Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access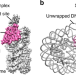 Nucleosome and ubiquitin position Set2 to methylate H3K36
Nucleosome and ubiquitin position Set2 to methylate H3K36
Set2 methyltransferase catalyzes the lysine 36 methylation of histone H3 (H3K36me) and the enzyme is mutated in many cancers. The authors provide mechanistic insights into how Set2 methylates nucleosomes by determining the 3.8 Å cryo-EM structure of Set2 bound to a H2B ubiquitinated nucleosome core particle.
- Silvija Bilokapic
- & Mario Halic
-
Article
| Open Access Atomic structure of PI3-kinase SH3 amyloid fibrils by cryo-electron microscopy
Atomic structure of PI3-kinase SH3 amyloid fibrils by cryo-electron microscopy
The Src-homology 3 domain of phosphatidyl-inositol-3-kinase (PI3K-SH3) is a model system for studying amyloid fibril formation. Here the authors present the 3.4 Å cryo-EM structure of the PI3K-SH3 amyloid fibril, which allows them to rationalize the effects of mutations on the kinetics of fibril formation.
- Christine Röder
- , Nicola Vettore
- & Gunnar F. Schröder
-
Article
| Open Access Divergent engagements between adeno-associated viruses with their cellular receptor AAVR
Divergent engagements between adeno-associated viruses with their cellular receptor AAVR
Multiple adeno-associated viruses (AAV) use the same receptor (AAVR), but the binding mode is not clear. Here, the authors determine the structures of the AAV1-AAVR and AAV5-AAVR complexes, identify residues necessary for virus entry and compare the receptor interfaces of different AAV capsids.
- Ran Zhang
- , Guangxue Xu
- & Zhiyong Lou
-
Article
| Open Access Visualizing structural transitions of ligand-dependent gating of the TRPM2 channel
Visualizing structural transitions of ligand-dependent gating of the TRPM2 channel
The transient receptor potential channel member 2 (TRPM2) ion channel has a function in redox-dependent signaling. Here the authors present the cryo-EM structures of zebrafish TRPM2 in the ligand-free form, with Ca2+ and both ADP-ribose/Ca2+ and observe two-fold symmetric quaternary structure rearrangements in the ligand-bound structures that likely represent intermediate gating states.
- Ying Yin
- , Mengyu Wu
- & Seok-Yong Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Structures of T7 bacteriophage portal and tail suggest a viral DNA retention and ejection mechanism
Structures of T7 bacteriophage portal and tail suggest a viral DNA retention and ejection mechanism
The genome of double-stranded DNA bacteriophages is delivered to host cells through the viral portal and tail structures. Here the authors describe structures of the bacteriophage T7 portal and the 1.5 MDa tail complex formed by the portal protein, adaptor protein and nozzle, providing insight into how the portal and tail machinery work during DNA packaging and ejection.
- Ana Cuervo
- , Montserrat Fàbrega-Ferrer
- & Miquel Coll
-
Article
| Open Access A one-gate elevator mechanism for the human neutral amino acid transporter ASCT2
A one-gate elevator mechanism for the human neutral amino acid transporter ASCT2
How the human Alanine Serine Cysteine Transporter 2 (ASCT2) binds its substrates, neutral amino acids, and releases them on the cytoplasmic side remains unclear. Here authors present an inward-open structure of the human ASCT2 which shows that a hairpin serves as a gate in the inward-facing state.
- Alisa A. Garaeva
- , Albert Guskov
- & Cristina Paulino
-
Article
| Open Access Structure of amyloid-β (20-34) with Alzheimer’s-associated isomerization at Asp23 reveals a distinct protofilament interface
Structure of amyloid-β (20-34) with Alzheimer’s-associated isomerization at Asp23 reveals a distinct protofilament interface
In patients with sporadic Alzheimer’s disease part of the Asp23 residues are isomerized to L-isoaspartate (L-isoAsp23). Here the authors present the MicroED structures of wild-type and L-isoAsp23 Aβ 20–34 amyloid fibrils that both form tightly packed cores and self-associate through two distinct interfaces with one of these interfaces being strengthened by the isoaspartyl modification.
- Rebeccah A. Warmack
- , David R. Boyer
- & Steven G. Clarke
-
Article
| Open Access The AAA + ATPase TorsinA polymerizes into hollow helical tubes with 8.5 subunits per turn
The AAA + ATPase TorsinA polymerizes into hollow helical tubes with 8.5 subunits per turn
Torsins are unusual AAA + ATPases of unknown function that reside in the endoplasmic reticulum of all animals. Here the authors report that TorsinA forms tubular helical filaments with an unusual periodicity and that filamentous TorsinA directly interacts with membranes to form tubular protrusions.
- F. Esra Demircioglu
- , Weili Zheng
- & Thomas U. Schwartz
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular mechanism of setron-mediated inhibition of full-length 5-HT3A receptor
Molecular mechanism of setron-mediated inhibition of full-length 5-HT3A receptor
Serotonin receptors (5-HT3R) belong to the pentameric ligand-gated ion channel superfamily and mediate excitatory postsynaptic signaling. Here the authors present the high-resolution cryo-EM structure of 5-HT3AR bound with the competitive antagonist granisetron and further validate the granisetron-binding mode with electrophysiology measurements and MD simulations.
- Sandip Basak
- , Yvonne Gicheru
- & Sudha Chakrapani
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis for the adsorption of a single-stranded RNA bacteriophage
Structural basis for the adsorption of a single-stranded RNA bacteriophage
Single-stranded RNA bacteriophages use a single maturation protein (Mat) to attach to a retractile pilus of the bacterial host. Here, the authors report the structures of the MS2 phage bound to the host receptor F-pili and define the orientations of Mat relative to the cell and emanating F-pili, providing new insights into the F-like type IV secretion systems.
- Ran Meng
- , Mengqiu Jiang
- & Junjie Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis for transcription antitermination at bacterial intrinsic terminator
Structural basis for transcription antitermination at bacterial intrinsic terminator
Bacteriophages reprogram the host transcriptional machinery. Here the authors provide insights into the mechanism of how bacteriophages regulate host transcription by determining the cryo-EM structures of two bacterial transcription elongation complexes bound with the bacteriophage master host-transcription regulator protein P7.
- Linlin You
- , Jing Shi
- & Yu Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Structures of autoinhibited and polymerized forms of CARD9 reveal mechanisms of CARD9 and CARD11 activation
Structures of autoinhibited and polymerized forms of CARD9 reveal mechanisms of CARD9 and CARD11 activation
CARD9 and CARD11 propagate signaling by nucleating Bcl10 polymerization in immune cells and are both held in an autoinhibited state prior to activation. Here, the authors combine structural, biochemical, and cell-based approaches to reveal the structural basis for CARD9/11 autoinhibition and show that the two proteins are activated through similar but distinct mechanisms.
- Michael J. Holliday
- , Axel Witt
- & Wayne J. Fairbrother
-
Article
| Open Access Structure-based mechanism for activation of the AAA+ GTPase McrB by the endonuclease McrC
Structure-based mechanism for activation of the AAA+ GTPase McrB by the endonuclease McrC
McrBC is a bacterial antiphage defense system that cleaves methylated DNA and is composed of the AAA+ GTPase motor McrB and the endonuclease McrC. Here, the authors present the cryo-EM structure of E. coli McrBC that reveals how McrC inserts a stalk-like structure into the pore of the ring-shaped McrB hexamer and discuss mechanistic implications.
- Neha Nirwan
- , Yuzuru Itoh
- & Kayarat Saikrishnan
-
Article
| Open Access Lamin A molecular compression and sliding as mechanisms behind nucleoskeleton elasticity
Lamin A molecular compression and sliding as mechanisms behind nucleoskeleton elasticity
Lamin A is critical for nuclear architecture but its structure and assembly are not fully understood. Here, the authors use quantitative cross-linking mass spectrometry to map intra- and intermolecular interactions within lamin homomers, providing insights into the molecular basis for lamin’s mechanical properties.
- Alex A. Makarov
- , Juan Zou
- & Eric C. Schirmer
-
Article
| Open Access The cryo-electron microscopy supramolecular structure of the bacterial stressosome unveils its mechanism of activation
The cryo-electron microscopy supramolecular structure of the bacterial stressosome unveils its mechanism of activation
The bacterial stressosome is a large nanomachine and a key inducer of stress response. Here, the authors present the cryo-EM structure of the stressosome from the bacterial pathogen Listeria monocytogenes at 3.38 Å resolution and discuss its activation mechanism.
- Allison H. Williams
- , Adam Redzej
- & Pascale Cossart
-
Article
| Open Access Target preference of Type III-A CRISPR-Cas complexes at the transcription bubble
Target preference of Type III-A CRISPR-Cas complexes at the transcription bubble
Type III CRISPR-Cas systems are able to target transcriptionally active DNA sequences in phages and plasmids. Here, the authors reveal the mechanism of the target nucleic acid preference of Type III-A CRISPR-Cas complexes at the transcription bubble by a combination of structural and biochemical approaches.
- Tina Y. Liu
- , Jun-Jie Liu
- & Jennifer A. Doudna
-
Article
| Open Access Impact of ocean acidification on crystallographic vital effect of the coral skeleton
Impact of ocean acidification on crystallographic vital effect of the coral skeleton
Coral fossils can record climatic history, but teasing apart environmental signals remains a challenge. Here the authors show that crystallographic changes in coral skeletons grown under high CO2 conditions could be used as a sensitive pH proxy, enabling measurement of ocean acidification back in time.
- Ismael Coronado
- , Maoz Fine
- & Jarosław Stolarski
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis of TFIIH activation for nucleotide excision repair
Structural basis of TFIIH activation for nucleotide excision repair
The NER machinery contains the multisubunit transcription factor IIH (TFIIH) that opens the DNA repair bubble, scans for the lesion, and coordinates excision of the damaged site. Here the authors resolve the cryo-electron microscopy structure of the human core TFIIH-XPA-DNA complex and provide insights into its activation.
- Goran Kokic
- , Aleksandar Chernev
- & Patrick Cramer
-
Article
| Open Access Structural and functional analysis of the role of the chaperonin CCT in mTOR complex assembly
Structural and functional analysis of the role of the chaperonin CCT in mTOR complex assembly
β-propeller domains are an important class of folding substrates for the eukaryotic cytosolic chaperonin CTT. Here the authors find that CTT contributes to the folding and assembly of two β-propeller proteins from mTOR complexes, mLST8 and Raptor, and determine the 4.0 Å cryoEM structure of a human mLST8-CCT intermediate that shows mLST8 in a near-native state.
- Jorge Cuéllar
- , W. Grant Ludlam
- & José M. Valpuesta
-
Article
| Open Access Structure of the substrate-engaged SecA-SecY protein translocation machine
Structure of the substrate-engaged SecA-SecY protein translocation machine
Proteins are translocated across membranes through the Sec61/SecY channel. Here, the authors present the structure of a translocating peptide chain trapped inside the SecA-SecY complex which suggests how peptides are actively moved through the channel.
- Chengying Ma
- , Xiaofei Wu
- & Long Li
-
Article
| Open Access The structure of a 15-stranded actin-like filament from Clostridium botulinum
The structure of a 15-stranded actin-like filament from Clostridium botulinum
The plasmid-segregating actin-like protein ParM is encoded on the large, toxin carrying plasmid pCBH from Clostridium botulinum. Here the authors present the cryo-EM structure of the ParM filament that is formed from the association of 15 protofilaments and discuss its architecture.
- Fujiet Koh
- , Akihiro Narita
- & Robert C. Robinson
-
Article
| Open Access Conformational proofreading of distant 40S ribosomal subunit maturation events by a long-range communication mechanism
Conformational proofreading of distant 40S ribosomal subunit maturation events by a long-range communication mechanism
The biogenesis of eukaryotic ribosomes is a multi-step process involving the action of more than 200 different ribosome assembly factors. Here the authors show that Rps20 acts as a conduit to coordinate maturation steps across the head domain of the nascent small ribosomal subunit.
- Valentin Mitterer
- , Ramtin Shayan
- & Brigitte Pertschy
-
Article
| Open Access Integrated NMR and cryo-EM atomic-resolution structure determination of a half-megadalton enzyme complex
Integrated NMR and cryo-EM atomic-resolution structure determination of a half-megadalton enzyme complex
NMR structure determination is challenging for proteins with a molecular weight above 30 kDa and atomic-resolution structure determination from cryo-EM data is currently not the rule. Here the authors describe an integrated structure determination approach that simultaneously uses NMR and EM data and allows them to determine the structure of the 468 kDa dodecameric aminopeptidase TET2 complex.
- Diego F. Gauto
- , Leandro F. Estrozi
- & Jerome Boisbouvier
-
Article
| Open Access In situ structure and assembly of the multidrug efflux pump AcrAB-TolC
In situ structure and assembly of the multidrug efflux pump AcrAB-TolC
Multidrug efflux pumps actively expel a wide range of toxic substrates from bacteria and play a major role in drug resistance. Here authors show the in situ structure of the efflux pump AcrAB-TolC obtained by electron cryo-tomography and subtomogram averaging.
- Xiaodong Shi
- , Muyuan Chen
- & Zhao Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis for the inhibition of translation through eIF2α phosphorylation
Structural basis for the inhibition of translation through eIF2α phosphorylation
During stress, protein synthesis is inhibited through phosphorylation of the initiation factor eIF2 on its alpha subunit and its interaction with eIF2B. Here the authors describe a structure of the yeast eIF2B in complex with its substrate - the GDP-bound phosphorylated eIF2, providing insights into how phosphorylation results in a tighter interaction with eIF2B.
- Yuliya Gordiyenko
- , José Luis Llácer
- & V. Ramakrishnan
-
Article
| Open Access The pore structure of Clostridium perfringens epsilon toxin
The pore structure of Clostridium perfringens epsilon toxin
Epsilon toxin (Etx) is a potent pore forming toxin (PFT) produced by Clostridium perfringens. Here authors show the cryo-EM structure of the Etx pore assembled on the membrane of susceptible cells and shed light on pore formation and mutant phenotypes.
- Christos G. Savva
- , Alice R. Clark
- & Monika Bokori-Brown
-
Article
| Open Access Convergent allostery in ribonucleotide reductase
Convergent allostery in ribonucleotide reductase
Ribonucleotide reductase (RNR) catalyzes the conversion of ribonucleotides to deoxyribonucleotides, which is an essential step in DNA synthesis. Here the authors use small-angle X-ray scattering, X-ray crystallography, and cryo-electron microscopy to capture active and inactive forms of the Bacillus subtilis RNR and provide mechanistic insights into a convergent form of allosteric regulation.
- William C. Thomas
- , F. Phil Brooks III
- & Nozomi Ando
-
Article
| Open Access Cryo-electron microscopy structure of an archaeal ribonuclease P holoenzyme
Cryo-electron microscopy structure of an archaeal ribonuclease P holoenzyme
Ribonulease P is a conserved ribozyme present in all kingdoms of life that is involved in the 5′ maturation step of tRNAs. Here the authors determine the structure of an archaeal RNase P holoenzyme that reveals how archaeal RNase P recognizes its tRNA substrate and suggest a conserved catalytic mechanism amongst RNase Ps despite structural variability.
- Futang Wan
- , Qianmin Wang
- & Ming Lei
-
Article
| Open Access The structural basis for release-factor activation during translation termination revealed by time-resolved cryogenic electron microscopy
The structural basis for release-factor activation during translation termination revealed by time-resolved cryogenic electron microscopy
Translation termination is under strong selection pressure for high speed and accuracy. Here the authors provide a 3D view of the dynamics of a translating bacterial ribosome as it recruits a class-1 release factor (RF1 or RF2) upon encountering a stop codon, and propose a structure-based kinetic model for the early steps in bacterial translation termination.
- Ziao Fu
- , Gabriele Indrisiunaite
- & Joachim Frank
-
Article
| Open Access Single particle cryo-EM reconstruction of 52 kDa streptavidin at 3.2 Angstrom resolution
Single particle cryo-EM reconstruction of 52 kDa streptavidin at 3.2 Angstrom resolution
It remains a challenge to obtain high-resolution structures of molecules smaller than 200 kDa using single particle cryo-EM. Here, the authors apply the Cs-corrector-VPP coupled cryo-EM and solve structures of the 52 kDa streptavidin (SA) protein at near-atomic resolution.
- Xiao Fan
- , Jia Wang
- & Hong-Wei Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis for the clamping and Ca2+ activation of SNARE-mediated fusion by synaptotagmin
Structural basis for the clamping and Ca2+ activation of SNARE-mediated fusion by synaptotagmin
The neuronal Ca2+-sensor Synapotagmin-1 (Syt1) interacts with SNARE proteins and lipid membranes and synchronizes neurotransmitter release in response to Ca2+-influx. Here the authors provide insights into the underlying molecular mechanism by determining the cryo-EM structure of the Syt1–SNARE complex on a lipid membrane at 10 Å resolution.
- Kirill Grushin
- , Jing Wang
- & Shyam S. Krishnakumar
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis for substrate gripping and translocation by the ClpB AAA+ disaggregase
Structural basis for substrate gripping and translocation by the ClpB AAA+ disaggregase
Bacterial ClpB is a disaggregase that solubilizes protein aggregates. Here the authors present the 2.9 Å cryo-EM structure of a hyperactive variant of ClpB bound to the substrate casein in active translocation states and discuss its polypeptide translocation mechanism.
- Alexandrea N. Rizo
- , JiaBei Lin
- & Daniel R. Southworth
-
Article
| Open Access Structural assembly of the tailed bacteriophage ϕ29
Structural assembly of the tailed bacteriophage ϕ29
Mature particles of bacteriophage ϕ29 consist of a 33-MDa complex formed by over 450 subunits, assembled into a head and a short tail. Here, Xu et al. report the near-atomic structures of the ϕ29 prohead, the mature virion and the genome-emptied virion, providing insights into DNA packaging and release.
- Jingwei Xu
- , Dianhong Wang
- & Ye Xiang
-
Article
| Open Access Structure of the SARS-CoV nsp12 polymerase bound to nsp7 and nsp8 co-factors
Structure of the SARS-CoV nsp12 polymerase bound to nsp7 and nsp8 co-factors
The pathogenic human coronaviruses SARS- and MERS-CoV can cause severe respiratory disease. Here the authors present the 3.1Å cryo-EM structure of the SARS-CoV RNA polymerase nsp12 bound to its essential co-factors nsp7 and nsp8, which is of interest for antiviral drug development.
- Robert N. Kirchdoerfer
- & Andrew B. Ward
-
Article
| Open Access Atomic resolution cryo-EM structure of a native-like CENP-A nucleosome aided by an antibody fragment
Atomic resolution cryo-EM structure of a native-like CENP-A nucleosome aided by an antibody fragment
CENP-A histone variants replace histones H3 at centromeres. Here the authors use a single-chain antibody fragment (scFv) to stabilize human CENP-A nucleosome containing a native α-satellite DNA and solved its structure by cryo-EM to 2.6 Å resolution, providing insight into the structure and function of the CENP-A nucleosome.
- Bing-Rui Zhou
- , K. N. Sathish Yadav
- & Ping Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Inhibition of tetrameric Patched1 by Sonic Hedgehog through an asymmetric paradigm
Inhibition of tetrameric Patched1 by Sonic Hedgehog through an asymmetric paradigm
Hedgehog (Hh) controls embryonic development via interaction with its receptor Patched (Ptch). Here the authors report the cryo-EM structure of tetrameric Ptch1 in complex with the palmitoylated N-terminal signaling domain of human Sonic hedgehog (ShhNp) at a 4:2 stoichiometric ratio.
- Hongwu Qian
- , Pingping Cao
- & Xin Gong
-
Article
| Open Access In situ structures of rotavirus polymerase in action and mechanism of mRNA transcription and release
In situ structures of rotavirus polymerase in action and mechanism of mRNA transcription and release
Rotaviruses are of great medical significance because they cause gastroenteritis in children. Here the authors provide insights into the mechanism of viral mRNA transcription by determining the in situ cryo-EM structures of a working rotavirus’ RNA-dependent-RNA polymerase, which is of interest for antiviral drug design.
- Ke Ding
- , Cristina C. Celma
- & Z. Hong Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access Structure of the human frataxin-bound iron-sulfur cluster assembly complex provides insight into its activation mechanism
Structure of the human frataxin-bound iron-sulfur cluster assembly complex provides insight into its activation mechanism
The iron-sulfur cluster (ISC) assembly complex is activated by frataxin (FXN) and Friedreich’s ataxia is caused by FXN deficiency. Here the authors present the 3.2 Å resolution cryo-EM structure of the human frataxin bound ISC complex and discuss how FXN activates enzymatic activity.
- Nicholas G. Fox
- , Xiaodi Yu
- & Seungil Han
-
Article
| Open Access The structural basis of translational control by eIF2 phosphorylation
The structural basis of translational control by eIF2 phosphorylation
During the integrated stress response, translation is modulated through the phosphorylation of translation initiation factor eIF2 and the formation of a complex with eIF2B. Here the authors present structures of the eIF2:eIF2B complex with and without phosphorylation, shedding light on how eIF2 phosphorylation regulates translation.
- Tomas Adomavicius
- , Margherita Guaita
- & Graham D. Pavitt
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis for reversible amyloids of hnRNPA1 elucidates their role in stress granule assembly
Structural basis for reversible amyloids of hnRNPA1 elucidates their role in stress granule assembly
Low complexity (LC) domains can drive the formation of both amyloid fibrils and protein droplets. Here, the authors identify reversible amyloid cores from the LC of hnRNPA1, based on which they elucidate the structural basis of reversible fibrillation and its interplay with hnRNPA1 droplet formation.
- Xinrui Gui
- , Feng Luo
- & Dan Li
-
Article
| Open Access Cryo-EM structures of the pore-forming A subunit from the Yersinia entomophaga ABC toxin
Cryo-EM structures of the pore-forming A subunit from the Yersinia entomophaga ABC toxin
YenTcA is the pore-forming and membrane binding subunit of the ABC toxin YenTc, which is produced by the insect pathogen Yersinia entomophaga. Here authors present cryo-EM structures of YenTcA purified from the native source which implicate associated endochitinases in host cell recognition.
- Sarah J Piper
- , Lou Brillault
- & Michael J Landsberg
-
Article
| Open Access A 3.8 Å resolution cryo-EM structure of a small protein bound to an imaging scaffold
A 3.8 Å resolution cryo-EM structure of a small protein bound to an imaging scaffold
Proteins smaller than about 50 kDa are currently too small to be imaged at high resolution by cryo‐electron microscopy (cryo‐EM). Here authors design a protein scaffold that binds 12 copies of a small 26 kDa protein (GFP), which allowed visualizing GFP at a resolution of 3.8Å by cryo‐EM.
- Yuxi Liu
- , Duc T. Huynh
- & Todd O. Yeates
-
Article
| Open Access Retrieving high-resolution information from disordered 2D crystals by single-particle cryo-EM
Retrieving high-resolution information from disordered 2D crystals by single-particle cryo-EM
2D crystals of the MloK1 potassium channel diffract to only 10 Å. Here the authors present a method, where they apply cryo-EM single-particle image processing to recorded 2D crystal images, which reveals conformational conformational variability of MloK1 within the crystals and enabled them to determine the structure at 4 Å resolution.
- Ricardo D. Righetto
- , Nikhil Biyani
- & Henning Stahlberg
-
Article
| Open Access Bidirectional contraction of a type six secretion system
Bidirectional contraction of a type six secretion system
Bacteria use contractile injection systems, such as type VI secretion systems (T6SS), to secrete proteins that mediate cell-cell interactions. Here, Szwedziak & Pilhofer show that both ends of a T6SS can attach to opposite sides of the cell, enabling the structure to contract in two opposite directions.
- Piotr Szwedziak
- & Martin Pilhofer
-
Article
| Open Access Structures of the wild-type MexAB–OprM tripartite pump reveal its complex formation and drug efflux mechanism
Structures of the wild-type MexAB–OprM tripartite pump reveal its complex formation and drug efflux mechanism
In Pseudomonas aeruginosa, MexAB–OprM plays a central role in multidrug resistance by ejecting various drug compounds. Here the authors present the structure of wild-type MexAB–OprM in the presence or absence of drugs and propose mechanisms for complex formation and drug efflux.
- Kenta Tsutsumi
- , Ryo Yonehara
- & Eiki Yamashita
-
Article
| Open Access Assembly of complex viruses exemplified by a halophilic euryarchaeal virus
Assembly of complex viruses exemplified by a halophilic euryarchaeal virus
Here, the authors present the cryo-EM structure of the archaeal virus SH1 at 3.8 Å resolution and show how the major capsid proteins assemble into hetero-hexamers, providing insights into the assembly process of this and related PRD1-adeno lineage viruses.
- Luigi De Colibus
- , Elina Roine
- & David I. Stuart
-
Article
| Open Access Cryo-EM structure of cardiac amyloid fibrils from an immunoglobulin light chain AL amyloidosis patient
Cryo-EM structure of cardiac amyloid fibrils from an immunoglobulin light chain AL amyloidosis patient
Immunoglobulin Light Chain Amyloidosis (AL) is the most common systemic amyloidosis occurring in Western countries. Here the authors present the 4.0 Å cryo-EM structure of light chain AL55 fibrils that were isolated from the heart of an AL systemic amyloidosis patient.
- Paolo Swuec
- , Francesca Lavatelli
- & Martino Bolognesi
-
Article
| Open Access Cryo-EM structure of a light chain-derived amyloid fibril from a patient with systemic AL amyloidosis
Cryo-EM structure of a light chain-derived amyloid fibril from a patient with systemic AL amyloidosis
Systemic AL amyloidosis is caused by misfolding of immunoglobulin light chains and is one of the most frequently occurring forms of systemic amyloidosis. Here the authors present the 3.3 Å cryo-EM structure of a λ1 AL amyloid fibril that was isolated from an explanted human heart.
- Lynn Radamaker
- , Yin-Hsi Lin
- & Marcus Fändrich
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis for assembly of vertical single β-barrel viruses
Structural basis for assembly of vertical single β-barrel viruses
Here, the authors present the cryo-EM structures of two archaeal, halophilic, internal membrane-containing icosahedral viruses at 3.7 and 3.8 Å resolution, providing insights into the assembly process of these and related PRD1-adeno lineage viruses.
- Isaac Santos-Pérez
- , Diego Charro
- & Nicola G. A. Abrescia

 Structural basis of Cullin 2 RING E3 ligase regulation by the COP9 signalosome
Structural basis of Cullin 2 RING E3 ligase regulation by the COP9 signalosome