Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Over 90 endangered fish and invertebrates are caught in industrial fisheries
Over 90 endangered fish and invertebrates are caught in industrial fisheries
Due to legislative shortfalls, species of global conservation concern can still be captured in commercial fisheries. Here the authors show that 91 threatened species are reported in catch/landing databases, 13 of which are traded internationally despite their conservation concern.
- Leslie A. Roberson
- , Reg A. Watson
- & Carissa J. Klein
-
Article
| Open Access India’s potential for integrating solar and on- and offshore wind power into its energy system
India’s potential for integrating solar and on- and offshore wind power into its energy system
India currently relies heavily on fossil-based sources for its power needs. Here the authors show that renewable energy in India could be cheaper than fossil-based alternatives and could reduce CO2 emissions by 85% by 2040.
- Tianguang Lu
- , Peter Sherman
- & Michael McElroy
-
Article
| Open Access Carbon pricing and planetary boundaries
Carbon pricing and planetary boundaries
In the light of nine Earth System Processes (ESPs) and the corresponding planetary boundaries, here the authors assessed the global environmental impact of a global carbon pricing in a multi-boundary world. They show that a global carbon tax would relieve pressure on most ESPs and it is therefore stronger in a multi-boundary world than when considering climate change in isolation.
- Gustav Engström
- , Johan Gars
- & Badri Narayanan
-
Review Article
| Open Access Climate action requires new accounting guidance and governance frameworks to manage carbon in shelf seas
Climate action requires new accounting guidance and governance frameworks to manage carbon in shelf seas
Accounting guidelines exist for carbon flows in terrestrial and coastal ecosystems, but not shelf sea sediments. In this Review, the authors explore whether effective management of carbon stocks accumulating in shelf seas could contribute to a nation’s greenhouse gas emissions reduction targets.
- Tiziana Luisetti
- , Silvia Ferrini
- & Emmanouil Tyllianakis
-
Article
| Open Access Uncovering temporal changes in Europe’s population density patterns using a data fusion approach
Uncovering temporal changes in Europe’s population density patterns using a data fusion approach
Official data on the distribution of human population often ignores the changing spatio-temporal densities resulting from mobility. Here, authors apply an approach combining official statistics and geospatial data to assess intraday and monthly population variations at continental scale at 1 km2 resolution.
- Filipe Batista e Silva
- , Sérgio Freire
- & Carlo Lavalle
-
Article
| Open Access Using insurance data to quantify the multidimensional impacts of warming temperatures on yield risk
Using insurance data to quantify the multidimensional impacts of warming temperatures on yield risk
The impacts of climate change on agricultural productivity remain debated. Here, the authors present new evidence for the magnitude and causes of U.S. crop insurance losses, using a database of production risk from 1989–2014 across 1733 counties for corn and 1632 counties for soybeans, and find that crop production risk will increase in response to warmer temperatures.
- Edward D. Perry
- , Jisang Yu
- & Jesse Tack
-
Article
| Open Access Assessment of lithium criticality in the global energy transition and addressing policy gaps in transportation
Assessment of lithium criticality in the global energy transition and addressing policy gaps in transportation
The long-term availability of lithium in the event of significant demand growth of rechargeable lithium-ion batteries is important to assess. Here the authors assess lithium demand and supply challenges of a long-term energy transition using 18 scenarios, developed by combining 8 demand and 4 supply variations.
- Peter Greim
- , A. A. Solomon
- & Christian Breyer
-
Article
| Open Access Methane emissions from natural gas vehicles in China
Methane emissions from natural gas vehicles in China
The methane emissions from natural gas vehicles (NGVs) are unclear. Here the authors report high methane emissions from heavy-duty NGVs, and by using a scenario analysis show that strictly implementing the upcoming China VI standard could reduce GHG emissions by 509 Mt CO2eq for 2020-2030.
- Da Pan
- , Lei Tao
- & Mark A. Zondlo
-
Article
| Open Access Environmental-social-economic footprints of consumption and trade in the Asia-Pacific region
Environmental-social-economic footprints of consumption and trade in the Asia-Pacific region
The environmental and socio-economic implications of the growth in welfare and trade in Asia-Pacific (APAC) remain unclear. Here the authors show that over the past two decades (1995–2015), owing to intraregional trade, the APAC economies have grown increasingly interdependent in natural resource use, air emissions, and labor and economic productivity.
- Lan Yang
- , Yutao Wang
- & Yuanbo Qiao
-
Article
| Open Access Global correlates of terrestrial and marine coverage by protected areas on islands
Global correlates of terrestrial and marine coverage by protected areas on islands
Islands have disproportionate importance for biodiversity conservation, yet they may be underrepresented in protected areas. Here the authors assess how climate, geography, habitat diversity, and socio-economic conditions explain terrestrial and marine protected area coverage on inhabited islands and in the surrounding seas globally.
- David Mouillot
- , Laure Velez
- & Marc Troussellier
-
Article
| Open Access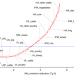 Societal benefits of halving agricultural ammonia emissions in China far exceed the abatement costs
Societal benefits of halving agricultural ammonia emissions in China far exceed the abatement costs
Global largest agricultural ammonia (NH3) emissions in China have caused severe damage to both ecosystem and human health, yet no policy is formulated to reduce NH3 emissions. Here, the authors show that halving agricultural NH3 emissions with feasible technical mitigation options in China generates far more societal benefits than abatement costs.
- Xiuming Zhang
- , Baojing Gu
- & Deli Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Effective plans for hospital system response to earthquake emergencies
Effective plans for hospital system response to earthquake emergencies
Hospital systems are critical, especially in providing healthcare services after disasters. Here, the authors revealed that in Lima the spatial distribution of health service demands mismatches the capacities of hospitals after earthquakes, leaving large zones on the periphery significantly underserved.
- Luis Ceferino
- , Judith Mitrani-Reiser
- & Celso Bambarén
-
Article
| Open Access Diffusion of flue gas desulfurization reveals barriers and opportunities for carbon capture and storage
Diffusion of flue gas desulfurization reveals barriers and opportunities for carbon capture and storage
The historical diffusion of SO2 control technology gives insights into the potential uptake of carbon capture and storage. Here the authors show that the global diffusion of flue gas desulfurization technology was very fast at times, especially for retrofit, and even after materiality, but strongly depended on regulation.
- Stijn van Ewijk
- & Will McDowall
-
Article
| Open Access Exposure to air pollution and scarlet fever resurgence in China: a six-year surveillance study
Exposure to air pollution and scarlet fever resurgence in China: a six-year surveillance study
The reason for a re-emergence of scarlet fever in China remains unclear. Here the authors show that the number of scarlet fever cases surged in 2011 peaking in 2018, this correlates with an increase in NO2 and O3 but does not necessarily imply causation.
- Yonghong Liu
- , Hui Ding
- & Shelan Liu
-
Comment
| Open AccessNew priorities for climate science and climate economics in the 2020s
Climate science and climate economics are critical sources of expertise in our pursuit of the Sustainable Development Goals. Effective use of this expertise requires a strengthening of its epistemic foundations and a renewed focus on more practical policy problems.
- David A. Stainforth
- & Raphael Calel
-
Article
| Open Access An equitable redistribution of unburnable carbon
An equitable redistribution of unburnable carbon
The allocation of remaining fossil fuel production has stimulated a discussion around issues of equitable allocation but the implications of different options are unclear. Here the authors show that shifting production to low-medium human development regions has limited economic benefits under strong climate policy.
- Steve Pye
- , Siân Bradley
- & Paul Ekins
-
Matters Arising
| Open AccessAlternative meta-analysis of behavioral interventions to promote action on climate change yields different conclusions
- Sander van der Linden
- & Matthew H. Goldberg
-
Matters Arising
| Open AccessReply to: Alternative meta-analysis of behavioural interventions to promote action on climate change yields different conclusions
- Claudia F. Nisa
- , Edyta M. Sasin
- & Jocelyn J. Belanger
-
Article
| Open Access The sponge effect and carbon emission mitigation potentials of the global cement cycle
The sponge effect and carbon emission mitigation potentials of the global cement cycle
Cement plays a dual role in the carbon cycle like a sponge. Here, the authors employ a dynamic model to quantify such sponge effect and concluded that deep decarbonization of the global cement cycle will require radical technology advancements and widespread deployment of material efficiency measures.
- Zhi Cao
- , Rupert J. Myers
- & Gang Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Future changes in the trading of virtual water
Future changes in the trading of virtual water
Assessments of future virtual water trading are still lacking. Here the authors estimated the global virtual water trade throughout the century and found that virtual green water exports and virtual blue water exports at least triple to more than 3200 bcm and 170 bcm, respectively, by the end of the century.
- Neal T. Graham
- , Mohamad I. Hejazi
- & Fernando Miralles-Wilhelm
-
Perspective
| Open Access A transition to sustainable ocean governance
A transition to sustainable ocean governance
Oceans provide important natural resources, but the management and governance of the ocean is complex and the ecosystem is suffering as a result. The authors discuss current barriers to sustainable ocean governance and suggest pathways forward.
- Tanya Brodie Rudolph
- , Mary Ruckelshaus
- & Philile Mbatha
-
Article
| Open Access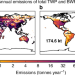 Atmospheric transport is a major pathway of microplastics to remote regions
Atmospheric transport is a major pathway of microplastics to remote regions
Plastic pollution is a critical concern across diverse ecosystems, yet most research has focused on terrestrial and aquatic transport, neglecting other mechanisms. Here the authors show that atmospheric transport is a major pathway for road plastic pollution over remote regions.
- N. Evangeliou
- , H. Grythe
- & A. Stohl
-
Perspective
| Open Access Scientists’ warning on affluence
Scientists’ warning on affluence
Current environmental impact mitigation neglects over-consumption from affluent citizens as a primary driver. The authors highlight the role of bottom-up movements to overcome structural economic growth imperatives spurring consumption by changing structures and culture towards safe and just systems.
- Thomas Wiedmann
- , Manfred Lenzen
- & Julia K. Steinberger
-
Article
| Open Access Association between ambient temperature and hypertensive disorders in pregnancy in China
Association between ambient temperature and hypertensive disorders in pregnancy in China
Hypertensive disorders in pregnancy are prevalent perinatal diseases. Here the authors report an association between ambient temperature before or after conception and risk of preeclampsia or eclampsia and gestational hypertension.
- Tao Xiong
- , Peiran Chen
- & Dezhi Mu
-
Article
| Open Access Rapid cost decrease of renewables and storage accelerates the decarbonization of China’s power system
Rapid cost decrease of renewables and storage accelerates the decarbonization of China’s power system
The decrease in costs of renewable energy and storage has not been well accounted for in energy modelling, which however will have a large effect on energy system investment and policies. Here the authors incorporated recent decrease in costs of renewable energy and storages to refine the pathways to decarbonize China’s power system by 2030 and show that if such cost trends for renewables continue, more than 60% of China’s electricity could come from non-fossil sources by 2030 at a cost that is about 10% lower than achieved through a business-as-usual approach.
- Gang He
- , Jiang Lin
- & Amol Phadke
-
Article
| Open Access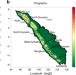 Social-media and newspaper reports reveal large-scale meteorological drivers of floods on Sumatra
Social-media and newspaper reports reveal large-scale meteorological drivers of floods on Sumatra
Floods are an important natural disaster on the Indonesian island of Sumatra, but their driving mechanisms are not well understood. Here, the authors utilize data from twitter messages and local newspaper reports to show that convectively coupled Kelvin waves play a key role in promoting floods on Sumatra.
- Dariusz B. Baranowski
- , Maria K. Flatau
- & Marzuki
-
Article
| Open Access Mapping global urban land for the 21st century with data-driven simulations and Shared Socioeconomic Pathways
Mapping global urban land for the 21st century with data-driven simulations and Shared Socioeconomic Pathways
Here the authors develop a set of global, long-term, spatial projections of urban land expansion for understanding the planet’s potential urban futures. The global total amount of urban land increases by a factor of 1.8-5.9 over the 21st century, and the developed world experiences as much new urban development as the developing world.
- Jing Gao
- & Brian C. O’Neill
-
Article
| Open Access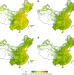 Mapping global carbon footprint in China
Mapping global carbon footprint in China
There lacks a spatially explicit mapping of global carbon footprint in China that considers both international and interprovincial trade. Here the authors map the carbon footprints of global regions in China and show the hotspots concentrated in key manufacturing hubs, including the Yangtze River Delta, Pearl River Delta, and North China Plain.
- Yuantao Yang
- , Shen Qu
- & Ming Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Taking stock of national climate policies to evaluate implementation of the Paris Agreement
Taking stock of national climate policies to evaluate implementation of the Paris Agreement
To evaluate the effectiveness of current national policies in achieving global temperature targets is important but a systematic multi-model evaluation is still lacking. Here the authors identified a reduction of 3.5 GtCO2 eq of current national policies relative to a baseline scenario without climate policies by 2030 due to the increasing low carbon share of final energy and the improving final energy intensity.
- Mark Roelfsema
- , Heleen L. van Soest
- & Saritha Sudharmma Vishwanathan
-
Article
| Open Access Assessing the impact of ETS trading profit on emission abatements based on firm-level transactions
Assessing the impact of ETS trading profit on emission abatements based on firm-level transactions
Carbon emission trading is an important market-based policy instrument to reduce GHG emission using reward-punishment mechanism. Here the authors show that the EU emission trading schemes operate at its designed purpose and there is a positive and linear relationship between firm profits and the firms’ efforts in abatement.
- Jianfeng Guo
- , Fu Gu
- & Ying Fan
-
Article
| Open Access Self-preservation strategy for approaching global warming targets in the post-Paris Agreement era
Self-preservation strategy for approaching global warming targets in the post-Paris Agreement era
The emission allocation strategies of global scenarios do not specify the potential benefits from extra climate mitigation efforts. Here the authors show that compared to the current Nationally Distributed Contributions, the proposed self-preservation strategy might generate 126–616 trillion dollars of additional benefits by 2100.
- Yi-Ming Wei
- , Rong Han
- & Zili Yang
-
Article
| Open Access The effects of contemporaneous peer punishment on cooperation with the future
The effects of contemporaneous peer punishment on cooperation with the future
Little is known about decentralized institutions that could facilitate cooperation for the sake of future generations. Here, the authors show that allowing for peer punishment within a generation is only partially successful in facilitating cooperation for the sake of later generations.
- Johannes Lohse
- & Israel Waichman
-
Article
| Open Access Heat health risk assessment in Philippine cities using remotely sensed data and social-ecological indicators
Heat health risk assessment in Philippine cities using remotely sensed data and social-ecological indicators
Evaluating the heat risk among city dwellers is important. Here, the authors assessed the heat risk in Philippine cities using remote sensing data and social-ecological indicators and found that the cities at high or very high risk are found in Metro Manila, where levels of heat hazard and exposure are high.
- Ronald C. Estoque
- , Makoto Ooba
- & Shogo Nakamura
-
Article
| Open Access Sustainability of global Golden Inland Waterways
Sustainability of global Golden Inland Waterways
The exploitation of rivers has been at the detriment of river ecosystems. Here the authors propose a concept of Golden Inland Waterways (GIWs) to represent large waterways and find that the exploitation ratio threshold around the turning point for most GIWs appear to be less than 80%, subject to ecological constraints.
- Yichu Wang
- , Xiabin Chen
- & Jinren Ni
-
Article
| Open Access Saving less in China facilitates global CO2 mitigation
Saving less in China facilitates global CO2 mitigation
The partial effects of saving rate changes on CO2 emissions remain unclear. Here the authors found that the increase in saving rates of China has led to increments of global industrial CO2 emissions by 189 million tonnes (Mt) during 2007-2012, while global CO2 emissions would be reduced by 186 Mt if the saving rates of China decreased by 15 percentage points.
- Chen Lin
- , Jianchuan Qi
- & Zhifeng Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Social and environmental analysis of food waste abatement via the peer-to-peer sharing economy
Social and environmental analysis of food waste abatement via the peer-to-peer sharing economy
Reducing food waste is important. Here the authors investigate whether digitally enabled social networks can efficiently reduce food waste and find that in 19 months, around 91t of food waste were collected by secondary consumers and diverted from disposal.
- Tamar Makov
- , Alon Shepon
- & Marian Chertow
-
Article
| Open Access Comparative performance of rural water supplies during drought
Comparative performance of rural water supplies during drought
The authors compared the performance of a range of rural water supply types during drought in Ethiopia. They show that prioritising access to groundwater via multiple improved water sources and technologies, such as hand-pumped and motorised boreholes, supported by monitoring and proactive operation and maintenance increases rural water supply resilience.
- D. J. MacAllister
- , A. M. MacDonald
- & R. Calow
-
Article
| Open Access Towards a more effective climate policy on international trade
Towards a more effective climate policy on international trade
Partners who actually reduce global emissions can be penalized under carbon accounting methods based on production or consumption give an idea of responsibility. Here the authors propose a new framework, emission responsibility allotment that penalizes/credits those that increase/decrease global emissions.
- Erik Dietzenbacher
- , Ignacio Cazcarro
- & Iñaki Arto
-
Article
| Open Access Managing energy infrastructure to decarbonize industrial parks in China
Managing energy infrastructure to decarbonize industrial parks in China
The contributions of industrial parks towards addressing climate change remains unclear. Here, the authors studied the energy infrastructure of 1604 industrial parks in China and found that by decarbonizing energy infrastructure stocks in the industrial parks, the GHG mitigation potential will achieve 8%~16% relative to the GHG emissions in the baseline scenario with positive economic benefits, water savings and air pollutant emission reductions.
- Yang Guo
- , Jinping Tian
- & Lyujun Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Impact of two of the world's largest protected areas on longline fishery catch rates
Impact of two of the world's largest protected areas on longline fishery catch rates
There are concerns that expansion of marine protected areas could have negative effects on the fishing industry. Here Lynham et al. demonstrate that the expansion of two of the world’s largest protected areas did not have a negative impact on catch rates in the Hawaii longline fishery.
- John Lynham
- , Anton Nikolaev
- & Juan Carlos Villaseñor-Derbez
-
Article
| Open Access Asian dust-storm activity dominated by Chinese dynasty changes since 2000 BP
Asian dust-storm activity dominated by Chinese dynasty changes since 2000 BP
How the Asian monsoon, earth surface processes and human development interact is not well known. Here, a new record of dust storm intensity shows a relationship between the stability of dynasties and dust storm activity for the last ~2200 years, which argues for a strong human control of dust storms in East Asia over this time.
- Fahu Chen
- , Shengqian Chen
- & Jianbao Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Air pollution control strategies directly limiting national health damages in the US
Air pollution control strategies directly limiting national health damages in the US
Decoupling emission reduction target determination, air pollution modelling, and health benefit estimation complicates control strategy design. Here an integrated approach identifies strategies to reduce health damages of air pollution, showing that benefits can be achieved cost-effectively by electrifying sources with high primary PM2.5 emission intensities.
- Yang Ou
- , J. Jason West
- & Daniel H. Loughlin
-
Matters Arising
| Open AccessReply to ‘A reexamination on how behavioral interventions can promote household action to limit climate change'
- Claudia F. Nisa
- , Jocelyn J. Bélanger
- & Daiane G. Faller
-
Matters Arising
| Open AccessA reexamination on how behavioral interventions can promote household action to limit climate change
- Paul C. Stern
-
Article
| Open Access Carbon footprint of global natural gas supplies to China
Carbon footprint of global natural gas supplies to China
The carbon footprints of natural gas supplies at the field level are unclear. Here the authors analysed the GHG intensities of gas supplies from 104 fields and show that their GHG intensities range from 6.2 to 43.3 g CO2eq MJ-1.
- Yu Gan
- , Hassan M. El-Houjeiri
- & Michael Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Using remarkability to define coastal flooding thresholds
Using remarkability to define coastal flooding thresholds
The degree of flooding in a particular location depends sensitively on local topography and bathymetry. Here the authors used the remarkability of flood events to estimate county-specific flood thresholds for shoreline counties along the Atlantic and Gulf coasts of the United States and found that several areas experience noticeable flooding at a height lower than existing thresholds.
- Frances C. Moore
- & Nick Obradovich
-
Article
| Open Access Pollution exacerbates China’s water scarcity and its regional inequality
Pollution exacerbates China’s water scarcity and its regional inequality
The impact on inadequate water quality on water scarcity is unclear. Here the authors quantify China’s present-day water scarcity and show that inadequate water quality exacerbates China’s water scarcity, which is unevenly distributed across the country.
- Ting Ma
- , Siao Sun
- & Chenghu Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access Global projections of future urban land expansion under shared socioeconomic pathways
Global projections of future urban land expansion under shared socioeconomic pathways
Shared socioeconomic pathways (SSPs) is a crucial scenario describing the potential of future socio-economic development. The authors here investigate long-term effects of various government policies suggested by different SSPs on urban land and reveal the impact of future urban expansion on other land and food production.
- Guangzhao Chen
- , Xia Li
- & Kangning Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Paris Climate Agreement passes the cost-benefit test
Paris Climate Agreement passes the cost-benefit test
Relative economic benefits of achieving temperature targets have not properly accounted for damages at higher temperatures. Here the authors integrate dynamic cost-benefit analysis with a damage-cost curve and show that the Paris Climate Agreement constitutes the economically optimal policy pathway for the future.
- Nicole Glanemann
- , Sven N. Willner
- & Anders Levermann

 The social and environmental complexities of extracting energy transition metals
The social and environmental complexities of extracting energy transition metals