Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Enterovirus particles expel capsid pentamers to enable genome release
Enterovirus particles expel capsid pentamers to enable genome release
Genome release of enteroviruses relies on exposure to acidic pH, but the mechanism of uncoating remains unclear. Here, Buchta et al. show that echovirus 18 loses one to three adjacent capsid-protein pentamers, resulting in an opening of more than 120 Å for genome release.
- David Buchta
- , Tibor Füzik
- & Pavel Plevka
-
Article
| Open Access Cryo-EM structure of the human ferritin–transferrin receptor 1 complex
Cryo-EM structure of the human ferritin–transferrin receptor 1 complex
The human transferrin receptor 1 (CD71) is a transmembrane protein responsible for iron uptake. Here the authors present the 3.9 Å resolution cryo-EM structure of the CD71 ectodomain-human ferritin (H-Ft) complex and find that H-Ft binds a CD71 region different from the transferrin one that overlaps with the surface recognized by select pathogens.
- Linda Celeste Montemiglio
- , Claudia Testi
- & Beatrice Vallone
-
Article
| Open Access Inner lumen proteins stabilize doublet microtubules in cilia and flagella
Inner lumen proteins stabilize doublet microtubules in cilia and flagella
Microtubules in cilia are sufficiently stable to withstand the beating motion, but how they are stabilized while serving as tracks for intraflagellar transport and axonemal dyneins remains unknown. Here authors identify two microtubule inner proteins, FAP45 and FAP52, which stabilize the ciliary axonemes in Chlamydomonas.
- Mikito Owa
- , Takayuki Uchihashi
- & Masahide Kikkawa
-
Article
| Open Access Cryo-EM fibril structures from systemic AA amyloidosis reveal the species complementarity of pathological amyloids
Cryo-EM fibril structures from systemic AA amyloidosis reveal the species complementarity of pathological amyloids
Systemic AA amyloidosis is caused by misfolding of the acute phase protein serum amyloid A1. Here the authors present the cryo-EM structures of murine and human AA amyloid fibrils that were isolated from tissue samples and describe how the fibrils differ in their fundamental structural properties.
- Falk Liberta
- , Sarah Loerch
- & Matthias Schmidt
-
Article
| Open Access High-resolution structure determination of sub-100 kDa complexes using conventional cryo-EM
High-resolution structure determination of sub-100 kDa complexes using conventional cryo-EM
Despite many recent advances in cryo-EM, imaging smaller macromolecules (below 100 kDa) has remained a challenge. Here the authors show that biological specimens amassing <100 kDa can be resolved to better than 3 Å resolution using conventional defocus-based single-particle analysis methods.
- Mark A. Herzik Jr.
- , Mengyu Wu
- & Gabriel C. Lander
-
Article
| Open Access Tightly-orchestrated rearrangements govern catalytic center assembly of the ribosome
Tightly-orchestrated rearrangements govern catalytic center assembly of the ribosome
In eukaryotes, ribosome biogenesis culminates in the cytoplasm with the maturation of the peptidyl transfer center (PTC). Here the authors describe several structures of intermediates in late nuclear and cytoplasmic maturation of the large ribosomal subunit that reveal the tightly-choreographed sequence of protein and RNA rearrangements that lead to the completion of the PTC.
- Yi Zhou
- , Sharmishtha Musalgaonkar
- & David W. Taylor
-
Article
| Open Access A sequestered fusion peptide in the structure of an HIV-1 transmitted founder envelope trimer
A sequestered fusion peptide in the structure of an HIV-1 transmitted founder envelope trimer
Here, the authors present the structure of the HIV envelope (Env) protein from a transmitted founder virus and show that, while the overall structure of the Env trimer is similar to other closed trimers, the fusion peptide is buried in the hydrophobic core of the trimer, which is similar to open state trimers.
- Neeti Ananthaswamy
- , Qianglin Fang
- & Venigalla B. Rao
-
Article
| Open Access The structure of a prokaryotic viral envelope protein expands the landscape of membrane fusion proteins
The structure of a prokaryotic viral envelope protein expands the landscape of membrane fusion proteins
Lipid membrane fusion is an essential function in many biological processes but little is known about membrane fusion in prokaryotes. The authors here study how haloarchaeal pleomorphic viruses (HRPVs) infect archaeal hosts. The structure-function analysis of the spike proteins shed light on prokaryotic membrane fusion.
- Kamel El Omari
- , Sai Li
- & Elina Roine
-
Article
| Open Access Chaperone activation and client binding of a 2-cysteine peroxiredoxin
Chaperone activation and client binding of a 2-cysteine peroxiredoxin
Many 2-Cystein Peroxiredoxins (Prx) can either function as peroxidases or chaperones when exposed to stress. Here the authors present the structures of Leishmania infantum mitochondrial Prx alone and with a bound model client protein, use crosslinking to reveal interaction regions that stabilize the bound client, and provide insights into the mechanism by which Prx’s adopt chaperone activity.
- Filipa Teixeira
- , Eric Tse
- & Ursula Jakob
-
Article
| Open Access Cryo-EM structure of the homohexameric T3SS ATPase-central stalk complex reveals rotary ATPase-like asymmetry
Cryo-EM structure of the homohexameric T3SS ATPase-central stalk complex reveals rotary ATPase-like asymmetry
Many Gram-negative bacteria rely on a type III secretion system (T3SS) for their pathogenicity. Here authors present the cryo-EM structure of the E.coli T3SS ATPase-central stalk complex, which forms a homohexameric, asymmetric pore with different functional states.
- Dorothy D. Majewski
- , Liam J. Worrall
- & Natalie C. J. Strynadka
-
Article
| Open Access Cryo-EM structure of the essential ribosome assembly AAA-ATPase Rix7
Cryo-EM structure of the essential ribosome assembly AAA-ATPase Rix7
Rix7 is a type II AAA-ATPase that is required for the assembly of the large ribosomal subunit. Here the authors present the 4.5 Å cryo-EM structure of the Rix7 homohexamer with a polypeptide fragment bound in its central channel and provide insights into the function of Rix7 as a molecular unfoldase.
- Yu-Hua Lo
- , Mack Sobhany
- & Robin E. Stanley
-
Article
| Open Access Near-atomic structure of a giant virus
Near-atomic structure of a giant virus
Nucleocytoplasmic large DNA viruses are a group of viruses that infect many eukaryotic hosts. Here, the authors provide a 3.5 Å resolution icosahedrally-averaged capsid structure of Paramecium bursaria chlorella virus 1 and show how 1800 minor capsid proteins form a hexagonal network below the outer capsid shell.
- Qianglin Fang
- , Dongjie Zhu
- & Michael G. Rossmann
-
Article
| Open Access Correlative cryo-electron microscopy reveals the structure of TNTs in neuronal cells
Correlative cryo-electron microscopy reveals the structure of TNTs in neuronal cells
The architecture of functional TNTs is still under debate. Here, the authors combine correlative FIB-SEM, light- and cryo-electron microscopy approaches to elucidate the structure of TNTs in neuronal cells, showing that they form structures that are distinct form other membrane protrusions.
- Anna Sartori-Rupp
- , Diégo Cordero Cervantes
- & Chiara Zurzolo
-
Article
| Open Access Structure of transcribing RNA polymerase II-nucleosome complex
Structure of transcribing RNA polymerase II-nucleosome complex
Eukaryotic transcription requires passage of RNA polymerase II (Pol II) through chromatin, which is impaired by nucleosomes. Here the authors report the cryo-EM structure of transcribing Pol II engaged with a downstream nucleosome core particle at an overall resolution of 4.4 Å, providing insights into the mechanism of chromatin transcription.
- Lucas Farnung
- , Seychelle M. Vos
- & Patrick Cramer
-
Article
| Open Access Structure of the type VI secretion system TssK–TssF–TssG baseplate subcomplex revealed by cryo-electron microscopy
Structure of the type VI secretion system TssK–TssF–TssG baseplate subcomplex revealed by cryo-electron microscopy
Type VI secretion systems (T6SSs) translocate effector proteins into eukaryotic and bacterial recipient cells and are present in many Gram-negative bacteria. Here the authors present the 3.7 Å cryoEM structure of the E.coli T6SS baseplate wedge comprising TssK–TssF–TssG and propose a model for the T6SS baseplate and needle complex.
- Young-Jun Park
- , Kaitlyn D. Lacourse
- & David Veesler
-
Article
| Open Access CryoEM reveals how the complement membrane attack complex ruptures lipid bilayers
CryoEM reveals how the complement membrane attack complex ruptures lipid bilayers
The complement membrane attack complex (MAC) is a lytic immune pore that kills pathogens. Here the authors use cryoEM to provide a structural and biophysical mechanism for how β-pore forming proteins breach the lipid bilayer, providing pathways to explore pore-formation in molecular detail.
- Anaïs Menny
- , Marina Serna
- & Doryen Bubeck
-
Article
| Open Access Implication for alphavirus host-cell entry and assembly indicated by a 3.5Å resolution cryo-EM structure
Implication for alphavirus host-cell entry and assembly indicated by a 3.5Å resolution cryo-EM structure
Alphaviruses are enveloped RNA viruses that contain several human pathogens. Here, the authors use block-based reconstruction method and provide a 3.5 Å cryo-EM structure of sindbis virus that identifies a conserved hydrophobic pocket near the viral membrane that is stabilized by an unknown pocket factor.
- Lihong Chen
- , Ming Wang
- & Xinzheng Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Structural assembly of the megadalton-sized receptor for intestinal vitamin B12 uptake and kidney protein reabsorption
Structural assembly of the megadalton-sized receptor for intestinal vitamin B12 uptake and kidney protein reabsorption
Cubilin and the transmembrane protein amnionless (AMN) form the endocytic receptor cubam that is essential for intestinal vitamin B12 uptake. Here the authors present the 2.3 Å crystal structure of AMN in complex with the amino-terminal region of cubilin and discuss cubam architecture and disease causing mutations.
- Casper Larsen
- , Anders Etzerodt
- & Christian Brix Folsted Andersen
-
Article
| Open Access Subcellular connectomic analyses of energy networks in striated muscle
Subcellular connectomic analyses of energy networks in striated muscle
Assessing biological circuit connections in single cells has been intractable due to lack of appropriate tools. Here, Bleck et al. develop a method to assess mitochondrial network connectivity in muscle cells and observe clear differences consistent with differing energy requirements.
- Christopher K. E. Bleck
- , Yuho Kim
- & Brian Glancy
-
Article
| Open Access Structure of the hyperosmolality-gated calcium-permeable channel OSCA1.2
Structure of the hyperosmolality-gated calcium-permeable channel OSCA1.2
In plants, hyperosmolality stimuli triggers opening of the osmosensitive channels, leading to a rapid downstream signaling cascade. Here, the authors solve the cryo-EM structure of an osmosensitive channel from Arabidopsis OSCA1.2 in its inactivated state.
- Xin Liu
- , Jiawei Wang
- & Linfeng Sun
-
Article
| Open Access Cryo-EM structures of KdpFABC suggest a K+ transport mechanism via two inter-subunit half-channels
Cryo-EM structures of KdpFABC suggest a K+ transport mechanism via two inter-subunit half-channels
The P-type ATPase subunit KdpB of KdpFABC hydrolyzes ATP while K+ transport was assumed to occur through channel-like subunit KdpA. Here, the authors show two cryo-EM structures of KdpFABC which suggest a translocation pathway through two inter-subunit half-channels formed by KdpA and KdpB.
- C. Stock
- , L. Hielkema
- & I. Hänelt
-
Article
| Open Access Structures of Coxsackievirus A10 unveil the molecular mechanisms of receptor binding and viral uncoating
Structures of Coxsackievirus A10 unveil the molecular mechanisms of receptor binding and viral uncoating
The disease-causing pathogen Coxsackievirus A10 (CVA10) is a human type-A Enterovirus. Here the authors present the cryo-EM structures of the mature CVA10 virion and the empty- and A-particles of CVA10, which is of interest for CVA10 vaccine development.
- Ling Zhu
- , Yao Sun
- & Xiangxi Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis of RIP2 activation and signaling
Structural basis of RIP2 activation and signaling
The pathogen recognition receptors NOD1/2 recognize bacterial cell wall components and signal through their downstream adapter kinase RIP2 via a CARD (Caspase activation and recruitment domain) mediated oligomerization process. Here the authors present the cryo-EM structure of the active RIP2-CARD filament and discuss implications for NOD1/2-RIP2 signalling.
- Qin Gong
- , Ziqi Long
- & Bin Wu
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular structure of promoter-bound yeast TFIID
Molecular structure of promoter-bound yeast TFIID
Transcription preinitiation complex assembly begins with the recognition of the gene promoter by the TATA-box Binding Protein-containing TFIID complex. Here the authors present a Cryo-EM structure of promoter-bound yeast TFIID complex, providing a detailed view of its subunit organization and promoter DNA contacts.
- Olga Kolesnikova
- , Adam Ben-Shem
- & Gabor Papai
-
Article
| Open Access The structure of a β2-microglobulin fibril suggests a molecular basis for its amyloid polymorphism
The structure of a β2-microglobulin fibril suggests a molecular basis for its amyloid polymorphism
Impaired kidney function can lead to an increase of β2-microglobulin (β2m) serum levels, which can cause β2m aggregation and amyloid fibril formation. Here the authors combine cryo-EM and magic angle spinning NMR measurements to determine the structure of a β2m fibril and they also present the low resolution model of a β2m fibril with a different morphology.
- Matthew G. Iadanza
- , Robert Silvers
- & Sheena E. Radford
-
Article
| Open Access The signalling conformation of the insulin receptor ectodomain
The signalling conformation of the insulin receptor ectodomain
The insulin receptor plays a key role in many physiological processes, yet how insulin effects receptor signaling at the structural level remains incomplete. Here the authors present a high-resolution cryo-EM structure of a high-affinity form of the insulin-bound insulin receptor ectodomain that sheds light on the mechanism of signal transduction.
- Felix Weis
- , John G. Menting
- & Michael C. Lawrence
-
Article
| Open Access Cryo-EM structures of human STEAP4 reveal mechanism of iron(III) reduction
Cryo-EM structures of human STEAP4 reveal mechanism of iron(III) reduction
Enzymes of the six-transmembrane epithelial antigen of the prostate (STEAP) family reduce Fe3+ and Cu2+ ions to facilitate metal-ion uptake by mammalian cells. Here, authors employ single-particle cryo-EM to gain insights into the molecular principles of iron reduction by human STEAP4 .
- Wout Oosterheert
- , Laura S. van Bezouwen
- & Piet Gros
-
Article
| Open Access Structural insights on TRPV5 gating by endogenous modulators
Structural insights on TRPV5 gating by endogenous modulators
TRPV5 is a kidney specific transient receptor potential (TRP) channel with an important role in calcium reabsorption. Here the authors provide mechanistic insights into TRPV5 modulation by determining the phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate and calmodulin bound TRPV5 cryo-EM structures.
- Taylor E. T. Hughes
- , Ruth A. Pumroy
- & Vera Y. Moiseenkova-Bell
-
Article
| Open Access Cryo-EM structure of the hibernating Thermus thermophilus 100S ribosome reveals a protein-mediated dimerization mechanism
Cryo-EM structure of the hibernating Thermus thermophilus 100S ribosome reveals a protein-mediated dimerization mechanism
During stress conditions bacterial ribosomes dimerize and form inactive but stable hibernating 100S particles, a process that is facilitated by the hibernation-promoting factor (HPF). Here the authors analyze 100S dimer formation as a function of HPF protein concentration and present the Thermus thermophilus 100S ribosome cryo-EM structure.
- Rasmus Kock Flygaard
- , Niels Boegholm
- & Lasse B. Jenner
-
Article
| Open Access Subtomogram averaging of COPII assemblies reveals how coat organization dictates membrane shape
Subtomogram averaging of COPII assemblies reveals how coat organization dictates membrane shape
The COPII coat assembles in two concentric layers and mediates protein export from the endoplasmic reticulum. Here the authors present the 4.9 Å resolution cryo-tomography and subtomogram averaging structure of the membrane bound COPII inner coat that was obtained by in vitro reconstitution and discuss mechanistic implications.
- Joshua Hutchings
- , Viktoriya Stancheva
- & Giulia Zanetti
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular architecture and regulation of BCL10-MALT1 filaments
Molecular architecture and regulation of BCL10-MALT1 filaments
The BCL10-MALT1 complex is a central signaling hub in lymphocytes and linked to various human immune pathologies. Here the authors present the cryo-EM structure of the BCL10-MALT1 filament core and verify the identified BCL10/MALT1 interface with mutagenesis studies.
- Florian Schlauderer
- , Thomas Seeholzer
- & Katja Lammens
-
Article
| Open Access RIP2 filament formation is required for NOD2 dependent NF-κB signalling
RIP2 filament formation is required for NOD2 dependent NF-κB signalling
Binding of bacterial peptidoglycan muramyl dipeptides induces NOD2 activation and signalling via the downstream adaptor kinase RIP2. Here the authors show that RIP2 forms filaments via its CARD domain, analyse the structure of the CARD filaments and demonstrate the requirement of RIP2 polymerisation for the activation of NF-κB by NOD2.
- Erika Pellegrini
- , Ambroise Desfosses
- & Stephen Cusack
-
Article
| Open Access Structure of Type-I Mycobacterium tuberculosis fatty acid synthase at 3.3 Å resolution
Structure of Type-I Mycobacterium tuberculosis fatty acid synthase at 3.3 Å resolution
The type-I fatty acid synthase (FAS-I) complex is essential for Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) and mediates the production of C26 fatty acids that are precursors for the synthesis of mycolic acids. Here the authors present the 3.3 Å resolution cryo-EM structure of Mtb FAS-I, which is of interest for tuberculosis drug development.
- Nadav Elad
- , Szilvia Baron
- & Ron Diskin
-
Article
| Open Access Cryo-EM analysis of the T3S injectisome reveals the structure of the needle and open secretin
Cryo-EM analysis of the T3S injectisome reveals the structure of the needle and open secretin
The bacterial type III secretion system of Gram-negative bacteria uses its core, the needle complex, to penetrate through the infected host cell membrane. Here authors show a near-atomic resolution structure of a needle complex which sheds light on the assembly and function of this nanomachine.
- J. Hu
- , L. J. Worrall
- & N. C. J. Strynadka
-
Article
| Open Access Development of an antibody fragment that stabilizes GPCR/G-protein complexes
Development of an antibody fragment that stabilizes GPCR/G-protein complexes
The determination of high resolution structures of G protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) in complex with heterotrimeric G proteins is challenging. Here authors develop an antibody fragment, mAB16, which stabilizes GPCR/G-protein complexes and facilitates the application of high resolution cryo-EM.
- Shoji Maeda
- , Antoine Koehl
- & Brian K. Kobilka
-
Article
| Open Access Structure of the herpes simplex virus type 2 C-capsid with capsid-vertex-specific component
Structure of the herpes simplex virus type 2 C-capsid with capsid-vertex-specific component
Herpes simplex virus type-2 (HSV-2) belongs to the α-herpesvirinae subfamily and is a sexually transmitted virus that causes genital ulcer disease. Here the authors present the 3.75 Å cryo-EM structure of the HSV-2 C-capsid with capsid-vertex-specific component and describe α-herpesvirus-specific structural features.
- Jialing Wang
- , Shuai Yuan
- & Xiangxi Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Sub-2 Å Ewald curvature corrected structure of an AAV2 capsid variant
Sub-2 Å Ewald curvature corrected structure of an AAV2 capsid variant
Single-particle cryo-EM is a powerful method for macromolecular structure determination. Here the authors demonstrate that Ewald sphere curvature correction, sub-Angstrom pixilation and per-particle CTF refinement can improve map quality and resolution and present the 1.86 Å cryo-EM structure of an adeno-associated virus serotype 2 variant.
- Yong Zi Tan
- , Sriram Aiyer
- & Dmitry Lyumkis
-
Article
| Open Access Structure of the human plasma membrane Ca2+-ATPase 1 in complex with its obligatory subunit neuroplastin
Structure of the human plasma membrane Ca2+-ATPase 1 in complex with its obligatory subunit neuroplastin
The plasma membrane Ca2+ ATPase (PMCA) is essential for maintaining Ca2+ homeostasis in eukaryotic cells, and neuroplastin (NPTN) was recently identified as an obligatory subunit of PMCA. Here the authors present the cryo-EM structure of NPTN bound to human PMCA1, which reveals that the NPTN transmembrane (TM) helix interacts with TM10 and the TM8-9-linker of PMCA1.
- Deshun Gong
- , Ximin Chi
- & Qiang Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access Cryo-EM of full-length α-synuclein reveals fibril polymorphs with a common structural kernel
Cryo-EM of full-length α-synuclein reveals fibril polymorphs with a common structural kernel
The intrinsically disordered protein alpha-synuclein (aSyn) forms polymorphic fibrils. Here the authors provide molecular insights into aSyn fibril polymorphism and present the cryo-EM structures of the two predominant species, a rod and a twister both determined at 3.7 Å resolution.
- Binsen Li
- , Peng Ge
- & Lin Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access Structural conservation in a membrane-enveloped filamentous virus infecting a hyperthermophilic acidophile
Structural conservation in a membrane-enveloped filamentous virus infecting a hyperthermophilic acidophile
Only a few archaeal filamentous viruses have been structurally characterized. Here the authors describe the membrane-enveloped Sulfolobus filamentous virus 1 that infects Sulfolobus shibatae and present its 3.7 Å resolution cryo-EM structure, which reveals that major coat proteins are structurally conserved among archaeal filamentous viruses.
- Ying Liu
- , Tomasz Osinski
- & Edward H. Egelman
-
Article
| Open Access The first transmembrane region of complement component-9 acts as a brake on its self-assembly
The first transmembrane region of complement component-9 acts as a brake on its self-assembly
The Complement component 9 (C9) is the pore-forming component of the Membrane Attack Complex which targets pathogens. Here authors use structural biology to compare monomeric C9 to C9 within the polymeric assembly and identify the element which inhibits C9 self-assembly in the absence of the target membrane.
- Bradley A. Spicer
- , Ruby H. P. Law
- & Michelle A. Dunstone
-
Article
| Open Access Structure of the mouse TRPC4 ion channel
Structure of the mouse TRPC4 ion channel
Members of the transient receptor potential (TRP) ion channels conduct cations into cells upon activation by a variety of signals. Here authors present the cryo-EM structure of TRPC4 in its unliganded (apo) state, which provides molecular insights into TRPC4's ion selectivity and TPR channel evolution.
- Jingjing Duan
- , Jian Li
- & Jin Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Visualization of translation termination intermediates trapped by the Apidaecin 137 peptide during RF3-mediated recycling of RF1
Visualization of translation termination intermediates trapped by the Apidaecin 137 peptide during RF3-mediated recycling of RF1
In bacteria, the process of translation termination is performed by three termination release factors RF1, RF2 and RF3. Here the authors provide detailed structural insights into the mechanism by which RF1 is dissociated from the ribosome by RF3 during termination.
- Michael Graf
- , Paul Huter
- & Daniel N. Wilson
-
Article
| Open Access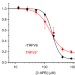 Structural bases of TRP channel TRPV6 allosteric modulation by 2-APB
Structural bases of TRP channel TRPV6 allosteric modulation by 2-APB
The transient receptor potential channel TRPV6 mediates calcium uptake in epithelia and its expression is increased in several cancer types. Here, authors present structures of TRPV6 bound to 2-APB, a TRPV6 inhibitor, and show that 2-APB induces TRPV6 channel closure by modulating protein–lipid interactions.
- Appu K. Singh
- , Kei Saotome
- & Alexander I. Sobolevsky
-
Article
| Open Access The 3.3 Å structure of a plant geminivirus using cryo-EM
The 3.3 Å structure of a plant geminivirus using cryo-EM
Geminiviruses are an important plant pathogen that causes large food crop losses globally. Here the authors describe a high resolution cryo-EM structure of the Ageratum yellow vein virus and reveal the molecular details of how a single capsid protein sequence can adopt the different conformations needed to build that geminate capsid.
- Emma L. Hesketh
- , Keith Saunders
- & Neil A. Ranson
-
Article
| Open Access In situ architecture of the algal nuclear pore complex
In situ architecture of the algal nuclear pore complex
While the architecture of vertebrate nuclear pore complexes (NPCs) is well understood, the extent of its evolutionary conservation is still unclear. Here, the authors analyze the in situ architecture of an algal NPC, revealing distinct structural features that provide insights into NPC evolution.
- Shyamal Mosalaganti
- , Jan Kosinski
- & Martin Beck
-
Article
| Open Access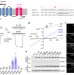 Hydrophobic pore gates regulate ion permeation in polycystic kidney disease 2 and 2L1 channels
Hydrophobic pore gates regulate ion permeation in polycystic kidney disease 2 and 2L1 channels
Mutations in the cation channel PKD2 cause human autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease but its channel function and gating mechanism are poorly understood. Here authors study PKD2 using electrophysiology and cryo-EM, which identifies hydrophobic gates and proposes a gating mechanism for PKD2.
- Wang Zheng
- , Xiaoyong Yang
- & Xing-Zhen Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis for cofilin binding and actin filament disassembly
Structural basis for cofilin binding and actin filament disassembly
Cofilin is a small actin-binding protein that accelerates actin turnover by disassembling actin filaments. Here the authors present the 3.8 Å cryo-EM structure of a cofilin-decorated actin filament and discuss mechanistic implications.
- Kotaro Tanaka
- , Shuichi Takeda
- & Akihiro Narita
-
Article
| Open Access Structure and mechanism of the two-component α-helical pore-forming toxin YaxAB
Structure and mechanism of the two-component α-helical pore-forming toxin YaxAB
The Yersinia YaxAB system is a pore-forming toxin of so far unknown structure. Here authors present X-ray and cryo-EM to structures of individual subunits and of the YaxAB pore complex, and find that YaxA binds to membranes first and recruits YaxB for subsequent oligomerization.
- Bastian Bräuning
- , Eva Bertosin
- & Michael Groll

 CryoEM structure of adenovirus type 3 fibre with desmoglein 2 shows an unusual mode of receptor engagement
CryoEM structure of adenovirus type 3 fibre with desmoglein 2 shows an unusual mode of receptor engagement