Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Coupling to octahedral tilts in halide perovskite nanocrystals induces phonon-mediated attractive interactions between excitons
Coupling to octahedral tilts in halide perovskite nanocrystals induces phonon-mediated attractive interactions between excitons
Time-resolved measurements show that coupling between electrons and phonons in lead halide perovskites can mediate attractive interactions between excitons, although the interaction strength depends on the specific material.
- Nuri Yazdani
- , Maryna I. Bodnarchuk
- & Aaron M. Lindenberg
-
News & Views |
 Phonon slowdown
Phonon slowdown
A detailed understanding of phonon transport is crucial for engineering the thermal properties of materials. A particular doping strategy is now shown to lead to good thermoelectric performance with low thermal conductivity.
- Zhilun Lu
-
Article |
 Quantum simulation of an exotic quantum critical point in a two-site charge Kondo circuit
Quantum simulation of an exotic quantum critical point in a two-site charge Kondo circuit
The quantum critical behaviour of a two-impurity Kondo model variant is observed in a system of hybrid-semiconductor islands that could provide a scalable platform for solid-state quantum simulation
- Winston Pouse
- , Lucas Peeters
- & David Goldhaber-Gordon
-
Article |
 Visualization of bulk and edge photocurrent flow in anisotropic Weyl semimetals
Visualization of bulk and edge photocurrent flow in anisotropic Weyl semimetals
Understanding the fundamental mechanisms of photocurrent generation is important for photodetector design. Now, the anisotropy of the thermal properties of Weyl semimetals is shown to generate circulating photocurrents.
- Yu-Xuan Wang
- , Xin-Yue Zhang
- & Brian B. Zhou
-
Letter |
 Direct determination of the topological thermal conductance via local power measurement
Direct determination of the topological thermal conductance via local power measurement
Careful thermal transport measurements identify the topological nature of transverse thermal conductance in the fractional quantum Hall regime.
- Ron Aharon Melcer
- , Sofia Konyzheva
- & Vladimir Umansky
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrafast X-ray imaging of the light-induced phase transition in VO2
Ultrafast X-ray imaging of the light-induced phase transition in VO2
The intermediate states in photo-excited phase transitions are expected to be inhomogeneous. However, ultrafast X-ray imaging shows the early part of the metal–insulator transition in VO2 is homogeneous but then becomes heterogeneous.
- Allan S. Johnson
- , Daniel Perez-Salinas
- & Simon E. Wall
-
-
Article |
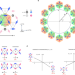 Piezomagnetic switching of the anomalous Hall effect in an antiferromagnet at room temperature
Piezomagnetic switching of the anomalous Hall effect in an antiferromagnet at room temperature
Control of magnetization is important for applications in spintronics. Now, the piezomagnetic effect allows strain to control the anomalous Hall effect in a metal at room temperature by rotating its antiferromagnetic order.
- M. Ikhlas
- , S. Dasgupta
- & S. Nakatsuji
-
Article
| Open Access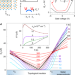 Evidence for equilibrium exciton condensation in monolayer WTe2
Evidence for equilibrium exciton condensation in monolayer WTe2
Exciton condensation has been observed in various three-dimensional (3D) materials. Now, monolayer WTe2—a 2D topological insulator—also shows the phenomenon. Strong electronic interactions allow the excitons to form and condense at high temperature.
- Bosong Sun
- , Wenjin Zhao
- & David H. Cobden
-
Article |
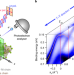 Detecting photoelectrons from spontaneously formed excitons
Detecting photoelectrons from spontaneously formed excitons
Excitons have been predicted to form spontaneously—without external excitation—in some materials. Low-temperature ARPES measurements on Ta2NiSe5 now provide evidence for such an excitonic insulator and for so-called preformed excitons.
- Keisuke Fukutani
- , Roland Stania
- & Han Woong Yeom
-
Letter |
 One-dimensional Kronig–Penney superlattices at the LaAlO3/SrTiO3 interface
One-dimensional Kronig–Penney superlattices at the LaAlO3/SrTiO3 interface
The two-dimensional electron gas at an oxide interface is patterned to form a channel with a periodic potential imposed on top. This replicates the textbook Kronig–Penney model and leads to fractionalization of electron bands in the channel.
- Megan Briggeman
- , Hyungwoo Lee
- & Jeremy Levy
-
Letter |
 Long-range ballistic propagation of carriers in methylammonium lead iodide perovskite thin films
Long-range ballistic propagation of carriers in methylammonium lead iodide perovskite thin films
Charge-carrier dynamics are fundamental to the operation and performance of semiconductor devices. In methylammonium lead iodide perovskites, carriers in the non-equilibrium regime after excitation propagate ballistically over 150 nm within 20 fs.
- Jooyoung Sung
- , Christoph Schnedermann
- & Akshay Rao
-
Letter |
 Giant gate-controlled proximity magnetoresistance in semiconductor-based ferromagnetic–non-magnetic bilayers
Giant gate-controlled proximity magnetoresistance in semiconductor-based ferromagnetic–non-magnetic bilayers
The authors demonstrate magnetoresistance of 80% from a two-dimensional electron gas proximity coupled to a ferromagnetic layer. This extends spintronics functionality to semiconductor devices.
- Kosuke Takiguchi
- , Le Duc Anh
- & Masaaki Tanaka
-
News & Views |
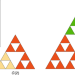 Quantum fractals
Quantum fractals
Electrons with fractional dimension have been observed in an artificial Sierpiński triangle, demonstrating their quantum fractal nature.
- Dario Bercioux
- & Ainhoa Iñiguez
-
Letter |
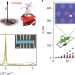 Excess resistivity in graphene superlattices caused by umklapp electron–electron scattering
Excess resistivity in graphene superlattices caused by umklapp electron–electron scattering
An increase in electrical resistance caused by the fundamental process of electrons scattering off of each other (umklapp scattering) is observed in graphene superlattice devices. This will limit the electrical properties of such devices.
- J. R. Wallbank
- , R. Krishna Kumar
- & V. I. Fal’ko
-
Letter |
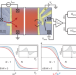 Direct entropy measurement in a mesoscopic quantum system
Direct entropy measurement in a mesoscopic quantum system
The entropy of a few-electron quantum system is measured for the first time by tracking the movement of charge in and out of the system. This could allow the unambiguous detection of Majorana fermions in solid state devices.
- Nikolaus Hartman
- , Christian Olsen
- & Joshua Folk
-
Letter |
 Giant anomalous Nernst effect and quantum-critical scaling in a ferromagnetic semimetal
Giant anomalous Nernst effect and quantum-critical scaling in a ferromagnetic semimetal
A magnetic field and temperature gradient produce a large electric potential in a ferromagnet, indicating the possible presence of Weyl points. The specific structure of Weyl points gives the electrons quantum-critical properties.
- Akito Sakai
- , Yo Pierre Mizuta
- & Satoru Nakatsuji
-
Perspective |
 Beyond CMOS computing with spin and polarization
Beyond CMOS computing with spin and polarization
- Sasikanth Manipatruni
- , Dmitri E. Nikonov
- & Ian A. Young
-
Review Article |
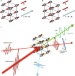 Antiferromagnetic opto-spintronics
Antiferromagnetic opto-spintronics
An overview of how electromagnetic radiation can be used for probing and modification of the magnetic order in antiferromagnets, and possible future research directions.
- P. Němec
- , M. Fiebig
- & A. V. Kimel
-
Article |
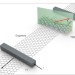 Strongly anisotropic spin relaxation in graphene–transition metal dichalcogenide heterostructures at room temperature
Strongly anisotropic spin relaxation in graphene–transition metal dichalcogenide heterostructures at room temperature
Large spin–orbit coupling can be induced when graphene interfaces with semiconducting transition metal dichalcogenides, leading to strongly anisotropic spin dynamics. As a result, orientation-dependent spin relaxation is observed.
- L. Antonio Benítez
- , Juan F. Sierra
- & Sergio O. Valenzuela
-
News & Views |
 Window of opportunity
Window of opportunity
A crystalline organic semiconductor that combines the long spin-relaxation times of organic semiconductors with the high charge-carrier mobilities typically found in inorganic semiconductors provides unprecedented prospects for organic spintronics.
- Christoph Boehme
-
Review Article |
 Emergent functions of quantum materials
Emergent functions of quantum materials
Topology and collective phenomena give quantum materials emergent functions that provide a platform for developing next-generation quantum technologies, as surveyed in this Review.
- Yoshinori Tokura
- , Masashi Kawasaki
- & Naoto Nagaosa
-
Article |
 Coexistence of ultra-long spin relaxation time and coherent charge transport in organic single-crystal semiconductors
Coexistence of ultra-long spin relaxation time and coherent charge transport in organic single-crystal semiconductors
A linear relationship between spin and momentum relaxation shows that the spin relaxation in an organic semiconductor crystal that has ultra-long spin lifetimes and coherent band-like transport is governed by the Elliott–Yafet mechanism.
- Junto Tsurumi
- , Hiroyuki Matsui
- & Jun Takeya
-
Letter |
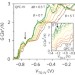 Signatures of interaction-induced helical gaps in nanowire quantum point contacts
Signatures of interaction-induced helical gaps in nanowire quantum point contacts
Signatures of spin–momentum-locked gap states in nanowire quantum point contacts that have all-electrical origin could provide the conditions for the quasiparticle excitations required for topological quantum computing.
- S. Heedt
- , N. Traverso Ziani
- & Th. Schäpers
-
Letter |
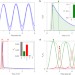 Signatures of two-photon pulses from a quantum two-level system
Signatures of two-photon pulses from a quantum two-level system
An excited two-level system emits a single photon, but in special circumstances it can emit two. The reason for this unexpected two-photon emission lies with modified Rabi oscillations.
- Kevin A. Fischer
- , Lukas Hanschke
- & Kai Müller
-
News & Views |
 The anharmonicity blacksmith
The anharmonicity blacksmith
Anharmonicity is a property of lattice vibrations governing how they interact and how well they conduct heat. Experiments on tin selenide, the most efficient thermoelectric material known, now provide a link between anharmonicity and electronic orbitals.
- Joseph P. Heremans
-
Article |
 Orbitally driven giant phonon anharmonicity in SnSe
Orbitally driven giant phonon anharmonicity in SnSe
Tin selenide is at present the best thermoelectric conversion material. Neutron scattering results and ab initio simulations show that the large phonon scattering is due to the development of a lattice instability driven by orbital interactions.
- C. W. Li
- , J. Hong
- & O. Delaire
-
Letter |
 Orbital textures and charge density waves in transition metal dichalcogenides
Orbital textures and charge density waves in transition metal dichalcogenides
A theoretical and experimental study reveals the relation between charge density waves and orbital textures for different stackings in a two-dimensional layered material.
- T. Ritschel
- , J. Trinckauf
- & J. Geck
-
News & Views |
 Power inequality
Power inequality
Non-reciprocal components are useful in microwave engineering and photonics, but they are not without their drawbacks. A compact design now provides non-reciprocity without resorting to magnets or nonlinearity.
- Ari Sihvola
-
Letter |
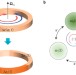 Magnetic-free non-reciprocity and isolation based on parametrically modulated coupled-resonator loops
Magnetic-free non-reciprocity and isolation based on parametrically modulated coupled-resonator loops
Communication systems require non-reciprocal electromagnetic propagation, which is difficult to realize in circuits. An alternative is demonstrated by modulating the phase of strongly coupled resonators in a circular configuration.
- Nicholas A. Estep
- , Dimitrios L. Sounas
- & Andrea Alù
-
-
Article |
 Exotic circuit elements from zero-modes in hybrid superconductor–quantum-Hall systems
Exotic circuit elements from zero-modes in hybrid superconductor–quantum-Hall systems
A superconductor placed near a quantum Hall edge can show emergent excitations with a range of exotic features. For instance, such heterostructures are predicted to exhibit non-local signatures that are direct extensions of ‘Andreev reflection’.
- David J. Clarke
- , Jason Alicea
- & Kirill Shtengel
-
News & Views |
 Orbital control
Orbital control
On cooling, transition metal oxides often undergo a phase change from an electrically conducting to an insulating state. Now it is shown that the metal–insulator transition temperature of vanadium dioxide thin films can be controlled by applying strain.
- Takashi Mizokawa

 Long-lived valley states in bilayer graphene quantum dots
Long-lived valley states in bilayer graphene quantum dots Qubit readout in miniature
Qubit readout in miniature