Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access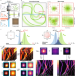 Focus image scanning microscopy for sharp and gentle super-resolved microscopy
Focus image scanning microscopy for sharp and gentle super-resolved microscopy
Super-resolution microscopy techniques can be challenging for live cells and thick samples. Here, the authors propose a method to reduce beam intensity and remove out-of-focus fluorescence background in image-scanning microscopy (ISM) and its combination with stimulated emission depletion (STED).
- Giorgio Tortarolo
- , Alessandro Zunino
- & Giuseppe Vicidomini
-
Article
| Open Access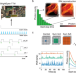 The BrightEyes-TTM as an open-source time-tagging module for democratising single-photon microscopy
The BrightEyes-TTM as an open-source time-tagging module for democratising single-photon microscopy
The authors developed an open-source, low-cost, multi-channel time-tagging module for fluorescence lifetime image scanning microscopy and correlation spectroscopy that can tag in parallel multiple single-photon events with 30 ps precision.
- Alessandro Rossetta
- , Eli Slenders
- & Giuseppe Vicidomini
-
Article
| Open Access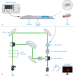 Acousto-holographic reconstruction of whole-cell stiffness maps
Acousto-holographic reconstruction of whole-cell stiffness maps
Traditional methods for cell stiffness measurements are limited by long processing times and unsuitability for multiple cell analysis. Here, the authors demonstrate a fast technique based on acoustic stimulation and holographic imaging to reconstruct whole-cell stiffness maps of individual and multiple cells.
- Rahmetullah Varol
- , Zeynep Karavelioglu
- & Huseyin Uvet
-
Article
| Open Access Anti-phase boundary accelerated exsolution of nanoparticles in non-stoichiometric perovskite thin films
Anti-phase boundary accelerated exsolution of nanoparticles in non-stoichiometric perovskite thin films
Exsolution of transition metal cations from non-stoichiometric perovskites offer a route for the formation of stable nanoparticles on the surface. Here authors present an anti-phase boundaries-accelerated exsolution and two-step crystallisation of nanoparticles in non-stoichiometric perovskite thin films.
- Hyeon Han
- , Yaolong Xing
- & Sang Ho Oh
-
Article
| Open Access Super-resolution microscopy enabled by high-efficiency surface-migration emission depletion
Super-resolution microscopy enabled by high-efficiency surface-migration emission depletion
The authors report high-efficiency emission depletion through a surface migration emission depletion mechanism, which takes advantage of the effects of surface quenching and energy migration in nanocrystals. They demonstrate super-resolution microscopy with very low depletion saturation intensities.
- Rui Pu
- , Qiuqiang Zhan
- & Xiaogang Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Nanoscale heterogeneity of ultrafast many-body carrier dynamics in triple cation perovskites
Nanoscale heterogeneity of ultrafast many-body carrier dynamics in triple cation perovskites
The optoelectronic performance of lead halide perovskite in highfluence applications are hindered by heterogeneous multi-polaron interactions in the nanoscale. Here, Nishda et al. spatially resolve sub-ns relaxation dynamics on the nanometer scale by ultrafast infrared pumpprobe nanoimaging.
- Jun Nishida
- , Peter T. S. Chang
- & Markus B. Raschke
-
Article
| Open Access High-resolution neutron imaging of salt precipitation and water transport in zero-gap CO2 electrolysis
High-resolution neutron imaging of salt precipitation and water transport in zero-gap CO2 electrolysis
The electrochemical reduction of CO2 is pivotal for the chemical industry to reach climate neutrality. Here, the authors utilize high-resolution neutron imaging to unravel electrode flooding and salt precipitation, both major hurdles to steady operation of CO2 electrolyzers.
- Joey Disch
- , Luca Bohn
- & Severin Vierrath
-
Article
| Open Access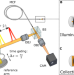 Real-time holographic lensless micro-endoscopy through flexible fibers via fiber bundle distal holography
Real-time holographic lensless micro-endoscopy through flexible fibers via fiber bundle distal holography
Fiber-based micro-endoscopes are minimally invasive, but 3D imaging is limited by the need for bulky optical elements or rigid fibers. Here, the authors demonstrate holographic imaging through flexible and dynamically bent multi-core fibers by adding partially reflecting mirror to the distal fiber-tip.
- Noam Badt
- & Ori Katz
-
Article
| Open Access Direct observation of ultrafast singlet exciton fission in three dimensions
Direct observation of ultrafast singlet exciton fission in three dimensions
Here, the authors use quantitative ultrafast interferometric pump-probe microscopy to track photoexcitations with sub-10 nm spatial precision in three dimensions and 15 fs temporal resolution to study the spatiotemporal dynamics of singlet exciton fission in polycrystalline pentacene films.
- Arjun Ashoka
- , Nicolas Gauriot
- & Akshay Rao
-
Article
| Open Access Direct strain correlations at the single-atom level in three-dimensional core-shell interface structures
Direct strain correlations at the single-atom level in three-dimensional core-shell interface structures
Understanding 3D interfacial strain at the atomic level has been a long-sought challenge in the field of core-shell nanomaterials. Here, the authors address this challenge by revealing the full 3D atomic structures of Pd@Pt core-shell nanoparticles
- Hyesung Jo
- , Dae Han Wi
- & Yongsoo Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Real-space measurement of orbital electron populations for Li1-xCoO2
Real-space measurement of orbital electron populations for Li1-xCoO2
Experimentally probing the orbital population is highly desirable to resolve the redox mechanism of cathodes materials. Here the authors quantify the orbital populations of Co and O in LiCoO2 and identify the ligand-to-metal charge transfer.
- Tongtong Shang
- , Dongdong Xiao
- & Jing Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access Metasurface-enhanced light detection and ranging technology
Metasurface-enhanced light detection and ranging technology
Mimicking human vision with metasurfaces, the authors propose a new paradigm for high field of view and ultrafast LiDAR, achieving performances also relevant for the next generation of imaging system for ADAS and robotic systems.
- Renato Juliano Martins
- , Emil Marinov
- & Patrice Genevet
-
Article
| Open Access Quantum and non-local effects offer over 40 dB noise resilience advantage towards quantum lidar
Quantum and non-local effects offer over 40 dB noise resilience advantage towards quantum lidar
Sensitivity to noise is currently an obstacle to the use of quantum imaging techniques in real-world scenarios. Here, exploiting non-local cancellation of dispersion on time-frequency entangled photons, the authors show a 43dB improvement in resilience to noise for imaging protocols towards a quantum LiDAR.
- Phillip S. Blakey
- , Han Liu
- & Amr S. Helmy
-
Article
| Open Access Vacancy driven surface disorder catalyzes anisotropic evaporation of ZnO (0001) polar surface
Vacancy driven surface disorder catalyzes anisotropic evaporation of ZnO (0001) polar surface
Evaporation and crystal growth occur at different rates on different surfaces. Here authors show dissociative evaporation from ZnO (0001) polar surfaces is accelerated by the formation of a Zn-deficient quasi-liquid layer derived from the formation and inward diffusion of Zn vacancies that stabilize the polar surface.
- Zhen Wang
- , Jinho Byun
- & Sang Ho Oh
-
Article
| Open Access Tunable quantum gaps to decouple carrier and phonon transport leading to high-performance thermoelectrics
Tunable quantum gaps to decouple carrier and phonon transport leading to high-performance thermoelectrics
Defects are believed to always scatter carriers. Here, the authors find that the quantum gaps in GeTe-based materials do not scatter carriers, which decouple the carriers and phonons transport leading to high thermoelectric performance.
- Yong Yu
- , Xiao Xu
- & Jiaqing He
-
Article
| Open Access Resolving molecular diffusion and aggregation of antibody proteins with megahertz X-ray free-electron laser pulses
Resolving molecular diffusion and aggregation of antibody proteins with megahertz X-ray free-electron laser pulses
The European X-ray FreeElectron Laser Facility generates ultrashort hard X-ray pulses with megahertz repetition rate. Here, the authors probe the dynamics of dense antibody protein (Ig-PEG) solutions using megahertz X-ray photon correlation spectroscopy at the European XFEL.
- Mario Reiser
- , Anita Girelli
- & Christian Gutt
-
Article
| Open Access Wide field imaging of van der Waals ferromagnet Fe3GeTe2 by spin defects in hexagonal boron nitride
Wide field imaging of van der Waals ferromagnet Fe3GeTe2 by spin defects in hexagonal boron nitride
Hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN) has been used extensively to encapsulate other van der Waals materials, protecting them from environmental degradation, and allowing integration into more complex heterostructures. Here, the authors make use of boron vacancy spin defects in h-BN using them to image the magnetic properties of a Fe3GeTe2 flake.
- Mengqi Huang
- , Jingcheng Zhou
- & Chunhui Rita Du
-
Article
| Open Access High-fluence and high-gain multilayer focusing optics to enhance spatial resolution in femtosecond X-ray laser imaging
High-fluence and high-gain multilayer focusing optics to enhance spatial resolution in femtosecond X-ray laser imaging
Here, the authors realize an ultra-high fluence X-ray laser by high-gain multilayer focusing optics. This enables in-solution imaging with 2-nm resolution in a single-pulse exposure, making strides toward biomolecular imaging under physiological conditions.
- Hirokatsu Yumoto
- , Takahisa Koyama
- & Haruhiko Ohashi
-
Article
| Open Access Enhanced detection of threat materials by dark-field x-ray imaging combined with deep neural networks
Enhanced detection of threat materials by dark-field x-ray imaging combined with deep neural networks
Dark-field X-ray imaging is sensitive to the microstructure of a material. Here, the authors combine this with a neural network algorithm to provide efficient material discrimination, e.g., of explosives vs non-threat materials.
- T. Partridge
- , A. Astolfo
- & A. Olivo
-
Article
| Open Access Optical-Tweezers-integrating-Differential-Dynamic-Microscopy maps the spatiotemporal propagation of nonlinear strains in polymer blends and composites
Optical-Tweezers-integrating-Differential-Dynamic-Microscopy maps the spatiotemporal propagation of nonlinear strains in polymer blends and composites
The authors present an approach to connect polymer dynamics to force response by integrating optical tweezers with differential dynamic microscopy. They measure blends of ring and linear DNA and observe a resonant response, which is suppressed by the presence of microtubules.
- Karthik R. Peddireddy
- , Ryan Clairmont
- & Rae M. Robertson-Anderson
-
Article
| Open Access Imaging Cu2O nanocube hollowing in solution by quantitative in situ X-ray ptychography
Imaging Cu2O nanocube hollowing in solution by quantitative in situ X-ray ptychography
Observing morphological changes of nanoparticles in solution requires advanced in-situ imaging methods. Here, the authors use X-ray ptychography to image the growth and hollowing of Cu2O nanocubes in 3D.
- Lukas Grote
- , Martin Seyrich
- & Dorota Koziej
-
Article
| Open Access Biomimetic material degradation for synergistic enhanced therapy by regulating endogenous energy metabolism imaging under hypothermia
Biomimetic material degradation for synergistic enhanced therapy by regulating endogenous energy metabolism imaging under hypothermia
Metal organic frameworks (MOF) coated with mammalian cell membranes have good biocompatibility. Here, the authors develop a cobalt based hydrogen sulphide producing MOF cloaked with a macrophage membrane and show that the subsequent system can reduce tumour growth in mice.
- Kai Cheng
- , Bo Liu
- & Yuan-Di Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Fermi surface tomography
Fermi surface tomography
The Fermi surface is related to the energy distribution of electrons in a solid, and governs physical properties of metals and semiconductors. A new type of angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy, probing the Fermi surface and combining short recording time with high resolution, is now presented.
- Sergey Borisenko
- , Alexander Fedorov
- & Bernd Büchner
-
Article
| Open Access Computational imaging of moving objects obscured by a random corridor via speckle correlations
Computational imaging of moving objects obscured by a random corridor via speckle correlations
The authors demonstrate an approach for imaging moving objects through a tortuous corridor filled with a random media. Their reduced spatial- and ensemble-speckle intensity correlation method allows for reconstruction of centimeter-sized hidden object with sub-millimeter resolution.
- Tian Shi
- , Liangsheng Li
- & Ning Zheng
-
Article
| Open Access Identification of a quasi-liquid phase at solid–liquid interface
Identification of a quasi-liquid phase at solid–liquid interface
Solid–liquid interfaces are ubiquitous in natural and technological processes, but their imaging at the atomic scale has been challenging. The authors, using liquid-phase transmission electron microscopy, identify a quasi-liquid phase and the mass transport between the surface of In and Sn nanocrystals and an aqueous solution.
- Xinxing Peng
- , Fu-Chun Zhu
- & Haimei Zheng
-
Article
| Open Access Pixel super-resolution with spatially entangled photons
Pixel super-resolution with spatially entangled photons
Pixelation is common in quantum imaging systems and limit the image spatial resolution. Here, the authors introduce a pixel super-resolution approach based on measuring the full spatially-resolved joint probability distribution of spatially-entangled photons, and improve pixel resolution by a factor two.
- Hugo Defienne
- , Patrick Cameron
- & Daniele Faccio
-
Article
| Open Access Light-sheet photonic force optical coherence elastography for high-throughput quantitative 3D micromechanical imaging
Light-sheet photonic force optical coherence elastography for high-throughput quantitative 3D micromechanical imaging
The authors introduce photonic force optical coherence elastography that uses a light-sheet for parallelised and localised mechanical loading. They demonstrate the combination of 3D imaging of extracellular matrix mechanics with cellular-scale resolution and dynamic monitoring of cell-mediated changes.
- Yuechuan Lin
- , Nichaluk Leartprapun
- & Steven G. Adie
-
Article
| Open Access Compact light field photography towards versatile three-dimensional vision
Compact light field photography towards versatile three-dimensional vision
Light field imaging typically requires large format detectors and yet often compromises resolution or speed. Here, compact light field photography is presented to lift both restrictions to see through and around severe occlusions in 3D and real time.
- Xiaohua Feng
- , Yayao Ma
- & Liang Gao
-
Article
| Open Access A boundary migration model for imaging within volumetric scattering media
A boundary migration model for imaging within volumetric scattering media
Imaging in scattering media is challenging due to signal attenuation and strong coupling of scattered and signal photons. The authors present a boundary migration model of the scattered field, converting scattered measurements in spectral form to scene information in temporal domain, and image Lambertian objects in highly scattering media.
- Dongyu Du
- , Xin Jin
- & Jingyan Song
-
Article
| Open Access Paramagnetic encoding of molecules
Paramagnetic encoding of molecules
Molecules offer enormous capacity for information storage. Here, the authors show that information can be encoded into molecules with sequences of paramagnetic lanthanide ions, and decoded using nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy.
- Jan Kretschmer
- , Tomáš David
- & Miloslav Polasek
-
Article
| Open Access The interplay between vapour, liquid, and solid phases in laser powder bed fusion
The interplay between vapour, liquid, and solid phases in laser powder bed fusion
Complexities of laser-material interactions pose a challenge to minimize defects in additively manufactured metal parts. Here the authors visualize all phases of matter simultaneously to expand understanding of the interactions and show atmospheric information can characterize process stability.
- I. Bitharas
- , N. Parab
- & A. J. Moore
-
Article
| Open Access Achieving low-power single-wavelength-pair nanoscopy with NIR-II continuous-wave laser for multi-chromatic probes
Achieving low-power single-wavelength-pair nanoscopy with NIR-II continuous-wave laser for multi-chromatic probes
The authors introduce stimulated-emission induced excitation depletion (STExD) nanoscopy using a single pair of low-power, near-infrared, continue-wave lasers. Emission of multichromatic probes is inhibited by cascade amplified depletion in lanthanide upconversion systems induced by manipulating their common sensitizer.
- Xin Guo
- , Rui Pu
- & Qiuqiang Zhan
-
Article
| Open Access Ultra-compact snapshot spectral light-field imaging
Ultra-compact snapshot spectral light-field imaging
The authors demonstrate compact spectral light-field imaging by using a transversely dispersive metalens array and a monochrome imaging sensor. They show that 4D images can be obtained in a single shot, and demonstrate discrimination of visually indistinguishable objects.
- Xia Hua
- , Yujie Wang
- & Shining Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrafast orbital tomography of a pentacene film using time-resolved momentum microscopy at a FEL
Ultrafast orbital tomography of a pentacene film using time-resolved momentum microscopy at a FEL
Ultrafast pulses are useful to investigate the electron dynamics in excited atoms, molecules and other complex systems. Here, the authors measure transient photoelectron momentum maps following the free-electron laser pulse-induced ionization of a bilayer pentacene thin film on Ag (110) by using time-resolved orbital tomography.
- Kiana Baumgärtner
- , Marvin Reuner
- & Markus Scholz
-
Matters Arising
| Open Access The overwhelming role of ballistic photons in ultrasonically guided light through tissue
The overwhelming role of ballistic photons in ultrasonically guided light through tissue
- Eitan Edrei
- & Giuliano Scarcelli
-
Matters Arising
| Open Access Reply to: The overwhelming role of ballistic photons in ultrasonically guided light through tissue
Reply to: The overwhelming role of ballistic photons in ultrasonically guided light through tissue
- Maysamreza Chamanzar
- , Matteo Giuseppe Scopelliti
- & Michel M. Maharbiz
-
Article
| Open Access Video-rate high-precision time-frequency multiplexed 3D coherent ranging
Video-rate high-precision time-frequency multiplexed 3D coherent ranging
Frequency-modulated continuous wave LiDAR has suffered from limited 3D frame rates. Here, the authors combine a grating for beam steering with a compressed time-frequency analysis for depth retrieval, and demonstrate real-time densely sampled 3D imaging of moving objects with submillimetre localization accuracy.
- Ruobing Qian
- , Kevin C. Zhou
- & Joseph A. Izatt
-
Article
| Open Access High-speed 4D neutron computed tomography for quantifying water dynamics in polymer electrolyte fuel cells
High-speed 4D neutron computed tomography for quantifying water dynamics in polymer electrolyte fuel cells
Characterisation of water dynamics in polymer electrolyte fuel cells is important for technology development. Here, the authors demonstrate a 4D neutron imaging technique, enabling quantitative analysis of the local water evolution, and identify performance parameters for water management.
- Ralf F. Ziesche
- , Jennifer Hack
- & Paul R. Shearing
-
Article
| Open Access Large field-of-view non-invasive imaging through scattering layers using fluctuating random illumination
Large field-of-view non-invasive imaging through scattering layers using fluctuating random illumination
The authors demonstrate non-invasive fluorescence imaging behind scattering layers beyond the optical memory effect. They achieve this by demixing speckle patterns emitted by a fluorescent object under variable unknown random illumination, using matrix factorization and a fingerprint-based reconstruction.
- Lei Zhu
- , Fernando Soldevila
- & Sylvain Gigan
-
Article
| Open Access Binary-state scanning probe microscopy for parallel imaging
Binary-state scanning probe microscopy for parallel imaging
High-throughput imaging has generally been challenging for scanning probe microscopy techniques. Here, the authors introduce binary-state scanning probe microscopy, which uses a cantilever-free elastomeric probes and a hierarchical measurement architecture for parallel topography imaging.
- Gwangmook Kim
- , Eoh Jin Kim
- & Wooyoung Shim
-
Article
| Open Access An achromatic X-ray lens
An achromatic X-ray lens
X-ray diffractive and refractive optical elements suffer from chromatic aberrations, limiting high-resolution X-ray microscopes mainly to bright synchrotron sources. Here, the authors experimentally realise an achromatic X-ray lens by combing a focusing diffractive Fresnel zone plate and a defocusing refractive lens.
- Adam Kubec
- , Marie-Christine Zdora
- & Christian David
-
Article
| Open Access Bacteria eat nanoprobes for aggregation-enhanced imaging and killing diverse microorganisms
Bacteria eat nanoprobes for aggregation-enhanced imaging and killing diverse microorganisms
The authors demonstrate a strategy for bacterial uptake of gold nanoparticles modified with glucose polymer. The particles aggregate in the bacterial cells upon laser irradiation, resulting in enhanced photoacoustic signal and antibacterial activity, enabling sensitive imaging of bacteria in vivo.
- Yunmin Yang
- , Binbin Chu
- & Yao He
-
Article
| Open Access Parallel detection and spatial mapping of large nuclear spin clusters
Parallel detection and spatial mapping of large nuclear spin clusters
Nuclear magnetic resonance imaging at the atomic scale has been limited to detection and localisation of single nuclear spins. Here, the authors extend imaging to large nuclear spin clusters in 3D by combining weak quantum measurements, phase encoding and simulated annealing.
- K. S. Cujia
- , K. Herb
- & C. L. Degen
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrafast infrared nano-imaging of far-from-equilibrium carrier and vibrational dynamics
Ultrafast infrared nano-imaging of far-from-equilibrium carrier and vibrational dynamics
Ultrafast infrared nano-imaging has enabled the study of nanoscale dynamics, but has been limited to probing short-lived carrier lifetimes. Here, the authors present pump-probe nano-spectroscopy with enhanced sensitivity to image both carrier and vibrational dynamics associated with long-lived excitations.
- Jun Nishida
- , Samuel C. Johnson
- & Markus B. Raschke
-
Article
| Open Access Wide-field mid-infrared single-photon upconversion imaging
Wide-field mid-infrared single-photon upconversion imaging
The authors present a simple yet effective solution to dramatically boost the performances of an upconversion imaging system, which leads to unprecedented mid-infrared imaging features with large field of view, single-photon sensitivity and a MHz-level frame rate.
- Kun Huang
- , Jianan Fang
- & Heping Zeng
-
Article
| Open Access Defect-driven antiferromagnetic domain walls in CuMnAs films
Defect-driven antiferromagnetic domain walls in CuMnAs films
Antiferromagnets offer the potential for higher speed and density than ferromagnetic materials for spintronic devices. Here, Reimers et al study the domain structure of CuMnAs, demonstrating the role of defects in stabilizing the location and orientation of antiferromagnetic domain walls.
- Sonka Reimers
- , Dominik Kriegner
- & Kevin W. Edmonds
-
Article
| Open Access 3D atomic-scale imaging of mixed Co-Fe spinel oxide nanoparticles during oxygen evolution reaction
3D atomic-scale imaging of mixed Co-Fe spinel oxide nanoparticles during oxygen evolution reaction
3D imaging of catalyst nanoparticles during reactions is important but challenging. Here, the authors provide atomic-scale details of compositional and structural changes of 10 nm sized Co-Fe spinel nanoparticles during oxygen evolution reactions.
- Weikai Xiang
- , Nating Yang
- & Tong Li
-
Article
| Open Access Visualizing nanometric structures with sub-millimeter waves
Visualizing nanometric structures with sub-millimeter waves
The authors demonstrate a far-field approach for height profile measurements with sub-millimetre waves. By evaluating Fabry-Pérot oscillations within surface-structured samples, combined with a Hilbert-transform approach, they visualize structures with a height of 49 nm, with 31 nm precision.
- Alonso Ingar Romero
- , Amlan kusum Mukherjee
- & Sascha Preu
-
Article
| Open Access Revealing nano-scale lattice distortions in implanted material with 3D Bragg ptychography
Revealing nano-scale lattice distortions in implanted material with 3D Bragg ptychography
Atomic point defects formed by irradiation can dramatically alter material properties, but are difficult to probe, limiting understanding of their impact. Here, the authors introduce an x-ray microscopy approach, based on Bragg ptychography, to visualise the distortion caused by these otherwise invisible defects.
- Peng Li
- , Nicholas W. Phillips
- & Virginie Chamard

 A photoacoustic patch for three-dimensional imaging of hemoglobin and core temperature
A photoacoustic patch for three-dimensional imaging of hemoglobin and core temperature