Abstract
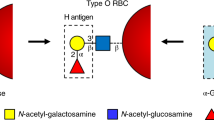
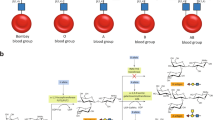
The human ABO(H) blood group antigens are produced by specific glycosyltransferase enzymes. An N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase (GTA) uses a UDP-GalNAc donor to convert the H-antigen acceptor to the A antigen, whereas a galactosyltransferase (GTB) uses a UDP-galactose donor to convert the H-antigen acceptor to the B antigen. GTA and GTB differ only in the identity of four critical amino acid residues. Crystal structures at 1.8–1.32 Å resolution of the GTA and GTB enzymes both free and in complex with disaccharide H-antigen acceptor and UDP reveal the basis for donor and acceptor specificity and show that only two of the critical amino acid residues are positioned to contact donor or acceptor substrates. Given the need for stringent stereo- and regioselectivity in this biosynthesis, these structures further demonstrate that the ability of the two enzymes to distinguish between the A and B donors is largely determined by a single amino acid residue.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$189.00 per year
only $15.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Landsteiner, K. Wein Klin. Wschr. 14, 1132–1134 (1901).
Watkins, W.M. & Morgan, W.T.J. Nature 180, 1038–1040 (1957).
Kabat, E.A. Blood Group Substances: Their Chemistry and Immunochemistry (Academic Press, New York; 1956).
Watkins, W.M. & Morgan, W.T.J. Vox. Sang. 4, 97–119 (1959).
Tuppy, H. & Staudenbauer, W.L. Nature 210, 316–317 (1966).
Hearn, V.M., Smith, Z.G. & Watkins, W.M. Biochem. J. 109, 315–317 (1968).
Kobata, A., Grollman, E.F. & Ginsburg, V. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 32, 272–277 (1968).
Yamamoto, F., Clausen, H., White, T., Marken, J. & Hakomori, S. Nature 345, 229–233 (1990).
Gastinel, L.N. et al. EMBO J. 20, 638–649 (2001).
Boix, E. et al. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 48608–48614 (2001).
Breton, C., Bettler, E., Joziasse, D.H., Geremia, R.A. & Imberty, A. J. Biochem. 123, 1000–1009 (1998).
Busch, C. et al. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 19566–19572 (1998).
Persson, K. et al. Nature Struct. Biol. 8, 166–175 (2001).
Charnock, S.J. & Davies, G.J. Biochemistry 38, 6380–6385 (1999).
Ünligil, U.M. et al. EMBO J. 19, 5269–5280 (2000).
Pedersen, L.C. et al. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 34580–34585 (2000).
Gastinel, L.N., Cambillau, C. & Bourne, Y. EMBO J. 18, 3546–3557 (1999).
Lowary, T.L. & Hindsgaul, O. Carbhydr. Res. 249, 163–195 (1993).
Lowary, T.L. & Hindsgaul, O. Carbhydr. Res. 251, 33–67 (1994).
Mukherjee, A., Palcic, M.M. & Hindsgaul, O. Carbhydr. Res. 326, 1–21 (2000).
Kamath, V.P., Seto, N.O.L., Compston, C.A., Hindsgaul, O. & Palcic, M.M. Glycoconj. J. 16, 599–606 (1999).
Seto, N.O.L. et al. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 14133–14138 (1997).
Seto, N.O.L. et al. Eur. J. Biochem. 259, 770–775 (1999).
Vrielink, A., Rüger, W., Driessen, H.P.C. & Freemont, P.S. EMBO J. 13, 3413–3422 (1994).
Moréra, S., Imberty, A., Aschke-Sonnenborn, U., Rüger, W. & Freemont, P.S. J. Mol. Biol. 292, 717–730 (1999).
Takayama, S. et al. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 7, 401–409 (1999).
Davies, G.J., Sinnott, M.L. & Withers, S.G. in Comprehensive Biological Catalysis Vol. I (ed. Sinnott, M.L.) 119–209 (Academic Press, San Diego; 1998).
Sinnott, M.L. Chem. Rev. 90, 1171–1202 (1990)
Ly, H.D. & Withers, S.G. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 68, 487–522 (1999).
Seto, N.O.L., Compston, C.A., Szpacenko, A. & Palcic, M.M. Carbohydr. Res. 324, 161–169 (2000).
Otwinowski, Z. & Minor, W. Methods Enzymol. 276, 307–326 (1997).
Smith, G.D., Nagar, B., Rini, J.M., Hauptman, H.A & Blessing, R.H. Acta Crystallogr. D 54, 799–804 (1998).
Brünger, A.T. et al. Acta Crystallogr. D 54, 905–921 (1998).
van Asselt, E.J., Perrakis, A., Kalk, K.H., Lamzin, V.S. & Dijkstra, B.W. Acta Crystallogr. D 54, 58–73 (1998).
Evans, S.V. J. Mol. Graph. 11, 134–138 (1993).
Acknowledgements
S.I.P. and S.V.E. thank the Canadian Institutes of Health Research for salary support and funding. M.M.P. thanks the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada for funding. The authors thank D.R. Bundle and O. Hindsgaul for helpful discussions, as well as C. Weeks, J. Berendzen and R.W. Grosse-Kuntsleeve for help while at Brookhaven National Laboratories beamlines X4A, X8C and X12C.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Patenaude, S., Seto, N., Borisova, S. et al. The structural basis for specificity in human ABO(H) blood group biosynthesis. Nat Struct Mol Biol 9, 685–690 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/nsb832
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsb832
This article is cited by
-
Turning universal O into rare Bombay type blood
Nature Communications (2023)
-
The stem region of group A transferase is crucial for its specificity, and its alteration promotes heterologous Forssman synthase activity
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
A historical overview of advances in molecular genetic/genomic studies of the ABO blood group system
Glycoconjugate Journal (2022)
-
UGT74AF3 enzymes specifically catalyze the glucosylation of 4-hydroxy-2,5-dimethylfuran-3(2H)-one, an important volatile compound in Camellia sinensis
Horticulture Research (2020)
-
Amino acid substitutions at sugar-recognizing codons confer ABO blood group system-related α1,3 Gal(NAc) transferases with differential enzymatic activity
Scientific Reports (2019)