Research Highlights |
Featured
-
-
Article |
 Towards graphene plasmon-based free-electron infrared to X-ray sources
Towards graphene plasmon-based free-electron infrared to X-ray sources
Scientists theoretically show infrared to X-ray sources that can be implemented on-chip by scattering high-energy electrons with graphene plasmons and predict that they are capable of producing tunable radiation.
- Liang Jie Wong
- , Ido Kaminer
- & Marin Soljačić
-
Letter |
 Graphene electro-optic modulator with 30 GHz bandwidth
Graphene electro-optic modulator with 30 GHz bandwidth
Scientists have realized a graphene electro-optic modulator operating with a 30 GHz bandwidth and with a state-of-the-art modulation efficiency of 1.5 dB V−1, paving the way for fast digital communications.
- Christopher T. Phare
- , Yoon-Ho Daniel Lee
- & Michal Lipson
-
News & Views |
 Lift off for graphene
Lift off for graphene
The finding that a graphene sponge structure can undergo light-driven levitation exposes both fundamentally interesting physics and thought-provoking potential for next-generation space propulsion.
- Nathaniel Gabor
-
Article |
 Macroscopic and direct light propulsion of bulk graphene material
Macroscopic and direct light propulsion of bulk graphene material
The observation of macroscopic and direct light propulsion of bulk-graphene-based material offers an exciting opportunity for realizing long-sought proposals in areas such as space transportation driven directly by sunlight.
- Tengfei Zhang
- , Huicong Chang
- & Yongsheng Chen
-
-
-
-
-
Article |
 Fundamental limits and near-optimal design of graphene modulators and non-reciprocal devices
Fundamental limits and near-optimal design of graphene modulators and non-reciprocal devices
Recent demonstrations of modulators, polarization rotators and isolators have indicated the potential of graphene for photonic applications. The present study investigates the fundamental limits and near-optimal design of graphene modulators and non-reciprocal devices.
- Michele Tamagnone
- , Arya Fallahi
- & Julien Perruisseau-Carrier
-
-
-
Commentary |
 Nanotube and graphene saturable absorbers for fibre lasers
Nanotube and graphene saturable absorbers for fibre lasers
Nanotubes and graphene have emerged as promising materials for use in ultrafast fibre lasers. Their unique electrical and optical properties enable them to be used as saturable absorbers that have fast responses and broadband operation and that can be easily integrated in fibre lasers.
- Amos Martinez
- & Zhipei Sun
-
News & Views |
 Graphene benefits
Graphene benefits
Silicon-waveguide-integrated graphene photodetectors offer high responsivities, high speeds and broad spectral bandwidths, paving the way for graphene-based optical interconnects.
- Ming Liu
- & Xiang Zhang
-
Letter |
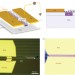 Chip-integrated ultrafast graphene photodetector with high responsivity
Chip-integrated ultrafast graphene photodetector with high responsivity
A chip-integrated graphene photodetector with a high responsivity of over 0.1 A W−1, high speed and broad spectral bandwidth is realized through enhanced absorption due to near-field coupling. Under zero-bias operation, response rates above 20 GHz and an instrumentation-limited 12 Gbit s−1 optical data link are demonstrated.
- Xuetao Gan
- , Ren-Jye Shiue
- & Dirk Englund
-
Letter |
 CMOS-compatible graphene photodetector covering all optical communication bands
CMOS-compatible graphene photodetector covering all optical communication bands
A CMOS-compatible photodetector based on graphene with multi-gigahertz operation ranging from the O- to U-band of telecommunication bands is demonstrated, highlighting the promise of graphene as a new material for integrated photonics.
- Andreas Pospischil
- , Markus Humer
- & Thomas Mueller
-
Letter |
 High-responsivity graphene/silicon-heterostructure waveguide photodetectors
High-responsivity graphene/silicon-heterostructure waveguide photodetectors
A CMOS-compatible graphene/silicon-heterostructure photodetector formed by integrating graphene onto a silicon optical waveguide on silicon-on-insulator and operating in the near- and mid-infrared regions is demonstrated. A responsivity as high as 0.13 A W−1 is obtained at a bias of 1.5 V for 2.75-μm light at room temperature.
- Xiaomu Wang
- , Zhenzhou Cheng
- & Jian-Bin Xu
-
-
-
-
Interview |
 Graphene versus metal plasmons
Graphene versus metal plasmons
Although there is much debate regarding whether graphene is more suitable than metals for use in plasmonics, the useful operational frequency ranges of these materials are complementary. Nature Photonics spoke with Fengnian Xia about his team's recent work on graphene plasmonics.
- David Pile
-
News & Views |
 Damping of plasmons in graphene
Damping of plasmons in graphene
The damping of surface plasmons hinders the realization of nanophotonic devices. Researchers have now uncovered some of the mid-infrared damping mechanisms for plasmons in graphene, which offer a number of unique and interesting properties.
- Hrvoje Buljan
- , Marinko Jablan
- & Marin Soljačić
-
Article |
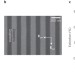 Damping pathways of mid-infrared plasmons in graphene nanostructures
Damping pathways of mid-infrared plasmons in graphene nanostructures
Researchers clarify damping pathways for mid-infrared graphene plasmons, including graphene intrinsic optical phonons and edge scattering. They also demonstrate the guiding of mid-infrared graphene plasmons in 50-nm-wide structures with an electromagnetic mode area of 10−3μm2 and a propagation length of 200 nm.
- Hugen Yan
- , Tony Low
- & Fengnian Xia
-
News & Views |
 Achieving robust Weyl points
Achieving robust Weyl points
The isolated symmetry points of photonic graphene are unstable in three dimensions. Researchers have now proposed topologically robust points by using minimal surfaces and employing symmetry-breaking ideas from quantum field theory.
- Jason Fleischer
-
Article |
 Photoconductivity of biased graphene
Photoconductivity of biased graphene
Scientists report that the photovoltaic effect and a photo-induced bolometric effect, rather than thermoelectric effects, dominate the photoresponse during a classic photoconductivity experiment in biased graphene. The findings shed light on the hot-electron-driven photoresponse in graphene and its energy loss pathway via phonons.
- Marcus Freitag
- , Tony Low
- & Phaedon Avouris
-
-
Review Article |
 Graphene plasmonics
Graphene plasmonics
Many researchers hope to merge plasmonics and graphene photonics to combine their useful features. The properties and characteristics of plasmons on graphene are reviewed. Prospects for possible future applications are discussed.
- A. N. Grigorenko
- , M. Polini
- & K. S. Novoselov
-
News & Views |
 Graphene–silicon fusion
Graphene–silicon fusion
A single sheet of graphene dramatically changes the nonlinear response of a silicon photonic crystal, enabling ultralow-power optical bistability, self-induced regenerative oscillation and coherent four-wave mixing.
- Kinam Kim
- , Seong-Ho Cho
- & Chang-Won Lee
-
Article |
 Regenerative oscillation and four-wave mixing in graphene optoelectronics
Regenerative oscillation and four-wave mixing in graphene optoelectronics
Scientists report the observation of ultralow-power resonant optical bistability, self-induced regenerative oscillations and coherent four-wave mixing in graphene–silicon hybrid optoelectronic devices at cavity recirculating energies of a few femtojoules. The findings indicate the feasibility and versatility of such devices for use in next-generation chip-scale high-speed optical communications, radiofrequency optoelectronics and all-optical signal processing.
- T. Gu
- , N. Petrone
- & C. W. Wong
-
-
-
Letter |
 Extremely efficient flexible organic light-emitting diodes with modified graphene anode
Extremely efficient flexible organic light-emitting diodes with modified graphene anode
By replacing conventional indium tin oxide (ITO) anodes with high-work-function, low-sheet-resistance graphene anodes, researchers demonstrate flexible fluorescent organic LEDs with extremely high luminous efficiencies of 37.2 lm W–1 for fluorescent devices and 102.7 lm W–1 for phosphorescent devices. These values are significantly higher than those of optimized organic LEDs based on ITO anodes.
- Tae-Hee Han
- , Youngbin Lee
- & Tae-Woo Lee
-
-
Article |
 Giant broadband nonlinear optical absorption response in dispersed graphene single sheets
Giant broadband nonlinear optical absorption response in dispersed graphene single sheets
Researchers show that dispersed functionalized graphene can exhibit broadband nonlinear optical absorption at fluences well below the damage threshold. An optical energy-limiting onset benchmark of 10 mJ cm−2 at a linear transmittance of 70% was obtained for nanosecond visible and near-infrared pulses. The findings shed light on the formation of practical thin films with broadband optical limiting characteristics.
- Geok-Kieng Lim
- , Zhi-Li Chen
- & Lay-Lay Chua
-
Letter |
 Broadband graphene polarizer
Broadband graphene polarizer
Scientists study the coupling, guiding and polarizing of electromagnetic waves in graphene and demonstrate a graphene-based fibre polarizer that exhibits a transverse-electric-pass polarization at an extinction ratio of up to ∼27 dB in the telecommunications band.
- Qiaoliang Bao
- , Han Zhang
- & Kian Ping Loh
-
Editorial |
 Celebrating graphene
Celebrating graphene
Graphene — a form of carbon isolated only six years ago — is the topic of this year's Nobel Prize for Physics, giving hope for future applications of this intriguing material in the field of photonics.
-
News & Views |
 Bridging the terahertz gap
Bridging the terahertz gap
Graphene has had a big impact in optics and optoelectronics for both fundamental physics and real-world applications, and there is now considerable excitement about its prospects for terahertz science.
- Rachel Won
-
-
-
-
Letter |
 Flat dielectric grating reflectors with focusing abilities
Flat dielectric grating reflectors with focusing abilities
Microscale planar optical elements based on high-reflectivity, non-periodic gratings provide a compact and convenient means for focusing and shaping light.
- David Fattal
- , Jingjing Li
- & Raymond G. Beausoleil
-
Interview |
 Detecting light with graphene
Detecting light with graphene
Will graphene optoelectronics be able to displace silicon technology? Thomas Mueller explains that a new design of graphene photodetector is showing great promise.
- David Pile
-
Editorial |
 Carbon optimism
Carbon optimism
The use of diamond, graphene and carbon nanotubes is becoming increasingly common in photonic applications, and several recent notable achievements suggest that carbon has a bright future in photonics.
-
Letter |
 Graphene photodetectors for high-speed optical communications
Graphene photodetectors for high-speed optical communications
A graphene-based photodetector with unprecedented photoresponsivity and the ability to perform error-free detection of 10 Gbit s−1s data streams is demonstrated. The results suggest that graphene-based photonic devices have a bright future in telecommunications and other optical applications.
- Thomas Mueller
- , Fengnian Xia
- & Phaedon Avouris

 Fibre integration
Fibre integration Molecular engine
Molecular engine Graphene shrinks light
Graphene shrinks light High photoresponsitivity
High photoresponsitivity Switching terahertz waves
Switching terahertz waves Double-layer graphene boost
Double-layer graphene boost Graphene photodetection
Graphene photodetection Graphene photonics and optoelectronics
Graphene photonics and optoelectronics Graphene–silicon solar cells
Graphene–silicon solar cells