living cells, comprising the tips of the ‘sticky fingers’.
- Frederic Lagarrigue
- , Praju Vikas Anekal
- & Mark H. Ginsberg
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular architecture of native fibronectin fibrils
Molecular architecture of native fibronectin fibrils
Fibronectin fibres are an important component of the extracellular matrix, supporting cell adhesion, growth and migration. Here the authors combine site-specific protein labelling with single-molecule localization microscopy to provide detailed insights into the molecular organization of native fibronectin fibrils.
- Susanna Maria Früh
- , Ingmar Schoen
- & Viola Vogel

 Canonical and non-canonical integrin-based adhesions dynamically interconvert
Canonical and non-canonical integrin-based adhesions dynamically interconvert