Abstract
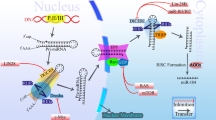
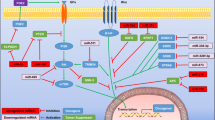
It has become clear that particular microRNAs (miRNAs) function either as tumour suppressors or oncogenes, whose loss or overexpression, respectively, has diagnostic and prognostic significance. In several cases, miRNAs have been shown to affect target genes that are involved in the control of cell proliferation and apoptosis. However, malignant tumours display additional traits beyond the acquisition of enhanced growth potential and decreased cell death. Malignant disease is associated with altered tumour–host interactions leading to sustained angiogenesis and the ability to invade and metastasize. It is possible that miRNAs may act as master regulators of these aspects of tumour biology. Bioinformatic analysis of putative miRNA binding sites has indicated several novel potential gene targets of cancer-associated miRNAs that function in aspects of cell adhesion, neovascularization and tissue invasion. Among others, we speculate that miRNAs may find new roles in the regulation of E-cadherin, integrin αvβ3, hypoxia-inducible factor-1α, syndecan-1, lysyl oxidase, adamalysin metalloproteinase-17, tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinase-3, c-Met and CXCR-4 that underpin the tissue architectural changes associated with malignancy.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahonen M, Poukkula M, Baker A, Kashiwagi M, Hideaki N, Eriksson JE et al. (2003). Oncogene 22: 2121–2134.
Baker A, Edwards DR, Murphy G . (2002). J Cell Sci 115: 3719–3727.
Bergers G, Benjamin LE . (2003). Nat Rev Cancer 3: 401–410.
Blobel CP . (2005). Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 6: 32–43.
Cavallaro U, Christofori G . (2004). Nat Rev Cancer 4: 118–132.
Chan JA, Krichevsky AM, Kosik KS . (2005). Cancer Res 65: 6029–6033.
Cruz-Munoz W, Sanchez OH, Di Grappa M, English JL, Hill RP, Khokha R . (2006). Oncogene advance online publication 15 May 2006; doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1209663.
Egeblad M, Werb Z . (2002). Nat Rev Cancer 2: 161–174.
Endo K, Takino T, Miyamori H, Kinsen H, Yoshizaki T, Furukawa M et al. (2003). J Biol Chem 278: 40764–40770.
Erler JT, Bennewith KL, Nicolau M, Dornhöfer N, Kong C, Le Q-T et al. (2006). Nature 440: 1222–1226.
Esquela-Kerscher A, Slack FJ . (2006). Nat Rev Cancer 6: 259–269.
Esteller M, Corn PG, Baylin S, Herman JG . (2001). Cancer Res 61: 3225–3229.
Fidler IJ . (2003). Nat Rev Cancer 3: 453–458.
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA . (2000). Cell 100: 57–70.
Harris AL . (2002). Nat Rev 2: 38–47.
He H, Jazdzewski K, Li W, Liyanarachchi S, Nagy R, Volinia S et al. (2005). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102: 19075–19080.
Hirohashi S . (1998). Am J Pathol 153: 333–339.
Hood JD, Cheresh DA . (2002). Nat Rev Cancer 2: 91–100.
Hwang H-W, Mendell JT . (2006). Br J Cancer 94: 776–780.
Iorio MV, Ferracin M, Liu C-G, Veronese A, Spizzo R, Sabbioni S et al. (2005). Cancer Res 65: 7065–7070.
Johnson SM, Grosshans H, Shingara J, Byrom M, Jarvis R, Cheng A et al. (2005). Cell 120: 635–647.
Krutzfeldt J, Rajewsky N, Braich R, Rajeev KG, Tuschl T, Manoharan M et al. (2005). Nature 438: 685–689.
Lagos-Quintana M, Rauhut R, Yalcin A, Meyer J, Lendeckel W, Tuschl T . (2002). Curr Biol 12: 735–739.
Lewis BP, Burge CB, Bartel DP . (2005). Cell 120: 15–20.
Lim LP, Lau NC, Garrett-Engele P, Grimson A, Schelter JM, Castle J et al. (2005). Nature 433: 769–773.
Lu C, Kerbel RS . (1993). J Cell Biol 120: 1281–1288.
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, Alvarez-Saavedra E, Lamb J, Peck D et al. (2005). Nature 435: 834–838.
Liu MC, Choong DY, Hooi CS, Williams LH, Campbell IG . (2006). Cancer Lett doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2006.03.024.
Mohammed FF, Smookler DS, Taylor SEM, Fingleton B, Kassiri Z, Sanchez OH et al. (2004). Nat Genet 36: 969–977.
Mueller MM, Fusenig NE . (2004). Nat Rev Cancer 4: 838–849.
Müller A, Homey B, Soto H, Ge N, Catron D, Buchanan ME et al. (2001). Nature 410: 40–56.
O'Donnell KA, Wentzel EA, Zeller KI, Dang CV, Mendell JT . (2005). Nature 435: 839–843.
Oh J, Takahashi R, Kondo S, Mizoguchi A, Adachi E, Sasahara RM et al. (2001). Cell 107: 789–800.
Qi JH, Ebrahem Q, Moore N, Murphy G, Claesson-Welsh L, Bond M et al. (2003). Nat Med 9: 407–415.
Thiery JP . (2002). Nat Rev Cancer 2: 442–454.
Volinia S, Calin GA, Liu C-G, Ambs S, Cimmino A, Petrocca F et al. (2006). PNAS 103: 2257–2261.
Voorhoeve PM, le Sage C, Schrier M, Gillis AJM, Stoop H, Nagel R et al. (2006). Cell 124: 1169–1181.
Yanaihara N, Caplen N, Bowman E, Seike M, Kumamoto K, Yi M et al. (2006). Cancer Cell 9: 189–198.
Yang AD, Camp ER, Fan F, Shen L, Gray MJ, Liu W et al. (2006). Cancer Res 66: 46–51.
Zhang L, Huang J, Yang N, Greshock J, Megraw MS, Giannakakis A et al. (2006). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103: 9136–9141.
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by grants from the Breast Cancer Campaign, Big C Appeal and the Cancerdegradome project LSHC-CT-2003-503297 from the European Union Framework Programme 6.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dalmay, T., Edwards, D. MicroRNAs and the hallmarks of cancer. Oncogene 25, 6170–6175 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209911
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209911
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Diagnostic applications and therapeutic option of Cascade CRISPR/Cas in the modulation of miRNA in diverse cancers: promises and obstacles
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology (2023)
-
Chromosome 1p status in neuroblastoma correlates with higher expression levels of miRNAs targeting neuronal differentiation pathway
In Vitro Cellular & Developmental Biology - Animal (2023)
-
An improved unsupervised learning approach for potential human microRNA–disease association inference using cluster knowledge
Network Modeling Analysis in Health Informatics and Bioinformatics (2021)
-
MicroRNA-340-5p inhibits colon cancer cell migration via targeting of RhoA
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
MicroRNA regulating stanniocalcin-1 is a metastasis and dissemination promoting factor in glioblastoma
Journal of Neuro-Oncology (2019)