Abstract
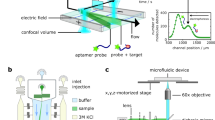
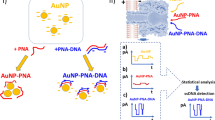
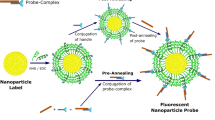
The colorimetric bio-barcode assay is a red-to-blue color change-based protein detection method with ultrahigh sensitivity. This assay is based on both the bio-barcode amplification method that allows for detecting miniscule amount of targets with attomolar sensitivity and gold nanoparticle-based colorimetric DNA detection method that allows for a simple and straightforward detection of biomolecules of interest (here we detect interleukin-2, an important biomarker (cytokine) for many immunodeficiency-related diseases and cancers). The protocol is composed of the following steps: (i) conjugation of target capture molecules and barcode DNA strands onto silica microparticles, (ii) target capture with probes, (iii) separation and release of barcode DNA strands from the separated probes, (iv) detection of released barcode DNA using DNA-modified gold nanoparticle probes and (v) red-to-blue color change analysis with a graphic software. Actual target detection and quantification steps with premade probes take ∼3 h (whole protocol including probe preparations takes ∼3 days).
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Elghanian, R., Storhoff, J.J., Mucic, R.C., Letsinger, R.L. & Mirkin, C.A. Selective colorimetric detection of polynucleotides based on the distance-dependent optical properties of gold nanoparticles. Science 277, 1078–1080 (1997).
Storhoff, J.J., Elghanian, R., Mucic, R.C., Mirkin, C.A. & Letsinger, R.L. One-pot colorimetric differentiation of polynucleotides with single base imperfections using gold nanoparticle probes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 120, 1959–1964 (1998).
Nam, J.-M., Thaxton, C.S. & Mirkin, C.A. Nanoparticle-based bio-bar codes for the ultrasensitive detection of proteins. Science 301, 1884–1886 (2003).
Nam, J.-M., Stoeva, S.I. & Mirkin, C.A. Bio-bar-code-based DNA detection with PCR-like sensitivity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 126, 5932–5933 (2004).
Thaxton, C.S., Hill, H.D., Georganopoulou, D.G., Stoeva, S.I. & Mirkin, C.A. A bio-bar-code assay based upon dithiothreitol-induced oligonucleotide release. Anal. Chem. 77, 8174–8178 (2005).
Bao, Y.P. et al. Detection of protein analytes via nanoparticle-based bio bar code technology. Anal. Chem. 78, 2055–2059 (2006).
Oh, B.K., Nam, J.-M., Lee, S.W. & Mirkin, C.A. A fluorophore-based bio-barcode amplification assay for proteins. Small 2, 103–108 (2006).
Hill, H.D. & Mirkin, C.A. The bio-barcode assay for the detection of protein and nucleic acid targets using DTT-induced ligand exchange. Nat. Protoc. 1, 324–336 (2006).
Georganopoulou, D. et al. Nanoparticle-based detection of a soluble pathogenic biomarker for Alzheimer's disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102, 2273–2276 (2005).
Stoeva, S.I., Lee, J.-S., Thaxton, C.S. & Mirkin, C.A. Multiplexed DNA detection with bio-barcoded nanoparticle probes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 118, 3381–3384 (2006).
Stoeva, S.I., Lee, J.-S., Smith, J.E., Rosen, S.T. & Mirkin, C.A. Multiplexed detection of protein cancer markers with bio-barcoded nanoparticle probes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 128, 8378–8379 (2006).
Shaikh, K.A. et al. A modular microfluidic architecture for integrated biochemical analysis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102, 9745 (2005).
Goluch, E.D. et al. A bio-barcode assay for on-chip attomolar-sensitivity protein detection. Lab on a Chip 6, 1293 (2006).
Nam, J.-M., Wise, A.R. & Groves, J.T. Colorimetric bio-barcode amplification assay for cytokines. Anal. Chem. 77, 6985–6988 (2005).
Ferrua, B., Aussel, C. & Fehlmann, M. Human interleukin 2. Detection at the picomolar level by sandwich enzyme immunoassay. J. Immunol. Methods 97, 215–220 (1987).
Carson, R.T. & Vignali, D.A.A. Simultaneous quantitation of 15 cytokines using a multiplexed flow cytometric assay. J. Immunol. Methods 227, 41–52 (1999).
Janeway, C.A., Travers, P., Walport, M. & Capra, J.D. Immunobiology: The Immune System in Health and Disease 6th edn. (Garland Science Publishing, 2005).
Mullenix, M.C. et al. Rolling circle amplification improves sensitivity in multiplex immunoassays on microspheres. Clin. Chem. 48, 1855–1858 (2002).
Schweitzer, B. et al. Multiplexed protein profiling on microarrays by rolling-circle amplification. Nat. Biotechnol. 20, 359–365 (2002).
Kingsmore, S.F. & Patel, D.D. Multiplexed protein profiling on antibody-based microarrays by rolling circle amplification. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 14, 74–81 (2003).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Korea Research Foundation Grant funded by Korea Government (MOEHRD, Basic Research Promotion Fund; KRF-2006-C00217), the Ministry of Commerce and Seoul RNBD program(11001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nam, JM., Jang, KJ. & Groves, J. Detection of proteins using a colorimetric bio-barcode assay. Nat Protoc 2, 1438–1444 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2007.201
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2007.201
This article is cited by
-
A Competitive Bio-Barcode Amplification Immunoassay for Small Molecules Based on Nanoparticles
Scientific Reports (2016)
-
Bio-barcode gel assay for microRNA
Nature Communications (2014)
-
Helium beam shadowing for high spatial resolution patterning of antibodies on microstructured diagnostic surfaces
Biointerphases (2013)
-
Utilization of unmodified gold nanoparticles in colorimetric detection
Science China Physics, Mechanics and Astronomy (2011)
-
Gold nanoparticles for the development of clinical diagnosis methods
Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry (2008)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.