Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Evolutionary origin of genomic structural variations in domestic yaks
Evolutionary origin of genomic structural variations in domestic yaks
Yaks have been subject to natural selection, human domestication and interspecific introgression during their evolution. Here, the authors have identified genomic structural variations and the linked genes involved in these processes in domestic yaks, to reveal new insight into genetic basis of phenotypic diversity.
- Xinfeng Liu
- , Wenyu Liu
- & Jianquan Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Interlocking of co-opted developmental gene networks in Drosophila and the evolution of pre-adaptive novelty
Interlocking of co-opted developmental gene networks in Drosophila and the evolution of pre-adaptive novelty
During evolution, genes can be recruited to new positions to perform novel functions. This study shows one such co-option event, where the reused gene networks are initially interlocked, so that any changes because of their function in one organ are mirrored in the other organs even if they provide no selective advantage, opening the potential for acquiring a novel function.
- Sara Molina-Gil
- , Sol Sotillos
- & James C.-G. Hombría
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamics of transposable element accumulation in the non-recombining regions of mating-type chromosomes in anther-smut fungi
Dynamics of transposable element accumulation in the non-recombining regions of mating-type chromosomes in anther-smut fungi
In the absence of recombination, the number of transposable elements (TEs) increases, but their accumulation dynamics are not well characterized. This study shows that TEs rapidly accumulated in non-recombining fungal mating-type chromosomes before reaching a plateau, possibly forming a TE reservoir.
- Marine Duhamel
- , Michael E. Hood
- & Tatiana Giraud
-
Article
| Open Access Evolutionary dynamics of genome size and content during the adaptive radiation of Heliconiini butterflies
Evolutionary dynamics of genome size and content during the adaptive radiation of Heliconiini butterflies
The diverse Heliconius butterflies have evolved key innovations, including pollen feeding, and are a quintessential example of adaptive radiation. Using comparative genomics, Cicconardi et al. identify targets of selection at coding and non-coding loci during major ecological transitions in Heliconius.
- Francesco Cicconardi
- , Edoardo Milanetti
- & Stephen H. Montgomery
-
Article
| Open Access The genomic footprint of whaling and isolation in fin whale populations
The genomic footprint of whaling and isolation in fin whale populations
Industrial whaling drove several species to near extinction. From an analysis of 50 whole-genomes from fin whale populations, this study shows that the fin whale population in the Eastern North Pacific was reduced 99% during whaling but has maintained genomic diversity, whereas the Gulf of California population remained small and isolated, resulting in increased genetic load.
- Sergio F. Nigenda-Morales
- , Meixi Lin
- & Robert K. Wayne
-
Article
| Open Access Phylotranscriptomics unveil a Paleoproterozoic-Mesoproterozoic origin and deep relationships of the Viridiplantae
Phylotranscriptomics unveil a Paleoproterozoic-Mesoproterozoic origin and deep relationships of the Viridiplantae
Evolutionary relationships among green plants are unresolved and, in particular, the phylogenetic position of Prasinodermophyta remains controversial. Here, the authors conduct phylogenomic analyses to resolve relationships within Viridiplantae, suggesting that this group diverged between the Great Oxidation Event and the Neoproterozoic Oxygenation Event.
- Zhiping Yang
- , Xiaoya Ma
- & Bojian Zhong
-
Article
| Open Access Dominance vs epistasis: the biophysical origins and plasticity of genetic interactions within and between alleles
Dominance vs epistasis: the biophysical origins and plasticity of genetic interactions within and between alleles
The authors examine how mutations combine to alter phenotypes in biophysical models of proteins and conclude that non-additive interactions (epistasis and dominance) are frequent, context-dependent and so challenging to predict in even the simplest of biological systems.
- Xuan Xie
- , Xia Sun
- & Xianghua Li
-
Article
| Open Access Subtelomeric 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase copy number variation confers glyphosate resistance in Eleusine indica
Subtelomeric 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase copy number variation confers glyphosate resistance in Eleusine indica
Resistance to herbicide glyphosate can be evolved trough copy number variation (CNV) of its target gene EPSPS in goosegrass. Here, the authors assemble the genomes of glyphosate susceptible and resistance lines and provide evidence of sub-telomeric-repeat driven CNV of EPSPS could lead to glyphosate resistance.
- Chun Zhang
- , Nicholas A. Johnson
- & Eric L. Patterson
-
Article
| Open Access Evolutionary genomics of camouflage innovation in the orchid mantis
Evolutionary genomics of camouflage innovation in the orchid mantis
Camouflage is a widespread phenomenon in nature, and the orchid mantis is a particularly striking example. Here the authors use evolutionary genomics to uncover the genetic mechanisms behind the colour and morphology that produce innovative camouflage in the orchid mantis and dead leaf mantis.
- Guangping Huang
- , Lingyun Song
- & Fuwen Wei
-
Article
| Open Access Rapid gene content turnover on the germline-restricted chromosome in songbirds
Rapid gene content turnover on the germline-restricted chromosome in songbirds
Songbirds have an extra chromosome with unknown function found only in their germline. This study assembles and compares this chromosome in two closely related nightingale species, finding large differences in genetic content and only one conserved gene with probable essential function.
- Stephen A. Schlebusch
- , Jakub Rídl
- & Radka Reifová
-
Article
| Open Access Comparative genomics reveals a unique nitrogen-carbon balance system in Asteraceae
Comparative genomics reveals a unique nitrogen-carbon balance system in Asteraceae
Asteraceae is the largest family of flowering plants. Here, the authors assemble the genomes of stem lettuce (within Asteraceae) and beach cabbage (within Goodeniaceae) for evolutionary genomics analyses and reveal the absence of the core regulatory gene of nitrogen and carbon assimilation in Asteraceae.
- Fei Shen
- , Yajuan Qin
- & Xiaozeng Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Characterizing the evolution and phenotypic impact of ampliconic Y chromosome regions
Characterizing the evolution and phenotypic impact of ampliconic Y chromosome regions
A major part of the human Y chromosome consists of palindromes with multiple copies of genes primarily expressed in testis. Here, the authors investigate copy number variation in these palindromes based on whole genome sequence data from 11,527 Icelandic men.
- Elise A. Lucotte
- , Valdís Björt Guðmundsdóttir
- & Kari Stefansson
-
Article
| Open Access Parallel and convergent genomic changes underlie independent subterranean colonization across beetles
Parallel and convergent genomic changes underlie independent subterranean colonization across beetles
The genomic underpinnings of cave-related phenotypes are underexplored. Here, the authors investigate adaptation to underground life in cave beetle lineages using transcriptomic and genomic data, finding both parallel and convergent changes in six independent episodes of subterranean colonization.
- Pau Balart-García
- , Leandro Aristide
- & Rosa Fernández
-
Article
| Open Access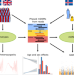 Sequence variants affecting the genome-wide rate of germline microsatellite mutations
Sequence variants affecting the genome-wide rate of germline microsatellite mutations
Microsatellites are tandem repeats of short DNA motifs and represent some of the most polymorphic sites in the genome. Here, the authors report that the human germline microsatellite mutation rate is, in part, under genetic control.
- Snaedis Kristmundsdottir
- , Hakon Jonsson
- & Kari Stefansson
-
Article
| Open Access Evolvability-enhancing mutations in the fitness landscapes of an RNA and a protein
Evolvability-enhancing mutations in the fitness landscapes of an RNA and a protein
Whether evolvability itself can be a product of adaptive Darwinian evolution is a debated question. This study proposes that adaptive landscapes harbor mutations that enhance the evolvability of evolving molecules and help populations of these molecules to evolve high fitness.
- Andreas Wagner
-
Article
| Open Access Bacteria evolve macroscopic multicellularity by the genetic assimilation of phenotypically plastic cell clustering
Bacteria evolve macroscopic multicellularity by the genetic assimilation of phenotypically plastic cell clustering
Diverse bacteria exhibit phenotypically plastic multicellular clustering. Here the authors show that a single mutation can genetically assimilate ancestrally inducible multicellularity by modulating plasticity at multiple levels of organization to make E. coli grow constitutively as macroscopic multicellular clusters.
- Yashraj Chavhan
- , Sutirth Dey
- & Peter A. Lind
-
Article
| Open Access Divergent molecular signatures in fish Bouncer proteins define cross-fertilization boundaries
Divergent molecular signatures in fish Bouncer proteins define cross-fertilization boundaries
The egg membrane protein Bouncer is an important mediator of gamete interaction and prevents cross-fertilisation between medaka and zebrafish. This study demonstrates unique functional and structural differences in Bouncer proteins of these and other distantly related fish species which may determine which species can hybridize.
- Krista R. B. Gert
- , Karin Panser
- & Andrea Pauli
-
Article
| Open Access Breakdown of self-incompatibility due to genetic interaction between a specific S-allele and an unlinked modifier
Breakdown of self-incompatibility due to genetic interaction between a specific S-allele and an unlinked modifier
Breakdown of self-incompatibility in plants is often attributed to S-locus mutations. Here, by crossing between populations of Arabidopsis lyrate that differ in their breeding system, the authors propose that a modifier unlinked to the S-locus causes self-compatibility by disrupting S-locus function.
- Yan Li
- , Ekaterina Mamonova
- & Marc Stift
-
Article
| Open Access Genomics of cold adaptations in the Antarctic notothenioid fish radiation
Genomics of cold adaptations in the Antarctic notothenioid fish radiation
The notothenioid radiation is a remarkable group of fish adapted to life in the icy waters of the Southern Ocean. This study investigates the evolutionary history of this group and the basis of their adaption to cold environments through genomic analysis of 24 new genome assemblies.
- Iliana Bista
- , Jonathan M. D. Wood
- & Richard Durbin
-
Article
| Open Access The monoaminergic system is a bilaterian innovation
The monoaminergic system is a bilaterian innovation
Monoamines act as neuromodulators in the nervous system, but their evolutionary origins are unclear. Here, the authors examine the evolution of genes involved in monoamine production, and processing suggesting that the monoaminergic system evolved in the bilaterian stem-group.
- Matthew Goulty
- , Gaelle Botton-Amiot
- & Roberto Feuda
-
Article
| Open Access Transposon signatures of allopolyploid genome evolution
Transposon signatures of allopolyploid genome evolution
Assigning assembled chromosomes to subgenome in allopolypoid genome analysis is challenging. Here, the authors report a statistical formwork for identifying evolutionarily coherent subgneomes relying on transposable elements to group chromosomes into sets with shared ancestry and apply it in cyprinids, false flax and strawberry.
- Adam M. Session
- & Daniel S. Rokhsar
-
Article
| Open Access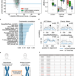 A previously uncharacterized Factor Associated with Metabolism and Energy (FAME/C14orf105/CCDC198/1700011H14Rik) is related to evolutionary adaptation, energy balance, and kidney physiology
A previously uncharacterized Factor Associated with Metabolism and Energy (FAME/C14orf105/CCDC198/1700011H14Rik) is related to evolutionary adaptation, energy balance, and kidney physiology
The human genome still contains numerous uncharacterized genes. Here, the authors identify a fast evolving Factor associated with Metabolism and Energy (FAME) that is associated with altered body weight, energy expenditure, and metabolism and study its function in knockout mouse models.
- Julian Petersen
- , Lukas Englmaier
- & Igor Adameyko
-
Article
| Open Access Odor-regulated oviposition behavior in an ecological specialist
Odor-regulated oviposition behavior in an ecological specialist
There is much interest in how animals adapt behaviorally to their ecological niche. Here, the authors demonstrate a role for olfaction in the oviposition preference of the noni fruit specialist Drosophila sechellia, and evidence for an important contribution of Ir75b, a receptor for the noni odor hexanoic acid.
- Raquel Álvarez-Ocaña
- , Michael P. Shahandeh
- & Richard Benton
-
Article
| Open Access Independent rediploidization masks shared whole genome duplication in the sturgeon-paddlefish ancestor
Independent rediploidization masks shared whole genome duplication in the sturgeon-paddlefish ancestor
Whole genome duplication can generate new genes and support survival through mass extinctions. Here, the authors show that paddlefish and sturgeon shared a genome duplication event 200 million years ago that was previously unrecognised due to the mixed signals from independent rediploidisation.
- Anthony K. Redmond
- , Dearbhaile Casey
- & Aoife McLysaght
-
Article
| Open Access Distinct genomic routes underlie transitions to specialised symbiotic lifestyles in deep-sea annelid worms
Distinct genomic routes underlie transitions to specialised symbiotic lifestyles in deep-sea annelid worms
Annelid worms have colonised extreme ecological niches, such as hydrothermal vents and whale falls thanks to symbiotic bacteria. This study finds that Osedax worms and the related Vestimentifera have evolved different genomic adaptations to sustain their bacterial symbioses and exploit different resources, such as decaying bone.
- Giacomo Moggioli
- , Balig Panossian
- & José M. Martín-Durán
-
Article
| Open Access Selection-driven trait loss in independently evolved cavefish populations
Selection-driven trait loss in independently evolved cavefish populations
Repeated evolution provides valuable insight into adaptation. In this study, the authors found that repeated evolution of cave-adapted phenotypes of a fish (Astyanax mexicanus) was driven by selection on standing genetic variation and novel mutations and genes repeatedly under selection are longer compared to the rest of the genome.
- Rachel L. Moran
- , Emilie J. Richards
- & Suzanne E. McGaugh
-
Matters Arising
| Open AccessReply to “Subgenome-aware analyses suggest a reticulate allopolyploidization origin in three Papaver genomes”
- Xiaofei Yang
- , Shenghan Gao
- & Kai Ye
-
Matters Arising
| Open Access Subgenome-aware analyses suggest a reticulate allopolyploidization origin in three Papaver genomes
Subgenome-aware analyses suggest a reticulate allopolyploidization origin in three Papaver genomes
- Ren-Gang Zhang
- , Chaoxia Lu
- & Wei Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Selection and adaptive introgression guided the complex evolutionary history of the European common bean
Selection and adaptive introgression guided the complex evolutionary history of the European common bean
Common bean has two distinct domestication centers in Mesoamerica and in the Andes. The authors show that the Andean is the first gene pool successfully introduced in Europe and identify signature of pervasive introgression among gene pools and of selection for flowering underlying adaptation.
- Elisa Bellucci
- , Andrea Benazzo
- & Roberto Papa
-
Article
| Open Access Large haploblocks underlie rapid adaptation in the invasive weed Ambrosia artemisiifolia
Large haploblocks underlie rapid adaptation in the invasive weed Ambrosia artemisiifolia
Ambrosia artemisiifolia is an invasive weed and primary cause of pollen-induced hayfever. Here, the authors report its chromosome-level phased genome assembly, examine genome-wide variation among modern and historic accessions, and identify large haploblocks underling rapid adaptation.
- Paul Battlay
- , Jonathan Wilson
- & Kathryn A. Hodgins
-
Article
| Open Access Pan-genome inversion index reveals evolutionary insights into the subpopulation structure of Asian rice
Pan-genome inversion index reveals evolutionary insights into the subpopulation structure of Asian rice
Pan-genomes provide useful resources for evolutionary studies, functional genomics and breeding of cultivated plants. Here, the authors report a new rice pan-genome including 73 Asian rice and two wild relatives (Oryza rufipogon and O. punctata), and reveal the prevalence and scale of large inversions across the pan-genome.
- Yong Zhou
- , Zhichao Yu
- & Rod A. Wing
-
Article
| Open Access Evolutionary conservation of the fidelity of transcription
Evolutionary conservation of the fidelity of transcription
The molecular mechanisms that ensure faithful transcription of genetic information are still unclear. Chung et al. identify various genes, alleles and processes that affect the fidelity of transcription multiple organisms, suggesting evolutionary conservation of fidelity factors, and compare the error rate of transcription among these species.
- Claire Chung
- , Bert M. Verheijen
- & Marc Vermulst
-
Article
| Open Access Revealing evolution of tropane alkaloid biosynthesis by analyzing two genomes in the Solanaceae family
Revealing evolution of tropane alkaloid biosynthesis by analyzing two genomes in the Solanaceae family
Tropane alkaloids (TAs) are synthesized by some species in Solanaceae. Here, the authors assemble the genomes of two representative TAs producing species, show that gene loss shapes uneven distribution of TAs in Solanaceae, and identify a cytochrome P450 gene catalyzing N-demethylation of hyoscyamine to generate norhyoscyamine.
- Fangyuan Zhang
- , Fei Qiu
- & Zhihua Liao
-
Article
| Open Access Evolutionary differentiation of androgen receptor is responsible for sexual characteristic development in a teleost fish
Evolutionary differentiation of androgen receptor is responsible for sexual characteristic development in a teleost fish
How has the genome duplication impacted the diversification of sexual characteristics in the teleost lineage? This study shows that androgen receptor ohnologs in medaka appear to have diverged in their roles for regulating morphological and behavioural sexual characteristics after loss from an ancestral role in spermatogenesis.
- Yukiko Ogino
- , Satoshi Ansai
- & Taisen Iguchi
-
Article
| Open Access A male-killing gene encoded by a symbiotic virus of Drosophila
A male-killing gene encoded by a symbiotic virus of Drosophila
Maternally inherited symbionts that kill male insect hosts are well known in bacteria, but are also beginning to be recognised in viruses. In this study, the authors identify a gene from a symbiotic virus genome that is responsible for the male-killing phenotype of this virus in the fly Drosophila biauraria.
- Daisuke Kageyama
- , Toshiyuki Harumoto
- & Masayoshi Watada
-
Article
| Open Access The Torreya grandis genome illuminates the origin and evolution of gymnosperm-specific sciadonic acid biosynthesis
The Torreya grandis genome illuminates the origin and evolution of gymnosperm-specific sciadonic acid biosynthesis
Torreya grandis is a gymnosperm species that produces edible seeds with high level of sciadonic acid (SCA). Here, the authors assemble the genome of this species, preform methylone analysis of seeds at different developmental stages, and reveal two key genes involved in SCA biosynthesis.
- Heqiang Lou
- , Lili Song
- & Jiasheng Wu
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular exploration of fossil eggshell uncovers hidden lineage of giant extinct bird
Molecular exploration of fossil eggshell uncovers hidden lineage of giant extinct bird
The evolution and systematics of Madagascar’s extinct elephant birds remains unclear. Here, the authors recover genetic, stable isotope, morphological, and geographic data from fossil eggshell to describe variation among clades, identifying cryptic diversity and potential drivers of speciation.
- Alicia Grealy
- , Gifford H. Miller
- & Michael Bunce
-
Article
| Open Access Climate-induced range shifts drive adaptive response via spatio-temporal sieving of alleles
Climate-induced range shifts drive adaptive response via spatio-temporal sieving of alleles
The interplay of migration and adaptation was key in shaping species’ responses to Quaternary climate change. Illustrating this, Luqman et al. show that adaptive responses in a plant species emerged from climate-induced range shifts due to heterogenous sieving of adaptive alleles across space and time.
- Hirzi Luqman
- , Daniel Wegmann
- & Alex Widmer
-
Article
| Open Access Social complexity, life-history and lineage influence the molecular basis of castes in vespid wasps
Social complexity, life-history and lineage influence the molecular basis of castes in vespid wasps
A key hypothesis for the evolution of division of labour in social insects is that a shared set of genes – a genetic toolkit - regulates reproductive castes across species. Here, the authors analyze brain transcriptomes from nine species of social wasps to identify the factors that shape this toolkit.
- Christopher Douglas Robert Wyatt
- , Michael Andrew Bentley
- & Seirian Sumner
-
Article
| Open Access A thousand-genome panel retraces the global spread and adaptation of a major fungal crop pathogen
A thousand-genome panel retraces the global spread and adaptation of a major fungal crop pathogen
Zymoseptoria tritici is an important fungal pathogen of wheat which has spread globally. Here, the authors perform genomic analyses on a collection of ~1100 Z. tritici samples from 42 countries to describe its global spread and elucidate mechanisms of adaptation to different environmental conditions.
- Alice Feurtey
- , Cécile Lorrain
- & Daniel Croll
-
Article
| Open Access Amniotes co-opt intrinsic genetic instability to protect germ-line genome integrity
Amniotes co-opt intrinsic genetic instability to protect germ-line genome integrity
Pachytene Piwi-interacting RNAs (piRNAs) expressed in mammalian germ lines are abundant, but their evolution and function are not fully understood. Here, the authors find that pachytene piRNA loci are hotspots of structural variation, which underlies rapid piRNA birth, divergence, and loss.
- Yu H. Sun
- , Hongxiao Cui
- & Xin Zhiguo Li
-
Article
| Open Access Transcription factor binding sites are frequently under accelerated evolution in primates
Transcription factor binding sites are frequently under accelerated evolution in primates
Characterizing genomic elements under accelerated evolution is crucial for understanding the genomic basis of human evolution and disease. Here, Zhang et al. introduce GroupAcc, a collection of two pooling-based phylogenetic methods with enhanced sensitivity to examine accelerated evolution in transcription factor binding sites.
- Xinru Zhang
- , Bohao Fang
- & Yi-Fei Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Macroevolutionary diversity of traits and genomes in the model yeast genus Saccharomyces
Macroevolutionary diversity of traits and genomes in the model yeast genus Saccharomyces
Here, the authors describe the geographies, hosts, substrates, and phylogenetic relationships for 1,794 Saccharomyces strains. They provide insight into the genetic and phenotypic diversity in the genus, not seen through prior work focused on the model species Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
- David Peris
- , Emily J. Ubbelohde
- & Chris Todd Hittinger
-
Article
| Open Access Genome structure-based Juglandaceae phylogenies contradict alignment-based phylogenies and substitution rates vary with DNA repair genes
Genome structure-based Juglandaceae phylogenies contradict alignment-based phylogenies and substitution rates vary with DNA repair genes
The phylogenetic relationship among genera within the walnut family Juglandaceae remains unclear. Here, the authors assemble the genomes of Rhoiptelea chiliantha and Engelhardia roxburghiana, resolve the topology of this family, and propose a hybrid origin of the family from progenitors nested within or sister to Myricaceae.
- Ya-Mei Ding
- , Xiao-Xu Pang
- & Wei-Ning Bai
-
Article
| Open Access Inversions maintain differences between migratory phenotypes of a songbird
Inversions maintain differences between migratory phenotypes of a songbird
Rearrangements in the genome are important for local adaptation and speciation but are often difficult to identify reliably. Here the authors show that rearrangements underlie large chromosome regions that separate differentially migratory willow warblers.
- Max Lundberg
- , Alexander Mackintosh
- & Staffan Bensch
-
Article
| Open Access Evolution of giant pandoravirus revealed by CRISPR/Cas9
Evolution of giant pandoravirus revealed by CRISPR/Cas9
Until today, genetic tools have been lacking to enable manipulation of amoebal giant viruses (GVs) by CRISPR/Cas9 technology. Here, Bisio et al. apply S. pyogenes Cas9 together with pU6- driven guide RNAs to investigate the replication of pandoravirus, a GV replication in the nucleus. Using this tool, they provide evidence for stepwise evolution and genetic expansion of viral gigantism.
- Hugo Bisio
- , Matthieu Legendre
- & Chantal Abergel
-
Article
| Open Access Uncovering a miltiradiene biosynthetic gene cluster in the Lamiaceae reveals a dynamic evolutionary trajectory
Uncovering a miltiradiene biosynthetic gene cluster in the Lamiaceae reveals a dynamic evolutionary trajectory
A diterpenoid biosynthetic gene cluster (BGC) has been identified in a few species in the Lamiaceae (mint) family, but its origin and evolution remain unclear. Here, the authors report assembly of genomes of three species within the family and reveal the dynamic evolutionary trajectory of the BGC.
- Abigail E. Bryson
- , Emily R. Lanier
- & Björn Hamberger
-
Article
| Open Access Common evolutionary trajectory of short life-cycle in Brassicaceae ruderal weeds
Common evolutionary trajectory of short life-cycle in Brassicaceae ruderal weeds
Understanding origin and adaptation of weeds is important for their management. Here, via genome assembly, population genomics, and QTL mapping, the authors establish Cardamine occulta as a model to study weed ruderality and show FLC and CRY2 as genetic drivers for the establishment of short life cycle.
- Ling-Zi Li
- , Zhou-Geng Xu
- & Jia-Wei Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Migration direction in a songbird explained by two loci
Migration direction in a songbird explained by two loci
The genetic determinants of long-distance migration in birds are largely unknown. Sokolovskis et al. tracked genotyped hybrid willow warblers from a migratory divide in Sweden and find that autumn migration direction is consistent with a dominant inheritance pattern of two large effect loci that interact through epistasis.
- Kristaps Sokolovskis
- , Max Lundberg
- & Staffan Bensch

 Phylogenomics reveals the history of host use in mosquitoes
Phylogenomics reveals the history of host use in mosquitoes