Volume 14
-
No. 12 December 2018
The image shows knee articular cartilage from a chondrocyte-specific Bmal1-knockout mouse. The tissue was stained with safranin O and fast green. Deletion of the transcription factor brain and muscle Arnt-like protein 1 (BMAL1, also known as aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator-like protein 1), a core component of the circadian clock, results in the loss of circadian rhythm and leads to degeneration of knee cartilage. The circadian clock controls the rhythmic expression of several hundred genes in cartilage and its function can be affected by inflammation and ageing, both of which are risk factors for osteoarthritis. Studies of the circadian clock will help us better understand cartilage physiology in health and disease.
-
No. 11 November 2018
The image shows knee articular cartilage from a chondrocyte-specific Bmal1-knockout mouse. The tissue was stained with safranin O and fast green. Deletion of the transcription factor brain and muscle Arnt-like protein 1 (BMAL1, also known as aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator-like protein 1), a core component of the circadian clock, results in the loss of circadian rhythm and leads to degeneration of knee cartilage. The circadian clock controls the rhythmic expression of several hundred genes in cartilage and its function can be affected by inflammation and ageing, both of which are risk factors for osteoarthritis. Studies of the circadian clock will help us better understand cartilage physiology in health and disease.
-
No. 10 October 2018
The image shows knee articular cartilage from a chondrocyte-specific Bmal1-knockout mouse. The tissue was stained with safranin O and fast green. Deletion of the transcription factor brain and muscle Arnt-like protein 1 (BMAL1, also known as aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator-like protein 1), a core component of the circadian clock, results in the loss of circadian rhythm and leads to degeneration of knee cartilage. The circadian clock controls the rhythmic expression of several hundred genes in cartilage and its function can be affected by inflammation and ageing, both of which are risk factors for osteoarthritis. Studies of the circadian clock will help us better understand cartilage physiology in health and disease.
-
No. 9 September 2018
The image shows knee articular cartilage from a chondrocyte-specific Bmal1-knockout mouse. The tissue was stained with safranin O and fast green. Deletion of the transcription factor brain and muscle Arnt-like protein 1 (BMAL1, also known as aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator-like protein 1), a core component of the circadian clock, results in the loss of circadian rhythm and leads to degeneration of knee cartilage. The circadian clock controls the rhythmic expression of several hundred genes in cartilage and its function can be affected by inflammation and ageing, both of which are risk factors for osteoarthritis. Studies of the circadian clock will help us better understand cartilage physiology in health and disease.
-
No. 8 August 2018
The image shows knee articular cartilage from a chondrocyte-specific Bmal1-knockout mouse. The tissue was stained with safranin O and fast green. Deletion of the transcription factor brain and muscle Arnt-like protein 1 (BMAL1, also known as aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator-like protein 1), a core component of the circadian clock, results in the loss of circadian rhythm and leads to degeneration of knee cartilage. The circadian clock controls the rhythmic expression of several hundred genes in cartilage and its function can be affected by inflammation and ageing, both of which are risk factors for osteoarthritis. Studies of the circadian clock will help us better understand cartilage physiology in health and disease.
-
No. 7 July 2018
The image shows knee articular cartilage from a chondrocyte-specific Bmal1-knockout mouse. The tissue was stained with safranin O and fast green. Deletion of the transcription factor brain and muscle Arnt-like protein 1 (BMAL1, also known as aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator-like protein 1), a core component of the circadian clock, results in the loss of circadian rhythm and leads to degeneration of knee cartilage. The circadian clock controls the rhythmic expression of several hundred genes in cartilage and its function can be affected by inflammation and ageing, both of which are risk factors for osteoarthritis. Studies of the circadian clock will help us better understand cartilage physiology in health and disease.
-
No. 6 June 2018
The image shows knee articular cartilage from a chondrocyte-specific Bmal1-knockout mouse. The tissue was stained with safranin O and fast green. Deletion of the transcription factor brain and muscle Arnt-like protein 1 (BMAL1, also known as aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator-like protein 1), a core component of the circadian clock, results in the loss of circadian rhythm and leads to degeneration of knee cartilage. The circadian clock controls the rhythmic expression of several hundred genes in cartilage and its function can be affected by inflammation and ageing, both of which are risk factors for osteoarthritis. Studies of the circadian clock will help us better understand cartilage physiology in health and disease.
-
No. 5 May 2018
Image supplied by Dr Michal Dudek from the Faculty of Life Sciences, University of Manchester, Manchester, UK. The image shows knee articular cartilage from a chondrocyte-specific Bmal1-knockout mouse. The tissue was stained with safranin O and fast green. Deletion of the transcription factor brain and muscle Arnt-like protein 1 (BMAL1, also known as aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator-like protein 1), a core component of the circadian clock, results in the loss of circadian rhythm and leads to degeneration of knee cartilage. The circadian clock controls the rhythmic expression of several hundred genes in cartilage and its function can be affected by inflammation and ageing, both of which are risk factors for osteoarthritis. Studies of the circadian clock will help us better understand cartilage physiology in health and disease.
-
No. 4 April 2018
Image supplied by Dr Michal Dudek from the Faculty of Life Sciences, University of Manchester, Manchester, UK. The image shows knee articular cartilage from a chondrocyte-specific Bmal1-knockout mouse. The tissue was stained with safranin O and fast green. Deletion of the transcription factor brain and muscle Arnt-like protein 1 (BMAL1, also known as aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator-like protein 1), a core component of the circadian clock, results in the loss of circadian rhythm and leads to degeneration of knee cartilage. The circadian clock controls the rhythmic expression of several hundred genes in cartilage and its function can be affected by inflammation and ageing, both of which are risk factors for osteoarthritis. Studies of the circadian clock will help us better understand cartilage physiology in health and disease.
-
No. 3 March 2018
Image supplied by Dr Michal Dudek from the Faculty of Life Sciences, University of Manchester, Manchester, UK. The image shows knee articular cartilage from a chondrocyte-specific Bmal1-knockout mouse. The tissue was stained with safranin O and fast green. Deletion of the transcription factor brain and muscle Arnt-like protein 1 (BMAL1, also known as aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator-like protein 1), a core component of the circadian clock, results in the loss of circadian rhythm and leads to degeneration of knee cartilage. The circadian clock controls the rhythmic expression of several hundred genes in cartilage and its function can be affected by inflammation and ageing, both of which are risk factors for osteoarthritis. Studies of the circadian clock will help us better understand cartilage physiology in health and disease.
-
No. 2 February 2018
Image supplied by Dr Michal Dudek from the Faculty of Life Sciences, University of Manchester, Manchester, UK. The image shows knee articular cartilage from a chondrocyte-specific Bmal1-knockout mouse. The tissue was stained with safranin O and fast green. Deletion of the transcription factor brain and muscle Arnt-like protein 1 (BMAL1, also known as aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator-like protein 1), a core component of the circadian clock, results in the loss of circadian rhythm and leads to degeneration of knee cartilage. The circadian clock controls the rhythmic expression of several hundred genes in cartilage and its function can be affected by inflammation and ageing, both of which are risk factors for osteoarthritis. Studies of the circadian clock will help us better understand cartilage physiology in health and disease.
-
No. 1 January 2018
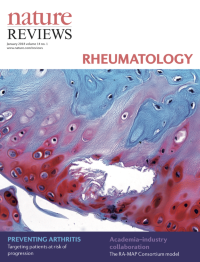
Image supplied by Dr Michal Dudek from the Faculty of Life Sciences, University of Manchester, Manchester, UK. The image shows knee articular cartilage from a chondrocyte-specific Bmal1-knockout mouse. The tissue was stained with safranin O and fast green. Deletion of the transcription factor brain and muscle Arnt-like protein 1 (BMAL1, also known as aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator-like protein 1), a core component of the circadian clock, results in the loss of circadian rhythm and leads to degeneration of knee cartilage. The circadian clock controls the rhythmic expression of several hundred genes in cartilage and its function can be affected by inflammation and ageing, both of which are risk factors for osteoarthritis. Studies of the circadian clock will help us better understand cartilage physiology in health and disease.