Featured
-
-
News & Views |
 A silicon memory of subduction
A silicon memory of subduction
Subduction processes may have operated very early in Earth’s history according to the heavy silicon isotope compositions of Archaean igneous rocks. The silicon that precipitated out of the Archaean oceans as chert was subducted and melted to yield seawater-like heavy isotope signatures in early granitic rocks.
- Franck Poitrasson
-
Article |
 Global fire emissions buffered by the production of pyrogenic carbon
Global fire emissions buffered by the production of pyrogenic carbon
Pyrogenic carbon produced from vegetation fires could be a globally important carbon sink, which amounts to 12% of the carbon emitted from wildfires annually, according to a global fire emission database that incorporates the estimate of pyrogenic carbon.
- Matthew W. Jones
- , Cristina Santín
- & Stefan H. Doerr
-
Editorial |
Cleaner air for China
China’s rigorous air-pollution control has greatly reduced the levels of fine particles in the atmosphere. Further progress for air quality more broadly will rely on fully accounting for complex chemical reactions between pollutants.
-
News & Views |
 Ancient rust
Ancient rust
Confidence that banded iron formations record oxic conditions during deposition is established, as a model demonstrates that they are formed of primary iron oxides rather than secondarily altered silicate minerals.
- Eva E. Stüeken
-
News & Views |
 China’s nitrogen management
China’s nitrogen management
Nitrogen deposition in China has stabilized over the past decade, thanks to efficient regulation of fertilizer use, suggests an analysis of wet and dry deposition.
- Maria Kanakidou
-
Article |
 Stabilization of atmospheric nitrogen deposition in China over the past decade
Stabilization of atmospheric nitrogen deposition in China over the past decade
Nitrogen deposition in China has been almost constant over the past decade, as decreasing wet deposition has balanced increasing dry deposition, according to analyses of extensive datasets on wet and dry nitrogen depositions in China.
- Guirui Yu
- , Yanlong Jia
- & Keith Goulding
-
Article |
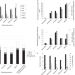 Atmospheric transport and deposition of microplastics in a remote mountain catchment
Atmospheric transport and deposition of microplastics in a remote mountain catchment
Microplastics can reach and affect regions far from where they are released because of atmospheric transport, suggest analyses of atmospheric deposition in a remote, pristine mountain catchment in France.
- Steve Allen
- , Deonie Allen
- & Didier Galop
-
Article |
 Glacially sourced dust as a potentially significant source of ice nucleating particles
Glacially sourced dust as a potentially significant source of ice nucleating particles
Dusts from glaciers may contribute significantly to ice nucleation in Arctic low-level clouds, according to analyses of glacial outwash sediments in Svalbard.
- Yutaka Tobo
- , Kouji Adachi
- & Makoto Koike
-
Article |
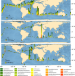 Biodegradation as an important sink of aromatic hydrocarbons in the oceans
Biodegradation as an important sink of aromatic hydrocarbons in the oceans
Microbial degradation is a key process for removing aromatic hydrocarbons from the oceans, according to measurements in plankton and seawater with 64 types of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and their microbial degradation genes in four ocean basins.
- Belén González-Gaya
- , Alicia Martínez-Varela
- & Jordi Dachs
-
News & Views |
 Anthropogenic chlorine under watch
Anthropogenic chlorine under watch
Atmospheric levels of chloroform, an ozone-depleting substance not part of the Montreal Protocol, have risen. The increase may be attributable to industrial emissions in Eastern China.
- Susann Tegtmeier
-
Article |
 Rapid increase in ozone-depleting chloroform emissions from China
Rapid increase in ozone-depleting chloroform emissions from China
Atmospheric levels of chloroform increased after 2010, as a result of emissions in eastern China, according to analyses of measurements and inverse modelling.
- Xuekun Fang
- , Sunyoung Park
- & Ronald G. Prinn
-
Perspective |
 CO2 evasion along streams driven by groundwater inputs and geomorphic controls
CO2 evasion along streams driven by groundwater inputs and geomorphic controls
Groundwater-derived CO2 inputs and emissions along streams are highly variable in both space and time, according to measurements of dissolved CO2 from two headwater catchments.
- Clément Duvert
- , David E. Butman
- & Lindsay B. Hutley
-
Article |
 Concomitant variability in high-latitude aerosols, water isotopes and the hydrologic cycle
Concomitant variability in high-latitude aerosols, water isotopes and the hydrologic cycle
On timescales of centuries and longer, aerosol concentrations in Antarctic ice are controlled by changes in the nature of mid- and high-latitude precipitation, according to analyses of palaeoclimate data.
- Bradley R. Markle
- , Eric J. Steig
- & Joseph R. McConnell
-
Article |
 Riverine evidence for isotopic mass balance in the Earth’s early sulfur cycle
Riverine evidence for isotopic mass balance in the Earth’s early sulfur cycle
The isotopic composition of sulfur minerals formed during the Archaean can be reconstructed from dissolved sulfur in rivers draining cratons. Analyses from Canada suggest that the Archaean sulfur cycle was in isotopic mass balance.
- Mark A. Torres
- , Guillaume Paris
- & Woodward W. Fischer
-
News & Views |
 New light on black carbon
New light on black carbon
Much of the carbon in rivers originates from wildfires and is ultimately buried in the oceanic carbon sink, suggest measurements from 18 rivers globally. Rivers transport almost a gigaton of carbon to the oceans every year.
- Lars J. Tranvik
-
Article |
 Links among warming, carbon and microbial dynamics mediated by soil mineral weathering
Links among warming, carbon and microbial dynamics mediated by soil mineral weathering
Soil weathering, rather than short-term warming, controls microbial community composition, nutrient availability and soil carbon content, according to observations from a 3-Myr-old soil chronosequence preserved in river terraces in California.
- S. Doetterl
- , A. A. Berhe
- & P. Boeckx
-
-
Editorial |
 Pervasive plastic
Pervasive plastic
Human manipulation of hydrocarbons — as fuel and raw materials for modern society — has changed our world and the indelible imprint we will leave in the rock record. Plastics alone have permeated our lives and every corner of our planet.
-
Article |
 Microbial decomposition of marine dissolved organic matter in cool oceanic crust
Microbial decomposition of marine dissolved organic matter in cool oceanic crust
Microbe-mediated oxidation may account for at least 5% of the global dissolved organic carbon loss from the deep ocean, according to carbon isotope analyses on cool crustal fluids circulating through the Mid-Atlantic Ridge.
- Sunita R. Shah Walter
- , Ulrike Jaekel
- & Peter R. Girguis
-
Article |
 A vegetation control on seasonal variations in global atmospheric mercury concentrations
A vegetation control on seasonal variations in global atmospheric mercury concentrations
Terrestrial vegetation contributes to the seasonal variation of atmospheric mercury concentrations, according to analyses of atmospheric trace gas dynamics and satellite data. The data show that the photosynthetic activity of vegetation correlates with atmospheric mercury.
- Martin Jiskra
- , Jeroen E. Sonke
- & Aurélien Dommergue
-
Article |
 Discrepancy between simulated and observed ethane and propane
levels explained by underestimated fossil emissions
Discrepancy between simulated and observed ethane and propane
levels explained by underestimated fossil emissions
Observations of ethane and propane distributions in the atmosphere are reproduced in simulations with an atmospheric chemistry transport model, if fossil emissions are a factor of two to three higher than previously assumed.
- Stig B. Dalsøren
- , Gunnar Myhre
- & Markus Wallasch
-
Article |
 Contribution of wetlands to nitrate removal at the watershed scale
Contribution of wetlands to nitrate removal at the watershed scale
Depending on their connectivity to the river network, wetlands can be much more efficient at removing nitrate in a watershed than common nitrogen mitigation strategies according to an analysis of the Minnesota River basin.
- Amy T. Hansen
- , Christine L. Dolph
- & Jacques C. Finlay
-
News & Views |
 An Archaean oxygen oasis
An Archaean oxygen oasis
The first of two stepwise increases in atmospheric oxygen occurred at the end of the Archaean eon. Analyses of sulfur and iron isotopes in pyrite reveal a near-shore environment that hosted locally oxygenated conditions in the Mesoarchaean era.
- Maya L. Gomes
-
News & Views |
 Hydrothermal stamp on the oceans
Hydrothermal stamp on the oceans
The composition of the oceans is altered by hydrothermal circulation. These chemical factories sustain microbial life, which in turn alters the chemistry of the fluids that enter the ocean. A decade of research details this complex interchange.
- Susan Q. Lang
-
News & Views |
 Tracking pollutant emissions
Tracking pollutant emissions
Progress in the post-combustion treatment of diesel vehicle exhaust has led to shifting proportions of the constituents of nitrogen oxides. Observations from 61 European cities suggest that the outlook on attaining NO2 standards is more optimistic than expected.
- Drew R. Gentner
- & Fulizi Xiong
-
Article |
 Lower vehicular primary emissions of NO2 in Europe than assumed in policy projections
Lower vehicular primary emissions of NO2 in Europe than assumed in policy projections
The fraction of NO2 in NO x emitted from European road transport is up to a factor of two smaller than used in policy projections, suggests an analysis of 130 million roadside observations. Roadside air quality standards may thus be obtained faster.
- Stuart K. Grange
- , Alastair C. Lewis
- & David C. Carslaw
-
Article |
 Comprehensive characterization of atmospheric organic carbon at a forested site
Comprehensive characterization of atmospheric organic carbon at a forested site
Atmospheric organic compounds are central to key chemical processes that influence air quality. Concurrent measurements of a wide range of these compounds, including previously unmeasured ones, provide closure on OH reactivity.
- James F. Hunter
- , Douglas A. Day
- & Jesse H. Kroll
-
News & Views |
 Enriched carbon source detected
Enriched carbon source detected
Estimates of carbon in the deep mantle vary by more than an order of magnitude. Coupled volcanic CO2 emission data and magma supply rates reveal a carbon-rich mantle plume source region beneath Hawai'i with 40% more carbon than previous estimates.
- Peter H. Barry
-
Article |
 High levels of endocrine pollutants in US streams during low flow due to insufficient wastewater dilution
High levels of endocrine pollutants in US streams during low flow due to insufficient wastewater dilution
Wastewater can make up a large fraction of stream flow. An analysis of over 14,000 US streams shows that under severe low-flow conditions, wastewater containing endocrine disruptors is poorly diluted, and many streams exceed safety thresholds.
- Jacelyn Rice
- & Paul Westerhoff
-
Editorial |
 For people and planet
For people and planet
The emerging field of geohealth links human well-being and ecosystem health. A deeper understanding of these linkages can help society mitigate the health costs of economic growth before they become crises.
-
Article |
 Transition from high- to low-NOx control of night-time oxidation in the southeastern US
Transition from high- to low-NOx control of night-time oxidation in the southeastern US
The influence of NOx levels at night on atmospheric oxidation is unclear. Analyses of aircraft observations suggest that night-time oxidation is transitioning from a high- to low-NOx regime in the southeast US due to declines in NOx levels.
- P. M. Edwards
- , K. C. Aikin
- & S. S. Brown
-
Article |
 Substantial inorganic carbon sink in closed drainage basins globally
Substantial inorganic carbon sink in closed drainage basins globally
Dissolved inorganic carbon is buried in dryland basins that do not drain to the sea. Based on measurements of sediment chemistry in twelve of these sites, closed basins are estimated to store 0.15 Pg of dissolved inorganic carbon annually.
- Yu Li
- , Chengqi Zhang
- & Wangting Ye
-
Article |
 Decline in Chinese lake phosphorus concentration accompanied by shift in sources since 2006
Decline in Chinese lake phosphorus concentration accompanied by shift in sources since 2006
Many lakes in China are subject to eutrophication. Water quality analyses on 862 Chinese lakes reveal that better sanitation has reduced phosphorus inputs in the most populated areas, but aquaculture and livestock offset improvements elsewhere.
- Yindong Tong
- , Wei Zhang
- & Yan Lin
-
News & Views |
 Cleaner Chinese lakes
Cleaner Chinese lakes
Phosphorus loading can cause eutrophication of lakes. Analyses of lake chemistry in China reveal that policies have led to lower phosphorus levels overall, but increasing trends in some lakes suggest that expanded policies may be needed.
- Jessica Corman
-
Article |
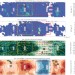 Large anomalies in lower stratospheric water vapour and ice during the 2015–2016 El Niño
Large anomalies in lower stratospheric water vapour and ice during the 2015–2016 El Niño
The El Niño of 2015–2016 was unusual and exceptionally strong. Satellite observations and modelling suggest that convective lofting and sublimation of ice particles during this event contributed to moistening of the lower stratosphere.
- Melody A. Avery
- , Sean M. Davis
- & Andrew E. Dessler
-
Correspondence |
 Save northern high-latitude catchments
Save northern high-latitude catchments
- Hjalmar Laudon
- , Christopher Spence
- & Doerthe Tetzlaff
-
Article |
 Global aquifers dominated by fossil groundwaters but wells vulnerable to modern contamination
Global aquifers dominated by fossil groundwaters but wells vulnerable to modern contamination
Groundwater that predates the Holocene is commonly assumed to be unaffected by modern contamination. A global analysis of fossil groundwater suggests that modern contaminants are present in deep wells that tap fossil aquifers.
- Scott Jasechko
- , Debra Perrone
- & James W. Kirchner
-
Article |
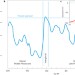 Groundwater salinity influenced by Holocene seawater trapped in incised valleys in the Red River delta plain
Groundwater salinity influenced by Holocene seawater trapped in incised valleys in the Red River delta plain
Brackish to salty waters have been found in inland areas of delta aquifers. Geophysical data and modelling suggest that salty groundwater in the Red River delta originates from trapped seawater contained in underlying Holocene marine deposits.
- Flemming Larsen
- , Long Vu Tran
- & Nhan Quy Pham
-
Article |
 Microbially driven export of labile organic carbon from the Greenland ice sheet
Microbially driven export of labile organic carbon from the Greenland ice sheet
Glacial systems are important sources of dissolved organic carbon to downstream ecosystems. Observations of carbon dynamics on the Greenland ice sheet reveal substantial melt season production and export of microbial dissolved organic carbon.
- Michaela Musilova
- , Martyn Tranter
- & Alexandre M. Anesio
-
Article |
 Black-carbon absorption enhancement in the atmosphere determined by particle mixing state
Black-carbon absorption enhancement in the atmosphere determined by particle mixing state
Mixing with non-black carbon can enhance the radiative effect of black-carbon aerosols. Lab and field measurements of aerosol properties reveal that the mass ratio of black to non-black carbon determines the amount of enhancement.
- Dantong Liu
- , James Whitehead
- & James D. Allan
-
Article |
 Iron persistence in a distal hydrothermal plume supported by dissolved–particulate exchange
Iron persistence in a distal hydrothermal plume supported by dissolved–particulate exchange
The largest known hydrothermal plume moves dissolved iron halfway across the Pacific. In situ measurements show that dissolved and particulate iron transport is facilitated by reversible exchange of dissolved iron onto organic compounds.
- Jessica N. Fitzsimmons
- , Seth G. John
- & Robert M. Sherrell
-
Editorial |
 Cleaner urban air tomorrow?
Cleaner urban air tomorrow?
Air pollution in large cities remains a persistent public health problem. Adapting air quality forecasts for use by decision makers could help mitigate severe pollution events.
-
News & Views |
 Early phosphorus redigested
Early phosphorus redigested
Atmospheric oxygen was maintained at low levels throughout huge swathes of Earth's early history. Estimates of phosphorus availability through time suggest that scavenging from anoxic, iron-rich oceans stabilized this low-oxygen world.
- Simon W. Poulton
-
Perspective |
 Historical carbon dioxide emissions caused by land-use changes are possibly larger than assumed
Historical carbon dioxide emissions caused by land-use changes are possibly larger than assumed
The net carbon flux on land comprises emissions from land-use change and uptake by vegetation. An evaluation of vegetation models suggests that emissions from land-use change, and thus the terrestrial sink, may be substantially underestimated.
- A. Arneth
- , S. Sitch
- & S. Zaehle
-
Article |
 A key role for green rust in the Precambrian oceans and the genesis of iron formations
A key role for green rust in the Precambrian oceans and the genesis of iron formations
Large iron deposits formed episodically in the Archaean oceans. Experimental data and geochemical modelling suggest that green rust was an important contributor to the formation of these deposits and the Archaean iron cycle in general.
- I. Halevy
- , M. Alesker
- & Y. Feldman
-
Article |
 Metabolism in anoxic permeable sediments is dominated by eukaryotic dark fermentation
Metabolism in anoxic permeable sediments is dominated by eukaryotic dark fermentation
Bacteria have been assumed to dominate organic matter decomposition in marine sediments. In flow-through reactor experiments, algae were revealed to be primarily responsible for anaerobically metabolizing organic matter in permeable sediments.
- Michael F. Bourke
- , Philip J. Marriott
- & Perran L. M. Cook
-
News & Views |
 Ocean dissolved organics matter
Ocean dissolved organics matter
Large quantities of organic carbon are stored in the ocean, but its biogeochemical behaviour is elusive. Size–age–composition relations now quantify the production of tiny organic molecules as a major pathway for carbon sequestration.
- Rainer M. W. Amon
-
Letter |
 Pacific carbon cycling constrained by organic matter size, age and composition relationships
Pacific carbon cycling constrained by organic matter size, age and composition relationships
Organic matter represents a large pool of carbon in the ocean. Radiocarbon and chemical analyses suggest that larger particles are preferentially remineralized in the Pacific Ocean, with smaller particles and molecules persisting longer.
- Brett D. Walker
- , Steven R. Beaupré
- & Ellen R. M. Druffel
-
Letter |
 Tropospheric ozone change from 1980 to 2010 dominated by equatorward redistribution of emissions
Tropospheric ozone change from 1980 to 2010 dominated by equatorward redistribution of emissions
Ozone is an air pollutant and a greenhouse gas. Simulations with a global chemistry transport model reveal that the spatial distribution of ozone precursor emissions dominates the global ozone burden, and that emissions in the tropics matter most.
- Yuqiang Zhang
- , Owen R. Cooper
- & J. Jason West

 A two-pollutant strategy for improving ozone and particulate air quality in China
A two-pollutant strategy for improving ozone and particulate air quality in China Swimming in sewage
Swimming in sewage