Abstract
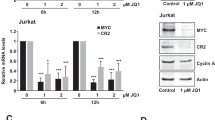
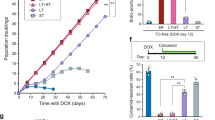
DNA tumor viruses are capable of driving quiescent cells into the cell cycle. In case of polyomaviridae, two viral proteins, the large and the small (ST) T antigens are responsible for this outcome. ST interacts with the protein phosphatase PP2A and with chaperons of the dnaK type and leads to the transactivation of several genes, which play a role in S-phase induction. One of these is the transcription factor myelocytomatosis (MYC), which by itself is an important regulator of growth. Microarray analysis has revealed several ST-induced genes, which are also targets of MYC; hence, ST may induce these genes via MYC. Experiments shown here are in line with this assumption. MYC-regulated genes are induced by ST at later times than MYC and a MYC responsive promoter is stimulated by ST. Regulation of MYC occurs through signal transduction pathways, which are co-ordinated by PP2A suggesting that they may be targets of ST. Here, we show that this is the case as important kinases involved in these pathways appear in the active phosphorylated form in the presence of ST. Inhibition of these kinases interferes with MYC induction and inhibition of MYC activity blocks ST-mediated transactivation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barker N, Morin PJ, Clevers H . (2000). The Yin-Yang of TCF/beta-catenin signalling. Adv Cancer Res 77: 1–24.
C W, Passamato R, Campbell KT, Plattner CA, Pallas DC, Hahn WC . (2004). Identification of specific PP2A complexes involved in human cell transformation. Cancer Cell 5: 127–136.
Frost JA, Alberts AS, Sontag E, Guan K, Mumby MC, Feramisco JR . (1994). Simian virus 40 small t antigen co-operates with mitogen-activated kinases to stimulate AP-1 activity. Mol Cell Biol 14: 6244–6252.
Hahn WC, Dessain SK, Brooks MW, King JE, Elenbaas B, Sabatini DM et al. (2002). Enumeration of the simian virus 40 early region elements necessary for human cell transformation. Mol Cell Biol 22: 2111–2123.
Harbour JW, Dean DC . (2000). The Rb/E2F pathway: expanding roles and emerging paradigms. Genes Dev 14: 2393–2409.
Howe AK, Gaillard S, Bennet JS, Rundell K . (1998). Cell cycle progression in monkey cells expressing Simian Virus 40 small t antigen from adenovirus vectors. J Virol 72: 9637–9644.
Klucky B, Koch B, Radolf M, Steinlein P, Wintersberger E . (2004). Polyomavirus tumorantigens have a profound effect on gene expression in mouse fibroblasts. Oncogene 23: 4707–4721.
Levens DL . (2003). Reconstructing MYC. Genes Dev 17: 1071–1077.
Millward TA, Zolnierowicz S, Hemmings BA . (1999). Regulation of protein kinase cascades by protein phosphatase 2A. Trends Biochem Sci 24: 186–191.
Moran E . (1993). DNA tumor virus transforming proteins and the cell cycle. Curr Opin Genet Dev 3: 63–70.
Nemethova M, Smutny M, Wintersberger E . (2004). Transactivation of E2F-regulated genes by polyomavirus large T antigen: evidence for a two-step mechanism. Mol Cell Biol 24: 10986–11994.
Nesbit CE, Tersak JM, Prochownik EV . (1999). MYC oncogenes and human neoplastic disease. Oncogene 18: 3004–3016.
Ogris E, Mudrak I, Wintersberger E . (1992). Polyomavirus large and small T antigens cooperate in induction of the S-phase in serum-starved 3T3 mouse fibroblasts. J Virol 66: 53–61.
Patel JH, Loboda AP, Showe MK, Showe LC, McMahon SB . (2004). Analysis of genomic targets reveals complex functions of MYC. Nat Rev Cancer 4: 562–568.
Pelengaris S, Khan M . (2003). The many faces of c-MYC. Arch Biochem Biophys 416: 129–136.
Porras A, Bennet J, Howe A, Tokos K, Bouk N, Henglein B et al. (1996). A novel Simian virus 40 early-region domain mediates transactivation of the cyclin A promoter by small-t antigen and is required for transformation in small-t antigen-dependent assays. J Virol 70: 6902–6908.
Porras A, Gaillard S, Rundell K . (1999). The Simian virus 40 small-t and large-T antigens jointly regulate cell cycle reentry in human fibroblasts. J Virol 73: 3102–3107.
Reiss K, Khalili K . (2003). Viruses and cancer: lessons from the human polyomavirus, JCV. Oncogene 22: 6517–6523.
Schüchner S, Nemethova M, Belisova A, Klucky B, Holnthoner W, Wintersberger E . (2001). Transactivation of murine cyclin A by polyomavirus large and small T antigens. J Virol 75: 6498–6507.
Schüchner S, Wintersberger E . (1999). Binding of polyomavirus small T antigen to protein phosphatase 2A is required for elimination of p27 and support of S-phase induction in concert with large T antigen. J Virol 73: 9266–9273.
Sears R, Nuckolls F, Haura E, Taya Y, Tamai K, Nevins JR . (2000). Multiple Rase-dependent phosphorylation pathways regulate Myc protein stability. Genes Dev 14: 2501–2514.
Sontag E, Fedorov S, Kamibayashi C, Robbins D, Cobb M, Mumby M . (1993). The interaction of SV40 small tumor antigen with protein phosphatase 2A stimulates the map kinase pathway and induces cell proliferation. Cell 75: 887–897.
Sullivan CS, Pipas JM . (2002). T antigens of Simian virus 40: molecular chaperones for viral replication and tumorigenesis. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 66: 179–202.
Virshup DM . (2000). Protein phosphatase 2A: a panoply of enzymes. Curr Opin Cell Biol 12: 180–185.
Watanabe G, Howe A, Lee RJ, Albanese C, Shu IW, Karnezis AN et al. (1996). Induction of cyclin D1 by Simian virus 40 small tumor antigen. Proc Natl Aad Sci USA 93: 12861–12866.
Yang SI, Lickteig RL, Estes R, Rundell K, Walter G, Mumby MC . (1991). Control of protein phosphatase 2A by simian virus 40 small-t antigen. Mol Cell Biol 11: 1988–1995.
Yeh E, Cunningham M, Arnold H, Chasse D, Montheit T, Ivaldi G et al. (2004). A signalling pathway controlling c-Myc degradation that impacts oncogenic transformation of human cells. Nat Cell Biol 6: 308–318.
Yu J, Boyapati A, Rundell K . (2001). Critical role for SV40 small-t antigen in human cell transformation. Virology 290: 192–198.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Peter Angel (DKFZ) and to Roland Foisner and Ernst Müllner from our department for kindly providing reagents. This work was supported by FWF and the Herzfelder Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Klucky, B., Wintersberger, E. Polyomavirus small T antigen transactivates genes by its ability to provoke the synthesis and the stabilization of MYC. Oncogene 26, 6356–6360 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210458
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210458