Abstract
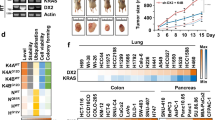
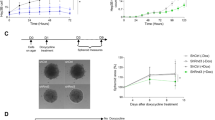
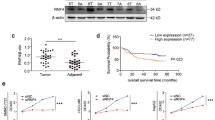
The MAPK MEK/ERK pathway is often upregulated in cancer cells and represents an attractive target for development of anticancer drugs. Only few data concerning the specific functions of ERK1 and 2 are reported in the literature. In this report, we investigated the specific role of ERK1 and 2 in liver tumor growth both in vitro and in vivo. DNA synthesis and cells in S phase analysed by flow cytometry, correlated with strong inhibition of Cdk1 and cyclin E levels, are strongly reduced after exposure to the MEK inhibitor, U0126. We obtained a significant reduction of colony formation in soft agar assays and a reduction in the size of tumor xenografts in nude mice treated with U0126. Then, we could specifically abolished ERK1 or 2 expression by small-interfering RNA (siRNA) and demonstrated that ERK2 knockdown but not ERK1 interferes with the process of replication. Moreover, we found that colony formation and tumor growth in vivo were significantly inhibited by targeting ERK2 using stable chemically modified siRNA. Taken together, our results emphasize the importance of the MEK/ERK pathway in liver cancer cell growth in vitro and in vivo and argue for a crucial role of ERK2 in this regulation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- cdk:
-
cyclin-dependent kinase
- ERK:
-
extracellular signal-regulated kinase
- HCC:
-
hepatocellular carcinoma
- LNA:
-
locked nucleic acid
- MEK:
-
mitogen-activated protein kinase
- siRNA:
-
small-interfering RNA
References
Aharinejad S, Paulus P, Sioud M, Hofmann M, Zins K, Schafer R et al. (2004). Colony-stimulating factor-1 blockade by antisense oligonucleotides and small interfering RNAs suppresses growth of human mammary tumor xenografts in mice. Cancer Res 64: 5378–5384.
Albrecht JH, Hoffman JS, Kren BT, Steer CJ . (1993). Cyclin and cyclin-dependent kinase 1 mRNA expression in models of regenerating liver and human liver diseases. Am J Physiol 265: G857–G864.
Albrecht JH, Hu MY, Cerra FB . (1995). Distinct patterns of cyclin D1 regulation in models of liver regeneration and human liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 209: 648–655.
Alessi DR, Cuenda A, Cohen P, Dudley DT, Saltiel AR . (1995). PD 098059 is a specific inhibitor of the activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase in vitro and in vivo. J Biol Chem 270: 27489–27494.
Andrieux LO, Fautrel A, Bessard A, Guillouzo A, Baffet G, Langouet S . (2007). GATA-1 is essential in EGF-mediated induction of nucleotide excision repair activity and ERCC1 expression through ERK2 in human hepatoma cells. Cancer Res 67: 2114–2123.
Arslan MA, Kutuk O, Basaga H . (2006). Protein kinases as drug targets in cancer. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 6: 623–634.
Behlke MA . (2006). Progress towards in vivo use of siRNAs. Mol Ther 13: 644–670.
Bessard A, Fremin C, Ezan F, Coutant A, Baffet G . (2007). MEK/ERK-dependent uPAR expression is required for motility via phosphorylation of P70S6K in human hepatocarcinoma cells. J Cell Physiol 212: 526–536.
Braasch DA, Jensen S, Liu Y, Kaur K, Arar K, White MA et al. (2003). RNA interference in mammalian cells by chemically modified RNA. Biochemistry 42: 7967–7975.
Brondello JM, McKenzie FR, Sun H, Tonks NK, Pouyssegur J . (1995). Constitutive MAP kinase phosphatase (MKP-1) expression blocks G1 specific gene transcription and S-phase entry in fibroblasts. Oncogene 10: 1895–1904.
Dahlgren C, Wahlestedt C, Thonberg H . (2006). No induction of anti-viral responses in human cell lines HeLa and MCF-7 when transfecting with siRNA or siLNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 341: 1211–1217.
Davies SP, Reddy H, Caivano M, Cohen P . (2000). Specificity and mechanism of action of some commonly used protein kinase inhibitors. Biochem J 351: 95–105.
Dudley DT, Pang L, Decker SJ, Bridges AJ, Saltiel AR . (1995). A synthetic inhibitor of the mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92: 7686–7689.
Duesbery NS, Resau J, Webb CP, Koochekpour S, Koo HM, Leppla SH et al. (2001). Suppression of ras-mediated transformation and inhibition of tumor growth and angiogenesis by anthrax lethal factor, a proteolytic inhibitor of multiple MEK pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98: 4089–4094.
Elbashir SM, Harborth J, Weber K, Tuschl T . (2002). Analysis of gene function in somatic mammalian cells using small interfering RNAs. Methods 26: 199–213.
Elmen J, Thonberg H, Ljungberg K, Frieden M, Westergaard M, Xu Y et al. (2005). Locked nucleic acid (LNA) mediated improvements in siRNA stability and functionality. Nucleic Acids Res 33: 439–447.
Fischer AM, Katayama CD, Pages G, Pouyssegur J, Hedrick SM . (2005). The role of erk1 and erk2 in multiple stages of T cell development. Immunity 23: 431–443.
Fremin C, Ezan F, Boisselier P, Bessard A, Pages G, Pouyssegur J et al. (2007). ERK2 but not ERK1 plays a key role in hepatocyte replication: an RNAi-mediated ERK2 knockdown approach in wild-type and ERK1 null hepatocytes. Hepatology 45: 1035–1045.
Gysin S, Lee SH, Dean NM, McMahon M . (2005). Pharmacologic inhibition of RAF–MEK–ERK signaling elicits pancreatic cancer cell cycle arrest through induced expression of p27Kip1. Cancer Res 65: 4870–4880.
Haass NK, Sproesser K, Nguyen TK, Contractor R, Medina CA, Nathanson KL et al. (2008). The mitogen-activated protein/extracellular signal-regulated kinase kinase inhibitor AZD6244 (ARRY-142886) induces growth arrest in melanoma cells and tumor regression when combined with docetaxel. Clin Cancer Res 14: 230–239.
Hilger RA, Scheulen ME, Strumberg D . (2002). The Ras-Raf-MEK-ERK pathway in the treatment of cancer. Onkologie 25: 511–518.
Huynh H, Nguyen TT, Chow KH, Tan PH, Soo KC, Tran E . (2003). Over-expression of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) kinase (MEK)-MAPK in hepatocellular carcinoma: its role in tumor progression and apoptosis. BMC Gastroenterol 3: 19.
Ito Y, Sasaki Y, Horimoto M, Wada S, Tanaka Y, Kasahara A et al. (1998). Activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases/extracellular signal-regulated kinases in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 27: 951–958.
Klein PJ, Schmidt CM, Wiesenauer CA, Choi JN, Gage EA, Yip-Schneider MT et al. (2006). The effects of a novel MEK inhibitor PD184161 on MEK-ERK signaling and growth in human liver cancer. Neoplasia 8: 1–8.
Lefloch R, Pouyssegur J, Lenormand P . (2008). Single and combined silencing of ERK1 and ERK2 reveals their positive contribution to growth signaling depending on their expression levels. Mol Cell Biol 28: 511–527.
Leung RK, Whittaker PA . (2005). RNA interference: from gene silencing to gene-specific therapeutics. Pharmacol Ther 107: 222–239.
Liu L, Cao Y, Chen C, Zhang X, McNabola A, Wilkie D et al. (2006). Sorafenib blocks the RAF/MEK/ERK pathway, inhibits tumor angiogenesis, and induces tumor cell apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma model PLC/PRF/5. Cancer Res 66: 11851–11858.
Liu X, Yan S, Zhou T, Terada Y, Erikson RL . (2004). The MAP kinase pathway is required for entry into mitosis and cell survival. Oncogene 23: 763–776.
Lorusso PM, Adjei AA, Varterasian M, Gadgeel S, Reid J, Mitchell DY et al. (2005). Phase I and pharmacodynamic study of the oral MEK inhibitor CI-1040 in patients with advanced malignancies. J Clin Oncol 23: 5281–5293.
Loyer P, Cariou S, Glaise D, Bilodeau M, Baffet G, Guguen-Guillouzo C . (1996). Growth factor dependence of progression through G1 and S phases of adult rat hepatocytes in vitro. Evidence of a mitogen restriction point in mid-late G1. J Biol Chem 271: 11484–11492.
Mook OR, Baas F, de Wissel MB, Fluiter K . (2007). Evaluation of locked nucleic acid-modified small interfering RNA in vitro and in vivo. Mol Cancer Ther 6: 833–843.
Morel-Chany E, Guillouzo C, Trincal G, Szajnert MF . (1978). Spontaneous neoplastic transformation in vitro of epithelial cell strains of rat liver: cytology, growth and enzymatic activities. Eur J Cancer 14: 1341–1352.
Normanno N, De Luca A, Maiello MR, Campiglio M, Napolitano M, Mancino M et al. (2006). The MEK/MAPK pathway is involved in the resistance of breast cancer cells to the EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor gefitinib. J Cell Physiol 207: 420–427.
Pages G, Guerin S, Grall D, Bonino F, Smith A, Anjuere F et al. (1999). Defective thymocyte maturation in p44 MAP kinase (Erk 1) knockout mice. Science 286: 1374–1377.
Pages G, Lenormand P, L'Allemain G, Chambard JC, Meloche S, Pouyssegur J . (1993). Mitogen-activated protein kinases p42mapk and p44mapk are required for fibroblast proliferation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90: 8319–8323.
Rescan C, Coutant A, Talarmin H, Theret N, Glaise D, Guguen-Guillouzo C et al. (2001). Mechanism in the sequential control of cell morphology and S phase entry by epidermal growth factor involves distinct MEK/ERK activations. Mol Biol Cell 12: 725–738.
Reuber MD . (1961). A transplantable bile-secreting hepatocellular carcinoma in the rat. J Natl Cancer Inst 26: 891–899.
Saba-El-Leil MK, Vella FD, Vernay B, Voisin L, Chen L, Labrecque N et al. (2003). An essential function of the mitogen-activated protein kinase Erk2 in mouse trophoblast development. EMBO Rep 4: 964–968.
Sanjo H, Hikida M, Aiba Y, Mori Y, Hatano N, Ogata M et al. (2007). Extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase 2 is required for efficient generation of B cells bearing antigen-specific immunoglobulin G. Mol Cell Biol 27: 1236–1246.
Schmidt CM, McKillop IH, Cahill PA, Sitzmann JV . (1997). Increased MAPK expression and activity in primary human hepatocellular carcinoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 236: 54–58.
Sebolt-Leopold JS, Dudley DT, Herrera R, Van Becelaere K, Wiland A, Gowan RC et al. (1999). Blockade of the MAP kinase pathway suppresses growth of colon tumors in vivo [see comments]. Nat Med 5: 810–816.
Sebolt-Leopold JS, English JM . (2006). Mechanisms of drug inhibition of signalling molecules. Nature 441: 457–462.
Sebolt-Leopold JS, Herrera R . (2004). Targeting the mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade to treat cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 4: 937–947.
Stennicke HR, Salvesen GS . (1997). Biochemical characteristics of caspases-3, -6, -7, and -8. J Biol Chem 272: 25719–25723.
Takei Y, Kadomatsu K, Yuzawa Y, Matsuo S, Muramatsu T . (2004). A small interfering RNA targeting vascular endothelial growth factor as cancer therapeutics. Cancer Res 64: 3365–3370.
Talarmin H, Rescan C, Cariou S, Glaise D, Zanninelli G, Bilodeau M et al. (1999). The mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase cascade activation is a key signalling pathway involved in the regulation of G(1) phase progression in proliferating hepatocytes. Mol Cell Biol 19: 6003–6011.
Vantaggiato C, Formentini I, Bondanza A, Bonini C, Naldini L, Brambilla R . (2006). ERK1 and ERK2 mitogen-activated protein kinases affect Ras-dependent cell signaling differentially. J Biol 5: 14.
Wabnitz PA, Mitchell D, Wabnitz DA . (2004). In vitro and in vivo metabolism of the anti-cancer agent CI-1040, a MEK inhibitor, in rat, monkey, and human. Pharm Res 21: 1670–1679.
Wang D, Boerner SA, Winkler JD, Lorusso PM . (2007). Clinical experience of MEK inhibitors in cancer therapy. Biochim Biophys Acta 1773: 1248–1255.
Yeh TC, Marsh V, Bernat BA, Ballard J, Colwell H, Evans RJ et al. (2007). Biological characterization of ARRY-142886 (AZD6244), a potent, highly selective mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1/2 inhibitor. Clin Cancer Res 13: 1576–1583.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr P Loyer for flow cytometry advices, Sigma-Aldrich and Dr Heike Lehrmann for giving us the LNA ERK2 oligonucleotides, and C Ribault for technical assistance. This research was supported by the Institut National de la Santé et de la Recherche Médicale and the Association pour la Recherche sur le Cancer (ARC). A Bessard and C Frémin are a recipient of fellowship from the Région Bretagne/INSERM and the Ministère de l′Education Nationale et de la Technologie, respectively, and the ARC.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bessard, A., Frémin, C., Ezan, F. et al. RNAi-mediated ERK2 knockdown inhibits growth of tumor cells in vitro and in vivo. Oncogene 27, 5315–5325 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2008.163
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2008.163
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Cordyceps bassiana inhibits smooth muscle cell proliferation via the ERK1/2 MAPK signaling pathway
Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters (2016)
-
Atorvastatin Prevents Glutamate Uptake Reduction Induced by Quinolinic Acid Via MAPKs Signaling
Neurochemical Research (2016)
-
Extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1 and 2 in cancer therapy: a focus on hepatocellular carcinoma
Molecular Biology Reports (2016)
-
Immunolocalization of dually phosphorylated MAPKs in dividing root meristem cells of Vicia faba, Pisum sativum, Lupinus luteus and Lycopersicon esculentum
Plant Cell Reports (2015)
-
Silencing AML1-ETO gene expression leads to simultaneous activation of both pro-apoptotic and proliferation signaling
Leukemia (2014)