Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access The impact of anthropogenic inputs on lithium content in river and tap water
The impact of anthropogenic inputs on lithium content in river and tap water
Lithium use in electronics has increased dramatically, but the environmental impacts are poorly understood. Here the authors show lithium in river and tap water in South Korea is coincident with population density, and that waste water treatment is ineffective at scrubbing this potential toxin.
- Hye-Bin Choi
- , Jong-Sik Ryu
- & Nathalie Vigier
-
Article
| Open Access Contribution of oxic methane production to surface methane emission in lakes and its global importance
Contribution of oxic methane production to surface methane emission in lakes and its global importance
Anoxic lake sediments are thought to be the major source of the high amount of methane emitted from freshwaters. Here Günthel and colleagues find unexpected quantities of this greenhouse gas are produced in lake surfaces, indicating an overlooked global importance from oxygenated sources.
- Marco Günthel
- , Daphne Donis
- & Kam W. Tang
-
Article
| Open Access A psychophysical measurement on subjective well-being and air pollution
A psychophysical measurement on subjective well-being and air pollution
Air pollution can affect people’s emotional status and well-being. Here, the authors simulate fixed-scene images to show that under the atmospheric conditions in Beijing, negative emotions occur when air quality index of PM2.5 increases to approximately 150.
- Yuan Li
- , Dabo Guan
- & Shu Tao
-
Article
| Open Access The role of cyclone activity in snow accumulation on Arctic sea ice
The role of cyclone activity in snow accumulation on Arctic sea ice
Snow cover can affect the Arctic sea-ice system in different ways. Here authors study the relationship between cyclone activity and the seasonal build-up of snow on Arctic sea ice at a multi-decadal and basin-wide scale and find that 44% of the variability in monthly snow accumulation was controlled by cyclone snowfall and 29% by sea-ice freeze-up with strong spatio-temporal differences.
- M. A. Webster
- , C. Parker
- & R. Kwok
-
Article
| Open Access Environmental co-benefits and adverse side-effects of alternative power sector decarbonization strategies
Environmental co-benefits and adverse side-effects of alternative power sector decarbonization strategies
There lacks a consistent and holistic evaluation of co-benefits of different mitigation pathways in studies on Integrated Assessment Models. Here the authors quantify environmental co-benefits and adverse side-effects of a portfolio of alternative power sector decarbonisation pathways and show that the scale of co-benefits as well as profiles of adverse side-effects depend strongly on technology choice.
- Gunnar Luderer
- , Michaja Pehl
- & Edgar G. Hertwich
-
Article
| Open Access Rice life cycle-based global mercury biotransport and human methylmercury exposure
Rice life cycle-based global mercury biotransport and human methylmercury exposure
Fish consumption is considered to be the only significant dietary source of MeHg. Here the authors show that rice could also be a significant global dietary source, especially in South and Southeast Asia. International rice trade and joint ingestion of fish and rice could aggravate the MeHg exposure levels in many areas.
- Maodian Liu
- , Qianru Zhang
- & Xuejun Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Regulation of priming effect by soil organic matter stability over a broad geographic scale
Regulation of priming effect by soil organic matter stability over a broad geographic scale
Global soil carbon dynamics are regulated by the modification of soil organic matter (SOM) decomposition by plant carbon input (priming effect). Here, the authors collect soil data along a 2200 km grassland transect on the Tibetan Plateau and find that SOM stability is the major control on priming effect.
- Leiyi Chen
- , Li Liu
- & Yuanhe Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Isotopic composition of oceanic dissolved black carbon reveals non-riverine source
Isotopic composition of oceanic dissolved black carbon reveals non-riverine source
Rivers are thought to be the largest source of the recalcitrant and abundant black carbon in the ocean. Here, Wagner and colleagues find distinct pools of black carbon between rivers and the open ocean, challenging the long-held assumption that marine black carbon is of terrestrial origin.
- Sasha Wagner
- , Jay Brandes
- & Aron Stubbins
-
Article
| Open Access Seasonal dynamics of stem N2O exchange follow the physiological activity of boreal trees
Seasonal dynamics of stem N2O exchange follow the physiological activity of boreal trees
Forest soil is known to be a source of the greenhouse gas N2O, but the impact of what is planted in that soil has long been overlooked. Here Machacova and colleagues quantify seasonal N2O fluxes from common boreal tree species in Finland, finding that all trees are net sources of this gas.
- Katerina Machacova
- , Elisa Vainio
- & Mari Pihlatie
-
Article
| Open Access Rice production threatened by coupled stresses of climate and soil arsenic
Rice production threatened by coupled stresses of climate and soil arsenic
Current projections on rice production do not consider the coupled stresses of impending climate change and the toxin arsenic in paddy soils. Here, the authors examined potential compounding impacts of soil arsenic and a changing climate on rice production and show that climate-induced changes in soil arsenic behaviour and plant response will lead to currently unforeseen losses in paddy rice grain productivity and quality.
- E. Marie Muehe
- , Tianmei Wang
- & Scott Fendorf
-
Article
| Open Access Carbon and health implications of trade restrictions
Carbon and health implications of trade restrictions
Carbon dioxide emissions and air pollution are often assessed on a national or regional level, but little is known about the role of trade structures. Here, a combination of models shows that trade restrictions can lead to massive reduction of gross domestic product in most countries, but also to a reduction of emissions and pollution.
- Jintai Lin
- , Mingxi Du
- & Klaus Hubacek
-
Article
| Open Access Moving from drought hazard to impact forecasts
Moving from drought hazard to impact forecasts
There still lacks a forecast system that inform end-users regarding the drought impacts, which will be however important for drought management. Here the authors assess the feasibility of forecasting drought impacts using machine-learning and confirm that models, which were built with sufficient amount of reported drought impacts in a certain sector, are able to forecast drought impacts a few months ahead.
- Samuel J. Sutanto
- , Melati van der Weert
- & Henny A. J. Van Lanen
-
Article
| Open Access Unexpected large evasion fluxes of carbon dioxide from turbulent streams draining the world’s mountains
Unexpected large evasion fluxes of carbon dioxide from turbulent streams draining the world’s mountains
Freshwater systems are important components of the carbon cycle, but the extent of their role in CO2 fluxes is poorly understood. Here Horgby and colleagues show that mountain streams are a surprisingly large source of CO2 to the atmosphere, with annual emissions that belie their spatial extent.
- Åsa Horgby
- , Pier Luigi Segatto
- & Tom J. Battin
-
Article
| Open Access Fouling-resistant biofilter of an anaerobic electrochemical membrane reactor
Fouling-resistant biofilter of an anaerobic electrochemical membrane reactor
Membrane use as a cathode is a common measure to retard fouling in anaerobic electrochemical membrane bioreactors, but this cannot avoid the fouling growth. Here the authors report on using membranes as anodes to create equilibrium between fouling and oxidation to maintain stable operation.
- Qilin Yu
- & Yaobin Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Lake sedimentary biogenic silica from diatoms constitutes a significant global sink for aluminium
Lake sedimentary biogenic silica from diatoms constitutes a significant global sink for aluminium
Diatoms drive biogeochemical cycling of aluminum by incorporating this element into their shells, but this process has not been quantified in freshwater systems. Here the authors quantify diatom-mediated aluminum fluxes in lakes and determine that they rival the aluminum sink in the global ocean.
- Dong Liu
- , Peng Yuan
- & Wenxiao Fan
-
Article
| Open Access The greenhouse gas impacts of converting food production in England and Wales to organic methods
The greenhouse gas impacts of converting food production in England and Wales to organic methods
The greenhouse gas (GHG) mitigation potential of organic methods is poorly understood. Here, the authors assess the GHG impact of a 100% shift to organic food production in England and Wales and find that direct GHG emissions are reduced with organic farming, but when increased land use abroad to allow for production shortfalls is factored in, GHG emissions are elevated well-above the baseline.
- Laurence G. Smith
- , Guy J. D. Kirk
- & Adrian G. Williams
-
Review Article
| Open Access The importance of Antarctic krill in biogeochemical cycles
The importance of Antarctic krill in biogeochemical cycles
Swarms of crustaceans called krill dominate Antarctic ecosystems, yet their influence on biogeochemical cycles remains a mystery. Here Cavan and colleagues review the role of krill in the Southern Ocean, and the impact of the krill fishery on ocean fertilisation and the carbon sink.
- E. L. Cavan
- , A. Belcher
- & P. W. Boyd
-
Matters Arising
| Open Access Reply to ‘Wiggle-match radiocarbon dating of the Taupo eruption’
Reply to ‘Wiggle-match radiocarbon dating of the Taupo eruption’
- Richard N. Holdaway
- , Brendan Duffy
- & Ben Kennedy
-
Article
| Open Access Global ocean methane emissions dominated by shallow coastal waters
Global ocean methane emissions dominated by shallow coastal waters
The ocean emits the greenhouse gas methane, but its vastness renders estimations challenging. Here the authors use machine learning to map global ocean methane fluxes, finding a disproportionate contribution from shallow coastal waters, and a link between primary production and methane cycling.
- Thomas Weber
- , Nicola A. Wiseman
- & Annette Kock
-
Perspective
| Open Access Engaging with research impact assessment for an environmental science case study
Engaging with research impact assessment for an environmental science case study
Existing approaches to research impact assessment fail to include a range of soft impacts. The authors present a 3-part impact mapping approach and apply it to an environmental initiative. They highlight that support for realising research impact is vital, and call on researchers to be open to new ideas and avenues for creating impact from their work.
- Kirstie A. Fryirs
- , Gary J. Brierley
- & Thom Dixon
-
Article
| Open Access Australian vegetated coastal ecosystems as global hotspots for climate change mitigation
Australian vegetated coastal ecosystems as global hotspots for climate change mitigation
Policies aiming to preserve vegetated coastal ecosystems (VCE) to mitigate greenhouse gas emissions require national assessments of blue carbon resources. Here the authors assessed organic carbon storage in VCE across Australian and the potential annual CO2 emission benefits of VCE conservation and find that Australia contributes substantially the carbon stored in VCE globally.
- Oscar Serrano
- , Catherine E. Lovelock
- & Carlos M. Duarte
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular identification of organic vapors driving atmospheric nanoparticle growth
Molecular identification of organic vapors driving atmospheric nanoparticle growth
Condensation of organic vapors is a main factor controlling the growth of atmospheric particles. Here the authors identify a distribution of organic vapors in a forested environment able to explain nanoparticle growth at the same location, contributing to understanding aerosol climate effects.
- Claudia Mohr
- , Joel A. Thornton
- & Taina Yli-Juuti
-
Article
| Open Access Inequality of household consumption and air pollution-related deaths in China
Inequality of household consumption and air pollution-related deaths in China
Considering air pollution-induced health risks from a consumption perspective is important. Here the authors evaluated the premature deaths resulting from household consumption across 30 Chinese provinces and find that rural households can cause a similar number of pollution-induced deaths as urban households despite a larger and wealthier urban population, due to the combustion of solid fuel.
- Hongyan Zhao
- , Guannan Geng
- & Kebin He
-
Article
| Open Access The role of highly oxygenated organic molecules in the Boreal aerosol-cloud-climate system
The role of highly oxygenated organic molecules in the Boreal aerosol-cloud-climate system
Forests emit compounds into the atmosphere that are oxidized into highly oxygenated molecules that serve as precursors for cloud condensation nuclei–a process that impacts the climate, but is poorly represented in models. Here the authors create a new model that accurately depicts highly oxygenated molecule and climate dynamics over Boreal forests.
- Pontus Roldin
- , Mikael Ehn
- & Michael Boy
-
Article
| Open Access Reducing greenhouse gas emissions of Amazon hydropower with strategic dam planning
Reducing greenhouse gas emissions of Amazon hydropower with strategic dam planning
Some dams produce large amounts of GHGs and it is important to see whether future dams will satisfy sustainable energy goals. Here the authors estimate the range of GHG emission intensities expected for 351 proposed and 158 existing Amazon dams and find that existing Amazon hydropower reservoirs collectively emit 14 Tg CO2eq per year, and that if all proposed Amazon dams are built, annual emissions would increase 5-fold.
- Rafael M. Almeida
- , Qinru Shi
- & Alexander S. Flecker
-
Article
| Open Access Stress-resistant corals may not acclimatize to ocean warming but maintain heat tolerance under cooler temperatures
Stress-resistant corals may not acclimatize to ocean warming but maintain heat tolerance under cooler temperatures
Coral populations from thermally extreme conditions may help restore reefs degraded by bleaching. Here, the authors show that these corals can maintain their heat tolerance despite acclimation to colder temperatures but have a limited capacity to acclimatize to ocean warming.
- Verena Schoepf
- , Steven A. Carrion
- & Malcolm T. McCulloch
-
Article
| Open Access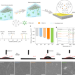 Metal-coordinated sub-10 nm membranes for water purification
Metal-coordinated sub-10 nm membranes for water purification
Ultrathin membranes have demonstrated great promise for water purification technologies owing to their high permeance. Here the authors fabricate sub-10 nm, defect-free, robust membranes for dye remediation from water through the coordination-driven assembly of metal-organophosphates.
- Xinda You
- , Hong Wu
- & Zhongyi Jiang
-
Comment
| Open AccessTowards Urbanome the genome of the city to enhance the form and function of future cities
The health of the city depends on how well all the elements of this system are interconnected and operating in harmony. Here the authors introduced the concept of urbanome which is analogous to the human genome that can be used to characterise the form and functioning of cities.
- Lidia Morawska
- , Wendy Miller
- & Marie Thynell
-
Article
| Open Access Microscale pH variations during drying of soils and desert biocrusts affect HONO and NH3 emissions
Microscale pH variations during drying of soils and desert biocrusts affect HONO and NH3 emissions
The mechanisms that determine the composition of nitrogen gas emissions from soil remain unclear. A biocrust mechanistic model was developed to resolve puzzling dynamics of nitrous acid and ammonia emissions from drying soil pointing to previously unknown microscale pH zonation in thinning water films that affect soil biogeochemical fluxes.
- Minsu Kim
- & Dani Or
-
Article
| Open Access Mekong delta much lower than previously assumed in sea-level rise impact assessments
Mekong delta much lower than previously assumed in sea-level rise impact assessments
Assessments of sea level rise risks depend on elevation data. Here, the authors present a new dataset on the Mekong Delta which shows it to have a much lower elevation (0.82 m above sea level) than previously thought – underlying principles may also imply major elevation uncertainties in other deltas.
- P. S. J. Minderhoud
- , L. Coumou
- & E. Stouthamer
-
Comment
| Open Access A short comment on statistical versus mathematical modelling
A short comment on statistical versus mathematical modelling
While the crisis of statistics has made it to the headlines, that of mathematical modelling hasn’t. Something can be learned comparing the two, and looking at other instances of production of numbers.Sociology of quantification and post-normal science can help.
- Andrea Saltelli
-
Article
| Open Access Significant contribution of metastable particulate organic matter to natural formation of silver nanoparticles in soils
Significant contribution of metastable particulate organic matter to natural formation of silver nanoparticles in soils
Silver nanoparticles are known environmental contaminants, however it is unclear whether they arise in soils through natural processes, anthropogenic processes, or both. Here Huang and colleagues offer fresh insight into the natural formation of these contaminants by soil particulate organic matter exposed to solar irradiation.
- Ying-Nan Huang
- , Ting-Ting Qian
- & Dong-Mei Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access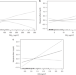 Air pollution exposure associates with increased risk of neonatal jaundice
Air pollution exposure associates with increased risk of neonatal jaundice
Air pollution has become a major health risk in China. Here Zhang et al. report that maternal and neonatal exposure to particulate matter increases the risk of neonatal jaundice based on the study of 25,782 newborns born in China between 2014 and 2017.
- Liqiang Zhang
- , Weiwei Liu
- & Yanhong Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Rainfall drives variation in rates of change in intrinsic water use efficiency of tropical forests
Rainfall drives variation in rates of change in intrinsic water use efficiency of tropical forests
How the water use efficiency of trees changes with atmospheric CO2 variations has mostly been studied on short time scales. Here, a newly compiled data set covering 1915 to 1995 shows how rates of change in water use efficiency vary with location and rainfall over the global tropics on a decadal scale.
- Mark A. Adams
- , Thomas N. Buckley
- & Tarryn L. Turnbull
-
Article
| Open Access Revisiting enteric methane emissions from domestic ruminants and their δ13CCH4 source signature
Revisiting enteric methane emissions from domestic ruminants and their δ13CCH4 source signature
Global average, geographical distribution and temporal variations of the 13C isotopic signature of enteric fermentation emissions are not well understood. Here the authors established a global dataset and show a larger emission increase between the two periods (2002–2006 and 2008–2012) than previous studies.
- Jinfeng Chang
- , Shushi Peng
- & Philippe Bousquet
-
Article
| Open Access Impacts of air pollutants from rural Chinese households under the rapid residential energy transition
Impacts of air pollutants from rural Chinese households under the rapid residential energy transition
Residential solid fuel use constitutes a large amount of air pollution but has been gradually replaced by other cleaner energy during the past three decades. Here the authors investigated the contribution of rural residential sector to ambient PM2.5 pollution and the resulting climate forcing and health impacts, and find that the remaining large quantities of solid fuels used in rural households are still a major contributor to ambient air pollution despite of decrease in its pollutant emissions and relative contribution to PM2.5 due to the clean energy transition.
- Guofeng Shen
- , Muye Ru
- & Shu Tao
-
Article
| Open Access The role of energy storage in deep decarbonization of electricity production
The role of energy storage in deep decarbonization of electricity production
Existing studies on the economic feasibility of energy storage are system-specific without considering the decarbonisation of electricity production or impacts of GHG taxes. Here the authors applied an optimization model to investigate the economic viability of nice selected energy storage technologies in California and found that renewable curtailment and GHG reductions highly depend on capital costs of energy storage.
- Maryam Arbabzadeh
- , Ramteen Sioshansi
- & Gregory A. Keoleian
-
Article
| Open Access The cascade of global trade to large climate forcing over the Tibetan Plateau glaciers
The cascade of global trade to large climate forcing over the Tibetan Plateau glaciers
To trace the sources of Black Carbon being transported into the Tibetan Plateau is crucial for guiding an effective mitigation strategy. Here the authors utilized the adjoint of the Goddard Earth Observing System-Chem model and find that international trade aggravates the BC pollution over the HTP glacier regions and may cause significant climate change.
- Kan Yi
- , Jing Meng
- & Shu Tao
-
Article
| Open Access Reduced marine phytoplankton sulphur emissions in the Southern Ocean during the past seven glacials
Reduced marine phytoplankton sulphur emissions in the Southern Ocean during the past seven glacials
Ice core derived marine biogenic sulphate does not agree with marine sediment records. Here based on new ice core records spanning the past 720,000 years obtained from Dome Fuji the authors propose that dust contributed a higher percentage of sulphate aerosols than previously thought.
- K. Goto-Azuma
- , M. Hirabayashi
- & Y. Fujii
-
Article
| Open Access Microbial spatial footprint as a driver of soil carbon stabilization
Microbial spatial footprint as a driver of soil carbon stabilization
The processes driving soil carbon accretion remain to be poorly understood. Here the authors combined X-ray micro-tomography and zymography to demonstrate that plant-stimulated soil pore formation is a major, hitherto unrecognized, determinant of whether new C inputs are stored or lost to the atmosphere.
- A. N. Kravchenko
- , A. K. Guber
- & Y. Kuzyakov
-
Article
| Open Access Future nitrogen availability and its effect on carbon sequestration in Northern Eurasia
Future nitrogen availability and its effect on carbon sequestration in Northern Eurasia
The impact of nitrogen availability on carbon sequestration in terrestrial ecosystems under climate change is understudied. Here the authors project that increases in N availability over the 21st century associated with warmer soils and the legacy of past N fertiliser use on abandoned croplands will be the primary drivers of a 21st century net carbon sink in Northern Eurasia.
- David W. Kicklighter
- , Jerry M. Melillo
- & Qianlai Zhuang
-
Article
| Open Access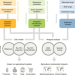 Global impacts of future cropland expansion and intensification on agricultural markets and biodiversity
Global impacts of future cropland expansion and intensification on agricultural markets and biodiversity
The increase in needs for agricultural commodities is projected to outpace the growth of farmland production globally, leading to high pressure on farming systems in the next decades. Here, the authors investigate the future impact of cropland expansion and intensification on agricultural markets and biodiversity, and suggest the need for balancing agricultural production with conservation goals.
- Florian Zabel
- , Ruth Delzeit
- & Tomáš Václavík
-
Article
| Open Access Improving risk assessments in conservation ecology
Improving risk assessments in conservation ecology
Risk estimates are important measures for the study and practice of conservation ecology. Here, the authors show that such estimates can be substantially biased, and propose an approach to improve accuracy.
- Kotaro Ono
- , Øystein Langangen
- & Nils Chr. Stenseth
-
Article
| Open Access Petroleum exploration increases methane emissions from northern peatlands
Petroleum exploration increases methane emissions from northern peatlands
Human disturbance of peatland environments due to geological exploration activities can significantly alter peatland greenhouse gas exchange. Here, the authors study peatland disturbance in Alberta, Canada, and estimate that induced methane emissions are approximately 4.4–5.1 kt higher per year than in undisturbed conditions.
- Maria Strack
- , Shari Hayne
- & Bin Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Distribution and dynamics of Greenland subglacial lakes
Distribution and dynamics of Greenland subglacial lakes
Subglacial lakes can influence basal hydrology and ice flow in Antarctica, but are poorly constrained in Greenland. Here the authors provide the first ice sheet-wide inventory of subglacial lakes beneath GrIS, including 54 uncharted lakes.
- J. S. Bowling
- , S. J. Livingstone
- & W. Chu
-
Article
| Open Access A global multi-hazard risk analysis of road and railway infrastructure assets
A global multi-hazard risk analysis of road and railway infrastructure assets
Spatial distribution has been rarely studied in global disaster risk models. Here the authors address damaged networked infrastructure at the asset level for a wider range of hazards and reveal a global Expected Annual Damages ranging from $3.1 to 22 billion with a particular vulnerability of transport infrastructure in Small Island Developing States.
- E. E. Koks
- , J. Rozenberg
- & S. Hallegatte
-
Perspective
| Open Access Inferring causation from time series in Earth system sciences
Inferring causation from time series in Earth system sciences
Questions of causality are ubiquitous in Earth system sciences and beyond, yet correlation techniques still prevail. This Perspective provides an overview of causal inference methods, identifies promising applications and methodological challenges, and initiates a causality benchmark platform.
- Jakob Runge
- , Sebastian Bathiany
- & Jakob Zscheischler
-
Article
| Open Access Impact hotspots of reduced nutrient discharge shift across the globe with population and dietary changes
Impact hotspots of reduced nutrient discharge shift across the globe with population and dietary changes
The environmental impacts of increasing wastewater management are poorly understood. Here, the authors simulate impacts for 173 countries between 1990 and 2050; despite the development of wastewater infrastructure, they identify hotspots of unexpected detrimental effects which are shifting from Asia to Africa.
- Xu Wang
- , Glen Daigger
- & David Butler
-
Article
| Open Access Tailoring sodium intercalation in graphite for high energy and power sodium ion batteries
Tailoring sodium intercalation in graphite for high energy and power sodium ion batteries
Graphite is a promising anode material for sodium-ion batteries but suffers from the high co-intercalation potential. Here, the authors examine the factors influencing this potential and tailor the stability of graphite intercalation compound, realizing high energy and power densities.
- Zheng-Long Xu
- , Gabin Yoon
- & Kisuk Kang

 Global urban expansion offsets climate-driven increases in terrestrial net primary productivity
Global urban expansion offsets climate-driven increases in terrestrial net primary productivity