Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access DeepPROTACs is a deep learning-based targeted degradation predictor for PROTACs
DeepPROTACs is a deep learning-based targeted degradation predictor for PROTACs
The rational design of PROTACs is difficult due to their obscure structure-activity relationship. Here the authors present a deep neural network model - DeepPROTACs - for predicting the degradation capacity of a proposed PROTAC molecule.
- Fenglei Li
- , Qiaoyu Hu
- & Fang Bai
-
Article
| Open Access Leveraging data-driven self-consistency for high-fidelity gene expression recovery
Leveraging data-driven self-consistency for high-fidelity gene expression recovery
Recovering dropout-affected gene expression values is a challenging problem in bioinformatics. Here, the authors propose a data-driven framework, that first learns the underlying data distribution and then recovers the expression values by imposing a self-consistency on the expression matrix.
- Md Tauhidul Islam
- , Jen-Yeu Wang
- & Lei Xing
-
Article
| Open Access Feedback between mechanosensitive signaling and active forces governs endothelial junction integrity
Feedback between mechanosensitive signaling and active forces governs endothelial junction integrity
Gap formation in the vasculature underpins immune and tumour cell infiltration. Here the authors propose a chemo-mechanical model to analyse how feedback between mechanosensitive signalling, active cellular forces and adhesion governs the breakdown, recovery, and integrity of endothelial junctions.
- Eoin McEvoy
- , Tal Sneh
- & Vivek B. Shenoy
-
Article
| Open Access Region-specific denoising identifies spatial co-expression patterns and intra-tissue heterogeneity in spatially resolved transcriptomics data
Region-specific denoising identifies spatial co-expression patterns and intra-tissue heterogeneity in spatially resolved transcriptomics data
Spatially resolved transcriptomics is a relatively new technique that maps transcriptional information within a tissue. Here the authors present MIST, which detects molecular regions from spatially resolved transcriptomics and denoises the missing gene expression values by region-specific imputation.
- Linhua Wang
- , Mirjana Maletic-Savatic
- & Zhandong Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Distinct immunological and molecular signatures underpinning influenza vaccine responsiveness in the elderly
Distinct immunological and molecular signatures underpinning influenza vaccine responsiveness in the elderly
Seasonal influenza vaccination is an important strategy to prevent serious disease in the elderly, but individual responsiveness to vaccination widely vary. Here authors establish, with an array of state-of-the art methods, the major immunological parameters that distinguish vaccine recipients developing robust antibody response and non-responders
- Peggy Riese
- , Stephanie Trittel
- & Carlos A. Guzmán
-
Article
| Open Access dcHiC detects differential compartments across multiple Hi-C datasets
dcHiC detects differential compartments across multiple Hi-C datasets
The organisation of mammalian genomes plays a role in many biological processes. Here the authors report dcHiC, a tool which uses a multivariate distance measure to identify changes in compartmentalisation among multiple genome-wide chromatin contact maps, and apply this to different human and mouse datasets.
- Abhijit Chakraborty
- , Jeffrey G. Wang
- & Ferhat Ay
-
Article
| Open Access Deep autoencoder for interpretable tissue-adaptive deconvolution and cell-type-specific gene analysis
Deep autoencoder for interpretable tissue-adaptive deconvolution and cell-type-specific gene analysis
Traditional bulk sequencing data lack information about cell-type-specific gene expression. Here, the authors develop a Tissue-AdaPtive autoEncoder (TAPE), a deep learning method connecting bulk RNA-seq and single-cell RNA-seq, and apply it to analyze the cell type fractions and cell-type-specific gene expression in clinical data.
- Yanshuo Chen
- , Yixuan Wang
- & Yu Li
-
Article
| Open Access Learning the histone codes with large genomic windows and three-dimensional chromatin interactions using transformer
Learning the histone codes with large genomic windows and three-dimensional chromatin interactions using transformer
Existing deep learning-based approaches for the prediction of gene expression by histone modifications (HMs) can only focus on narrow and linear genomic regions around promoters. Here, the authors address these problems by developing a transformer-based deep learning architecture named Chromoformer.
- Dohoon Lee
- , Jeewon Yang
- & Sun Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Parent-of-Origin inference for biobanks
Parent-of-Origin inference for biobanks
Studies on parent-of-origin effects have been limited in terms of sample size due to lack of parental genomes or known genealogies. Here, the authors develop a method to infer the parent-of-origin of an individual alleles in biobank-scale datasets, without requiring parental genomes or prior knowledge of genealogy, allowing discovery of parent-of-origin effects with an unprecedented sample size.
- Robin J. Hofmeister
- , Simone Rubinacci
- & Olivier Delaneau
-
Article
| Open Access UniTVelo: temporally unified RNA velocity reinforces single-cell trajectory inference
UniTVelo: temporally unified RNA velocity reinforces single-cell trajectory inference
RNA velocity can detect the differentiation directionality by modelling sparse unspliced RNAs, but suffers from high estimation errors. Here, the authors develop a computational method called UniTVelo to reinforce the velocity estimation by introducing a unified time and a top-down model design.
- Mingze Gao
- , Chen Qiao
- & Yuanhua Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Tempo: an unsupervised Bayesian algorithm for circadian phase inference in single-cell transcriptomics
Tempo: an unsupervised Bayesian algorithm for circadian phase inference in single-cell transcriptomics
Previous efforts to study the circadian clock using scRNA-seq have relied on time course designs that treat cell collection time as a proxy for circadian time. Here, the authors introduce a statistical method to infer circadian timing directly from expression, enabling researchers to study circadian phase heterogeneity.
- Benjamin J. Auerbach
- , Garret A. FitzGerald
- & Mingyao Li
-
Article
| Open Access Unsupervised learning of aging principles from longitudinal data
Unsupervised learning of aging principles from longitudinal data
Biomarkers of age and frailty may aid in understanding the aging process, predicting lifespan or health span and in assessing the effects of anti-aging interventions. Here, the authors show that combining physics-based models and deep learning may enhance understanding of aging from big biomedical data, observe effects of anti-aging interventions in laboratory animals, and discover signatures of longevity.
- Konstantin Avchaciov
- , Marina P. Antoch
- & Peter O. Fedichev
-
Article
| Open Access Understanding fibrosis pathogenesis via modeling macrophage-fibroblast interplay in immune-metabolic context
Understanding fibrosis pathogenesis via modeling macrophage-fibroblast interplay in immune-metabolic context
Renal fibrosis is a progressive process with complex etiopathology, causing organ failure. Here authors present a mathematical model, based on an in vitro system faithfully contemplating macrophage-fibroblast interaction and the metabolic-immunologic signals that are affecting kidney fibrosis, that is applicable to kidney transplant failure.
- Elisa Setten
- , Alessandra Castagna
- & Massimo Locati
-
Article
| Open Access Mendelian randomization accounting for complex correlated horizontal pleiotropy while elucidating shared genetic etiology
Mendelian randomization accounting for complex correlated horizontal pleiotropy while elucidating shared genetic etiology
Mendelian randomization uses genetic variation to study the causal effect of exposure on outcome, but results can be biased by confounders, such as horizontal pleiotropy. Here, the authors present MR-CUE, a method to determine causal effects by accounting for correlated and uncorrelated horizontal pleiotropic effects.
- Qing Cheng
- , Xiao Zhang
- & Jin Liu
-
Article
| Open Access De novo analysis of bulk RNA-seq data at spatially resolved single-cell resolution
De novo analysis of bulk RNA-seq data at spatially resolved single-cell resolution
Current methods to reanalyze bulk RNA-seq at spatially resolved single-cell resolution have limitations. Here, the authors develop Bulk2Space, a spatial deconvolution algorithm using single-cell and spatial transcriptomics as references, providing new insights into spatial heterogeneity within bulk tissue.
- Jie Liao
- , Jingyang Qian
- & Xiaohui Fan
-
Article
| Open Access Strain level microbial detection and quantification with applications to single cell metagenomics
Strain level microbial detection and quantification with applications to single cell metagenomics
Here the authors develop CAMMiQ, a combinatorial optimization approach that utilizes variable length, “unique” and “doubly-unique” genomic segments, showing improves identification and quantification of distinct microbes in metagenomic sequence data.
- Kaiyuan Zhu
- , Alejandro A. Schäffer
- & S. Cenk Sahinalp
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic HIV-1 spike motion creates vulnerability for its membrane-bound tripod to antibody attack
Dynamic HIV-1 spike motion creates vulnerability for its membrane-bound tripod to antibody attack
The membrane-proximal external region of HIV-1 spike protein is a broadly neutralizing antibody target. Here, cryo-electron microscopy and molecular dynamics reveal spontaneous ectodomain tilting, a vulnerability exploitable for vaccine design.
- Shuang Yang
- , Giorgos Hiotis
- & Thomas Walz
-
Article
| Open Access Proteogenomics refines the molecular classification of chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Proteogenomics refines the molecular classification of chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Proteomics can be used to refine cancer classification. Here, the authors characterise chronic lymphocytic leukaemia patients by proteogenomics, and identified a subtype of patients with poor prognosis associated with aberrant B cell receptor signalling.
- Sophie A. Herbst
- , Mattias Vesterlund
- & Sascha Dietrich
-
Article
| Open Access Online single-cell data integration through projecting heterogeneous datasets into a common cell-embedding space
Online single-cell data integration through projecting heterogeneous datasets into a common cell-embedding space
Integrative analyses of single-cell datasets are facing new challenges as data size and complexity grow. Here the authors present SCALEX, which projects cells from different datasets into a common latent space, allowing accurate online integration as well as cross-referencing with atlas-scale data.
- Lei Xiong
- , Kang Tian
- & Qiangfeng Cliff Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access A predictive computational platform for optimizing the design of bioartificial pancreas devices
A predictive computational platform for optimizing the design of bioartificial pancreas devices
Transplanting encapsulated insulin-producing cells may achieve a functional cure for type 1 diabetes, but efficacy is constrained by mass transfer limits. Here, the authors report a dynamic computational platform to investigate the therapeutic potency of such programmable bioartificial pancreas devices.
- Alexander U. Ernst
- , Long-Hai Wang
- & Minglin Ma
-
Article
| Open Access Elucidating tumor heterogeneity from spatially resolved transcriptomics data by multi-view graph collaborative learning
Elucidating tumor heterogeneity from spatially resolved transcriptomics data by multi-view graph collaborative learning
Multi-view graph approaches could enhance the analysis of tissue heterogeneity in spatial transcriptomics. Here, the authors develop the Spatial Transcriptomics data analysis by Multiple View Collaborative-learning - stMVC - framework, and apply it to detect spatial domains and cell states in brain and tumor tissues.
- Chunman Zuo
- , Yijian Zhang
- & Luonan Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Protein structural transitions critically transform the network connectivity and viscoelasticity of RNA-binding protein condensates but RNA can prevent it
Protein structural transitions critically transform the network connectivity and viscoelasticity of RNA-binding protein condensates but RNA can prevent it
In this work the authors propose a multiscale computational approach, integrating atomistic and coarse-grained models simulations, to study the thermodynamic and kinetic factors playing a major role in the liquid-to-solid transition of biomolecular condensates. It is revealed how the gradual accumulation of inter-protein β-sheets increases the viscosity of functional liquid-like condensates, transforming them into gel-like pathological aggregates, and it is also shown how high concentrations of RNA can decelerate such transition.
- Andres R. Tejedor
- , Ignacio Sanchez-Burgos
- & Jorge R. Espinosa
-
Article
| Open Access Gene expression based inference of cancer drug sensitivity
Gene expression based inference of cancer drug sensitivity
Predicting treatment response in cancer remains a highly complex task. Here, the authors develop Precily, a deep neural network framework to predict treatment response in cancer by considering gene expression, pathway activity estimates and drug features, and test this method in multiple datasets and preclinical models.
- Smriti Chawla
- , Anja Rockstroh
- & Debarka Sengupta
-
Article
| Open Access Using multiple sampling strategies to estimate SARS-CoV-2 epidemiological parameters from genomic sequencing data
Using multiple sampling strategies to estimate SARS-CoV-2 epidemiological parameters from genomic sequencing data
SARS-CoV-2 genome sequencing data can be used to infer epidemiological parameters, but the impact of the strategy used to select samples on these estimates is rarely considered. Here, the authors produce estimates using different sampling strategies and compare results to those based on case reporting data.
- Rhys P. D. Inward
- , Kris V. Parag
- & Nuno R. Faria
-
Article
| Open Access Intrinsic bias estimation for improved analysis of bulk and single-cell chromatin accessibility profiles using SELMA
Intrinsic bias estimation for improved analysis of bulk and single-cell chromatin accessibility profiles using SELMA
Genome-wide profiling of chromatin accessibility by DNase-seq or ATAC-seq has been widely used to identify regulatory DNA elements and transcription factor binding sites. Here the authors develop a computational model, SELMA, to estimate and correct enzymatic cleavage biases in chromatin accessibility profiling data.
- Shengen Shawn Hu
- , Lin Liu
- & Chongzhi Zang
-
Article
| Open Access Identification of spatially variable genes with graph cuts
Identification of spatially variable genes with graph cuts
Single-cell gene expression data with positional information is critical to dissect mechanisms and architectures of multicellular organisms, but the potential is limited by the scalability of current data analysis strategies. Here the authors develop a highly scalable method, scGCO, to identify genes whose expression values form spatial patterns from spatial transcriptomics data.
- Ke Zhang
- , Wanwan Feng
- & Peng Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Clustering by measuring local direction centrality for data with heterogeneous density and weak connectivity
Clustering by measuring local direction centrality for data with heterogeneous density and weak connectivity
Clustering is a powerful machine learning method for discovering similar patterns according to the proximity of elements in feature space. Here the authors propose a local direction centrality clustering algorithm that copes with heterogeneous density and weak connectivity issues.
- Dehua Peng
- , Zhipeng Gui
- & Huayi Wu
-
Article
| Open Access Water regulates the residence time of Benzamidine in Trypsin
Water regulates the residence time of Benzamidine in Trypsin
Water is an essential part of any biological system, yet many aspects of its role remain elusive. Here the authors show, in a paradigmatic ligand-protein system, that water modulates the ligand residence time in a complex and non-local way, with possible implications in drug design.
- Narjes Ansari
- , Valerio Rizzi
- & Michele Parrinello
-
Article
| Open Access Cytoplasmic forces functionally reorganize nuclear condensates in oocytes
Cytoplasmic forces functionally reorganize nuclear condensates in oocytes
Cytoskeletal activity generates mechanical forces known to agitate and displace membrane-bound organelles in the cytoplasm. In oocytes, Al Jord et al. discover that these cytoplasmic forces functionally remodel nuclear RNA-processing condensates across scales for developmental success.
- Adel Al Jord
- , Gaëlle Letort
- & Marie-Hélène Verlhac
-
Article
| Open Access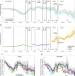 Comparison of the 2021 COVID-19 roadmap projections against public health data in England
Comparison of the 2021 COVID-19 roadmap projections against public health data in England
The ’Roadmap’ for relaxation of COVID-19 restrictions in England in 2021 was informed by mathematical modelling. Here, the authors perform a retrospective assessment of the accuracy of modelling predictions and identify the main sources of uncertainty that led to observed values deviating from projections.
- Matt J. Keeling
- , Louise Dyson
- & Samuel Moore
-
Article
| Open Access Designing isolation guidelines for COVID-19 patients with rapid antigen tests
Designing isolation guidelines for COVID-19 patients with rapid antigen tests
Utilizing viral test results to determine isolation length would minimize both the risk of prematurely ending isolation of infectious patients and the unnecessary individual burden of redundant isolation of noninfectious patients. Here, the authors develop a framework to compute the population-level risk of different isolation guidelines with rapid antigen tests.
- Yong Dam Jeong
- , Keisuke Ejima
- & Marco Ajelli
-
Article
| Open Access On maternity and the stronger immune response in women
On maternity and the stronger immune response in women
Women generally mount a stronger immune response to infections than men do, resulting in a higher impact of autoimmune diseases. Here, the authors show that pathogen transmission from mother-to-child during pregnancy drives the co-evolution of a stout defence against harmless pathogens in women.
- Evan Mitchell
- , Andrea L. Graham
- & Geoff Wild
-
Article
| Open Access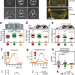 Intrinsic cell rheology drives junction maturation
Intrinsic cell rheology drives junction maturation
How intrinsic cell properties such as stiffness contribute to cell-cell junction stabilization is not well described. Here they show that higher levels of intrinsic cell mechanics at the cortex, cytoskeleton and nucleus of neighboring cells promote junctional maturation.
- K. Sri-Ranjan
- , J. L. Sanchez-Alonso
- & Vania M. M. Braga
-
Article
| Open Access Fate mapping of hematopoietic stem cells reveals two pathways of native thrombopoiesis
Fate mapping of hematopoietic stem cells reveals two pathways of native thrombopoiesis
Hematopoietic stem cells produce diverse cell lineages. Here, the authors apply single-cell RNA-seq, computational integration of non-perturbative approaches for fate-mapping, and mitotic tracking to chart lineage decisions in native hematopoiesis and identify megakaryocyte progenitors that directly link HSCs to megakaryocytes.
- Mina N. F. Morcos
- , Congxin Li
- & Alexander Gerbaulet
-
Article
| Open Access Knowledge-graph-based cell-cell communication inference for spatially resolved transcriptomic data with SpaTalk
Knowledge-graph-based cell-cell communication inference for spatially resolved transcriptomic data with SpaTalk
Cell-cell communication is a vital feature involving numerous biological processes. Here, the authors develop SpaTalk, a cell-cell communication inference method using knowledge graph for spatially resolved transcriptomic data, providing valuable insights into spatial intercellular tissue dynamics.
- Xin Shao
- , Chengyu Li
- & Xiaohui Fan
-
Article
| Open Access Drivers and trends of global soil microbial carbon over two decades
Drivers and trends of global soil microbial carbon over two decades
Soil microbial carbon is central to soil functions and services, but its spatial-temporal dynamics are unclear. Here the authors show global trends in soil microbial carbon, which suggests a global decrease in soil microbial carbon, mostly driven by temperature increases in northern areas.
- Guillaume Patoine
- , Nico Eisenhauer
- & Carlos A. Guerra
-
Article
| Open Access People infer communicative action through an expectation for efficient communication
People infer communicative action through an expectation for efficient communication
Humans can quickly infer when someone’s body movements are meant to be communicative. Here, the authors show that this capacity is underpinned by an expectation that communicative actions will efficiently reveal that they lack an external goal.
- Amanda Royka
- , Annie Chen
- & Julian Jara-Ettinger
-
Article
| Open Access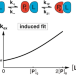 A litmus test for classifying recognition mechanisms of transiently binding proteins
A litmus test for classifying recognition mechanisms of transiently binding proteins
The authors provide a litmus test for the recognition mechanism of transiently binding proteins based on nuclear magnetic resonance and find a conformational selection binding mechanism through concentration-dependent kinetics of ubiquitin and SH3.
- Kalyan S. Chakrabarti
- , Simon Olsson
- & Christian Griesinger
-
Article
| Open Access Reconstruction of a catalogue of genome-scale metabolic models with enzymatic constraints using GECKO 2.0
Reconstruction of a catalogue of genome-scale metabolic models with enzymatic constraints using GECKO 2.0
Genome-scale metabolic models have been widely used for quantitative exploration of the relation between genotype and phenotype. Here the authors present GECKO 2, an automated framework for continuous and version controlled update of enzyme-constrained models of metabolism, producing an interesting catalogue of high-quality models for diverse yeasts, bacteria and human metabolism, aiming to facilitate their use in basic science, metabolic engineering and synthetic biology purposes.
- Iván Domenzain
- , Benjamín Sánchez
- & Jens Nielsen
-
Article
| Open Access Vertex protein PduN tunes encapsulated pathway performance by dictating bacterial metabolosome morphology
Vertex protein PduN tunes encapsulated pathway performance by dictating bacterial metabolosome morphology
Morphology of metabolosomes affects the encapsulated pathway performance. Here, the authors combine experimental characterizations with structural and kinetic modeling to reveal how the shell protein PduN changes the morphology of 1,2-propanediol utilization (Pdu) metabolosome and how this morphology shift impacts Pdu function.
- Carolyn E. Mills
- , Curt Waltmann
- & Danielle Tullman-Ercek
-
Article
| Open Access Context-aware deconvolution of cell–cell communication with Tensor-cell2cell
Context-aware deconvolution of cell–cell communication with Tensor-cell2cell
Cellular contexts such as disease state, organismal life stage and tissue microenvironment, shape intercellular communication, and ultimately affect an organism’s phenotypes. Here, the authors present Tensor-cell2cell, an unsupervised method for deciphering context-driven intercellular communication.
- Erick Armingol
- , Hratch M. Baghdassarian
- & Nathan E. Lewis
-
Article
| Open Access Probing TDP-43 condensation using an in silico designed aptamer
Probing TDP-43 condensation using an in silico designed aptamer
Here, the authors generated an artificial RNA molecule, or aptamer, specific for the Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis protein TDP-43. By interacting avidly with its target, the aptamer can be exploited to track TDP-43 phase transition in vitro and in cells.
- Elsa Zacco
- , Owen Kantelberg
- & Gian Gaetano Tartaglia
-
Article
| Open Access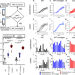 Evolutionary action of mutations reveals antimicrobial resistance genes in Escherichia coli
Evolutionary action of mutations reveals antimicrobial resistance genes in Escherichia coli
The emergence of antibiotic resistance, even against last-line antibiotics such as colistin, is a serious public health threat. To guide treatment and drug development strategies, Marciano et al. apply evolutionary action (EA) analysis to identify driver mutations in a noisy mutational background in experimental evolution experiments and inform about de novo colistin resistance drivers.
- David C. Marciano
- , Chen Wang
- & Olivier Lichtarge
-
Article
| Open Access Comparison of methods and resources for cell-cell communication inference from single-cell RNA-Seq data
Comparison of methods and resources for cell-cell communication inference from single-cell RNA-Seq data
Multiple methods to infer cell-cell communication (CCC) from single cell data are currently available. Here, the authors systematically compare 16 CCC inference resources and 7 methods, and develop the LIANA framework as an interface to use and compare all these approaches.
- Daniel Dimitrov
- , Dénes Türei
- & Julio Saez-Rodriguez
-
Article
| Open Access Mitigation of SARS-CoV-2 transmission at a large public university
Mitigation of SARS-CoV-2 transmission at a large public university
Safely opening university campuses has been a major challenge during the COVID-19 pandemic. Here, the authors describe a program of public health measures employed at a university in the United States which, combined with other non-pharmaceutical interventions, allowed the university to stay open in fall 2020 with limited evidence of transmission.
- Diana Rose E. Ranoa
- , Robin L. Holland
- & Martin D. Burke
-
Article
| Open Access A framework for reconstructing SARS-CoV-2 transmission dynamics using excess mortality data
A framework for reconstructing SARS-CoV-2 transmission dynamics using excess mortality data
Testing capacity continues to limit detection of COVID-19 infections and impacts reliability of mortality estimates. Here, the authors develop a statistical model to estimate COVID-19 attributable deaths using all-cause mortality data from Iran and estimate that around half of these deaths have been reported.
- Mahan Ghafari
- , Oliver J. Watson
- & Aris Katzourakis
-
Article
| Open Access CRISPR/Cas9 gRNA activity depends on free energy changes and on the target PAM context
CRISPR/Cas9 gRNA activity depends on free energy changes and on the target PAM context
CRISPR/Cas9-mediated cleavage efficiency varies at different target locations. Here the authors explain this variation with binding free energy changes and show that overlapping Cas9 binding sites influence cleavage efficiency by enabling Cas9 sliding.
- Giulia I. Corsi
- , Kunli Qu
- & Jan Gorodkin
-
Comment
| Open Access Addressing the socioeconomic divide in computational modeling for infectious diseases
Addressing the socioeconomic divide in computational modeling for infectious diseases
The COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted how structural social inequities fundamentally shape disease dynamics. Here, the authors provide a set of practical and methodological recommendations to address socioeconomic vulnerabilities in epidemic models.
- Michele Tizzoni
- , Elaine O. Nsoesie
- & Shweta Bansal
-
Article
| Open Access Predicting cancer prognosis and drug response from the tumor microbiome
Predicting cancer prognosis and drug response from the tumor microbiome
Computational approaches have been developed to estimate tumor microbial abundances from whole genomic and RNA-sequencing datasets. Here the authors report the predictive value of tumor microbial abundance, alone or in combination with gene expression data, for cancer prognosis and drug response.
- Leandro C. Hermida
- , E. Michael Gertz
- & Eytan Ruppin

 Spatially aware dimension reduction for spatial transcriptomics
Spatially aware dimension reduction for spatial transcriptomics