Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Memory and relatedness of transcriptional activity in mammalian cell lineages
Memory and relatedness of transcriptional activity in mammalian cell lineages
Phenotypically identical mammalian cells often display considerable variability in transcript levels of individual genes. Here the authors document how different genes propagate their expression levels in cell lineages and suggest a potential role of transcriptional memory for generating spatial patterns of gene expression.
- Nicholas E. Phillips
- , Aleksandra Mandic
- & David M. Suter
-
Article
| Open Access Inter-annual variation in seasonal dengue epidemics driven by multiple interacting factors in Guangzhou, China
Inter-annual variation in seasonal dengue epidemics driven by multiple interacting factors in Guangzhou, China
In 2014 Guangzhou, China experienced its worse dengue epidemic on record. To determine the reasons for this the authors model historical data under combinations of four time-varying factors and find that past epidemics were limited by one or more unfavourable conditions, but the 2014 epidemic faced none of these restraints.
- Rachel J. Oidtman
- , Shengjie Lai
- & Hongjie Yu
-
Article
| Open Access Model selection may not be a mandatory step for phylogeny reconstruction
Model selection may not be a mandatory step for phylogeny reconstruction
Model selection is a time-intensive step of molecular phylogenetic analysis. Here, Abadi, Azouri and colleagues show that all model selection criteria lead to similar inferences, and that for topology and ancestral sequence reconstruction, using the GTR+I+G model is as accurate.
- Shiran Abadi
- , Dana Azouri
- & Itay Mayrose
-
Article
| Open Access On the predictability of infectious disease outbreaks
On the predictability of infectious disease outbreaks
Forecasting of infectious disease outbreaks can inform appropriate intervention measures, but whether fundamental limits to accurate prediction exist is unclear. Here, the authors use permutation entropy as a model independent measure of predictability to study limitations across a broad set of infectious diseases.
- Samuel V. Scarpino
- & Giovanni Petri
-
Article
| Open Access Towards a data-integrated cell
Towards a data-integrated cell
Integration of omics data remains a challenge. Here, the authors introduce iCell, a framework to integrate tissue-specific protein–protein interaction, co-expression and genetic interaction data, enabling identification of the most rewired genes in cancer, unidentifiable in individual data layers.
- Noël Malod-Dognin
- , Julia Petschnigg
- & Nataša Pržulj
-
Article
| Open Access Optimal dosing of dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine for seasonal malaria chemoprevention in young children
Optimal dosing of dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine for seasonal malaria chemoprevention in young children
Seasonal malaria chemoprevention provides substantial benefit for young children, but resistance to used drugs will likely develop. Here, Chotsiri et al. evaluate the use of dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine as a regimen in 179 children, and population-based simulations suggest that small children would benefit from a higher and extended dosage.
- Palang Chotsiri
- , Issaka Zongo
- & Joel Tarning
-
Article
| Open Access Single-cell RNA-seq denoising using a deep count autoencoder
Single-cell RNA-seq denoising using a deep count autoencoder
Single-cell RNA sequencing is a powerful method to study gene expression, but noise in the data can obstruct analysis. Here the authors develop a denoising method based on a deep count autoencoder network that scales linearly with the number of cells, and therefore is compatible with large data sets.
- Gökcen Eraslan
- , Lukas M. Simon
- & Fabian J. Theis
-
Article
| Open Access Image-based modeling of kidney branching morphogenesis reveals GDNF-RET based Turing-type mechanism and pattern-modulating WNT11 feedback
Image-based modeling of kidney branching morphogenesis reveals GDNF-RET based Turing-type mechanism and pattern-modulating WNT11 feedback
Many organs develop through branching morphogenesis, but whether the underlying mechanisms are shared is unknown. Here, the authors show that a ligand-receptor based Turing mechanisms, similar to that observed in lung development, likely underlies branching morphogenesis of the kidney.
- Denis Menshykau
- , Odyssé Michos
- & Dagmar Iber
-
Article
| Open Access Kinetic analysis of multistep USP7 mechanism shows critical role for target protein in activity
Kinetic analysis of multistep USP7 mechanism shows critical role for target protein in activity
Deubiquitinating enzymes (DUBs) are critical regulators of cellular processes by removing ubiquitin from specific targets. Here global kinetic modelling reveals the mechanism by which the low intrinsic activity of USP7 is substantially enhanced on a specific physiological target.
- Robbert Q. Kim
- , Paul P. Geurink
- & Titia K. Sixma
-
Article
| Open Access Changing temporal context in human temporal lobe promotes memory of distinct episodes
Changing temporal context in human temporal lobe promotes memory of distinct episodes
Memories formed around the same time are linked together by a shared temporal context. Here, the authors show that the ability to selectively retrieve distinct episodic memories formed close together in time is related to how quickly neural representations of temporal context change over time during encoding.
- Mostafa M. El-Kalliny
- , John H. Wittig Jr
- & Kareem A. Zaghloul
-
Article
| Open Access Costless metabolic secretions as drivers of interspecies interactions in microbial ecosystems
Costless metabolic secretions as drivers of interspecies interactions in microbial ecosystems
In considering cross-feeding among microbes within communities, it is typically assumed that metabolic secretions are costly to produce. However, Pacheco et al. use metabolic models to show that ‘costless’ secretions could be common in some environments and important for structuring interactions among microbes.
- Alan R. Pacheco
- , Mauricio Moel
- & Daniel Segrè
-
Article
| Open Access Predicting wildlife reservoirs and global vulnerability to zoonotic Flaviviruses
Predicting wildlife reservoirs and global vulnerability to zoonotic Flaviviruses
Flaviviruses have emerged or re-emerged in several regions, but factors underlying emergence are incompletely understood. Here, Pandit et al. identify potential sylvatic reservoirs of flaviviruses and, in combination with vector distribution data, predict regions of global vulnerability.
- Pranav S. Pandit
- , Megan M. Doyle
- & Christine K. Johnson
-
Article
| Open Access The utility of serology for elimination surveillance of trachoma
The utility of serology for elimination surveillance of trachoma
Robust surveillance methods are needed for trachoma control and recrudescence monitoring, but existing methods have limitations. Here, Pinsent et al. analyse data from nine trachoma-endemic populations and provide operational thresholds for interpretation of serological data in low transmission and post-elimination settings.
- Amy Pinsent
- , Anthony W. Solomon
- & Michael. T. White
-
Article
| Open Access ATP-dependent membrane remodeling links EHD1 functions to endocytic recycling
ATP-dependent membrane remodeling links EHD1 functions to endocytic recycling
The GTPase dynamin catalyzes membrane fission but activity of the dynamin-related ATPase EHD1 is unknown. Here, using in vitro reconstitution assays and molecular dynamics simulations, the authors report that EHD1 hydrolyzes ATP to remodel, causing fission of membrane tubes and that this is necessary for endocytic recycling.
- Raunaq Deo
- , Manish S. Kushwah
- & Thomas J. Pucadyil
-
Article
| Open Access Predicting natural language descriptions of mono-molecular odorants
Predicting natural language descriptions of mono-molecular odorants
It is now possible to predict what a chemical smells like based on its chemical structure, however to date, this has only been done for a small number of odor descriptors. Here, using natural-language semantic representations, the authors demonstrate prediction of a much wider range of descriptors.
- E. Darío Gutiérrez
- , Amit Dhurandhar
- & Guillermo A. Cecchi
-
Article
| Open Access Using single nucleotide variations in single-cell RNA-seq to identify subpopulations and genotype-phenotype linkage
Using single nucleotide variations in single-cell RNA-seq to identify subpopulations and genotype-phenotype linkage
Identification of cell subpopulations using transcript abundance is noisy. Here, the authors developed a linear modeling framework, SSrGE, which utilizes effective and expressed nucleotide variations from single-cell RNA-seq to identify tumor subpopulations.
- Olivier Poirion
- , Xun Zhu
- & Lana X. Garmire
-
Article
| Open Access A majority of HIV persistence during antiretroviral therapy is due to infected cell proliferation
A majority of HIV persistence during antiretroviral therapy is due to infected cell proliferation
HIV infected cells persist for decades in patients under ART, but the mechanisms responsible remain unclear. Here, Reeves et al. use modeling approaches adapted from ecology to show that cellular proliferation, rather than viral replication, generates a majority of infected cells during ART.
- Daniel B. Reeves
- , Elizabeth R. Duke
- & Joshua T. Schiffer
-
Article
| Open Access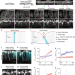 Differential lateral and basal tension drive folding of Drosophila wing discs through two distinct mechanisms
Differential lateral and basal tension drive folding of Drosophila wing discs through two distinct mechanisms
Epithelial folding has mainly been linked to forces acting in the apical actomyosin network of cells. Here, the authors show using live imaging that two distinct mechanisms, changes in basal surface tension and changes in lateral surface tension, drive the formation of two folds in the Drosophila wing disc.
- Liyuan Sui
- , Silvanus Alt
- & Christian Dahmann
-
Article
| Open Access Improved estimation of cancer dependencies from large-scale RNAi screens using model-based normalization and data integration
Improved estimation of cancer dependencies from large-scale RNAi screens using model-based normalization and data integration
Integrated analyses of multiple large-scale screenings can be complicated by batch effects and technical artefacts. McFarland et al. introduce DEMETER2, a hierarchical model coupled with model-based normalization, which allows the assessment of differential dependencies across genes and cell lines.
- James M. McFarland
- , Zandra V. Ho
- & Aviad Tsherniak
-
Article
| Open Access Substantiating freedom from parasitic infection by combining transmission model predictions with disease surveys
Substantiating freedom from parasitic infection by combining transmission model predictions with disease surveys
The decision when to stop an intervention is a critical component of parasite elimination programmes, but reliance on surveillance data alone can be inaccurate. Here, Michael et al. combine parasite transmission model predictions with disease survey data to more reliably determine when interventions can be stopped.
- Edwin Michael
- , Morgan E. Smith
- & Frank O. Richards
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic intercellular transport modulates the spatial patterning of differentiation during early neural commitment
Dynamic intercellular transport modulates the spatial patterning of differentiation during early neural commitment
How heterogeneities arise in stem cell populations remains unclear. Here, Glen et al. find that in ESC colonies cell cycle asynchronies modulate gap junctions, causing variation in intracellular signalling molecule diffusion between cells, and ultimately in spatial heterogeneity in differentiation.
- Chad M. Glen
- , Todd C. McDevitt
- & Melissa L. Kemp
-
Article
| Open Access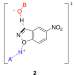 The evolution of multiple active site configurations in a designed enzyme
The evolution of multiple active site configurations in a designed enzyme
Generation and iterative optimization of designed enzymes can provide valuable insights for a more efficient catalysis. Here the authors have followed the iterative improvement of a designed Kemp eliminase and show that remote point mutations could remodel the designed active site via substantial conformational reorganization.
- Nan-Sook Hong
- , Dušan Petrović
- & Colin J. Jackson
-
Article
| Open Access Using both qualitative and quantitative data in parameter identification for systems biology models
Using both qualitative and quantitative data in parameter identification for systems biology models
Much of the data generated in biology is qualitative, but exploiting such data to inform models of biological systems remains a challenge. Here, the authors demonstrate an approach that allows use of both quantitative and qualitative data for parameterising dynamical models.
- Eshan D. Mitra
- , Raquel Dias
- & William S. Hlavacek
-
Article
| Open Access GraphDDP: a graph-embedding approach to detect differentiation pathways in single-cell-data using prior class knowledge
GraphDDP: a graph-embedding approach to detect differentiation pathways in single-cell-data using prior class knowledge
Inference and representation of differentiation trajectories from single cell RNA-seq data remains a challenge. Here, the authors offer a visualization approach that captures both continuous differentiation trajectories and discrete clusters representing metastable states along the trajectories.
- Fabrizio Costa
- , Dominic Grün
- & Rolf Backofen
-
Article
| Open Access microCLIP super learning framework uncovers functional transcriptome-wide miRNA interactions
microCLIP super learning framework uncovers functional transcriptome-wide miRNA interactions
AGO-PAR-CLIP is widely used for high-throughput miRNA target characterization. Here, the authors show that the previously neglected non-T-to-C clusters denote functional miRNA binding events, and develop microCLIP, a super learning framework that accurately detects miRNA interactions.
- Maria D. Paraskevopoulou
- , Dimitra Karagkouni
- & Artemis G. Hatzigeorgiou
-
Article
| Open Access Predicting the evolution of Escherichia coli by a data-driven approach
Predicting the evolution of Escherichia coli by a data-driven approach
How reproducible evolutionary processes are remains an important question in evolutionary biology. Here, the authors compile a compendium of more than 15,000 mutation events for Escherichia coli under 178 distinct environmental settings, and develop an ensemble of predictors to predict evolution at a gene level.
- Xiaokang Wang
- , Violeta Zorraquino
- & Ilias Tagkopoulos
-
Article
| Open Access Modeling the impact of drug interactions on therapeutic selectivity
Modeling the impact of drug interactions on therapeutic selectivity
While drugs can interact in both target and off-target cell types, more favorable interaction in the target cell may nevertheless allow for a therapeutic window. Here, the authors show, using two yeast species as a model, that differential drug interactions indeed adjust the selective window.
- Zohar B. Weinstein
- , Nurdan Kuru
- & Murat Cokol
-
Article
| Open Access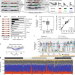 Decoding a cancer-relevant splicing decision in the RON proto-oncogene using high-throughput mutagenesis
Decoding a cancer-relevant splicing decision in the RON proto-oncogene using high-throughput mutagenesis
Alternative splicing is a critical step in eukaryotic gene expression but its molecular rules are not fully understood. Here, the authors develop a high-throughput mutagenesis approach to comprehensively characterise determinants of alternative splicing for the RON proto-oncogene.
- Simon Braun
- , Mihaela Enculescu
- & Kathi Zarnack
-
Article
| Open Access Network enhancement as a general method to denoise weighted biological networks
Network enhancement as a general method to denoise weighted biological networks
Technical noise in experiments is unavoidable, but it introduces inaccuracies into the biological networks we infer from the data. Here, the authors introduce a diffusion-based method for denoising undirected, weighted networks, and show that it improves the performances of downstream analyses.
- Bo Wang
- , Armin Pourshafeie
- & Jure Leskovec
-
Article
| Open Access Scutoids are a geometrical solution to three-dimensional packing of epithelia
Scutoids are a geometrical solution to three-dimensional packing of epithelia
Cell arrangement in the plane of epithelia is well studied, but its three-dimensional packing is largely unknown. Here the authors model curved epithelia and predict that cells adopt a geometrical shape they call “scutoid”, resulting in different apical and basal neighbours, and confirm the presence of scutoids in curved tissues.
- Pedro Gómez-Gálvez
- , Pablo Vicente-Munuera
- & Luis M. Escudero
-
Article
| Open Access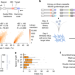 Pairwise library screen systematically interrogates Staphylococcus aureus Cas9 specificity in human cells
Pairwise library screen systematically interrogates Staphylococcus aureus Cas9 specificity in human cells
A rigorous understanding of off-target effects is necessary for SaCas9 to be used in therapeutic genome editing. Here the authors measure SaCas9 mismatch tolerance across a pairwise library screen of 88,000 guides and targets in human cells and develop a model which ranks off-target sites.
- Josh Tycko
- , Luis A. Barrera
- & Patrick D. Hsu
-
Article
| Open Access Lineage marker synchrony in hematopoietic genealogies refutes the PU.1/GATA1 toggle switch paradigm
Lineage marker synchrony in hematopoietic genealogies refutes the PU.1/GATA1 toggle switch paradigm
The timing of cell fate choices is usually unknown, because we have to rely on indirect evidence of their molecular basis. Here, the authors introduce a method to infer decision times from marker onset in cell genealogies, and find evidence refuting the paradigmatic PU.1/GATA1 cell fate switch.
- Michael K. Strasser
- , Philipp S. Hoppe
- & Carsten Marr
-
Article
| Open Access Prioritizing network communities
Prioritizing network communities
Community detection allows one to decompose a network into its building blocks. While communities can be identified with a variety of methods, their relative importance can’t be easily derived. Here the authors introduce an algorithm to identify modules which are most promising for further analysis.
- Marinka Zitnik
- , Rok Sosič
- & Jure Leskovec
-
Article
| Open Access A mixed antagonistic/synergistic miRNA repression model enables accurate predictions of multi-input miRNA sensor activity
A mixed antagonistic/synergistic miRNA repression model enables accurate predictions of multi-input miRNA sensor activity
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are important post-transcriptional regulators of gene expression but many quantitative aspects of miRNA biology remain to be elucidated. Based on a library of miRNA sensors, the authors quantify miRNA regulation at single cell level and develop a model to predict miRNA target interactions.
- Jeremy J. Gam
- , Jonathan Babb
- & Ron Weiss
-
Article
| Open Access Spatial maps of prostate cancer transcriptomes reveal an unexplored landscape of heterogeneity
Spatial maps of prostate cancer transcriptomes reveal an unexplored landscape of heterogeneity
Heterogeneity within tumors presents a challenge to cancer treatment. Here, the authors investigate transcriptional heterogeneity in prostate cancer, examining expression profiles of different tissue components and highlighting expression gradients in the tumor microenvironment.
- Emelie Berglund
- , Jonas Maaskola
- & Joakim Lundeberg
-
Article
| Open Access Interpretable dimensionality reduction of single cell transcriptome data with deep generative models
Interpretable dimensionality reduction of single cell transcriptome data with deep generative models
Although single-cell transcriptome data are increasingly available, their interpretation remains a challenge. Here, the authors present a dimensionality reduction approach that preserves both the local and global neighbourhood structures in the data thus enhancing its interpretability.
- Jiarui Ding
- , Anne Condon
- & Sohrab P. Shah
-
Article
| Open Access Networks of genetic similarity reveal non-neutral processes shape strain structure in Plasmodium falciparum
Networks of genetic similarity reveal non-neutral processes shape strain structure in Plasmodium falciparum
Plasmodium has evolved high genetic diversity in var genes, which encode for the major blood-stage antigen. Here, He et al. show how immune selection shapes the var gene repertoire in both simulated systems and a population in Ghana, by using neutral models and genetic similarity networks.
- Qixin He
- , Shai Pilosof
- & Mercedes Pascual
-
Article
| Open Access CE-BLAST makes it possible to compute antigenic similarity for newly emerging pathogens
CE-BLAST makes it possible to compute antigenic similarity for newly emerging pathogens
Sparse immune-binding data for emerging pathogens limits the ability of existing in silico antigenicity prediction methods to aid vaccine design. Here, the authors introduce a computational method that estimates antigenic pathogen similarity based on epitope structure.
- Tianyi Qiu
- , Yiyan Yang
- & Zhiwei Cao
-
Article
| Open Access Theoretical principles of transcription factor traffic on folded chromatin
Theoretical principles of transcription factor traffic on folded chromatin
How transcription factors find their targets in vivo is still poorly understood. Here the authors use molecular dynamics simulations to investigate how transcription factors diffuse on chromatin, providing a theoretical framework for understanding the key role of genome conformation in this process.
- Ruggero Cortini
- & Guillaume J. Filion
-
Article
| Open Access De novo main-chain modeling for EM maps using MAINMAST
De novo main-chain modeling for EM maps using MAINMAST
Main-chain tracing remains a time-consuming task for medium resolution cryo-EM maps. Here the authors describe MAINMAST, a computational approach for building main-chain structure models of proteins from EM maps of 4-5 Å resolution that builds main-chain models of the protein by tracing local dense points in the density distribution.
- Genki Terashi
- & Daisuke Kihara
-
Article
| Open Access Allelic decomposition and exact genotyping of highly polymorphic and structurally variant genes
Allelic decomposition and exact genotyping of highly polymorphic and structurally variant genes
Many genes of functional and clinical significance are highly polymorphic and experience structural alterations. Here, Numanagić et al. develop Aldy, a computational tool for resolving the copy number and the sequence content of each copy of a gene by analyzing whole or targeted genome sequencing data.
- Ibrahim Numanagić
- , Salem Malikić
- & S. Cenk Sahinalp
-
Article
| Open Access Enhancing Hi-C data resolution with deep convolutional neural network HiCPlus
Enhancing Hi-C data resolution with deep convolutional neural network HiCPlus
Despite its popularity for measuring the spatial organization of mammalian genomes, the resolution of most Hi-C datasets is coarse due to sequencing cost. Here, Zhang et al. develop HiCPlus, a computational approach based on deep convolutional neural network, to infer high-resolution Hi-C interaction matrices from low-resolution Hi-C data.
- Yan Zhang
- , Lin An
- & Feng Yue
-
Article
| Open Access Cell shape information is transduced through tension-independent mechanisms
Cell shape information is transduced through tension-independent mechanisms
It is not known whether the shape of a cell can regulate cellular phenotype independently. Here, the authors show that culturing kidney podocytes or smooth muscle cells on 3-D biomimetic surfaces results in phenotypic changes and that cell shape is sensed by integrin β3 in a tension-independent manner.
- Amit Ron
- , Evren U. Azeloglu
- & Ravi Iyengar
-
Article
| Open Access A general pharmacodynamic interaction model identifies perpetrators and victims in drug interactions
A general pharmacodynamic interaction model identifies perpetrators and victims in drug interactions
Assessment of pharmacodynamic interactions is at the heart of combination therapy development. Here the authors introduce a general drug interaction scoring model that enables quantification of synergistic and antagonistic interactions and determination of the directionality of the interactions.
- Sebastian G. Wicha
- , Chunli Chen
- & Ulrika S. H. Simonsson
-
Article
| Open Access Exocytosis-coordinated mechanisms for tip growth underlie pollen tube growth guidance
Exocytosis-coordinated mechanisms for tip growth underlie pollen tube growth guidance
Tip-growing cells can find their growing path toward the source of attractive signals. Here, using experimental data and mathematical modeling, Luo et al. demonstrate that tip-localized exocytosis can integrate guidance cues with Rho GTPase signaling to control cell wall mechanics and direct tip growth in Arabidopsis pollen tubes.
- Nan Luo
- , An Yan
- & Zhenbiao Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Deconvoluting interrelationships between concentrations and chemical shifts in urine provides a powerful analysis tool
Deconvoluting interrelationships between concentrations and chemical shifts in urine provides a powerful analysis tool
The NMR chemical shifts of a substance in urine strongly depend on the composition of the mixture itself, and this makes automatic assignment for quantification very difficult. Here the authors show the chemical shifts of signals and the concentration of NMR-invisible inorganic ions in urine, are predictable.
- Panteleimon G. Takis
- , Hartmut Schäfer
- & Claudio Luchinat
-
Article
| Open Access Assessing the impact of imperfect adherence to artemether-lumefantrine on malaria treatment outcomes using within-host modelling
Assessing the impact of imperfect adherence to artemether-lumefantrine on malaria treatment outcomes using within-host modelling
Artemether lumefantrine is widely used for the treatment of uncomplicated malaria. The impact of imperfect patient adherence to the six-dose regimen is hard to assess. Using adherence data for unsupervised patients, the authors model how suboptimal adherence affects treatment outcomes.
- Joseph D. Challenger
- , Katia Bruxvoort
- & Lucy C. Okell
-
Article
| Open Access Paradoxes in leaky microbial trade
Paradoxes in leaky microbial trade
Microbes live in communities and exchange metabolites, but the resulting dynamics are poorly understood. Here, the authors study the interplay between metabolite production strategies and population dynamics, and find that complex and unexpected dynamics emerge even in simple microbial economies.
- Yoav Kallus
- , John H. Miller
- & Eric Libby
-
Article
| Open Access Pan-cancer analysis of homozygous deletions in primary tumours uncovers rare tumour suppressors
Pan-cancer analysis of homozygous deletions in primary tumours uncovers rare tumour suppressors
Homozygous deletions are rare in cancers and often target tumour suppressor genes. Here, the authors conduct pan-cancer analyses and apply statistical modelling to identify 27 candidate tumour suppressors, including MAFTRR, KIAA1551, and IGF2BP2.
- Jiqiu Cheng
- , Jonas Demeulemeester
- & Peter Van Loo

 Mapping vaccination coverage to explore the effects of delivery mechanisms and inform vaccination strategies
Mapping vaccination coverage to explore the effects of delivery mechanisms and inform vaccination strategies