Featured
-
-
News |
 Missing data spark fears over land clean-up
Missing data spark fears over land clean-up
Proposed home for world's largest fish market is contaminated land.
- David Cyranoski
-
Letter |
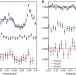 Possible thermochemical disequilibrium in the atmosphere of the exoplanet GJ 436b
Possible thermochemical disequilibrium in the atmosphere of the exoplanet GJ 436b
Here, the atmosphere of the extrasolar planet GJ 436b is studied during its 'secondary eclipse'. The findings reveal the presence of some H2O and traces of CO2. The best-fit compositional models contain a high CO abundance and a substantial methane deficiency relative to thermochemical equilibrium models for the predicted hydrogen-dominated atmosphere. Disequilibrium processes such as vertical mixing and polymerization of methane may be required to explain this small methane-to-CO ratio.
- Kevin B. Stevenson
- , Joseph Harrington
- & Nate B. Lust
-
Letter |
 Phosphate oxygen isotopic evidence for a temperate and biologically active Archaean ocean
Phosphate oxygen isotopic evidence for a temperate and biologically active Archaean ocean
It has been thought that ocean temperatures during the early Palaeoarchaean era (around 3.5 billion years ago) were 55–85 °C. But a recent study indicated that the temperatures might be no higher than 40 °C. Here, studies are reported of the oxygen isotope compositions of phosphates in sediments from the 3.2–3.5-billion-year-old Barberton Greenstone Belt in South Africa. The findings indicate a well-developed phosphorus cycle and evolved biological activity in an Archaean ocean with temperatures of 26–35 °C.
- Ruth E. Blake
- , Sae Jung Chang
- & Aivo Lepland
-
News & Views |
 Grazing and nitrous oxide
Grazing and nitrous oxide
Most emissions of nitrous oxide from semi-arid, temperate grasslands usually occur during the spring thaw. The effects that grazing has on plant litter and snow cover dramatically reduce these seasonal emissions.
- Stephen J. Del Grosso
-
-
News & Views |
 A frosty finding
A frosty finding
The asteroid belt is classically considered the domain of rocky bodies, being too close to the Sun for ice to survive. Or so we thought — not only is ice present, but at least one asteroid is covered in it.
- Henry H. Hsieh
-
News |
 Comet crash creates potential for life
Comet crash creates potential for life
Shock waves could force amino-acid forming chemistry.
- Katharine Sanderson
-
News |
 Cheaper catalyst cleans diesel-car fumes
Cheaper catalyst cleans diesel-car fumes
Platinum-free material means fuel-efficient engines at lower cost.
- Richard Van Noorden
-
News |
 Worries over electronic waste from the developing world
Worries over electronic waste from the developing world
Millions of computers heading for unregulated recyclers could poison water and soil.
- Richard A. Lovett
-
News |
 Purifying the sea one drop at a time
Purifying the sea one drop at a time
Microfluidic channels offer promise of cheap, portable desalination.
- Katharine Sanderson
-
Letter |
 A large atomic chlorine source inferred from mid-continental reactive nitrogen chemistry
A large atomic chlorine source inferred from mid-continental reactive nitrogen chemistry
The presence of gaseous chlorine atom precursors within the troposphere was thought only to occur in marine areas but now nitryl chloride has been found at a distance of 1,400 km from the nearest coastline. A model study shows that the amount of nitryl chloride production in the continental USA alone is similar to previous global estimates for marine regions. A significant fraction of tropospheric chlorine atoms may arise directly from anthropogenic pollutants.
- Joel A. Thornton
- , James P. Kercher
- & Steven S. Brown
-
-
News & Views |
50 & 100 years ago
-
News & Views |
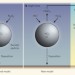 Wider role for airborne chlorine
Wider role for airborne chlorine
Unexpected chlorine chemistry in the lowest part of the atmosphere can affect the cycling of nitrogen oxides and the production of ozone, and reduce the lifetime of the greenhouse gas methane.
- Roland von Glasow
-
News |
 Old rocks drown dry Moon theory
Old rocks drown dry Moon theory
Samples collected during Apollo missions suggest a wet interior, raising questions about lunar origins.
- Eric Hand
-
Letter |
 Electric currents couple spatially separated biogeochemical processes in marine sediment
Electric currents couple spatially separated biogeochemical processes in marine sediment
It has been previously demonstrated that some microbes are capable of extracellular electron transport through so–called nanowires or electron shuttles. Here it is demonstrated that this may be a significant process in the marine sediment.
- Lars Peter Nielsen
- , Nils Risgaard-Petersen
- & Mikio Sayama
-
News & Views |
 Sediment reactions defy dogma
Sediment reactions defy dogma
Redox reactions in widely spatially separated layers of marine sediments are coupled to each other. This suggests that bacteria mediate the flow of electrons between the layers — an idea that would previously have been dismissed.
- Kenneth H. Nealson
-
News |
 Bacteria buzzing in the seabed
Bacteria buzzing in the seabed
Nanowires growing from bacteria might link up distant chemical reactions in sediments.
- Katharine Sanderson
-
News Feature |
 Carbon sequestration: Buried trouble
Carbon sequestration: Buried trouble
Protesters saying "no to CO2" are just one roadblock facing carbon sequestration — a strategy that could help prevent dangerous climate change. Richard Van Noorden investigates.
- Richard Van Noorden
-
News Feature |
 Planetary science: A whiff of mystery on Mars
Planetary science: A whiff of mystery on Mars
The surprising discovery of methane in Mars's atmosphere could be a sign of life there. Researchers are now working out how to find its source, reports Katharine Sanderson.
- Katharine Sanderson
-
News & Views |
More ozone over North America
Springtime ozone levels in the lower atmosphere over western North America are rising. The source of this pollution may be Asia, a finding that reaffirms the need for international air-quality control.
- Kathy Law
-
News |
 Pollutants plucked from air with copper
Pollutants plucked from air with copper
Fortuitous catalyst discovery offers a new way to suck carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
- Katharine Sanderson
-
Research Highlights |
Biogeochemistry: DDT in the ocean
-
Books & Arts |
 No crystal ball for natural disasters
No crystal ball for natural disasters
Floods and fires aside, the tricky science of prediction is explained in a book that treads a careful line between analysis and anecdotes of awful events, says Andrew Robinson.
- Andrew Robinson

 Oil spill endangers fragile marshland
Oil spill endangers fragile marshland The mystery of Don Juan Pond
The mystery of Don Juan Pond