Abstract
The anterior insular cortex (AIC) is implicated in a wide range of conditions and behaviours, from bowel distension and orgasm, to cigarette craving and maternal love, to decision making and sudden insight. Its function in the re-representation of interoception offers one possible basis for its involvement in all subjective feelings. New findings suggest a fundamental role for the AIC (and the von Economo neurons it contains) in awareness, and thus it needs to be considered as a potential neural correlate of consciousness.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$189.00 per year
only $15.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Craig, A. D. How do you feel? Interoception: the sense of the physiological condition of the body. Nature Rev. Neurosci. 3, 655–666 (2002).
Craig, A. D., Chen, K., Bandy, D. & Reiman, E. M. Thermosensory activation of insular cortex. Nature Neurosci. 3, 184–190 (2000).
Critchley, H. D., Wiens, S., Rotshtein, P., Ohman, A. & Dolan, R. J. Neural systems supporting interoceptive awareness. Nature Neurosci. 7, 189–195 (2004).
Barrett, L. F., Quigley, K. S., Bliss-Moreau, E. & Aronson, K. R. Interoceptive sensitivity and self-reports of emotional experience. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 87, 684–697 (2004).
Stephan, E. et al. Functional neuroimaging of gastric distention. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 7, 740–749 (2003).
Phillips, M. L. et al. The effect of negative emotional context on neural and behavioural responses to oesophageal stimulation. Brain 126, 669–684 (2003).
Brooks, J. C., Nurmikko, T. J., Bimson, W. E., Singh, K. D. & Roberts, N. fMRI of thermal pain: effects of stimulus laterality and attention. Neuroimage 15, 293–301 (2002).
Kong, J. et al. Using fMRI to dissociate sensory encoding from cognitive evaluation of heat pain intensity. Hum. Brain Mapp. 27, 715–721 (2006).
Singer, T. et al. Empathy for pain involves the affective but not sensory components of pain. Science 303, 1157–1162 (2004).
Henderson, L. A., Gandevia, S. C. & Macefield, V. G. Somatotopic organization of the processing of muscle and cutaneous pain in the left and right insula cortex: a single-trial fMRI study. Pain 128, 20–30 (2007).
Farrer, C. & Frith, C. D. Experiencing oneself vs another person as being the cause of an action: the neural correlates of the experience of agency. Neuroimage 15, 596–603 (2002).
Farrer, C. et al. Modulating the experience of agency: a positron emission tomography study. Neuroimage 18, 324–333 (2003).
Tsakiris, M., Hesse, M. D., Boy, C., Haggard, P. & Fink, G. R. Neural signatures of body ownership: a sensory network for bodily self-consciousness. Cereb. Cortex 17, 2235–2244 (2007).
Mutschler, I. et al. A rapid sound-action association effect in human insular cortex. PLoS ONE 2, e259 (2007).
Devue, C. et al. Here I am: the cortical correlates of visual self-recognition. Brain Res. 1143, 169–182 (2007).
Platel, H. et al. The structural components of music perception. A functional anatomical study. Brain 120, 229–243 (1997).
Koelsch, S., Fritz, T., v. Cramon, D. Y., Muller, K. & Friederici, A. D. Investigating emotion with music: an fMRI study. Hum. Brain Mapp. 27, 239–250 (2006).
Ackermann, H. & Riecker, A. The contribution of the insula to motor aspects of speech production: a review and a hypothesis. Brain Lang. 89, 320–328 (2004).
Seeley, W. W. et al. Dissociable intrinsic connectivity networks for salience processing and executive control. J. Neurosci. 27, 2349–2356 (2007).
Hennenlotter, A. et al. A common neural basis for receptive and expressive communication of pleasant facial affect. Neuroimage 26, 581–591 (2005).
Jabbi, M., Swart, M. & Keysers, C. Empathy for positive and negative emotions in the gustatory cortex. Neuroimage 34, 1744–1753 (2007).
Koechlin, E. & Jubault, T. Broca's area and the hierarchical organization of human behavior. Neuron 50, 963–974 (2006).
Klein, T. A. et al. Neural correlates of error awareness. Neuroimage 34, 1774–1781 (2007).
Seymour, B. et al. Temporal difference models describe higher-order learning in humans. Nature 429, 664–667 (2004).
Preuschoff, K., Quartz, S. R. & Bossaerts, P. Human insula activation reflects risk prediction errors as well as risk. J. Neurosci. 28, 2745–2752 (2008).
Knutson, B., Rick, S., Wimmer, G. E., Prelec, D. & Loewenstein, G. Neural predictors of purchases. Neuron 53, 147–156 (2007).
Kondo, H. M. & Kashino, M. Neural mechanisms of auditory awareness underlying verbal transformations. Neuroimage 36, 123–130 (2007).
Pressnitzer, D. & Hupe, J. M. Temporal dynamics of auditory and visual bistability reveal common principles of perceptual organization. Curr. Biol. 16, 1351–1357 (2006).
Sterzer, P. & Kleinschmidt, A. A neural basis for inference in perceptual ambiguity. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 104, 323–328 (2007).
Bushara, K. O., Grafman, J. & Hallett, M. Neural correlates of auditory-visual stimulus onset asynchrony detection. J. Neurosci. 21, 300–304 (2001).
Deary, I. J. et al. The functional anatomy of inspection time: an event-related fMRI study. Neuroimage 22, 1466–1479 (2004).
Kranczioch, C., Debener, S., Schwarzbach, J., Goebel, R. & Engel, A. K. Neural correlates of conscious perception in the attentional blink. Neuroimage 24, 704–714 (2005).
Coull, J. T. fMRI studies of temporal attention: allocating attention within, or towards, time. Brain Res. Cogn. Brain Res. 21, 216–226 (2004).
Livesey, A. C., Wall, M. B. & Smith, A. T. Time perception: manipulation of task difficulty dissociates clock functions from other cognitive demands. Neuropsychologia 45, 321–331 (2007).
Fan, J. et al. The relation of brain oscillations to attentional networks. J. Neurosci. 27, 6197–6206 (2007).
Koch, C. & Tsuchiya, N. Attention and consciousness: two distinct brain processes. Trends Cogn Sci. 11, 16–22 (2007).
Weissman, D. H., Roberts, K. C., Visscher, K. M. & Woldorff, M. G. The neural bases of momentary lapses in attention. Nature Neurosci. 9, 971–978 (2006).
Mason, M. F. et al. Wandering minds: the default network and stimulus-independent thought. Science 315, 393–395 (2007).
Ploran, E. J. et al. Evidence accumulation and the moment of recognition: dissociating perceptual recognition processes using fMRI. J. Neurosci. 27, 11912–11924 (2007).
Thielscher, A. & Pessoa, L. Neural correlates of perceptual choice and decision making during fear-disgust discrimination. J. Neurosci. 27, 2908–2917 (2007).
Kikyo, H., Ohki, K. & Miyashita, Y. Neural correlates for feeling-of-knowing: an fMRI parametric analysis. Neuron 36, 177–186 (2002).
Yonelinas, A. P., Otten, L. J., Shaw, K. N. & Rugg, M. D. Separating the brain regions involved in recollection and familiarity in recognition memory. J. Neurosci. 25, 3002–3008 (2005).
Cole, M. W. & Schneider, W. The cognitive control network: integrated cortical regions with dissociable functions. Neuroimage 37, 343–360 (2007).
Dosenbach, N. U. et al. Distinct brain networks for adaptive and stable task control in humans. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 104, 11073–11078 (2007).
Brass, M. & Haggard, P. To do or not to do: the neural signature of self-control. J. Neurosci. 27, 9141–9145 (2007).
Ramautar, J. R., Slagter, H. A., Kok, A. & Ridderinkhof, K. R. Probability effects in the stop-signal paradigm: the insula and the significance of failed inhibition. Brain Res. 1105, 143–154 (2006).
Eichele, T. et al. Prediction of human errors by maladaptive changes in event-related brain networks. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 105, 6173–6178 (2008).
Sridharan, D., Levitin, D. J. & Menon, V. A critical role for the right fronto-insular cortex in switching between central-executive and default-mode networks. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 105, 12569–12574 (2008).
Frith, C., Perry, R. & Lumer, E. The neural correlates of conscious experience: an experimental framework. Trends Cogn. Sci. 3, 105–114 (1999).
Lewis, M. in Handbook of Emotions 3rd edn (eds Lewis, M., Haviland-Jones, J. M. & Barrett, L. F.) 304–319 (Guilford, New York, 2008).
Damasio, A. R. Descartes' Error: Emotion, Reason, and the Human Brain (Putnam, New York, 1993).
Churchland, P. S. Self-representation in nervous systems. Science 296, 308–310 (2002).
Frith, C. D. & Frith, U. Social cognition in humans. Curr. Biol. 17, R724–R732 (2007).
Macphail, E. M. The Evolution of Consciousness (Oxford Univ. Press, Oxford, 1998).
de Waal, F. B. The thief in the mirror. PLoS Biol. 6, e201 (2008).
Reiss, D. & Marino, L. Mirror self-recognition in the bottlenose dolphin: a case of cognitive convergence. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 98, 5937–5942 (2001).
Prior, H., Schwarz, A. & Gunturkun, O. Mirror-induced behavior in the magpie (Pica pica): evidence of self-recognition. PLoS Biol. 6, e202 (2008).
Persaud, N., McLeod, P. & Cowey, A. Post-decision wagering objectively measures awareness. Nature Neurosci. 10, 257–261 (2007).
Ruys, K. I. & Stapel, D. A. The secret life of emotions. Psychol. Sci. 19, 385–391 (2008).
Duncan, S. & Barrett, L. F. Affect is a form of cognition: a neurobiological analysis. Cogn. Emot. 21, 1184–1211 (2007).
James, W. The Principles of Psychology. Classics in the History of Psychology [online], (1890).
Paulus, M. P. & Stein, M. B. An insular view of anxiety. Biol. Psychiatry 60, 383–387 (2006).
Mayer, E. A., Naliboff, B. D. & Craig, A. D. Neuroimaging of the brain-gut axis: from basic understanding to treatment of functional GI disorders. Gastroenterology 131, 1925–1942 (2006).
Wegner, D. M. The Illusion of Conscious Will (MIT Press, Cambridge, Massachusetts, 2008).
Amodio, D. M. & Frith, C. D. Meeting of minds: the medial frontal cortex and social cognition. Nature Rev. Neurosci. 7, 268–277 (2006).
Karnath, H. O., Baier, B. & Nagele, T. Awareness of the functioning of one's own limbs mediated by the insular cortex? J. Neurosci. 25, 7134–7138 (2005).
Spinazzola, L., Pia, L., Folegatti, A., Marchetti, C. & Berti, A. Modular structure of awareness for sensorimotor disorders: evidence from anosognosia for hemiplegia and anosognosia for hemianaesthesia. Neuropsychologia 46, 915–926 (2008).
Sterzer, P., Stadler, C., Poustka, F. & Kleinschmidt, A. A structural neural deficit in adolescents with conduct disorder and its association with lack of empathy. Neuroimage 37, 335–342 (2007).
King-Casas, B. et al. The rupture and repair of cooperation in borderline personality disorder. Science 321, 806–810 (2008).
Silani, G. et al. Levels of emotional awareness and autism: an fMRI study. Soc. Neurosci. 3, 97–112 (2008).
Moriguchi, Y. et al. Empathy and judging other's pain: an fMRI study of alexithymia. Cereb. Cortex 17, 2223–2234 (2007).
Kano, M. et al. Specific brain processing of facial expressions in people with alexithymia: an H215O-PET study. Brain 126, 1474–1484 (2003).
Manes, F., Paradiso, S. & Robinson, R. G. Neuropsychiatric effects of insular stroke. J. Nerv. Ment. Dis. 187, 707–712 (1999).
Boddaert, N. et al. Anatomical and functional brain imaging evidence of lenticulo-insular anomalies in Smith Magenis syndrome. Neuroimage 21, 1021–1025 (2004).
Sturm, V. E., Rosen, H. J., Allison, S., Miller, B. L. & Levenson, R. W. Self-conscious emotion deficits in frontotemporal lobar degeneration. Brain 129, 2508–2516 (2006).
Seeley, W. W. et al. Early frontotemporal dementia targets neurons unique to apes and humans. Ann. Neurol. 60, 660–667 (2006).
Christensen, M. S., Ramsoy, T. Z., Lund, T. E., Madsen, K. H. & Rowe, J. B. An fMRI study of the neural correlates of graded visual perception. Neuroimage 31, 1711–1725 (2006).
Craig, A. D. in Handbook of Emotions 3rd edn (eds Lewis, M., Haviland-Jones, J. M. & Barrett, L. F.) 272–288 (Guilford, New York, 2008).
Menon, V. & Levitin, D. J. The rewards of music listening: response and physiological connectivity of the mesolimbic system. Neuroimage 28, 175–184 (2005).
Dunbar, R. I. & Shultz, S. Evolution in the social brain. Science 317, 1344–1347 (2007).
Tse, P. U., Intriligator, J., Rivest, J. & Cavanagh, P. Attention and the subjective expansion of time. Percept. Psychophys. 66, 1171–1189 (2004).
Sarinopoulos, I., Dixon, G. E., Short, S. J., Davidson, R. J. & Nitschke, J. B. Brain mechanisms of expectation associated with insula and amygdala response to aversive taste: implications for placebo. Brain Behav. Immun. 20, 120–132 (2006).
Jabbi, M., Bastiaansen, J. & Keysers, C. A common anterior insula representation of disgust observation, experience and imagination shows divergent functional connectivity pathways. PLoS ONE 3, e2939 (2008).
Penfield, W. & Faulk, M. E. The insula. Brain 78, 30–470 (1955).
Mesulam, M.-M. & Mufson, E. J. Insula of the old world monkey. III: Efferent cortical output and comments on function. J. Comp. Neurol. 212, 38–52 (1982).
Saper, C. B. The central autonomic nervous system: conscious visceral perception and autonomic pattern generation. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 25, 433–469 (2002).
Heimer, L. & Van Hoesen, G. W. The limbic lobe and its output channels: implications for emotional functions and adaptive behavior. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 30, 126–147 (2006).
Nimchinsky, E. A. et al. A neuronal morphologic type unique to humans and great apes. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 96, 5268–5273 (1999).
Allman, J. M., Watson, K. K., Tetreault, N. A. & Hakeem, A. Y. Intuition and autism: a possible role for Von Economo neurons. Trends Cogn. Sci. 9, 367–373 (2005).
Seeley, W. W. et al. Dissociable intrinsic connectivity networks for salience processing and executive control. J. Neurosci. 27, 2349–2356 (2007).
Seeley, W. W. et al. Divergent social functioning in behavioral variant frontotemporal dementia and Alzheimer disease: reciprocal networks and neuronal evolution. Alzheimer Dis. Assoc. Disord. 21, S50–S57 (2007).
Hakeem, A. Y. et al. Von Economo neurons in the elephant brain. Anat. Rec. (in the press).
Hof, P. R. & Van der Gucht, E. Structure of the cerebral cortex of the humpback whale, Megaptera novaeangliae (Cetacea, Mysticeti, Balaenopteridae). Anat. Rec. (Hoboken) 290, 1–31 (2007).
Plotnik, J. M., de Waal, F. B. & Reiss, D. Self-recognition in an Asian elephant. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 103, 17053–17057 (2006).
Craig, A. D. Forebrain emotional asymmetry: a neuroanatomical basis? Trends Cogn. Sci. 9, 566–571 (2005).
Davidson, R. J. Well-being and affective style: neural substrates and biobehavioural correlates. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 359, 1395–1411 (2004).
Rosenkranz, M. A. et al. Neural circuitry underlying the interaction between emotion and asthma symptom exacerbation. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 102, 13319–13324 (2005).
Henderson, L. A. et al. Neural responses during Valsalva maneuvers in obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. J. Appl. Physiol. 94, 1063–1074 (2003).
Oppenheimer, S. M., Gelb, A., Girvin, J. P. & Hachinski, V. C. Cardiovascular effects of human insular cortex stimulation. Neurology 42, 1727–1732 (1992).
Gazzaniga, M. S. Forty-five years of split-brain research and still going strong. Nature Rev. Neurosci. 6, 653–659 (2005).
Uddin, L. Q., Rayman, J. & Zaidel, E. Split-brain reveals separate but equal self-recognition in the two cerebral hemispheres. Conscious. Cogn. 14, 633–640 (2005).
Lane, R. D. Neural substrates of implicit and explicit emotional processes: a unifying framework for psychosomatic medicine. Psychosom. Med. 70, 214–231 (2008).
Lieberman, M. D. Social cognitive neuroscience: a review of core processes. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 58, 259–289 (2007).
Parvizi, J., Van Hoesen, G. W., Buckwalter, J. & Damasio, A. Neural connections of the posteromedial cortex in the macaque. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 103, 1563–1568 (2006).
Vincent, J. L. et al. Intrinsic functional architecture in the anaesthetized monkey brain. Nature 447, 83–86 (2007).
Orfei, M. D. et al. Anosognosia for hemiplegia after stroke is a multifaceted phenomenon: a systematic review of the literature. Brain 130, 3075–3090 (2007).
Gray, M. A., Harrison, N. A., Wiens, S. & Critchley, H. D. Modulation of emotional appraisal by false physiological feedback during fMRI. PLoS ONE 2, e546 (2007).
Kringelbach, M. L. The human orbitofrontal cortex: linking reward to hedonic experience. Nature Rev. Neurosci. 6, 691–702 (2005).
Semendeferi, K. & Damasio, H. The brain and its main anatomical subdivisions in living hominoids using magnetic resonance imaging. J. Hum. Evol. 38, 317–332 (2000).
Schweinhardt, P. et al. An fMRI study of cerebral processing of brush-evoked allodynia in neuropathic pain patients. Neuroimage 32, 256–265 (2006).
Eisenberger, N. I., Lieberman, M. D. & Williams, K. D. Does rejection hurt? An fMRI study of social exclusion. Science 302, 290–292 (2003).
Roy, M., Peretz, I. & Rainville, P. Emotional valence contributes to music-induced analgesia. Pain 134, 140–147 (2008).
Droit-Volet, S. & Meck, W. H. How emotions colour our perception of time. Trends Cogn. Sci. 11, 504–513 (2007).
Naidich, T. P. et al. The insula: anatomic study and MR imaging display at 1.5 T. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 25, 222–232 (2004).
Augustine, J. R. The insular lobe in primates including humans. Neurol. Res. 7, 2–10 (1985).
Augustine, J. R. Circuitry and functional aspects of the insular lobe in primates including humans. Brain Res. Brain Res. Rev. 22, 229–244 (1996).
Mufson, E. J., Sobreviela, T. & Kordower, J. H. in Handbook of Chemical Neuroanatomy, Vol. 13: The Primate Nervous System, Part I. (eds Bloom, F. E., Bjorklund, A. & Hokfelt, T.) 377–454 (Elsevier Science, 1997).
Ture, U., Yasargil, D. C., Al Mefty, O. & Yasargil, M. G. Topographic anatomy of the insular region. J. Neurosurg. 90, 720–733 (1999).
Olausson, H. et al. Unmyelinated tactile afferents signal touch and project to insular cortex. Nature Neurosci. 5, 900–904 (2002).
Olausson, H. et al. Feelings of warmth correlate with neural activity in right anterior insular cortex. Neurosci. Lett. 389, 1–5 (2005).
Small, D. M., Zatorre, R. J., Dagher, A., Evans, A. C. & Jones-Gotman, M. Changes in brain activity related to eating chocolate: from pleasure to aversion. Brain 124, 1720–1733 (2001).
Veldhuizen, M. G., Bender, G., Constable, R. T. & Small, D. M. Trying to detect taste in a tasteless solution: modulation of early gustatory cortex by attention to taste. Chem. Senses 32, 569–581 (2007).
Frank, G. K. et al. Sucrose activates human taste pathways differently from artificial sweetener. Neuroimage 39, 1559–1569 (2008).
Wang, G. J. et al. Gastric distention activates satiety circuitry in the human brain. Neuroimage 39, 1824–1831 (2008).
Leibenluft, E., Gobbini, M. I., Harrison, T. & Haxby, J. V. Mothers' neural activation in response to pictures of their children and other children. Biol. Psychiatry 56, 225–232 (2004).
Bartels, A. & Zeki, S. The neural correlates of maternal and romantic love. Neuroimage 21, 1155–1166 (2004).
Johnstone, T., van Reekum, C. M., Oakes, T. R. & Davidson, R. J. The voice of emotion: an fMRI study of neural responses to angry and happy vocal expressions. Soc. Cogn. Affect. Neurosci. 1, 242–249 (2006).
Takahashi, H. et al. Brain activations during judgments of positive self-conscious emotion and positive basic emotion: pride and joy. Cereb. Cortex 18, 898–903 (2008).
Ortigue, S., Grafton, S. T. & Bianchi-Demicheli, F. Correlation between insula activation and self-reported quality of orgasm in women. Neuroimage 37, 551–560 (2007).
Acknowledgements
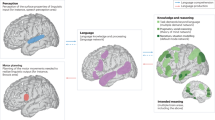
I thank J. Allman, L. Feldman Barrett, P. Churchland, M. Paulus and I. Strigo for their comments on the manuscript, and Professor T. P. Naidich for supplying the photograph in figure 1. I am grateful for funds from the James S. McDonnell Foundation and for continuous support from the Barrow Neurological Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The author declares no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Related links
Related links
FURTHER INFORMATION
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
(Bud) Craig, A. How do you feel — now? The anterior insula and human awareness. Nat Rev Neurosci 10, 59–70 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn2555
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn2555
This article is cited by
-
Trauma, early life stress, and mindfulness in adulthood
BMC Psychology (2024)
-
High-intensity sweet taste as a predictor of subjective alcohol responses to the ascending limb of an intravenous alcohol prime: an fMRI study
Neuropsychopharmacology (2024)
-
From early relational experiences to non-suicidal self-injury in anorexia and bulimia nervosa: a structural equation model unraveling the role of impairments in interoception
Eating and Weight Disorders - Studies on Anorexia, Bulimia and Obesity (2024)
-
Decoding auditory deprivation: resting-state fMRI insights into deafness and brain plasticity
Brain Structure and Function (2024)
-
Stress and reward in the maternal brain of mothers with borderline personality disorder: a script-based fMRI study
European Archives of Psychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience (2024)