Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Quantum simulation of the bosonic Kitaev chain
Quantum simulation of the bosonic Kitaev chain
Interesting non-Hermitian quantum dynamics can be accessed in analogue quantum simulators consisting of Hermitian bosonic systems with squeezing and antisqueezing terms. Here, the authors use a coplanar waveguide resonator connected to a SQUID to simulate the bosonic version of the Kitaev chain.
- Jamal H. Busnaina
- , Zheng Shi
- & Christopher M. Wilson
-
Article
| Open Access Intercavity polariton slows down dynamics in strongly coupled cavities
Intercavity polariton slows down dynamics in strongly coupled cavities
Band engineering in optics allows the design of unconventional forms of light with potential optoelectronic applications. Here, the authors realize slow-light intercavity polaritons in an array of coupled cavities, the photonic architecture enables the spatial segregation of photons and excitons
- Yesenia A. García Jomaso
- , Brenda Vargas
- & Giuseppe Pirruccio
-
Article
| Open Access Passive frequency comb generation at radiofrequency for ranging applications
Passive frequency comb generation at radiofrequency for ranging applications
In contrast to the commonly studied optical frequency combs, here, the authors demonstrate a radio frequency system able to wirelessly and passively generate frequency combs as a battery-free solution for far-field ranging of unmanned vehicles in GPS-denied settings.
- Hussein M. E. Hussein
- , Seunghwi Kim
- & Cristian Cassella
-
Article
| Open Access Velocities of transmission eigenchannels and diffusion
Velocities of transmission eigenchannels and diffusion
Wave scattering can be described with a diffusion model in which the velocity is randomized by scattering. Here the authors find that the velocities of different transmission eigenchannels are distinct on all length scales.
- Azriel Z. Genack
- , Yiming Huang
- & Zhou Shi
-
Article
| Open Access Electrically driven amplification of terahertz acoustic waves in graphene
Electrically driven amplification of terahertz acoustic waves in graphene
Electron–phonon interactions are a crucial aspect of high-quality graphene devices. Here, the authors show that graphene resistivity grows strongly in the direction of the carrier flow when the drift velocity exceeds the speed of sound due to the electrical amplification of acoustic terahertz phonons.
- Aaron H. Barajas-Aguilar
- , Jasen Zion
- & Javier D. Sanchez-Yamagishi
-
Article
| Open Access Cavity-coupled telecom atomic source in silicon
Cavity-coupled telecom atomic source in silicon
T centers in silicon are promising candidates for quantum applications yet suffer from weak optical transitions. Here, by integrating with a silicon nanocavity, the authors demonstrate an enhancement of the photon emission rate for a single T center.
- Adam Johnston
- , Ulises Felix-Rendon
- & Songtao Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Higher order gaps in the renormalized band structure of doubly aligned hBN/bilayer graphene moiré superlattice
Higher order gaps in the renormalized band structure of doubly aligned hBN/bilayer graphene moiré superlattice
In moiré superlattices, a multitude of higher order Bragg gaps and van Hove singularities emerges as the band structure renormalizes. Here, the authors map these gaps uniquely to the recently predicted topological Bragg indices of the underlying supermoiré lattice.
- Mohit Kumar Jat
- , Priya Tiwari
- & Aveek Bid
-
Article
| Open Access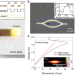 Ultra-compact exciton polariton modulator based on van der Waals semiconductors
Ultra-compact exciton polariton modulator based on van der Waals semiconductors
Miniaturized and efficient optical modulators are desired for data transmission, processing and communication. Here, the authors report the fabrication of exciton-polariton Mach–Zehnder modulators based on thin WS2 waveguides with a footprint of ~30 μm², modulation ratio up to −6.20 dB and nanosecond response times.
- Seong Won Lee
- , Jong Seok Lee
- & Su-Hyun Gong
-
Article
| Open Access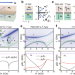 Ultrastrong to nearly deep-strong magnon-magnon coupling with a high degree of freedom in synthetic antiferromagnets
Ultrastrong to nearly deep-strong magnon-magnon coupling with a high degree of freedom in synthetic antiferromagnets
Deep-strong coupling in hybrid magnonic systems is yet to be explored. Here, the authors unveil unconventional coupling properties in synthetic antiferromagnets. The systems’ high degree of freedom enables a near-realization of deep-strong coupling.
- Yuqiang Wang
- , Yu Zhang
- & Guoqiang Yu
-
Article
| Open Access Selenium substitution for dielectric constant improvement and hole-transfer acceleration in non-fullerene organic solar cells
Selenium substitution for dielectric constant improvement and hole-transfer acceleration in non-fullerene organic solar cells
Dielectric constant of non-fullerene acceptors plays a critical role in organic solar cells in terms of exciton dissociation and charge recombination. Here, authors report selenium substitution on central core of acceptors to improve dielectric constant, realizing devices with efficiency of 19.0%.
- Xinjun He
- , Feng Qi
- & Wallace C. H. Choy
-
Article
| Open Access Voltage-based magnetization switching and reading in magnetoelectric spin-orbit nanodevices
Voltage-based magnetization switching and reading in magnetoelectric spin-orbit nanodevices
The authors realize voltage-based magnetization switching and reading in nanodevices at room temperature, through exchange coupling between multiferroic BiFeO3 and ferromagnetic CoFe, for writing, and spin-to-charge current conversion between CoFe and Pt, for reading.
- Diogo C. Vaz
- , Chia-Ching Lin
- & Fèlix Casanova
-
Article
| Open Access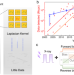 Reconfigurable perovskite X-ray detector for intelligent imaging
Reconfigurable perovskite X-ray detector for intelligent imaging
In-sensor computing requires detectors with polarity reconfigurability and linear responsivity. Pang et al. report a CsPbBr3 perovskite single crystal X-ray detector for edge extraction imaging with a data compression ratio of 46.4% and classification task with an accuracy of 100%.
- Jincong Pang
- , Haodi Wu
- & Guangda Niu
-
Article
| Open Access Femtosecond electron beam probe of ultrafast electronics
Femtosecond electron beam probe of ultrafast electronics
Modern electronic devices are too fast and too small to be measured by conventional electronic means. Here the authors combine electron microscopy with femtosecond laser technology and measure the functionality of terahertz electronics in space and time.
- Maximilian Mattes
- , Mikhail Volkov
- & Peter Baum
-
Article
| Open Access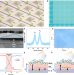 Non-volatile rippled-assisted optoelectronic array for all-day motion detection and recognition
Non-volatile rippled-assisted optoelectronic array for all-day motion detection and recognition
The authors create a rippled-assisted optoelectronic array (18 × 18 pixels) for the all-day motion detection and recognition, possessing negative and positive optical detection as well as memory and computation capabilities.
- Xingchen Pang
- , Yang Wang
- & Peng Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic X-ray imaging with screen-printed perovskite CMOS array
Dynamic X-ray imaging with screen-printed perovskite CMOS array
Biomedical X-ray imaging requires high spatial and temporal resolution of the detectors. Liu et al. report a screen-printed perovskite direct-conversion X-ray CMOS imager with a spatial resolution of 5 lp mm−1 and a speed of 300 fps for low-dose 2D radiography and 3D computed tomography imaging.
- Yanliang Liu
- , Chaosong Gao
- & Yongshuai Ge
-
Article
| Open Access Current-induced switching of a van der Waals ferromagnet at room temperature
Current-induced switching of a van der Waals ferromagnet at room temperature
Fe3GaTe2 is a van der Waals material with a Curie temperature well above room temperature, making it an attractive material for integration into spintronic devices. Here, Kajale et al demonstrate spin-orbit torque induced switching of the magnetization of Fe3GaTe2, above room temperature, using a Pt spin Hall layer.
- Shivam N. Kajale
- , Thanh Nguyen
- & Deblina Sarkar
-
Article
| Open Access Resolving the topology of encircling multiple exceptional points
Resolving the topology of encircling multiple exceptional points
When multiple oscillators are tuned, degeneracies occur on a knot-shaped region in the space of tuning parameters. This knot influences how such systems can be tuned. Here, the authors reconcile two common means for visualizing this influence.
- Chitres Guria
- , Qi Zhong
- & Jack Gwynne Emmet Harris
-
Article
| Open Access Real-time tracking of coherent oscillations of electrons in a nanodevice by photo-assisted tunnelling
Real-time tracking of coherent oscillations of electrons in a nanodevice by photo-assisted tunnelling
The authors demonstrate that the collective electron oscillations driven by light in a quantum nanodevice can be measured directly in the time domain, by recording the photo-assisted tunnelling currents using the technique of homodyne beating.
- Yang Luo
- , Frank Neubrech
- & Manish Garg
-
Article
| Open Access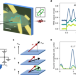 Electric control of optically-induced magnetization dynamics in a van der Waals ferromagnetic semiconductor
Electric control of optically-induced magnetization dynamics in a van der Waals ferromagnetic semiconductor
The combination of strong light-matter interactions and controllable magnetic properties make magnetic semiconductors attractive for both fundamental physics and the development of devices. Here, Hendriks et al show how the optically driven magnetization dynamics in Cr2Ge2Te6 can be controlled via electrostatic gating.
- Freddie Hendriks
- , Rafael R. Rojas-Lopez
- & Marcos H. D. Guimarães
-
Article
| Open Access Effect of sub-bandgap defects on radiative and non-radiative open-circuit voltage losses in perovskite solar cells
Effect of sub-bandgap defects on radiative and non-radiative open-circuit voltage losses in perovskite solar cells
The efficiency of perovskite solar cells is affected by open-circuit voltage losses due to radiative and non-radiative charge recombination. Here, authors report photocurrent and electroluminescence spectroscopy to probe radiative recombination at sub-bandgap defects in wide-bandgap solar cells.
- Guus J. W. Aalbers
- , Tom P. A. van der Pol
- & René A. J. Janssen
-
Article
| Open Access Acoustic-driven magnetic skyrmion motion
Acoustic-driven magnetic skyrmion motion
Skyrmions, a type of topological spin texture, have garnered interest for use in spintronic devices. Typically, these devices necessitate moving the skyrmions via applied currents. Here, Yang et al demonstrate the driving of skyrmions by surface acoustic waves.
- Yang Yang
- , Le Zhao
- & Tianxiang Nan
-
Article
| Open Access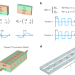 Floquet parity-time symmetry in integrated photonics
Floquet parity-time symmetry in integrated photonics
Here the authors unveil an approach rooted in non-Hermitian physics to precisely control light amplification in an integrated photonic platform, paving the way for innovative on-chip functionalities, like coherent control of light amplification and routing.
- Weijie Liu
- , Quancheng Liu
- & Feng Chen
-
Article
| Open Access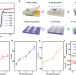 Strain-restricted transfer of ferromagnetic electrodes for constructing reproducibly superior-quality spintronic devices
Strain-restricted transfer of ferromagnetic electrodes for constructing reproducibly superior-quality spintronic devices
To optimize the interfacial quality and electrode magnetism in spintronic devices, the authors develop an electrode transfer technique that can greatly improve device interfacial quality, performance and reproducibility, universal to various spacers.
- Lidan Guo
- , Xianrong Gu
- & Xiangnan Sun
-
Article
| Open Access Toward grouped-reservoir computing: organic neuromorphic vertical transistor with distributed reservoir states for efficient recognition and prediction
Toward grouped-reservoir computing: organic neuromorphic vertical transistor with distributed reservoir states for efficient recognition and prediction
Existing neuromorphic hardware, focusing mainly on shallow-reservoir computing, is challenged in providing adequate spatial and temporal scales characteristic for effective computing. Here, Gao et al. report an ultra-short channel organic neuromorphic vertical transistor with distributed reservoir states.
- Changsong Gao
- , Di Liu
- & Huipeng Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Giant optical polarisation rotations induced by a single quantum dot spin
Giant optical polarisation rotations induced by a single quantum dot spin
Light-matter interfaces implementing arbitrary conditional operations on incoming photons would have several applications in quantum computation and communications. Here, the authors demonstrate conditional polarization rotation induced by a single quantum dot spin embedded in an electrically contacted micropillar, spanning up to a pi flip.
- E. Mehdi
- , M. Gundín
- & L. Lanco
-
Article
| Open Access High crosstalk suppression in InGaAs/InP single-photon avalanche diode arrays by carrier extraction structure
High crosstalk suppression in InGaAs/InP single-photon avalanche diode arrays by carrier extraction structure
Opticalelectrical crosstalk, rather than optical crosstalk, is the primary issue in InGaAs/InP single-photon avalanche diode arrays. Here, Tang et al. propose a carrier-extraction structures to replace the trenching method, effectively reducing crosstalk and maintaining device reliability.
- Yongsheng Tang
- , Rui Wang
- & Meng Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Differential perovskite hemispherical photodetector for intelligent imaging and location tracking
Differential perovskite hemispherical photodetector for intelligent imaging and location tracking
Differential spectrometers recognise different wavelength via their differential photodetector responsivity. The authors combine an 8-pixel hemispherical perovskite photodetector with neural network algorithms to realise 3D trajectory tracking and 2D location tacking with colour classification.
- Xiaopeng Feng
- , Chenglong Li
- & Haotong Wei
-
Article
| Open Access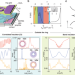 Tunable quantum interferometer for correlated moiré electrons
Tunable quantum interferometer for correlated moiré electrons
Gate-defined superconducting moiré devices offer high tunability for probing the nature of superconducting and correlated insulating states. Here, the authors report the Little–Parks and Aharonov–Bohm effects in a single gate-defined magic-angle twisted bilayer graphene device.
- Shuichi Iwakiri
- , Alexandra Mestre-Torà
- & Klaus Ensslin
-
Article
| Open Access Observation and manipulation of quantum interference in a superconducting Kerr parametric oscillator
Observation and manipulation of quantum interference in a superconducting Kerr parametric oscillator
D. Iyama et al. study the generation and quantum coherence of Schrödinger cat states in a superconducting Kerr parametric oscillator, a Kerr nonlinear resonator with a two-photon pump. They also manipulate the quantum interference of the cat states by implementing single cat-state gate operations.
- Daisuke Iyama
- , Takahiko Kamiya
- & Jaw-Shen Tsai
-
Article
| Open Access Programmable high-dimensional Hamiltonian in a photonic waveguide array
Programmable high-dimensional Hamiltonian in a photonic waveguide array
Photonic waveguide lattices implementing continuous quantum walks have a wide range of applications yet remain based on static devices. Here, the authors demonstrated a fully programmable waveguide array by implementing various Hamiltonians.
- Yang Yang
- , Robert J. Chapman
- & Alberto Peruzzo
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrafast THz probing of nonlocal orbital current in transverse multilayer metallic heterostructures
Ultrafast THz probing of nonlocal orbital current in transverse multilayer metallic heterostructures
By optically driving the magnetization in a magnetic system, terahertz emission can be induced from an adjacent normal metal, as a result of spin-to-charge conversion. Here, Kumar and Kumar successfully show the equivalent effect arising from orbital-to-charge conversion.
- Sandeep Kumar
- & Sunil Kumar
-
Article
| Open Access Real-time photonic blind interference cancellation
Real-time photonic blind interference cancellation
The authors demonstrate real-time blind photonic interference cancellation using FPGA-photonic coordinated processing with zero calibration micro-ring resonator control and sub-second cancellation weight identification.
- Joshua C. Lederman
- , Weipeng Zhang
- & Paul R. Prucnal
-
Article
| Open Access Bolometric detection of Josephson inductance in a highly resistive environment
Bolometric detection of Josephson inductance in a highly resistive environment
The predicted dissipative quantum phase transition in a Josephson junction coupled to resistive environment has been examined in recent experiments. In a heat transport experiment, Subero et al. show that the junction acts as an inductor at high frequencies, while DC charge transport confirms insulating behaviour.
- Diego Subero
- , Olivier Maillet
- & Jukka P. Pekola
-
Article
| Open Access All-fiber frequency agile triple-frequency comb light source
All-fiber frequency agile triple-frequency comb light source
The authors introduce an agile, all-fiber laser source with three frequency combs. Three EOM combs from a single laser are expanded in a tri-core nonlinear fiber, maintaining high mutual coherence. This system’s performance is showcased through a 2D four-wave mixing spectroscopy experiment.
- Eve-Line Bancel
- , Etienne Genier
- & Arnaud Mussot
-
Article
| Open Access Thermal and electrostatic tuning of surface phonon-polaritons in LaAlO3/SrTiO3 heterostructures
Thermal and electrostatic tuning of surface phonon-polaritons in LaAlO3/SrTiO3 heterostructures
Phonon polaritons are promising for infrared applications while it is difficult to tune the phonon polariton properties. Here, authors report a thermal and electrostatic tuning of surface phonon polaritons in heterostructures of LaAlO3/SrTiO3.
- Yixi Zhou
- , Adrien Waelchli
- & Alexey B. Kuzmenko
-
Article
| Open Access Electron pairing and nematicity in LaAlO3/SrTiO3 nanostructures
Electron pairing and nematicity in LaAlO3/SrTiO3 nanostructures
SrTiO3-based heterostructures display intriguing low-temperature transport features. Here the authors study LaAlO3/SrTiO3 nanoscale crossbar devices, revealing correlations between electron pairing without superconductivity, anomalous Hall effect, and electronic nematicity, suggesting a shared microscopic origin.
- Aditi Nethwewala
- , Hyungwoo Lee
- & Jeremy Levy
-
Article
| Open Access Apparent nonlinear damping triggered by quantum fluctuations
Apparent nonlinear damping triggered by quantum fluctuations
Nonlinear damping is a ubiquitous phenomenon in technological applications involving oscillators, but its origin is sometimes poorly understood. Here, the authors highlight how the interplay between quantum noise and Kerr anharmonicity introduces an effect resembling nonlinear damping.
- Mario F. Gely
- , Adrián Sanz Mora
- & Gary A. Steele
-
Article
| Open Access Time, momentum, and energy resolved pump-probe tunneling spectroscopy of two-dimensional electron systems
Time, momentum, and energy resolved pump-probe tunneling spectroscopy of two-dimensional electron systems
Pump-probe techniques—where a system is driven into a nonequilibrium state and then studied as a function of time—provide rich information about the behaviour of charge carriers and their interactions. Here, Yoo et al extend this class of techniques by injecting electrons at a selected energy and observing their decay in energy and momentum space.
- H. M. Yoo
- , M. Korkusinski
- & R. C. Ashoori
-
Article
| Open Access Phase biasing of a Josephson junction using Rashba–Edelstein effect
Phase biasing of a Josephson junction using Rashba–Edelstein effect
The authors study transport in Nb-(Pt/Cu)-Nb Josephson junctions (JJ), where Pt/Cu is a Rashba interface. Due to the Rashba–Edelstein effect, a charge current leads to a non-equilibrium spin moment at the Pt/Cu interface, which can be measured from a shift of the Fraunhofer pattern of the JJ.
- Tapas Senapati
- , Ashwin Kumar Karnad
- & Kartik Senapati
-
Article
| Open Access Observing the universal screening of a Kondo impurity
Observing the universal screening of a Kondo impurity
Previous work on charge Kondo circuits, in which a spin is formed by two degenerate charge states of a metallic island, has been limited to transport measurements of multi-channel Kondo problems. Piquard et al. use thermodynamic measurements via a charge sensor to study the evolution of a single Kondo impurity.
- C. Piquard
- , P. Glidic
- & F. Pierre
-
Article
| Open Access Frequency stable and low phase noise THz synthesis for precision spectroscopy
Frequency stable and low phase noise THz synthesis for precision spectroscopy
The authors demonstrate a very stable yet broadly tunable photonic THz source, characterized from 2 GHz to 1.4 THz. A very narrow Lamb dip feature is observed in a water absorption line, showcasing its potential for sub-kHz resolution spectroscopy.
- Léo Djevahirdjian
- , Loïc Lechevallier
- & Samir Kassi
-
Article
| Open Access Heat current-driven topological spin texture transformations and helical q-vector switching
Heat current-driven topological spin texture transformations and helical q-vector switching
Topological spin textures, such as skyrmions and antiskyrmions are of interest for use in information storage, owing to their inherent robustness. Critical to this use is the ability to manipulate these spin textures. Here, Yasin et al. demonstrate heat current driven transformation of a topological spin texture in a ferromagnet at room temperature.
- Fehmi Sami Yasin
- , Jan Masell
- & Xiuzhen Yu
-
Article
| Open Access Phase-engineering the Andreev band structure of a three-terminal Josephson junction
Phase-engineering the Andreev band structure of a three-terminal Josephson junction
The authors study Andreev bound states (ABSs) in 3-terminal InAs/Al Josephson-junction devices. They find signatures of hybridization between two ABSs, with band structure tunable by electric currents that generate magnetic fluxes threading superconducting loops in the device.
- Marco Coraiola
- , Daniel Z. Haxell
- & Fabrizio Nichele
-
Article
| Open Access Room-temperature high-speed electrical modulation of excitonic distribution in a monolayer semiconductor
Room-temperature high-speed electrical modulation of excitonic distribution in a monolayer semiconductor
2D excitonic devices hold potential for on-chip optoelectronic applications. Here, the authors report high-speed in-plane electrical modulations of the excitonic distribution in monolayer semiconductor/Au electrode junctions, showing switching times as low as 5 ns at room temperature.
- Guangpeng Zhu
- , Lan Zhang
- & Qihua Xiong
-
Article
| Open Access Multi-scale molecular dynamics simulations of enhanced energy transfer in organic molecules under strong coupling
Multi-scale molecular dynamics simulations of enhanced energy transfer in organic molecules under strong coupling
Placing an organic material in an optical cavity can enhance exciton transport, but the mechanism is poorly understood. Here, using molecular dynamics simulations, the authors obtained atomistic insights into that mechanism.
- Ilia Sokolovskii
- , Ruth H. Tichauer
- & Gerrit Groenhof
-
Article
| Open Access In-situ electro-responsive through-space coupling enabling foldamers as volatile memory elements
In-situ electro-responsive through-space coupling enabling foldamers as volatile memory elements
Molecular electronics holds promise for building memristor at nanoscales for in-memory computing. Li et al. design tailored foldamers with furan-benzene and thiophene-benzene stacking to achieve voltage triggered quantum interference switching for potential random number generator application.
- Jinshi Li
- , Pingchuan Shen
- & Zujin Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Transmission-type photonic doping for high-efficiency epsilon-near-zero supercoupling
Transmission-type photonic doping for high-efficiency epsilon-near-zero supercoupling
The authors present a transmission-type doping approach to reduce resonant losses in photonic doping. Assisted by the approach, proximate ideal epsilon-near-zero (ENZ) supercoupling with neartotal energy transmission and zero-phase advance is achieved in experiments.
- Wendi Yan
- , Ziheng Zhou
- & Yue Li
-
Article
| Open Access An anisotropic van der Waals dielectric for symmetry engineering in functionalized heterointerfaces
An anisotropic van der Waals dielectric for symmetry engineering in functionalized heterointerfaces
Here, the authors demonstrate that a layered anisotropic dielectric material, SiP2, can break the rotational symmetry of 2D MoS2, leading to linearly polarized photoluminescence emission and conductance anisotropy ratios up to 1000 in gated SiP2/MoS2 heterostructures.
- Zeya Li
- , Junwei Huang
- & Hongtao Yuan
-
Article
| Open Access Synergistic correlated states and nontrivial topology in coupled graphene-insulator heterostructures
Synergistic correlated states and nontrivial topology in coupled graphene-insulator heterostructures
Here, the authors theoretically predict the formation of synergistic correlated and topological states in Coulomb-coupled and gate-tunable graphene/insulator heterostructures, proposing a number of promising substrate candidates and a possible explanation for recent experimental observations in graphene/CrOCl heterostructures.
- Xin Lu
- , Shihao Zhang
- & Jianpeng Liu

 A bionic self-driven retinomorphic eye with ionogel photosynaptic retina
A bionic self-driven retinomorphic eye with ionogel photosynaptic retina