Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access The liver and muscle secreted HFE2-protein maintains central nervous system blood vessel integrity
The liver and muscle secreted HFE2-protein maintains central nervous system blood vessel integrity
Blood vessel integrity is critical to maintain brain health. Here, the authors show that both the liver and the muscles secrete HFE2, a protein that promotes blood vessel integrity in healthy animals and in an animal model for multiple sclerosis.
- Xue Fan Wang
- , Robin Vigouroux
- & Philippe P. Monnier
-
Article
| Open Access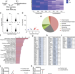 15-Lipoxygenase promotes resolution of inflammation in lymphedema by controlling Treg cell function through IFN-β
15-Lipoxygenase promotes resolution of inflammation in lymphedema by controlling Treg cell function through IFN-β
Specialised pro-resolving lipid mediators can reduce inflammatory responses and may be active in lymphedema. Here the authors show that in a mouse model 15-LO derived lipid mediators are reduced during inflammation and that a lack of the 15-LO producing enzyme aggravated disease and addition of 15-LO enzyme or Treg cells reduced disease.
- A. Zamora
- , M. Nougué
- & B. Garmy-Susini
-
Article
| Open Access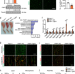 FNIP1 abrogation promotes functional revascularization of ischemic skeletal muscle by driving macrophage recruitment
FNIP1 abrogation promotes functional revascularization of ischemic skeletal muscle by driving macrophage recruitment
Functional revascularization is vital to the recovery of blood flow. Here, Sun et al. show that myofiber FNIP1 is a negative regulator of muscle functional angiogenesis and revascularization after ischemia by controlling macrophage recruitment.
- Zongchao Sun
- , Likun Yang
- & Zhenji Gan
-
Article
| Open Access Deficiency of endothelial sirtuin1 in mice stimulates skeletal muscle insulin sensitivity by modifying the secretome
Deficiency of endothelial sirtuin1 in mice stimulates skeletal muscle insulin sensitivity by modifying the secretome
Endothelial Sirtuin1 downregulation in metabolic disorders causes vascular dysfunction and inflammation. Here, the authors show that deficiency of endothelial Sirtuin1, while having deleterious effects on the vasculature, stimulates skeletal muscle insulin sensitivity and improves glucose disposal.
- Qiuxia Li
- , Quanjiang Zhang
- & Kaikobad Irani
-
Article
| Open Access MTH1 protects platelet mitochondria from oxidative damage and regulates platelet function and thrombosis
MTH1 protects platelet mitochondria from oxidative damage and regulates platelet function and thrombosis
MTH1 hydrolyzes oxidized nucleotides to prevent their mis-incorporation into DNA under oxidative stress. Here, the authors show that MTH1 is expressed in platelets and its deficiency increases mitochondrial DNA oxidative damage, impairs platelet function and hemostasis.
- Yangyang Ding
- , Xiang Gui
- & Jianlin Qiao
-
Article
| Open Access Highly efficient platelet generation in lung vasculature reproduced by microfluidics
Highly efficient platelet generation in lung vasculature reproduced by microfluidics
Highly efficient generation of platelets in the vasculature. Here, Zhao et al. show that the mouse platelet precursor cell, megakaryocytes, generate physiological numbers of functional platelets when passaged repeatedly through pulmonary vasculature.
- Xiaojuan Zhao
- , Dominic Alibhai
- & Alastair W. Poole
-
Article
| Open Access SVEP1 is an endogenous ligand for the orphan receptor PEAR1
SVEP1 is an endogenous ligand for the orphan receptor PEAR1
SVEP1 is linked to numerous human diseases, though its disease-promoting mechanism has remained unclear. Here, the authors identify SVEP1 as a ligand for the orphan receptor PEAR1 and provide insight into the role of this interaction in cardiovascular disease.
- Jared S. Elenbaas
- , Upasana Pudupakkam
- & Nathan O. Stitziel
-
Article
| Open Access Integration of single-cell transcriptomes and biological function reveals distinct behavioral patterns in bone marrow endothelium
Integration of single-cell transcriptomes and biological function reveals distinct behavioral patterns in bone marrow endothelium
Here Kim et al. show that primary BMECs can be maintained ex vivo as distinct sinusoidal- and arterial-like populations and that the presence of macrophages is critical to preserve their native transcriptomic profiles and functional heterogeneity.
- Young-Woong Kim
- , Greta Zara
- & Nadia Carlesso
-
Article
| Open Access Endothelial alpha globin is a nitrite reductase
Endothelial alpha globin is a nitrite reductase
In mammals, hypoxia causes dilation of small arteries for increased metabolic demand. Keller et al used novel transgenic mice to show alpha hemoglobin in endothelium, once thought only in red blood cells, can regulate hypoxic-mediated dilation.
- T. C. Stevenson Keller IV
- , Christophe Lechauve
- & Brant E. Isakson
-
Article
| Open Access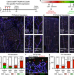 Endothelial cell cycle state determines propensity for arterial-venous fate
Endothelial cell cycle state determines propensity for arterial-venous fate
During blood vessel development, endothelial cells become specified toward arterial or venous fates. Chavkin et al find that distinct endothelial cell cycle states provide windows of opportunity for the molecular induction of arterial or venous fate.
- Nicholas W. Chavkin
- , Gael Genet
- & Karen K. Hirschi
-
Article
| Open Access A brainstem monosynaptic excitatory pathway that drives locomotor activities and sympathetic cardiovascular responses
A brainstem monosynaptic excitatory pathway that drives locomotor activities and sympathetic cardiovascular responses
Functional brain architecture underlying autonomic adjustments to exercise has remained unknown. Here, the authors reveal a subcortical pathway that relays volitional motor signals to drive locomotor activities and sympathetic cardiovascular responses.
- Satoshi Koba
- , Nao Kumada
- & Tatsuo Watanabe
-
Article
| Open Access Genome-wide associations of aortic distensibility suggest causality for aortic aneurysms and brain white matter hyperintensities
Genome-wide associations of aortic distensibility suggest causality for aortic aneurysms and brain white matter hyperintensities
Aortic distensibility is a risk factor for multiple cardiovascular events, but the genetic etiology is not well understood. Here, the authors identify genetic variants linked to aortic distensibility, highlighting mechanistic pathways and causal relationships between distensibility and both aortic aneurysms and brain small vessel disease.
- Catherine M. Francis
- , Matthias E. Futschik
- & Paul M. Matthews
-
Article
| Open Access CO2 signaling mediates neurovascular coupling in the cerebral cortex
CO2 signaling mediates neurovascular coupling in the cerebral cortex
The mechanism of neurovascular coupling ensures that the brain energy supply is sufficient to meet demand. Here the authors show that in this mechanism CO2 plays an important role in neuronal activity-dependent regulation of local brain blood flow.
- Patrick S. Hosford
- , Jack A. Wells
- & Alexander V. Gourine
-
Article
| Open Access Pyridine nucleotide redox potential in coronary smooth muscle couples myocardial blood flow to cardiac metabolism
Pyridine nucleotide redox potential in coronary smooth muscle couples myocardial blood flow to cardiac metabolism
Physiological matching of blood flow to the demand for oxygen by the heart is required for sustained cardiac health, yet the underlying mechanisms are obscure. Here, the authors report a key role for acute modifications to the redox state of intracellular pyridine nucleotides in coronary smooth muscle and their impact on voltage-gated K + channels in metabolic vasodilation
- Marc M. Dwenger
- , Sean M. Raph
- & Matthew A. Nystoriak
-
Article
| Open Access βIV-spectrin as a stalk cell-intrinsic regulator of VEGF signaling
βIV-spectrin as a stalk cell-intrinsic regulator of VEGF signaling
Defective angiogenesis remains a high source of morbidity in multiple disorders. Here they show that βIV-spectrin, a membrane-associated cytoskeletal protein, is essential for regulation of endothelial tip cell populations and VEGF signaling during sprouting angiogenesis.
- Eun-A Kwak
- , Christopher C. Pan
- & Nam Y. Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Network-driven anomalous transport is a fundamental component of brain microvascular dysfunction
Network-driven anomalous transport is a fundamental component of brain microvascular dysfunction
Blood microcirculation supplies neurons with oxygen and nutrients, and contributes to clearing their neurotoxic waste. Here, the authors analyse blood flow simulations to establish the physical laws linking the microvascular architecture to the macroscopic transport properties that control oxygen supply and waste clearance.
- Florian Goirand
- , Tanguy Le Borgne
- & Sylvie Lorthois
-
Article
| Open Access Efficacy and safety of next-generation tick transcriptome-derived direct thrombin inhibitors
Efficacy and safety of next-generation tick transcriptome-derived direct thrombin inhibitors
Bleeding complications limits the use of effective antithrombotics therapeutics. Here, the authors developed next-generation direct thrombin inhibitors with low bleeding risks as safe peri-percutaneous coronary intervention anticoagulants when used in combination with antiplatelets.
- Cho Yeow Koh
- , Norrapat Shih
- & Mark Y. Chan
-
Article
| Open Access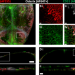 Quantitative 3D imaging of the cranial microvascular environment at single-cell resolution
Quantitative 3D imaging of the cranial microvascular environment at single-cell resolution
Vascularization is critical for cranial bone growth, maintenance, and healing, but it remains unknown how blood vessels are spatially distributed in the calvarium, and how they interact with skeletal progenitors during these processes. Here, the authors apply a quantitative light-sheet imaging platform to visualize and analyze the relationship between blood vessels and skeletal progenitors throughout the murine calvarium.
- Alexandra N. Rindone
- , Xiaonan Liu
- & Warren L. Grayson
-
Article
| Open Access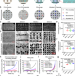 Microchannelled alkylated chitosan sponge to treat noncompressible hemorrhages and facilitate wound healing
Microchannelled alkylated chitosan sponge to treat noncompressible hemorrhages and facilitate wound healing
Developing effective treatments for noncompressible hemorrhages remains a challenge. Here the authors engineer alkylated chitosan sponges with highly interconnective microchannels and demonstrate anti-infective activity, as well as higher pro-coagulant, hemostatic and wound healing capacities compared to clinically-used materials in rat and pig liver models.
- Xinchen Du
- , Le Wu
- & Meifeng Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access Importance of the renal ion channel TRPM6 in the circadian secretion of renin to raise blood pressure
Importance of the renal ion channel TRPM6 in the circadian secretion of renin to raise blood pressure
Circadian variation of blood pressure, with higher values in the active period, is associated with the risk of fatal cardiovascular events. Here, we show the importance of renal TRPM6, a Magnesium-permeable cation channel, in raising blood pressure by stimulating renin secretion.
- Yosuke Funato
- , Daisuke Yamazaki
- & Hiroaki Miki
-
Article
| Open Access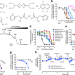 Zinc drives vasorelaxation by acting in sensory nerves, endothelium and smooth muscle
Zinc drives vasorelaxation by acting in sensory nerves, endothelium and smooth muscle
Metals such as calcium and potassium have long been known to regulate the diameter of arteries that control blood flow. Here, we report that zinc causes relaxation of blood vessels and reduces blood pressure by its coordinated action in sensory nerves, endothelium and smooth muscle cells.
- Ashenafi H. Betrie
- , James A. Brock
- & Scott Ayton
-
Article
| Open Access Mitofusin-2 stabilizes adherens junctions and suppresses endothelial inflammation via modulation of β-catenin signaling
Mitofusin-2 stabilizes adherens junctions and suppresses endothelial inflammation via modulation of β-catenin signaling
Endothelial tissues must have intact barrier function, but this may be disrupted during inflammation. Here, the authors show that the mitochondrial protein Mitofusin-2 stabilizes cell–cell adherens junctions in endothelial cells during homeostasis and binds the transcriptional activator β-catenin upon inflammatory stimulation.
- Young-Mee Kim
- , Sarah Krantz
- & Jalees Rehman
-
Article
| Open Access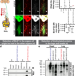 Proteomics of protein trafficking by in vivo tissue-specific labeling
Proteomics of protein trafficking by in vivo tissue-specific labeling
The network of proteins secreted for interorgan communication is poorly understood. Here, the authors develop a method, based on protein labeling, to study cell-specific secretomes and interorgan protein trafficking, and demonstrate their approach in Drosophila and mouse models.
- Ilia A. Droujinine
- , Amanda S. Meyer
- & Norbert Perrimon
-
Review Article
| Open Access Renal metabolism and hypertension
Renal metabolism and hypertension
Hypertension is one of the most important risk factors for cardiovascular disease. The kidneys, which have a very high metabolic rate, play a fundamental role in blood pressure regulation. In this review, the authors discuss recent studies on the role of renal metabolism in the development of hypertension.
- Zhongmin Tian
- & Mingyu Liang
-
Article
| Open Access Adaptive modulation of brain hemodynamics across stereotyped running episodes
Adaptive modulation of brain hemodynamics across stereotyped running episodes
Theta and gamma rhythms are essential to ensure timely communication between brain structures during locomotion. Here the authors investigate the association between cerebral blood flow and neural oscillations in freely behaving mice running a linear track.
- Antoine Bergel
- , Elodie Tiran
- & Ivan Cohen
-
Article
| Open Access High-speed volumetric two-photon fluorescence imaging of neurovascular dynamics
High-speed volumetric two-photon fluorescence imaging of neurovascular dynamics
Monitoring hemodynamics in the brain is important in understanding medical imaging data and mechanisms of disease. Here the authors use high-throughput two-photon microscopy with an axially-extended Bessel focus to measure vessel size and blood flow down to capillary scale in the awake mouse brain.
- Jiang Lan Fan
- , Jose A. Rivera
- & Na Ji
-
Article
| Open Access Vascular surveillance by haptotactic blood platelets in inflammation and infection
Vascular surveillance by haptotactic blood platelets in inflammation and infection
Breakdown of vascular barriers is a major complication of inflammatory diseases. However, the mechanisms underlying platelet recruitment to inflammatory micro-environments remains unclear. Here, the authors identify haptotaxis as a key effector function of immune-responsive platelets
- Leo Nicolai
- , Karin Schiefelbein
- & Florian Gaertner
-
Article
| Open Access Cardio-centric hemodynamic management improves spinal cord oxygenation and mitigates hemorrhage in acute spinal cord injury
Cardio-centric hemodynamic management improves spinal cord oxygenation and mitigates hemorrhage in acute spinal cord injury
Clinical neuroprotective strategies for acute spinal cord injury (SCI) have largely overlooked the heart. Here the authors show cardiac contractility is immediately impaired in a porcine model of T2 SCI, and cardio-centric treatment with dobutamine optimizes cord oxygenation and mitigates haemorrhage.
- Alexandra M. Williams
- , Neda Manouchehri
- & Christopher R. West
-
Article
| Open Access Remote ischemic conditioning counteracts the intestinal damage of necrotizing enterocolitis by improving intestinal microcirculation
Remote ischemic conditioning counteracts the intestinal damage of necrotizing enterocolitis by improving intestinal microcirculation
Necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) is one of the most lethal gastrointestinal emergencies in neonates needing precision treatment. Here the authors show that remote ischemic conditioning is a non-invasive therapeutic method that enhances blood flow in the intestine, reduces damage, and improves NEC outcome.
- Yuhki Koike
- , Bo Li
- & Agostino Pierro
-
Article
| Open Access Modeling lung perfusion abnormalities to explain early COVID-19 hypoxemia
Modeling lung perfusion abnormalities to explain early COVID-19 hypoxemia
Early stages of the novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19) have been associated with silent hypoxia and poor oxygenation despite relatively small fractions of afflicted lung. Here, the authors present a mathematical model which reproduces the vascular pulmonary mechanisms observed in patients with early COVID-19.
- Jacob Herrmann
- , Vitor Mori
- & Béla Suki
-
Article
| Open Access Macrophage secretion of miR-106b-5p causes renin-dependent hypertension
Macrophage secretion of miR-106b-5p causes renin-dependent hypertension
Myeloid cells are involved in hypertension, but their exact role in renin-induced hypertension remains unclear. Here the authors show that impaired vitamin D signaling in myeloid cells causes hypertension via macrophage-specific miR-106b-5p secretion, which activates renin production in the kidney.
- J. Oh
- , S. J. Matkovich
- & C. Bernal-Mizrachi
-
Article
| Open Access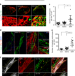 Meningeal lymphatics clear erythrocytes that arise from subarachnoid hemorrhage
Meningeal lymphatics clear erythrocytes that arise from subarachnoid hemorrhage
Extravasated erythrocytes in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) contribute to the pathogenesis of subarachnoid haemorrhage (SAH). Here, the authors show that meningeal lymphatics drain extravasated erythorcytes and that blockage of this drainage aggravates SAH severity.
- Jinman Chen
- , Linmei Wang
- & Yongjun Wang
-
Article
| Open Access β4GALT1 controls β1 integrin function to govern thrombopoiesis and hematopoietic stem cell homeostasis
β4GALT1 controls β1 integrin function to govern thrombopoiesis and hematopoietic stem cell homeostasis
Mutations affecting sialylation and galactosylation affect megakaryocyte function and thrombopoiesis. Here the authors show that the enzyme β4GalT1 regulates thrombopoiesis and hematopoietic stem cell homeostasis by controlling beta-1 integrin function.
- Silvia Giannini
- , Melissa M. Lee-Sundlov
- & Karin M. Hoffmeister
-
Article
| Open Access Astrocytes monitor cerebral perfusion and control systemic circulation to maintain brain blood flow
Astrocytes monitor cerebral perfusion and control systemic circulation to maintain brain blood flow
The brain receives 20% of cardiac output, but in accord with the current knowledge lacks a specialized sensor of its own blood flow. Here, the authors show that brain astrocytes detect drops in perfusion and trigger compensatory increases in arterial pressure and heart rate to preserve brain blood flow and oxygen delivery.
- Nephtali Marina
- , Isabel N. Christie
- & Alexander V. Gourine
-
Article
| Open Access Crystal structure and substrate-induced activation of ADAMTS13
Crystal structure and substrate-induced activation of ADAMTS13
The plasma metalloprotease ADAMTS13 regulates the platelet-tethering function of von Willebrand factor (VWF) in a shear-dependent manner. Here the authors present the ADAMTS13 crystal structure of the 70kDa N-terminal metalloprotease to spacer domains, and using kinetic measurements they identify a substrate binding induced allosteric mechanism for ADAMTS13, where VWF functions both as an activating cofactor and substrate.
- Anastasis Petri
- , Hyo Jung Kim
- & James T. B. Crawley
-
Article
| Open Access Aortic pathology from protein kinase G activation is prevented by an antioxidant vitamin B12 analog
Aortic pathology from protein kinase G activation is prevented by an antioxidant vitamin B12 analog
Individuals carrying a gain-of-function mutation in PKG1 develop thoracic aortic aneurysms and dissections. Here Schwaerzer et al. show that mice carrying the same mutation recapitulate the human disease, and find that treatment with anti-oxidants including cobinamide, a vitamin B12 analog, prevents disease progression.
- Gerburg K. Schwaerzer
- , Hema Kalyanaraman
- & Renate B. Pilz
-
Article
| Open Access Identification of a pro-angiogenic functional role for FSP1-positive fibroblast subtype in wound healing
Identification of a pro-angiogenic functional role for FSP1-positive fibroblast subtype in wound healing
Activated fibroblasts are key contributors to tissue repair after cardiac injury. Here, Saraswati et al. identify and characterize a subpopulation of FSP1-positive cardiac fibroblasts with proangiogenic properties in infarcted hearts.
- Sarika Saraswati
- , Stephanie M. W. Marrow
- & Pampee P. Young
-
Article
| Open Access The cyclooxygenase-1/mPGES-1/endothelial prostaglandin EP4 receptor pathway constrains myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury
The cyclooxygenase-1/mPGES-1/endothelial prostaglandin EP4 receptor pathway constrains myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury
The use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs inhibiting COX-1/2 is associated with an increased risk of heart failure. Here the authors show that mPGES-1, a therapeutic target downstream of COX enzymes, protects from cardiac ischemia/reperfusion injury, limiting leukocyte-endothelial interactions and preserving microvascular perfusion partly via the endothelial EP4 receptor.
- Liyuan Zhu
- , Chuansheng Xu
- & Miao Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Interethnic analyses of blood pressure loci in populations of East Asian and European descent
Interethnic analyses of blood pressure loci in populations of East Asian and European descent
Blood pressure (BP) is a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease and more than 200 genetic loci associated with BP are known. Here, the authors perform discovery GWAS for BP in East Asians and meta-analysis in East Asians and Europeans and report ancestry-specific BP SNPs and selection signals.
- Fumihiko Takeuchi
- , Masato Akiyama
- & Norihiro Kato
-
Article
| Open Access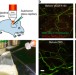 Intravital imaging-based analysis tools for vessel identification and assessment of concurrent dynamic vascular events
Intravital imaging-based analysis tools for vessel identification and assessment of concurrent dynamic vascular events
Different stimuli can induce dynamic changes in blood flow velocity, vessel diameter and permeability. Here the authors develop a multi-photon microscopy-based image analysis tool allowing the identification of vessels and the assessment of rapid changes in large vascular networks.
- Naoki Honkura
- , Mark Richards
- & Lena Claesson-Welsh
-
Correspondence
| Open Access Correspondence: Challenging a proposed role for TRPC5 in aortic baroreceptor pressure-sensing
Correspondence: Challenging a proposed role for TRPC5 in aortic baroreceptor pressure-sensing
- Pratish Thakore
- , Susan D. Brain
- & David J. Beech
-
Article
| Open Access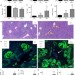 The podoplanin-CLEC-2 axis inhibits inflammation in sepsis
The podoplanin-CLEC-2 axis inhibits inflammation in sepsis
Sepsis is a life-threatening condition where exaggerated inflammatory responses lead to severe tissue damage. Here, Rayes and colleagues show that the interaction between podoplanin and its receptor CLEC-2 on platelets plays a critical role in limiting inflammation during sepsis.
- Julie Rayes
- , Siân Lax
- & Steve P. Watson
-
Article
| Open Access Rhythmic potassium transport regulates the circadian clock in human red blood cells
Rhythmic potassium transport regulates the circadian clock in human red blood cells
Circadian rhythms usually rely on cyclic variations in gene expression. Red blood cells, however, display circadian rhythms while being devoid of nuclear DNA. Here, Henslee and colleagues show that circadian rhythms in isolated human red blood cells are dependent on rhythmic transport of K+ ions.
- Erin A. Henslee
- , Priya Crosby
- & Fatima H. Labeed
-
Article
| Open Access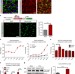 NOTCH1 is a mechanosensor in adult arteries
NOTCH1 is a mechanosensor in adult arteries
The arterial wall is subjected to mechanical forces that modulate endothelial cell responses. Here, Mack and colleagues identify a novel role for Notch1 as a mechanosensor in adult arteries, where it ensures junctional integrity through modulation of calcium signalling and limits atherosclerosis.
- Julia J. Mack
- , Thiago S. Mosqueiro
- & M. Luisa Iruela-Arispe
-
Article
| Open Access Quantitative structural mechanobiology of platelet-driven blood clot contraction
Quantitative structural mechanobiology of platelet-driven blood clot contraction
Blood clot contraction is a cellular (patho)physiological process essential for wound healing, hemostasis, and thrombosis. Here, the authors describe the physical structural mechanism by which platelet filopodia pull “hand-over-hand” on fibrin fibers to compact them into bundled agglomerates.
- Oleg V. Kim
- , Rustem I. Litvinov
- & John W. Weisel
-
Article
| Open Access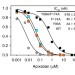 Engineered factor Xa variants retain procoagulant activity independent of direct factor Xa inhibitors
Engineered factor Xa variants retain procoagulant activity independent of direct factor Xa inhibitors
A major drawback in the clinical use of the oral anticoagulants that directly inhibit factor Xa in order to prevent blood clot formation is the potential for life threatening bleeding events. Here the authors describe factor Xa variants that are refractory to inhibition by these anticoagulants and could serve as rescue agents in treated patients.
- Daniël Verhoef
- , Koen M. Visscher
- & Mettine H. A. Bos
-
Article
| Open Access Platelet function is modified by common sequence variation in megakaryocyte super enhancers
Platelet function is modified by common sequence variation in megakaryocyte super enhancers
Numerous genetic variants, including those located in the non-coding regions of the genome, are known to be associated with blood cells traits. Here, Frontini and colleagues investigate their potential regulatory functions using epigenomic data and promoter long-range interactions.
- Romina Petersen
- , John J. Lambourne
- & Mattia Frontini
-
Article
| Open Access Exploiting macrophage autophagy-lysosomal biogenesis as a therapy for atherosclerosis
Exploiting macrophage autophagy-lysosomal biogenesis as a therapy for atherosclerosis
Dysfunction of autophagy in plaque macrophages aggravates atherosclerosis. Here the authors show that induction of macrophage autophagy–lysosomal biogenesis either genetically by overexpression of the master transcriptional regulator of this process, TFEB, or pharmacologically with trehalose is atheroprotective.
- Ismail Sergin
- , Trent D. Evans
- & Babak Razani
-
Article
| Open Access Leukocyte integrin Mac-1 regulates thrombosis via interaction with platelet GPIbα
Leukocyte integrin Mac-1 regulates thrombosis via interaction with platelet GPIbα
The binding of the leukocyte integrin Mac1 to the platelet receptor GPIbα is important for the physiological response to tissue injury. Here the authors show that this interaction also regulates thrombosis, without influencing bleeding time, which may provide clues for the development of new anti-thrombotic drugs.
- Yunmei Wang
- , Huiyun Gao
- & Daniel I. Simon

 Functional analysis of the human perivascular subarachnoid space
Functional analysis of the human perivascular subarachnoid space