Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Waveguide holography for 3D augmented reality glasses
Waveguide holography for 3D augmented reality glasses
Near-eye displays are pivotal for building augmented and virtual reality platforms, but hurdles remain in achieving comfort and realistic visual experiences. Here, authors demonstrate compact 3D holographic glasses with focus cues by combining merits of waveguide displays and holographic displays.
- Changwon Jang
- , Kiseung Bang
- & Douglas Lanman
-
Article
| Open Access Off-axis metasurfaces for folded flat optics
Off-axis metasurfaces for folded flat optics
The authors show how concepts from metasurface flat optics and folded optics can be combined to push the limits in miniaturization of optical systems. Such optical systems can be fabricated using low-index materials, opening up a path for large-area fabrication using nanoimprint lithography.
- Brandon Born
- , Sung-Hoon Lee
- & Mark L. Brongersma
-
Article
| Open Access Deep learning-based incoherent holographic camera enabling acquisition of real-world holograms for holographic streaming system
Deep learning-based incoherent holographic camera enabling acquisition of real-world holograms for holographic streaming system
The authors develop a deep learning-based incoherent holographic camera system in order to deliver visually enhanced holograms in real-time. The neural network filters the noise in the captured holograms, and by integrating a holographic camera and a display, they demonstrate a holographic streaming system.
- Hyeonseung Yu
- , Youngrok Kim
- & Hong-Seok Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Super-resolution orbital angular momentum holography
Super-resolution orbital angular momentum holography
The resolution of orbital angular momentum holography is limited by a fundamental sampling criterion. Here, the authors break the resolution barrier by temporal multiplexing of binary holograms and enhance the resolution and capacity by several times.
- Zijian Shi
- , Zhensong Wan
- & Xing Fu
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic complex opto-magnetic holography
Dynamic complex opto-magnetic holography
Holography recreates both the amplitude and wave front of a three dimensional object, meaning that the observer perceives the image in the nearly same way as they would the true object. Creating such holographic images is challenging computationally, and requires extremely fast display update. Here, the authors combine a fast memoryless computation algorithm with the ultra-rapid writing based on all-optical switching of a ferrimagnetic film.
- M. Makowski
- , J. Bomba
- & A. Stupakiewicz
-
Article
| Open Access Diffraction-engineered holography: Beyond the depth representation limit of holographic displays
Diffraction-engineered holography: Beyond the depth representation limit of holographic displays
Improving the image depth perception of holograms while maintaining high image quality is a current challenge. Here the authors propose an efficient solution relying on a multi-plane hologram technique that reconstruct different blurred images and sharply focused images depending on a propagation distance.
- Daeho Yang
- , Wontaek Seo
- & Hong-Seok Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Soft shape-programmable surfaces by fast electromagnetic actuation of liquid metal networks
Soft shape-programmable surfaces by fast electromagnetic actuation of liquid metal networks
Low modulus materials that can change shape in response to external stimuli are promising for a wide range of applications. The authors here introduce a shape-reprogrammable construct, based on liquid metal microfluidic networks and electromagnetic actuation, that supports a unique collection of capabilities.
- Xinchen Ni
- , Haiwen Luan
- & John A. Rogers
-
Article
| Open Access Freeze-derived heterogeneous structural color films
Freeze-derived heterogeneous structural color films
While most of the structural colored materials only present isotropic colors, limiting their functions and many practical applications, while realizing anisotropic structural color materials remains challenging. Here, the authors develop a freeze-derived heterogeneous structural color hydrogels for information encryption and decryption.
- Shuangshuang Miao
- , Yu Wang
- & Yuanjin Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access A self-healing ferroelectric liquid crystal electro-optic shutter based on vertical surface-relief grating alignment
A self-healing ferroelectric liquid crystal electro-optic shutter based on vertical surface-relief grating alignment
Ferroelectric liquid crystals (FLCs) have faster optical response times than nematic crystals, but they are also less robust to external shock. Here the authors develop an FLC geometry that reduces the sensitivity to external disruption through self-healing, making them more stable for applications.
- Peter J. M. Wyatt
- , James Bailey
- & J. Cliff Jones
-
Article
| Open Access High-resolution light field prints by nanoscale 3D printing
High-resolution light field prints by nanoscale 3D printing
Light field prints displaying 3D information often appear pixelated due to limited resolution and misalignment between lenses and colour pixels. Here, the authors present a one-step process via two-photon polymerization lithography to fabricate light field prints with high spatial and angular resolution.
- John You En Chan
- , Qifeng Ruan
- & Joel K. W. Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Pixelated bifunctional metasurface-driven dynamic vectorial holographic color prints for photonic security platform
Pixelated bifunctional metasurface-driven dynamic vectorial holographic color prints for photonic security platform
The authors present a bi-functional metasurface, combining structural color printing observed under white light and polarization encoded It is appropriate. vectorial holography. A pixelated design is used encode multiple holographic images, and they demonstrate an electrically tunable optical security platform.
- Inki Kim
- , Jaehyuck Jang
- & Junsuk Rho
-
Article
| Open Access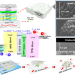 Highly efficient, heat dissipating, stretchable organic light-emitting diodes based on a MoO3/Au/MoO3 electrode with encapsulation
Highly efficient, heat dissipating, stretchable organic light-emitting diodes based on a MoO3/Au/MoO3 electrode with encapsulation
A transparent twistable and stretchable MoO3/Au/MoO3 electrode is demonstrated by Choi et al. for organic light-emitting diodes. The device fabricated on thin elastomer shows enhanced EQE with minimum efficiency roll-off owing to the improved charge injection and heat dissipation from the substrate.
- Dae Keun Choi
- , Dong Hyun Kim
- & Seung Yoon Ryu
-
Article
| Open Access Slim-panel holographic video display
Slim-panel holographic video display
Holographic displays that are both compact and produce realistic holograms without eyestrain are still difficult to realize. Here the authors implement a steering-backlight unit and a holographic video processor to produce a realistic holographic display in a slim panel.
- Jungkwuen An
- , Kanghee Won
- & Hong-Seok Lee
-
Article
| Open Access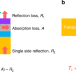 Ultrathin-metal-film-based transparent electrodes with relative transmittance surpassing 100%
Ultrathin-metal-film-based transparent electrodes with relative transmittance surpassing 100%
Designing flexible and transparent electrodes for high-performance optoelectronic devices remains a challenge. Here, the authors presented conductive and flexible dielectric-metal-dielectric multi-layers electrodes based on Cu-doped Ag film (thickness of 6.5 nm) with 100.3% relative transmittance.
- Chengang Ji
- , Dong Liu
- & L. Jay Guo
-
Article
| Open Access Tuning molecular emission of organic emitters from fluorescence to phosphorescence through push-pull electronic effects
Tuning molecular emission of organic emitters from fluorescence to phosphorescence through push-pull electronic effects
Though organic emitters with room temperature phosphorescence (RTP) are attractive for various applications, realizing highly efficient and long lifetime emission remains a challenge. Here, the authors report the role of push-pull electronic effects on emission for organic RTP emitters.
- Hai-Tao Feng
- , Jiajie Zeng
- & Ben Zhong Tang
-
Article
| Open Access All-dielectric metasurface for high-performance structural color
All-dielectric metasurface for high-performance structural color
Here, the authors fabricate a metasurface with high brightness and large gamut structured colors by combining a silicon metasurface with a refractive index matching layer. The experimentally demonstrated gamut is 181.8% of sRGB, 135.6% of Adobe RGB, and 97.2% of Rec.2020.
- Wenhong Yang
- , Shumin Xiao
- & Din-Ping Tsai
-
Article
| Open Access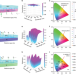 Towards full-colour tunability of inorganic electrochromic devices using ultracompact fabry-perot nanocavities
Towards full-colour tunability of inorganic electrochromic devices using ultracompact fabry-perot nanocavities
Electrochromic devices are generally not capable of tuning more than one color. Here, the authors use Fabry-Perot nanocavities to create electrochromic devices with a wide color tuning range and vibrant color.
- Zhen Wang
- , Xiaoyu Wang
- & Zhigang Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Pen drawing display
Pen drawing display
Designing free-style display technology with rapid manufacturing process at low production cost and high flexibility for the substrate´s choice remains a challenge. Here, the authors propose a pen drawing display technology that facilitates display production using liquid light-emitting materials.
- Sang-Mi Jeong
- , Taekyung Lim
- & Sanghyun Ju
-
Article
| Open Access Tomographic near-eye displays
Tomographic near-eye displays
Creating realistic 3D displays that are comfortable to use is both a complicated and important problem. Here the authors present a tomographic near-eye display that uses high-speed synchronization of a lens focus and backlight to produce realistic depth cues for effective and comfortable 3D viewing.
- Seungjae Lee
- , Youngjin Jo
- & Byoungho Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrathin wide-angle large-area digital 3D holographic display using a non-periodic photon sieve
Ultrathin wide-angle large-area digital 3D holographic display using a non-periodic photon sieve
3D holographic displays still face many challenges such as small viewing angle and image size. Here the authors present a scalable method for displaying large holographic images with a wide viewing angle using a wide-angle diffracting element in a flat panel; a non-periodic photon sieve.
- Jongchan Park
- , KyeoReh Lee
- & YongKeun Park
-
Article
| Open Access Full-color laser displays based on organic printed microlaser arrays
Full-color laser displays based on organic printed microlaser arrays
In the next generation of display technology for portable devices, lasers could replace LEDs to achieve more vibrant colours. Here, Zhao et al. demonstrate a dynamic full-color display in which each pixel is made up of three printed organic microlasers to cover the RGB space.
- Jinyang Zhao
- , Yongli Yan
- & Yong Sheng Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Electrochromic semiconductors as colorimetric SERS substrates with high reproducibility and renewability
Electrochromic semiconductors as colorimetric SERS substrates with high reproducibility and renewability
Electrochromic technology has diverse cutting-edge applications, but it has never been used to overcome the critical problems in the field of surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS). Here, the authors demonstrate a generic electrochromic strategy for ensuring the reproducibility and renewability of SERS substrates.
- Shan Cong
- , Zhen Wang
- & Zhigang Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access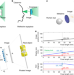 Metasurface eyepiece for augmented reality
Metasurface eyepiece for augmented reality
Here, the authors demonstrate a metasurface application to realize a compact near-eye display system for augmented reality with a wide field of view, full-color imaging, high resolution and a sufficiently large eyebox.
- Gun-Yeal Lee
- , Jong-Young Hong
- & Byoungho Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Actively addressed single pixel full-colour plasmonic display
Actively addressed single pixel full-colour plasmonic display
Tuning of plasmonic nanostructures has yet to cover a full colour basis set with a single nanostructure. Franklinet al. demonstrate a liquid crystal-plasmonic system that covers the full red-green-blue colour basis set as a function of voltage and which can be actively addressed with thin-film-transistor technology.
- Daniel Franklin
- , Russell Frank
- & Debashis Chanda
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic plasmonic colour display
Dynamic plasmonic colour display
Here Duanet al. demonstrate dynamic plasmonic colour displays using catalytic magnesium metasurfaces. Controlled hydrogenation and dehydrogenation of the constituent nanoparticles, which serve as dynamic pixels, allow plasmonic colour printing, tuning, erasing, restoration of colour and encoding of information.
- Xiaoyang Duan
- , Simon Kamin
- & Na Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Projection-type see-through holographic three-dimensional display
Projection-type see-through holographic three-dimensional display
The design of holographic displays usually involves a trade-off between size and viewing angle. Here, the authors combine holographic projection with a digitally designed holographic optical element so that display size and the visual angle can be designed independently.
- Koki Wakunami
- , Po-Yuan Hsieh
- & Kenji Yamamoto
-
Article |
 Transparent displays enabled by resonant nanoparticle scattering
Transparent displays enabled by resonant nanoparticle scattering
Transparent displays find increasing use in a variety of applications that project information to a viewer. Here, Hsu and colleagues realize a transparent display that uses nanoparticles for a wavelength-selective scattering of incoming light.
- Chia Wei Hsu
- , Bo Zhen
- & Marin Soljačić
-
Article |
 All-solution processed polymer light-emitting diode displays
All-solution processed polymer light-emitting diode displays
Polymer light-emitting diodes promise cheap and flexible lighting and displays, but their fabrication is hindered by high-vacuum methods for creating cathodes. Zheng et al.show an all-solution processing approach to polymer diodes that removes this obstacle, offering roll-to-roll fabrication of devices.
- Hua Zheng
- , Yina Zheng
- & Yong Cao

 Neural étendue expander for ultra-wide-angle high-fidelity holographic display
Neural étendue expander for ultra-wide-angle high-fidelity holographic display