Abstract
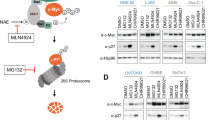
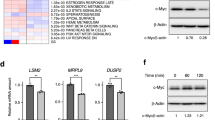
Serine 62 (Ser62) phosphorylation affects the c-Myc protein stability in cancer cells. However, the mechanism for dephosphorylating c-Myc is not well understood. In this study, we identified carboxyl-terminal domain RNA polymerase II polypeptide A small phosphatase 1 (SCP1) as a novel phosphatase specifically dephosphorylating c-Myc Ser62. Ectopically expressed SCP1 strongly dephosphorylated c-Myc Ser62, destabilized c-Myc protein and suppressed c-Myc transcriptional activity. Knockdown of SCP1 increased the c-Myc protein levels in liver cancer cells. SCP1 interacted with c-Myc both in vivo and in vitro. In addition, Ser245 at the C-terminus of SCP1 was essential for its phosphatase activity towards c-Myc. Functionally, SCP1 negatively regulated the cancer cell proliferation. Collectively, our findings indicate that SCP1 is a potential tumor suppressor for liver cancers through dephosphorylating c-Myc Ser62.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dang CV . MYC on the path to cancer. Cell 2012; 149: 22–35.
Sears RC . The life cycle of C-myc: from synthesis to degradation. Cell Cycle 2004; 3: 1133–1137.
Farrell AS, Sears RC . MYC degradation. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 2014. 4.
Lin CY, Loven J, Rahl PB, Paranal RM, Burge CB, Bradner JE et al. Transcriptional amplification in tumor cells with elevated c-Myc. Cell 2012; 151: 56–67.
Hsu T, Moroy T, Etiemble J, Louise A, Trepo C, Tiollais P et al. Activation of c-myc by woodchuck hepatitis virus insertion in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell 1988; 55: 627–635.
Conacci-Sorrell M, Eisenman RN . Post-translational control of Myc function during differentiation. Cell Cycle 2011; 10: 604–610.
Gupta S, Seth A, Davis RJ . Transactivation of gene expression by Myc is inhibited by mutation at the phosphorylation sites Thr-58 and Ser-62. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1993; 90: 3216–3220.
Sears R, Nuckolls F, Haura E, Taya Y, Tamai K, Nevins JR . Multiple Ras-dependent phosphorylation pathways regulate Myc protein stability. Genes Dev 2000; 14: 2501–2514.
Welcker M, Orian A, Jin J, Grim JE, Harper JW, Eisenman RN et al. The Fbw7 tumor suppressor regulates glycogen synthase kinase 3 phosphorylation-dependent c-Myc protein degradation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2004; 101: 9085–9090.
Arnold HK, Sears RC . Protein phosphatase 2A regulatory subunit B56alpha associates with c-myc and negatively regulates c-myc accumulation. Mol Cell Biol 2006; 26: 2832–2844.
Farrell AS, Pelz C, Wang X, Daniel CJ, Wang Z, Su Y et al. Pin1 regulates the dynamics of c-Myc DNA binding to facilitate target gene regulation and oncogenesis. Mol Cell Biol 2013; 33: 2930–2949.
Amati B . Myc degradation: dancing with ubiquitin ligases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2004; 101: 8843–8844.
Yada M, Hatakeyama S, Kamura T, Nishiyama M, Tsunematsu R, Imaki H et al. Phosphorylation-dependent degradation of c-Myc is mediated by the F-box protein Fbw7. EMBO J 2004; 23: 2116–2125.
Zhang X, Farrell AS, Daniel CJ, Arnold H, Scanlan C, Laraway BJ et al. Mechanistic insight into Myc stabilization in breast cancer involving aberrant Axin1 expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2012; 109: 2790–2795.
Yeh E, Cunningham M, Arnold H, Chasse D, Monteith T, Ivaldi G et al. A signalling pathway controlling c-Myc degradation that impacts oncogenic transformation of human cells. Nat Cell Biol 2004; 6: 308–318.
Liu L, Eisenman RN . Regulation of c-Myc protein abundance by a protein phosphatase 2A-glycogen synthase kinase 3beta-negative feedback pathway. Genes Cancer 2012; 3: 23–36.
Tan J, Lee PL, Li Z, Jiang X, Lim YC, Hooi SC et al. B55beta-associated PP2A complex controls PDK1-directed myc signaling and modulates rapamycin sensitivity in colorectal cancer. Cancer Cell 2010; 18: 459–471.
Arnold HK, Zhang X, Daniel CJ, Tibbitts D, Escamilla-Powers J, Farrell A et al. The Axin1 scaffold protein promotes formation of a degradation complex for c-Myc. EMBO J 2009; 28: 500–512.
Janghorban M, Farrell AS, Allen-Petersen BL, Pelz C, Daniel CJ, Oddo J et al. Targeting c-MYC by antagonizing PP2A inhibitors in breast cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2014; 111: 9157–9162.
Strack S, Chang D, Zaucha JA, Colbran RJ, Wadzinski BE . Cloning and characterization of B delta, a novel regulatory subunit of protein phosphatase 2A. FEBS Lett 1999; 460: 462–466.
Barford D . Molecular mechanisms of the protein serine/threonine phosphatases. Trends Biochem Sci 1996; 21: 407–412.
Shi Y . Serine/threonine phosphatases: mechanism through structure. Cell 2009; 139: 468–484.
Zhang Y, Kim Y, Genoud N, Gao J, Kelly JW, Pfaff SL et al. Determinants for dephosphorylation of the RNA polymerase II C-terminal domain by Scp1. Mol Cell 2006; 24: 759–770.
Yeo M, Lin PS, Dahmus ME, Gill GN . A novel RNA polymerase II C-terminal domain phosphatase that preferentially dephosphorylates serine 5. J Biol Chem 2003; 278: 26078–26085.
Wu Y, Evers BM, Zhou BP . Small C-terminal domain phosphatase enhances snail activity through dephosphorylation. J Biol Chem 2009; 284: 640–648.
Wrighton KH, Willis D, Long J, Liu F, Lin X, Feng XH . Small C-terminal domain phosphatases dephosphorylate the regulatory linker regions of Smad2 and Smad3 to enhance transforming growth factor-beta signaling. J Biol Chem 2006; 281: 38365–38375.
Lin X, Duan X, Liang YY, Su Y, Wrighton KH, Long J et al. PPM1A functions as a Smad phosphatase to terminate TGFbeta signaling. Cell 2006; 125: 915–928.
Kim SY, Herbst A, Tworkowski KA, Salghetti SE, Tansey WP . Skp2 regulates Myc protein stability and activity. Mol Cell 2003; 11: 1177–1188.
Chan CH, Lee SW, Li CF, Wang J, Yang WL, Wu CY et al. Deciphering the transcriptional complex critical for RhoA gene expression and cancer metastasis. Nat Cell Biol 2010; 12: 457–467.
O'Donnell KA, Wentzel EA, Zeller KI, Dang CV, Mendell JT . c-Myc-regulated microRNAs modulate E2F1 expression. Nature 2005; 435: 839–843.
Feng XH, Liang YY, Liang M, Zhai W, Lin X . Direct interaction of c-Myc with Smad2 and Smad3 to inhibit TGF-beta-mediated induction of the CDK inhibitor p15 (Ink4B). Mol Cell 2002; 9: 133–143.
Crouch DH, Fisher F, Clark W, Jayaraman PS, Goding CR, Gillespie DA . Gene-regulatory properties of Myc helix-loop-helix/leucine zipper mutants: Max-dependent DNA binding and transcriptional activation in yeast correlates with transforming capacity. Oncogene 1993; 8: 1849–1855.
Xue Y, Zhou F, Zhu M, Ahmed K, Chen G, Yao X . GPS: a comprehensive www server for phosphorylation sites prediction. Nucleic Acids Res 2005; 33: W184–W187.
Amanchy R, Periaswamy B, Mathivanan S, Reddy R, Tattikota SG, Pandey A . A curated compendium of phosphorylation motifs. Nat Biotechnol 2007; 25: 285–286.
Meyer N, Penn LZ . Reflecting on 25 years with MYC. Nat Rev Cancer 2008; 8: 976–990.
Liu L, Ulbrich J, Muller J, Wustefeld T, Aeberhard L, Kress TR et al. Deregulated MYC expression induces dependence upon AMPK-related kinase 5. Nature 2012; 483: 608–612.
Wang X, Cunningham M, Zhang X, Tokarz S, Laraway B, Troxell M et al. Phosphorylation regulates c-Myc's oncogenic activity in the mammary gland. Cancer Res 2011; 71: 925–936.
Nie Z, Hu G, Wei G, Cui K, Yamane A, Resch W et al. c-Myc is a universal amplifier of expressed genes in lymphocytes and embryonic stem cells. Cell 2012; 151: 68–79.
Yeo M, Lee SK, Lee B, Ruiz EC, Pfaff SL, Gill GN, Small CTD . phosphatases function in silencing neuronal gene expression. Science 2005; 307: 596–600.
Stolk M, Cooper E, Vilk G, Litchfield DW, Hammond JR . Subtype-specific regulation of equilibrative nucleoside transporters by protein kinase CK2. Biochem J 2005; 386: 281–289.
Song DH, Sussman DJ, Seldin DC . Endogenous protein kinase CK2 participates in Wnt signaling in mammary epithelial cells. J Biol Chem 2000; 275: 23790–23797.
Liu N, Li H, Li S, Shen M, Xiao N, Chen Y et al. The Fbw7/human CDC4 tumor suppressor targets proproliferative factor KLF5 for ubiquitination and degradation through multiple phosphodegron motifs. J Biol Chem 2010; 285: 18858–18867.
Liao P, Wang W, Shen M, Pan W, Zhang K, Wang R et al. A positive feedback loop between EBP2 and c-Myc regulates rDNA transcription, cell proliferation, and tumorigenesis. Cell Death Dis 2014; 5: e1032.
Zhang M, Liu J, Kim Y, Dixon JE, Pfaff SL, Gill GN et al. Structural and functional analysis of the phosphoryl transfer reaction mediated by the human small C-terminal domain phosphatase, Scp1. Protein Sci 2010; 19: 974–986.
Kops O, Zhou XZ, Lu KP . Pin1 modulates the dephosphorylation of the RNA polymerase II C-terminal domain by yeast Fcp1. FEBS Lett 2002; 513: 305–311.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from National Basic Research Program of China (973 program 2012CB910404 and 2010CB529704), National Natural Science Foundation of China (30971521, 31171338 and 31222037), 'Shu Guang' project supported by Shanghai Municipal Education Commission and Shanghai Education Development Foundation (11SG27), Shanghai Key Laboratory of Regulatory Biology (11DZ2260300) and Shanghai Rising-Star program (09QA1401900 and 13QH1401300). PW is a scholar of the Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University (NCET-10-0387).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, W., Liao, P., Shen, M. et al. SCP1 regulates c-Myc stability and functions through dephosphorylating c-Myc Ser62. Oncogene 35, 491–500 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2015.106
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2015.106
This article is cited by
-
Dexmedetomidine inhibits mitochondria damage and apoptosis of enteric glial cells in experimental intestinal ischemia/reperfusion injury via SIRT3-dependent PINK1/HDAC3/p53 pathway
Journal of Translational Medicine (2021)
-
miR-144/451 cluster plays an oncogenic role in esophageal cancer by inhibiting cell invasion
Cancer Cell International (2018)
-
Disruption of the c-Myc/miR-200b-3p/PRDX2 regulatory loop enhances tumor metastasis and chemotherapeutic resistance in colorectal cancer
Journal of Translational Medicine (2017)
-
Two-track virtual screening approach to identify both competitive and allosteric inhibitors of human small C-terminal domain phosphatase 1
Journal of Computer-Aided Molecular Design (2017)