Featured
-
-
Article |
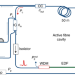 Temporal solitons in a coherently driven active resonator
Temporal solitons in a coherently driven active resonator
By adding a carefully designed amplification section in a passive resonator, but pumping it below the lasing threshold, ultra-stable high-power cavity solitons can be formed, effectively removing the important barrier of having to work in low-loss environments.
- Nicolas Englebert
- , Carlos Mas Arabí
- & François Leo
-
Books & Arts |
New titles at a glance
-
-
Article |
 Inverse four-wave mixing and self-parametric amplification in optical fibre
Inverse four-wave mixing and self-parametric amplification in optical fibre
Self-parametric amplification, a nonlinear optical effect, is observed in optical fibre and results in optical spectrum narrowing and stable propagation.
- Sergei K. Turitsyn
- , Anastasia E. Bednyakova
- & Wallace R. L. Clements
-
-
-
Article |
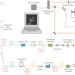 Stimulated Raman scattering microscopy with a robust fibre laser source
Stimulated Raman scattering microscopy with a robust fibre laser source
A dual-wavelength fibre laser source has been developed for stimulated Raman scattering microscopy. It is precisely tunable over the entire high-wavenumber region of Raman spectra, where most stimulated Raman scattering imaging is performed. Imaging speeds of up to 1 frame s−1 with shot-noise-limited sensitivity were achieved.
- Christian W. Freudiger
- , Wenlong Yang
- & Khanh Q. Kieu
-
Editorial |
 Fibre laser focus
Fibre laser focus
With their ultrafast and high-power characteristics, fibre lasers are penetrating conventional laser markets as well as opening up exciting new opportunities.
-
Interview |
 Fibre laser directions
Fibre laser directions
Nature Photonics spoke to Anatoly Grudinin, founder of the fibre laser company Fianium, to gain insight into the vicissitudes in the industry over the past decade and future challenges that academia can help solve.
- David Pile
-
Commentary |
 Nanotube and graphene saturable absorbers for fibre lasers
Nanotube and graphene saturable absorbers for fibre lasers
Nanotubes and graphene have emerged as promising materials for use in ultrafast fibre lasers. Their unique electrical and optical properties enable them to be used as saturable absorbers that have fast responses and broadband operation and that can be easily integrated in fibre lasers.
- Amos Martinez
- & Zhipei Sun
-
Review Article |
 High-power fibre lasers
High-power fibre lasers
High-power fibre lasers are in demand for industrial, defence and scientific applications. This review provides an overview of the present state of the art in the field and discusses present challenges and the future outlook.
- Cesar Jauregui
- , Jens Limpert
- & Andreas Tünnermann
-
Review Article |
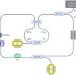 Ultrafast fibre lasers
Ultrafast fibre lasers
Ultrafast fibre lasers are an important optical system with industrial, medical and purely scientific applications. Essential components and the operation regimes of ultrafast fibre laser systems are reviewed, as are their use in various applications.
- Martin E. Fermann
- & Ingmar Hartl
-
Review Article |
 Recent advances in fibre lasers for nonlinear microscopy
Recent advances in fibre lasers for nonlinear microscopy
This Review discusses recent advances, and identifies challenges and opportunities regarding the use of fibre lasers in nonlinear bioimaging.
- C. Xu
- & F. W. Wise
-
Interview |
 Turbulent transition
Turbulent transition
Clustering of dark and grey solitons in fibre lasers has been found to induce a turbulent regime similar to that of a rapidly flowing fluid in a pipe. Sergei Turitsyn from the University of Aston, UK, explains.
- Oliver Graydon
-
News & Views |
 Turbulent times
Turbulent times
Researchers show that the breakdown of temporal coherence in a fibre laser has strong similarities with the onset of turbulence in fluids. Establishing a conceptual connection between these different systems can offer new perspectives for both fields.
- Fatih Ömer Ilday
-
News & Views |
 A closer look at LIFE
A closer look at LIFE
Inertial fusion energy is one potential path towards realizing sustainable energy. The development of a laser power plant capable of delivering high-energy laser pulses is crucial for realizing laser-driven inertial fusion energy.
- Rachel Won
-
Letter |
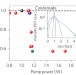 The laminar–turbulent transition in a fibre laser
The laminar–turbulent transition in a fibre laser
The transition between operation in a stable coherent state and that in a disordered turbulent state is studied in a fibre laser. The loss of coherence following the transition is associated with the appearance of solitons, which proliferate and cluster.
- E. G. Turitsyna
- , S. V. Smirnov
- & S. K. Turitsyn
-
Commentary |
 The future is fibre accelerators
The future is fibre accelerators
Could massive arrays of thousands of fibre lasers be the driving force behind next-generation particle accelerators? The International Coherent Amplification Network project believes so and is currently performing a feasibility study.
- Gerard Mourou
- , Bill Brocklesby
- & Jens Limpert
-
Review Article |
 Towards high-power mid-infrared emission from a fibre laser
Towards high-power mid-infrared emission from a fibre laser
Fibre lasers in the mid-infrared regime are useful for a diverse range of fields, including chemical and biomedical sensing, military applications and materials processing. This Review summarizes the different rare-earth cations and host materials used in mid-infrared fibre laser technology, and discusses the future applications and challenges for the field.
- Stuart D. Jackson
-
News & Views |
 Perfect ring-like beam
Perfect ring-like beam
Fibre lasers capable of producing stable, axially symmetric ring-like radiation from an extended surface may prove to be an important new light source for applications in medical imaging, sensing, bio-sensing and security systems.
- Andrei A. Fotiadi
- & Patrice Mégret
-
Letter |
 Microfluidic directional emission control of an azimuthally polarized radial fibre laser
Microfluidic directional emission control of an azimuthally polarized radial fibre laser
Researchers realize a zero-angular-momentum radial-emission laser by filling a cylindrical photonic crystal fibre cavity with a microfluidic gain medium. Control of the electromagnetic fields is provided by electrically contacted and independently addressable liquid-crystal microchannels in the fibre.
- Alexander M. Stolyarov
- , Lei Wei
- & Yoel Fink
-
Letter |
 Phase-locking of a 2.7-THz quantum cascade laser to a mode-locked erbium-doped fibre laser
Phase-locking of a 2.7-THz quantum cascade laser to a mode-locked erbium-doped fibre laser
The phase locking of a longitudinal mode of a 2.7 THz quantum cascade laser was achieved using the spectral bandwidth of a mode-locked erbium-doped fibre laser. This technique is applicable to any terahertz quantum cascade laser source, and is an ideal tool for controlling the phase of different quantum cascade lasers.
- Stefano Barbieri
- , Pierre Gellie
- & David Ritchie
-
Industry Perspective |
 Delivering power
Delivering power
With its high wall-plug efficiency and record-breaking power output, the fibre laser has made the use of lasers in manufacturing more acceptable and cost-effective.
- Bill Shiner
-
Research Highlights |
 Milestones in laser development
Milestones in laser development
-
News & Views |
 An incoherent fibre laser
An incoherent fibre laser
The demonstration of a 'mirrorless' ultralong Raman fibre laser that provides stable, spatially incoherent continuous-wave lasing may prove to be an important new light source for applications in nonlinear optics, sensing and telecommunications.
- Andrei A. Fotiadi
-
News & Views |
 OPCPA boosts high-field physics
OPCPA boosts high-field physics
Optical parametric chirped pulse amplification is a promising approach for amplifying few-cycle laser pulses to unprecedented powers. However, the future success of the scheme depends on the availability of suitable pump sources.
- Rachel Won
-
Letter |
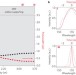 Soliton–similariton fibre laser
Soliton–similariton fibre laser
Scientists report a mode-locking regime of an erbium-doped fibre laser in which the laser pulse evolves as a similariton in the gain segment of the cavity and transforms into a soliton in the rest of the cavity. The findings constitute the first observation of amplifier similaritons in a laser cavity and are likely to be applicable to various other nonlinear systems.
- Bulent Oktem
- , Coşkun Ülgüdür
- & F. Ömer Ilday
-
Article |
 Random distributed feedback fibre laser
Random distributed feedback fibre laser
The combination of distributed Rayleigh back-scatter and Raman gain in an optical fibre yields an open cavity, mirror-less fibre laser that offers stable operation at the telecommunications wavelength of 1.5 µm.
- Sergei K. Turitsyn
- , Sergey A. Babin
- & Evgenii V. Podivilov
-
Interview |
 Single-cycle light
Single-cycle light
Few-cycle light pulses are important for attosecond science and extremely nonlinear optics. Alfred Leitenstorfer from the University of Konstanz spoke to Nature Photonics about how erbium-doped fibre laser technology can generate single-cycle pulses at telecommunications wavelengths.
- Rachel Won

 Kilowatt-average-power single-mode laser light transmission over kilometre-scale hollow-core fibre
Kilowatt-average-power single-mode laser light transmission over kilometre-scale hollow-core fibre