Featured
-
-
News & Views |
 Plants water the planet
Plants water the planet
Greening of the planet has increased global surface water availability, but vegetation changes can have diverse local and remote impacts across different regions.
- Arie Staal
-
Article |
 Temporal patterns of soil carbon emission in tropical forests under long-term nitrogen deposition
Temporal patterns of soil carbon emission in tropical forests under long-term nitrogen deposition
Field experiments suggest that long-term responses of soil respiration and carbon emissions to nitrogen deposition in tropical forests can be divided into different phases as soil environment and biological response change.
- Mianhai Zheng
- , Tao Zhang
- & Wei Zhang
-
Perspective |
 Potential impacts of atmospheric microplastics and nanoplastics on cloud formation processes
Potential impacts of atmospheric microplastics and nanoplastics on cloud formation processes
Microplastics and nanoplastics may affect cloud formation processes by acting as ice-nucleating particles and cloud condensation nuclei.
- Mischa Aeschlimann
- , Guangyu Li
- & Denise M. Mitrano
-
Article |
 Global water availability boosted by vegetation-driven changes in atmospheric moisture transport
Global water availability boosted by vegetation-driven changes in atmospheric moisture transport
Vegetation change over the past two decades has limited the decline in global water availability by enhancing rainfall over evapotranspiration, according to analysis of observation-based atmospheric moisture transport data.
- Jiangpeng Cui
- , Xu Lian
- & Shilong Piao
-
Article |
 Enhanced dust emission following large wildfires due to vegetation disturbance
Enhanced dust emission following large wildfires due to vegetation disturbance
Enhanced dust emissions are associated with more than half of the global large wildfire events occurring between 2003 and 2020, according to analyses of satellite measurements of aerosol abundance following more than 150,000 global wildfires.
- Yan Yu
- & Paul Ginoux
-
Brief Communication
| Open Access Substantial contribution of iodine to Arctic ozone destruction
Substantial contribution of iodine to Arctic ozone destruction
Iodine chemistry plays a more important role than bromine chemistry in tropospheric ozone losses in the Arctic, according to ship-based observations of halogen oxides from March to October 2020.
- Nuria Benavent
- , Anoop S. Mahajan
- & Alfonso Saiz-Lopez
-
All Minerals Considered |
 An apatite for kidney stones
An apatite for kidney stones
Bruce Fouke explores the biomineralization of calcium oxalate and apatite kidney stones and the opportunities that lie at the intersection of geology, biology and medicine; a transdisciplinary effort traced back some 350 years.
- Bruce W. Fouke
-
News & Views |
 Thermal bridging by Arctic shrubs
Thermal bridging by Arctic shrubs
Shrubs act as thermal bridges to conduct heat through the tundra snowpack, fostering heat loss from the ground in winter and heat gain in the spring.
- Michael M. Loranty
-
News & Views |
 A step forward to mitigate ozone
A step forward to mitigate ozone
For decades, ozone pollution mitigation efforts relied on two chemical regimes. A global modelling analysis has revealed a third regime involving aerosols that would help with the concurrent control of both ozone and particulate pollution.
- Audrey Gaudel
-
Article
| Open Access Suppression of surface ozone by an aerosol-inhibited photochemical ozone regime
Suppression of surface ozone by an aerosol-inhibited photochemical ozone regime
Global chemical transport simulations reveal an ozone photochemistry regime where the uptake of hydroperoxyl radicals onto aerosol particles dominates ozone production.
- Peter D. Ivatt
- , Mathew J. Evans
- & Alastair C. Lewis
-
Research Briefing |
 Preferential phosphorus retention in lakes alters the balance of global nutrient cycles
Preferential phosphorus retention in lakes alters the balance of global nutrient cycles
Preferential P retention emerges in almost 90% of global lakes. This retention leads to a strong elevation in the N:P ratios in lakes outflow, exacerbates the imbalance of the nutrient cycles and can potentially result in biodiversity losses and algal blooms in lakes and downstream ecosystems.
-
Article |
 Imbalance of global nutrient cycles exacerbated by the greater retention of phosphorus over nitrogen in lakes
Imbalance of global nutrient cycles exacerbated by the greater retention of phosphorus over nitrogen in lakes
Lakes preferentially retain phosphorous over nitrogen, amplifying the imbalance of nutrient cycles caused by anthropogenic inputs, according to analyses of more than 5,000 lakes globally.
- Zhen Wu
- , Jincheng Li
- & Yong Liu
-
Research Briefing |
 Biological soil crusts play a key role in current and future global dust cycling
Biological soil crusts play a key role in current and future global dust cycling
This study shows that by stabilizing the soil, biological soil crusts reduce global atmospheric dust emissions by 60%, corresponding to ~700 Tg of dust per year. According to models of biocrust cover loss, this effect will be reduced in the future, leading to increases in not only dust emissions but also global radiative cooling.
-
Article
| Open Access Global cycling and climate effects of aeolian dust controlled by biological soil crusts
Global cycling and climate effects of aeolian dust controlled by biological soil crusts
Biocrusts reduce global atmospheric dust emission by 60%, and future biocrust losses due to climate and land-use changes will exacerbate this effect, according to global models of dust cycling.
- E. Rodriguez-Caballero
- , T. Stanelle
- & B. Weber
-
Research Briefing |
 Wetter and drier regions as large-scale tree restoration shifts water fluxes
Wetter and drier regions as large-scale tree restoration shifts water fluxes
Tree restoration is a popular approach to mitigating climate change, but its hydrological impacts are often overlooked. Tree restoration increases evaporation, as well as increasing downwind precipitation due to enhanced moisture recycling. Our study shows that these combined effects can affect regions’ wetness or dryness, streamflow and water availability.
-
Article
| Open Access Shifts in regional water availability due to global tree restoration
Shifts in regional water availability due to global tree restoration
Global tree restoration could cause substantial and regionally variable changes in water availability, according to an ensemble of Budyko models and moisture recycling data.
- Anne J. Hoek van Dijke
- , Martin Herold
- & Adriaan J. Teuling
-
Article |
 Increasing atmospheric helium due to fossil fuel exploitation
Increasing atmospheric helium due to fossil fuel exploitation
Mass spectrometry measurements show that the concentration of helium in the atmosphere has risen over the past five decades due to fossil fuel emissions.
- Benjamin Birner
- , Jeffrey Severinghaus
- & Ralph F. Keeling
-
Article |
 Contrasting effects of aridity and seasonality on global salinization
Contrasting effects of aridity and seasonality on global salinization
Aridity and rainfall seasonality have contrasting effects on global salinization, according to an analysis combining soil observations and ecohydrological modelling.
- Saverio Perri
- , Annalisa Molini
- & Amilcare Porporato
-
Article |
 Winter particulate pollution severity in North China driven by atmospheric teleconnections
Winter particulate pollution severity in North China driven by atmospheric teleconnections
Recurring climatic patterns can be used to predict severe winter particulate air pollution over North China, according to an analysis of wintertime particulate concentrations and atmospheric circulation.
- Jiandong Li
- , Xin Hao
- & Jia Zhu
-
Article |
 Secondary organic aerosol formed by condensing anthropogenic vapours over China’s megacities
Secondary organic aerosol formed by condensing anthropogenic vapours over China’s megacities
The formation of secondary organic aerosol in Chinese megacities is dominated by the condensation of anthropogenic organic vapours, according to measurements across three urbanized regions.
- Wei Nie
- , Chao Yan
- & Aijun Ding
-
Article
| Open Access Equal abundance of summertime natural and wintertime anthropogenic Arctic organic aerosols
Equal abundance of summertime natural and wintertime anthropogenic Arctic organic aerosols
Organic aerosols in the Arctic are predominantly fuelled by anthropogenic sources in winter and natural sources in summer, according to observations from eight sites across the Arctic
- Vaios Moschos
- , Katja Dzepina
- & Imad El Haddad
-
Article |
 Decline in bulk deposition of air pollutants in China lags behind reductions in emissions
Decline in bulk deposition of air pollutants in China lags behind reductions in emissions
Deposition of sulfate and nitrate in China has declined more slowly than emissions of their precursors, sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides, according to a combination of emissions inventory and air quality and statistical modelling.
- Yu Zhao
- , Mengxiao Xi
- & Lei Zhang
-
Perspective |
 Managing nitrogen legacies to accelerate water quality improvement
Managing nitrogen legacies to accelerate water quality improvement
Agricultural nitrogen legacies are delaying improvements to water quality. Comprehensive management strategies that address legacy issues are needed to ensure better environmental outcomes.
- Nandita B. Basu
- , Kimberly J. Van Meter
- & Søren Bøye Olsen
-
Comment |
 Machine learning in Earth and environmental science requires education and research policy reforms
Machine learning in Earth and environmental science requires education and research policy reforms
Leveraging advances in artificial intelligence could revolutionize the Earth and environmental sciences. We must ensure that our research funding and training choices give the next generation of geoscientists the capacity to realize this potential.
- Sean W. Fleming
- , James R. Watson
- & Velimir C. Vesselinov
-
Article |
 Marsh resilience to sea-level rise reduced by storm-surge barriers in the Venice Lagoon
Marsh resilience to sea-level rise reduced by storm-surge barriers in the Venice Lagoon
Sediment supply to the Venice Lagoon is substantially reduced by flood barriers inhibiting storm-related sediment reworking and transport, according to observations through multiple storm events before and after barrier installation.
- Davide Tognin
- , Andrea D’Alpaos
- & Luca Carniello
-
Article
| Open Access Fluvial organic carbon cycling regulated by sediment transit time and mineral protection
Fluvial organic carbon cycling regulated by sediment transit time and mineral protection
Particulate organic carbon oxidation in rivers is regulated by both transit time and mineral protection, according to modelling and analysis of organic matter transported nearly 1,300 km through a lowland river.
- Marisa Repasch
- , Joel S. Scheingross
- & Dirk Sachse
-
Comment |
 Minimizing trade-offs for sustainable irrigation
Minimizing trade-offs for sustainable irrigation
A more comprehensive understanding of the role of irrigation in coupled natural–human systems is needed to minimize the negative consequences for climate, ecosystems and public health.
- Sonali Shukla McDermid
- , Rezaul Mahmood
- & Zoe Lieberman
-
Article |
 Temperature control on CO2 emissions from the weathering of sedimentary rocks
Temperature control on CO2 emissions from the weathering of sedimentary rocks
The release of carbon dioxide during oxidative weathering of sedimentary rocks acts as a positive feedback to warming, according to 2.5 years of CO2 flux measurements from the Draix-Bléone Critical Zone Observatory, France.
- Guillaume Soulet
- , Robert G. Hilton
- & Caroline Le Bouteiller
-
Article |
 Muted multidecadal climate variability in central Europe during cold stadial periods
Muted multidecadal climate variability in central Europe during cold stadial periods
Central European multidecadal climate variability was subdued during cold stadials through the last glacial cycle due to atmospheric and oceanic circulation shifts, according to almost annual-resolution terrestrial climate proxy records from varved maar lakes in Germany.
- Frank Sirocko
- , Alfredo Martínez-García
- & Gerald H. Haug
-
Editorial |
Provenance matters
An update to our policy on reporting requirements for geological and palaeontological materials aims to tackle ethical issues surrounding the collection, traceability and archiving of field samples.
-
Article |
 Eocene to Oligocene terrestrial Southern Hemisphere cooling caused by declining pCO2
Eocene to Oligocene terrestrial Southern Hemisphere cooling caused by declining pCO2
Terrestrial Southern Hemisphere cooling through the Eocene–Oligocene transition points to decreasing atmospheric CO2 dominantly driving global change, according to biomarker records from southeast Australian coals and palaeoclimate modelling.
- Vittoria Lauretano
- , Alan T. Kennedy-Asser
- & B. David A. Naafs
-
Review Article |
 Past abrupt changes, tipping points and cascading impacts in the Earth system
Past abrupt changes, tipping points and cascading impacts in the Earth system
A synthesis of intervals of rapid climatic change evident in the geological record reveals some of the Earth system processes and tipping points that could lead to similar events in the future.
- Victor Brovkin
- , Edward Brook
- & Zicheng Yu
-
Article |
 Drivers of PM2.5 air pollution deaths in China 2002–2017
Drivers of PM2.5 air pollution deaths in China 2002–2017
Emission controls avoided some 870,000 deaths in China between 2002 and 2017 but further air quality improvements need energy-climate policies and changed economic structure, according to index decomposition analysis and chemical transport models.
- Guannan Geng
- , Yixuan Zheng
- & Steven J. Davis
-
Article |
 Rivers as the largest source of mercury to coastal oceans worldwide
Rivers as the largest source of mercury to coastal oceans worldwide
Rivers transport about 1,000 Mg mercury annually to coastal oceans, which is threefold greater than the amount delivered by atmospheric deposition, according to a global analysis of mercury measurements in rivers.
- Maodian Liu
- , Qianru Zhang
- & Peter A. Raymond
-
Comment |
 Manage fire regimes, not fires
Manage fire regimes, not fires
Globally, land- and fire-management policies have counterproductively caused cascading ecosystem changes that exacerbate, rather than mitigate, wildfires. Given rapidly changing climate and land-use conditions that amplify wildfire risk, a policy shift to adaptive management of fire regimes is urgently needed.
- Mark A. Cochrane
- & David M. J. S. Bowman
-
News & Views |
 Planting trees to combat drought
Planting trees to combat drought
Reforestation of agricultural lands in Europe increases local and downwind summer rainfall, according to a new analysis of rain-gauge measurements from across the continent. Realistic levels of tree planting could therefore mitigate future droughts expected with climate change.
- Jessica C. A. Baker
-
Matters Arising |
 No support for carbon storage of >1,000 GtC in northern peatlands
No support for carbon storage of >1,000 GtC in northern peatlands
- Zicheng Yu
- , Fortunat Joos
- & Jochen Schmitt
-
Article
| Open Access Large subglacial source of mercury from the southwestern margin of the Greenland Ice Sheet
Large subglacial source of mercury from the southwestern margin of the Greenland Ice Sheet
Meltwaters from the southwestern margin of the Greenland Ice Sheet contain exceptionally high concentrations of mercury, exporting up to more than 200 kmol of dissolved mercury every year, suggest mercury measurements from three glacial catchments.
- Jon R. Hawkings
- , Benjamin S. Linhoff
- & Robert G. M. Spencer
-
Article |
 Open ocean and coastal new particle formation from sulfuric acid and amines around the Antarctic Peninsula
Open ocean and coastal new particle formation from sulfuric acid and amines around the Antarctic Peninsula
New particles can form rapidly in Antarctica through the reactions of sulfuric acid and amines, suggest ship and station measurements around the Antarctic Peninsula.
- James Brean
- , Manuel Dall’Osto
- & Roy M. Harrison
-
Comment |
 A UK perspective on tackling the geoscience racial diversity crisis in the Global North
A UK perspective on tackling the geoscience racial diversity crisis in the Global North
Geoscientists will play key roles in the grand challenges of the twenty-first century, but this requires our field to address its past when it comes to diversity and inclusion. Considering the bleak picture of racial diversity in the UK, we put forward steps institutions can take to break down barriers and make the geosciences equitable.
- Natasha Dowey
- , Jenni Barclay
- & Rebecca Williams
-
Article |
 Control of particulate nitrate air pollution in China
Control of particulate nitrate air pollution in China
Reduction of ammonia emissions may be effective in reducing the nitrate component of fine particulate matter air pollution across the North China Plain, according to the simulation of nitrate trends using the GEOS-Chem atmospheric chemistry model.
- Shixian Zhai
- , Daniel J. Jacob
- & Hong Liao
-
Article |
 Microbial methylation potential of mercury sulfide particles dictated by surface structure
Microbial methylation potential of mercury sulfide particles dictated by surface structure
The environmental behaviour of mercury and other toxic soft elements is in part dictated by the surface structure of nanoparticulates, according to a combination of microcosm bioassays and theoretical calculations.
- Li Tian
- , Wenyu Guan
- & Tong Zhang
-
Matters Arising |
 Reply to: Climate did not drive Common Era Maldivian sea-level lowstands
Reply to: Climate did not drive Common Era Maldivian sea-level lowstands
- Paul S. Kench
- , Roger F. McLean
- & Keven Roy
-
News & Views |
 A world view of pesticides
A world view of pesticides
Pesticide pollution is a widespread issue. A global risk assessment of 92 active pesticide ingredients suggests 2.5 billion hectares of agricultural land are at risk of pollution by more than one active ingredient.
- Rupert Lloyd Hough
-
Article |
 Risk of pesticide pollution at the global scale
Risk of pesticide pollution at the global scale
Pesticide pollution is a risk for two-thirds of agriculture land. A third of high-risk areas are in high-biodiversity regions and a fifth are in low- and lower-middle-income areas, according to environmental modelling combined with pesticide application data.
- Fiona H. M. Tang
- , Manfred Lenzen
- & Federico Maggi
-
Article |
 Drivers of river reactivation in North Africa during the last glacial cycle
Drivers of river reactivation in North Africa during the last glacial cycle
The presence of large rivers in North Africa critical for Quaternary human migrations were controlled by a combination of orbital forcing and Mediterranean storminess, according to terrestrial proxy records from a marine core off Libya integrated with paleoclimate modelling.
- Cécile L. Blanchet
- , Anne H. Osborne
- & Martin Frank
-
News & Views |
 Clearing smog’s particulate problem
Clearing smog’s particulate problem
Chloride-rich particulate matter has been identified as a major contributor to air-quality deterioration in cities across India. Identification and reduction of chloride emissions could therefore improve visibility and human health across the region.
- Gufran Beig
-
Article |
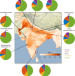 Enhanced aerosol particle growth sustained by high continental chlorine emission in India
Enhanced aerosol particle growth sustained by high continental chlorine emission in India
Half of the reduced visibility due to haze formation in cities in India is attributed to local emission of gas-phase hydrochloric acid from waste-burning and industry, according to measurements of particulate matter and thermodynamic modelling.
- Sachin S. Gunthe
- , Pengfei Liu
- & Hugh Coe
-
Article |
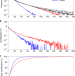 Disproportionate control on aerosol burden by light rain
Disproportionate control on aerosol burden by light rain
Light rain plays a disproportionate role in aerosol wet removal, according to improved simulations on rain intensity and frequency in global climate models.
- Yong Wang
- , Wenwen Xia
- & Guang J. Zhang

 Phased variation of soil respiration in tropical forests in response to nitrogen deposition
Phased variation of soil respiration in tropical forests in response to nitrogen deposition