Featured
-
-
Matters Arising
| Open AccessOn the reporting and analysis of a cancer evolutionary adaptive dosing trial
- Hitesh B. Mistry
-
Article
| Open Access Spite is contagious in dynamic networks
Spite is contagious in dynamic networks
As spiteful behaviors harm both the actor and the target, it is challenging to understand how these behaviors could be adaptive. Here Fulker et al. show that spite can be favored by feedbacks with network structure that create correlated and anti-correlated behavioral interactions simultaneously.
- Zachary Fulker
- , Patrick Forber
- & Christoph Riedl
-
Article
| Open Access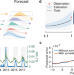 Optimizing respiratory virus surveillance networks using uncertainty propagation
Optimizing respiratory virus surveillance networks using uncertainty propagation
Lack of a widespread surveillance network hampers accurate infectious disease forecasting. Here the authors provide a framework to optimize the selection of surveillance site locations and show that accurate forecasting of respiratory diseases for locations without surveillance is feasible.
- Sen Pei
- , Xian Teng
- & Jeffrey Shaman
-
Article
| Open Access Survey data and human computation for improved flu tracking
Survey data and human computation for improved flu tracking
Digital trace data from search engines lacks information about the experiences of the individuals generating the data. Here the authors link search data and human computation to build a tracking model of influenza-like illness.
- Stefan Wojcik
- , Avleen S. Bijral
- & David Lazer
-
Article
| Open Access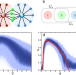 Coherence resonance in influencer networks
Coherence resonance in influencer networks
Influencer networks include a small set of highly-connected nodes and can reach synchrony only via strong node interaction. Tönjes et al. show that introducing an optimal amount of noise enhances synchronization of such networks, which may be relevant for neuroscience or opinion dynamics applications.
- Ralf Tönjes
- , Carlos E. Fiore
- & Tiago Pereira
-
Article
| Open Access Quantifying accuracy and heterogeneity in single-molecule super-resolution microscopy
Quantifying accuracy and heterogeneity in single-molecule super-resolution microscopy
Standard benchmarking of single-molecule localization microscopy cannot quantify nanoscale accuracy of arbitrary datasets. Here, the authors present Wasserstein-induced flux, a method using a chosen perturbation and knowledge of the imaging system to measure confidence of individual localizations.
- Hesam Mazidi
- , Tianben Ding
- & Matthew D. Lew
-
Article
| Open Access A social engineering model for poverty alleviation
A social engineering model for poverty alleviation
Current inequality and market consumption modelling appears to be subjective. Here the authors combined all three axes of poverty modelling - Engel-Krishnakumar’s microeconomics, Aoki-Chattopadhyay’s mathematical precept and found that multivariate construction is a key component of economic data analysis, implying all modes of income and expenditure need to be considered to arrive at a proper weighted prediction of poverty.
- Amit K. Chattopadhyay
- , T. Krishna Kumar
- & Iain Rice
-
Article
| Open Access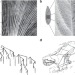 Discontinuous transition to loop formation in optimal supply networks
Discontinuous transition to loop formation in optimal supply networks
Supply networks with optimal structure do not contain loops but these can arise as a result of damages or fluctuations. Here Kaiser et al. uncover the mechanisms of loop formation, predict their location and draw analogies with loop formation in biological networks such as plants and animal vasculature.
- Franz Kaiser
- , Henrik Ronellenfitsch
- & Dirk Witthaut
-
Article
| Open Access Navigating the landscape of multiplayer games
Navigating the landscape of multiplayer games
Multiplayer games can be used as testbeds for the development of learning algorithms for artificial intelligence. Omidshafiei et al. show how to characterize and compare such games using a graph-based approach, generating new games that could potentially be interesting for training in a curriculum.
- Shayegan Omidshafiei
- , Karl Tuyls
- & Rémi Munos
-
Article
| Open Access Mutualistic networks emerging from adaptive niche-based interactions
Mutualistic networks emerging from adaptive niche-based interactions
Nested and modular patterns are vastly observed in mutualistic networks across genres and geographic conditions. Here, the authors show a unified mechanism that underlies the assembly and evolution of such networks, based on adaptive niche interactions of the participants.
- Weiran Cai
- , Jordan Snyder
- & Raissa M. D’Souza
-
Article
| Open Access Optical framed knots as information carriers
Optical framed knots as information carriers
Beam shaping methods can generate optical fields with nontrivial topologies, which are invariant against perturbations and thus interesting for information encoding. Here, the authors introduce the realization of framed optical knots to encode programs with the conjoined use of prime factorization.
- Hugo Larocque
- , Alessio D’Errico
- & Ebrahim Karimi
-
Article
| Open Access A network model of Italy shows that intermittent regional strategies can alleviate the COVID-19 epidemic
A network model of Italy shows that intermittent regional strategies can alleviate the COVID-19 epidemic
An ongoing global debate concerns effective and sustainable lockdown release strategies in the current pandemic. Here, the authors implement a network model at healthcare-relevant spatial scale to show that coordinated local strategies can be effective in containing further resurgence of the disease.
- Fabio Della Rossa
- , Davide Salzano
- & Mario di Bernardo
-
Article
| Open Access Clustering earthquake signals and background noises in continuous seismic data with unsupervised deep learning
Clustering earthquake signals and background noises in continuous seismic data with unsupervised deep learning
The authors here tackle the problem that too much seismic data is acquired worldwide to be evaluated in a timely fashion. Seydoux and colleagues develop a machine learning framework that can detect and cluster seismic signals in continuous seismic records.
- Léonard Seydoux
- , Randall Balestriero
- & Richard Baraniuk
-
Article
| Open Access Reconciling contrasting views on economic complexity
Reconciling contrasting views on economic complexity
Both the mathematics and outcomes of the Method of Reflections (MR) and Fitness and Complexity algorithm (FC) approaches differ largely. Here the authors recast both methods in a mathematical and multidimensional framework to reconcile both and show that the conflicts between the two methodologies to measure economic complexity can be resolved by a neat mathematical method based on linear-algebra tools within a bipartite-networks framework.
- Carla Sciarra
- , Guido Chiarotti
- & Francesco Laio
-
Article
| Open Access Representation of molecular structures with persistent homology for machine learning applications in chemistry
Representation of molecular structures with persistent homology for machine learning applications in chemistry
The choice of molecular representations can severely impact the performances of machine-learning methods. Here the authors demonstrate a persistence homology based molecular representation through an active-learning approach for predicting CO2/N2 interaction energies at the density functional theory (DFT) level.
- Jacob Townsend
- , Cassie Putman Micucci
- & Konstantinos D. Vogiatzis
-
Article
| Open Access Search and rescue at sea aided by hidden flow structures
Search and rescue at sea aided by hidden flow structures
Every year, hundreds of people die at sea because of vessel accidents, and a key challenge in reducing these fatalities is to make Search and Rescue (SAR) planning more efficient. Here, the authors uncover hidden flow features that attract floating objects, providing specific information for optimal SAR planning.
- Mattia Serra
- , Pratik Sathe
- & George Haller
-
Article
| Open Access Partial cross mapping eliminates indirect causal influences
Partial cross mapping eliminates indirect causal influences
It is crucial yet challenging to identify cause-consequence relation in complex dynamical systems where direct causal links can mix with indirect ones. Leng et al. propose a data-driven model-independent method to distinguish direct from indirect causality and test its applicability to real-world data.
- Siyang Leng
- , Huanfei Ma
- & Luonan Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Evolution of cooperation on temporal networks
Evolution of cooperation on temporal networks
Population structure enables emergence of cooperation among individuals, but the impact of the dynamic nature of real interaction networks is not understood. Here, the authors study the evolution of cooperation on temporal networks and find that temporality enhances the evolution of cooperation.
- Aming Li
- , Lei Zhou
- & Simon A. Levin
-
Article
| Open Access Data-driven analysis and forecasting of highway traffic dynamics
Data-driven analysis and forecasting of highway traffic dynamics
The demands on transportation systems continue to grow while the methods for analyzing and forecasting traffic conditions remain limited. Here the authors show a parameter-independent approach for an accurate description, identification and forecasting of spatio-temporal traffic patterns directly from data.
- A. M. Avila
- & I. Mezić
-
Article
| Open Access Prostate-specific antigen dynamics predict individual responses to intermittent androgen deprivation
Prostate-specific antigen dynamics predict individual responses to intermittent androgen deprivation
Prostate specific antigen (PSA) is a biomarker for prostate cancer. Here, the authors develop a mathematical model where longitudinal changes in PSA levels predict responses to intermittent androgen deprivation in patients with prostate cancer.
- Renee Brady-Nicholls
- , John D. Nagy
- & Heiko Enderling
-
Article
| Open Access Identifying degradation patterns of lithium ion batteries from impedance spectroscopy using machine learning
Identifying degradation patterns of lithium ion batteries from impedance spectroscopy using machine learning
Forecasting the state of health and remaining useful life of batteries is a challenge that limits technologies such as electric vehicles. Here, the authors build an accurate battery performance forecasting system using machine learning.
- Yunwei Zhang
- , Qiaochu Tang
- & Alpha A. Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Social media usage reveals recovery of small businesses after natural hazard events
Social media usage reveals recovery of small businesses after natural hazard events
Natural hazards can have huge impacts on individuals and societies, however, monitoring the economic recovery in the aftermath of extreme events remains a challenge. Here, the authors find that Facebook posting activity of small businesses can be used to monitor post-disaster economic recovery, and can allow local governments to better target distribution of resources.
- Robert Eyre
- , Flavia De Luca
- & Filippo Simini
-
Article
| Open Access Systematic selection between age and household structure for models aimed at emerging epidemic predictions
Systematic selection between age and household structure for models aimed at emerging epidemic predictions
Models of emerging epidemics can be exceedingly helpful in planning the response, but early on model selection is a difficult task. Here, the authors explore the joint contribution of age stratification and household structure on epidemic spread, and provides a rule of thumb to guide model choice.
- Lorenzo Pellis
- , Simon Cauchemez
- & Christophe Fraser
-
Article
| Open Access A first-principle mechanism for particulate aggregation and self-assembly in stratified fluids
A first-principle mechanism for particulate aggregation and self-assembly in stratified fluids
Aggregation of matter, common in stratified fluid systems, is essential to the carbon cycle and ocean ecology. Although the current understanding of aggregation involves only collision and adhesion, here Camassa et al. reveal a self-assembly phenomenon arising solely from diffusion-induced flows.
- Roberto Camassa
- , Daniel M. Harris
- & Richard M. McLaughlin
-
Article
| Open Access Learning dynamical information from static protein and sequencing data
Learning dynamical information from static protein and sequencing data
Reconstructing system dynamics on complex high-dimensional energy landscapes from static experimental snapshots remains challenging. Here, the authors introduce a framework to infer the essential dynamics of physical and biological systems without need for time-dependent measurements.
- Philip Pearce
- , Francis G. Woodhouse
- & Jörn Dunkel
-
Article
| Open Access Taming out-of-equilibrium dynamics on interconnected networks
Taming out-of-equilibrium dynamics on interconnected networks
Network properties can be modified when they interact with other networks, yet most previous results have focused on equilibrium states exclusively. Here the authors introduce a framework to examine the out-of-equilibrium dynamics of evolutionary processes to mimic real-world interconnected networks.
- Javier M. Buldú
- , Federico Pablo-Martí
- & Jacobo Aguirre
-
Article
| Open Access A general method for the creation of dilational surfaces
A general method for the creation of dilational surfaces
Methods for dilation are currently limited to specific shapes and curvatures, with the potential for some of the structure's shape to encroach onto the final dilated volume. Here, the authors develop a method for creating dilational structures from arbitrary surfaces that avoids volume encroachment.
- Freek G. J. Broeren
- , Werner W. P. J. van de Sande
- & Just L. Herder
-
Article
| Open Access Evolutionary games on isothermal graphs
Evolutionary games on isothermal graphs
The spatial structure of a population is often critical for the evolution of cooperation. Here, Allen and colleagues show that when spatial structure is represented by an isothermal graph, the effective number of neighbors per individual determines whether or not cooperation can evolve.
- Benjamin Allen
- , Gabor Lippner
- & Martin A. Nowak
-
Article
| Open Access Topological control of extreme waves
Topological control of extreme waves
Theories state that transitions between extreme waves are allowed but experimental confirmations are lacking because of lack of control strategies. Here, the authors propose and experimentally report, for the first time, the use of topological indices to control the generation of extreme waves.
- Giulia Marcucci
- , Davide Pierangeli
- & Claudio Conti
-
Article
| Open Access Network curvature as a hallmark of brain structural connectivity
Network curvature as a hallmark of brain structural connectivity
The brain can often continue to function despite lesions in many areas, but damage to particular locations may have serious effects. Here, the authors use the concept of Ollivier-Ricci curvature to investigate the robustness of brain networks.
- Hamza Farooq
- , Yongxin Chen
- & Christophe Lenglet
-
Article
| Open Access Structural puzzles in virology solved with an overarching icosahedral design principle
Structural puzzles in virology solved with an overarching icosahedral design principle
Viruses have evolved protein containers with a wide spectrum of icosahedral architectures but the geometric constraints defining these container designs remain to be understood. Here authors revisit the construction of icosahedral architectures using the Archimedean lattices that explain the outliers to the current classification scheme.
- Reidun Twarock
- & Antoni Luque
-
Article
| Open Access Inferring neural signalling directionality from undirected structural connectomes
Inferring neural signalling directionality from undirected structural connectomes
Neural signalling is directional, but non-invasive neuroimaging methods are unable to map directed connections between brain regions. Here, the authors show how network communication measures can be used to infer signalling directionality from the undirected topology of brain structural connectomes.
- Caio Seguin
- , Adeel Razi
- & Andrew Zalesky
-
Article
| Open Access Invariant and smooth limit of discrete geometry folded from bistable origami leading to multistable metasurfaces
Invariant and smooth limit of discrete geometry folded from bistable origami leading to multistable metasurfaces
The mechanisms behind origami having saddle shapes made from concentrically pleated squares remain elusive. Here, the authors connect geometry and mechanics to show that this type of origami is invariantly a hyperbolic paraboloid that exhibits bistability between two symmetric configurations.
- Ke Liu
- , Tomohiro Tachi
- & Glaucio H. Paulino
-
Article
| Open Access Active control of viscous fingering using electric fields
Active control of viscous fingering using electric fields
When a viscous fluid is displaced by a less viscous phase between two plates, a finger-like instability occurs. Here the authors demonstrate how applying an external electric field can suppress the fingering instability without the need to alter the fluid flow rate or the gap geometry.
- Tao Gao
- , Mohammad Mirzadeh
- & Martin Z. Bazant
-
Article
| Open Access Field theory for recurrent mobility
Field theory for recurrent mobility
Systematic methods to characterize human mobility can lead to more accurate forecasting of epidemic spreading and better urban planning. Here the authors present a methodology to analyse daily commuting data by representing it with an irrotational vector field and a corresponding scalar potential.
- Mattia Mazzoli
- , Alex Molas
- & José J. Ramasco
-
Article
| Open Access Controlling intercellular flow through mechanosensitive plasmodesmata nanopores
Controlling intercellular flow through mechanosensitive plasmodesmata nanopores
Plasmodesmata channels connect neighbouring plant cells and respond to external stimuli via changes in permeability. Here Park et al. propose that mechanical forces can displace the dumbbell-shaped ER-desmotubule complex that spans the central plasmodesmatal cylinder leading to closure of the pore.
- Keunhwan Park
- , Jan Knoblauch
- & Kaare H. Jensen
-
Article
| Open Access Programmable coupled oscillators for synchronized locomotion
Programmable coupled oscillators for synchronized locomotion
Designing alternative paradigms for bio-inspired analog computing that harnesses collective dynamics remains a challenge. Here, the authors exploit the synchronization dynamics of coupled vanadium dioxide-based insulator-to-metal phase-transition nano-oscillators for adaptive locomotion control.
- Sourav Dutta
- , Abhinav Parihar
- & Suman Datta
-
Article
| Open Access Establishing microbial composition measurement standards with reference frames
Establishing microbial composition measurement standards with reference frames
Most microbiome studies make conclusions based on changes in relative abundance of taxa, inferred from sequencing data. Here, the authors highlight common pitfalls in comparing relative abundance across samples, and identify solutions that reveal microbial changes without the need to estimate total microbial load.
- James T. Morton
- , Clarisse Marotz
- & Rob Knight
-
Article
| Open Access Accounting for corner flow unifies the understanding of droplet formation in microfluidic channels
Accounting for corner flow unifies the understanding of droplet formation in microfluidic channels
T-junctions are a tool for droplet generation; they are well-described by models that distinguish for squeezing and jetting regimes for different capillary numbers. By considering the usually neglected corner flow, the authors identify an additional leaking regime for very low capillary numbers.
- Piotr M. Korczyk
- , Volkert van Steijn
- & Piotr Garstecki
-
Article
| Open Access Introducing risk inequality metrics in tuberculosis policy development
Introducing risk inequality metrics in tuberculosis policy development
Failure to account for heterogeneity in TB risk can mislead model-based evaluation of proposed interventions. Here, the authors introduce a metric to estimate the distribution of risk in populations from routinely collected data and find that variation in infection acquisition is the most impactful.
- M. Gabriela M. Gomes
- , Juliane F. Oliveira
- & Christian Lienhardt
-
Article
| Open Access A unified relationship for evaporation kinetics at low Mach numbers
A unified relationship for evaporation kinetics at low Mach numbers
Evaporation plays a key role in applications such as cooling and desalination. Here, the authors experimentally demonstrated a unifying relationship between dimensionless flux and driving potential for evaporation kinetics under different working conditions.
- Zhengmao Lu
- , Ikuya Kinefuchi
- & Evelyn N. Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Exact invariant solution reveals the origin of self-organized oblique turbulent-laminar stripes
Exact invariant solution reveals the origin of self-organized oblique turbulent-laminar stripes
It is known from experiments and simulations that stripes of alternating laminar and turbulent regions can form in plane Couette flow. Here the authors find an exact invariant solution which captures the detail of the spatial structures of these patterns and identifies their origin.
- Florian Reetz
- , Tobias Kreilos
- & Tobias M. Schneider
-
Article
| Open Access Microfluidic multipoles theory and applications
Microfluidic multipoles theory and applications
Microfluidic multipoles use arrays of sources and sinks to confine fluids and reagents without the use of physical channels. Here the authors use conformal mappings to predict both convective and diffusive transport in these flows and 3D print multipoles to automate surface-based immunoassays.
- Pierre-Alexandre Goyette
- , Étienne Boulais
- & Thomas Gervais
-
Article
| Open Access Unmasking Clever Hans predictors and assessing what machines really learn
Unmasking Clever Hans predictors and assessing what machines really learn
Nonlinear machine learning methods have good predictive ability but the lack of transparency of the algorithms can limit their use. Here the authors investigate how these methods approach learning in order to assess the dependability of their decision making.
- Sebastian Lapuschkin
- , Stephan Wäldchen
- & Klaus-Robert Müller
-
Article
| Open Access Percolation thresholds for photonic quantum computing
Percolation thresholds for photonic quantum computing
Universal cluster states for quantum computing can be assembled without feed-forward by fusing n-photon clusters with linear optics if the fusion success probability is above a threshold p. The authors bound p in terms of n and provide protocols for n = 3 clusters requiring lower fusion probability than before.
- Mihir Pant
- , Don Towsley
- & Saikat Guha
-
Article
| Open Access Extortion strategies resist disciplining when higher competitiveness is rewarded with extra gain
Extortion strategies resist disciplining when higher competitiveness is rewarded with extra gain
In game theory, ‘extortionate’ tactics in two-player games are predicted to give way to ‘generous’ strategies. Here, the authors show in a human experimental sample that extortion can prevail as a strategy in games in which there is a specific reward for doing better than the other player.
- Lutz Becks
- & Manfred Milinski
-
Article
| Open Access Bond percolation in coloured and multiplex networks
Bond percolation in coloured and multiplex networks
Percolation is a tool used to investigate a network’s response as random links are removed. Here the author presents a generic analytic theory to describe how percolation properties are affected in coloured networks, where the colour can represent a network feature such as multiplexity or the belonging to a community.
- Ivan Kryven
-
Article
| Open Access Quantum majorization and a complete set of entropic conditions for quantum thermodynamics
Quantum majorization and a complete set of entropic conditions for quantum thermodynamics
Similarly to entropy, majorization allows to quantify deviation from uniformity in a wide range of fields. In this paper, the authors use its generalization to the quantum realm to derive a complete set of necessary and sufficient conditions for thermal transformations of quantum states.
- Gilad Gour
- , David Jennings
- & Iman Marvian
-
Article
| Open Access Adaptive particle representation of fluorescence microscopy images
Adaptive particle representation of fluorescence microscopy images
Modern microscopes can generate high volumes of 3D images, driving difficulties in data handling and processing. Here, the authors present a content-adaptive image representation as an alternative to standard pixels that goes beyond data compression to overcome storage, memory, and processing bottlenecks.
- Bevan L. Cheeseman
- , Ulrik Günther
- & Ivo F. Sbalzarini

 Non-invasive suppression of essential tremor via phase-locked disruption of its temporal coherence
Non-invasive suppression of essential tremor via phase-locked disruption of its temporal coherence