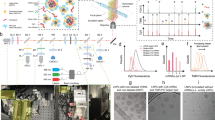
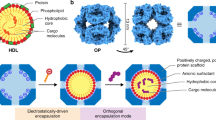
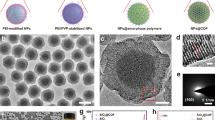
Abstract
A detailed protocol for the synthesis of core/shell semiconductor nanocrystal, their encapsulation into phospholipid micelles, their purification and their coupling to a controlled number of small molecules is given. The protocol for the core/shell quantum dot (QD) CdSe/CdZnS synthesis has been specifically designed with two constraints in mind: green and reproducible core/shell QD synthesis with thick shell structure and QDs that can easily be encapsulated in poly(ethylene glycol)-phospholipid micelles with one QD per micelle. We present two procedures for the QD purification that are suitable for the use of QD micelles for in vivo imaging: ultracentrifugation and size-exclusion chromatography. We also discuss the different coupling chemistry for covalently linking a controlled number of molecules to the QD micelles. The total time durations for the different protocols are as follows: QD synthesis: 6 h; encapsulation: 15 min; purification: 1–4 h; coupling: reaction dependent.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Efros, A.L. & Rosen, M. The electronic structure of semiconductor nanocrystals. Annu. Rev. Mater. Sci. 30, 475–521 (2000).
Murray, C.B., Kagan, C.R. & Bawendi, M.G. Synthesis and characterization of monodisperse nanocrystals and close-packed nanocrystal assemblies. Annu. Rev. Mater. Sci. 30, 545–610 (2000).
Medintz, I.L., Uyeda, H.T., Goldman, E.R. & Mattoussi, H. Quantum dot bioconjugates for imaging, labelling and sensing. Nat. Mater. 4, 435–446 (2005).
Michalet, X. et al. Quantum dots for live cells, in vivo imaging, and diagnostics. Science 307, 538–544 (2005).
Dubertret, B. et al. In vivo imaging of quantum dots encapsulated in phospholipid micelles. Science 298, 1759–1762 (2002).
Murray, C.B., Norris, D.J. & Bawendi, M.G. Synthesis and characterization of nearly monodisperse Cde (E = S, Se, Te) semiconductor nanocrystallites. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 115, 8706–8715 (1993).
Hines, M.A. & GuyotSionnest, P. Synthesis and characterization of strongly luminescing ZnS-capped CdSe nanocrystals. J. Phys. Chem. 100, 468–471 (1996).
Qu, L.H., Peng, Z.A. & Peng, X.G. Alternative routes toward high quality CdSe nanocrystals. Nano Lett. 1, 333–337 (2001).
Yu, W.W., Wang, Y.A. & Peng, X.G. Formation and stability of size-, shape-, and structure-controlled CdTe nanocrystals: ligand effects on monomers and nanocrystals. Chem. Mater. 15, 4300–4308 (2003).
Talapin, D.V., Rogach, A.L., Kornowski, A., Haase, M. & Weller, H. Highly luminescent monodisperse CdSe and CdSe/ZnS nanocrystals synthesized in a hexadecylamine–trioctylphosphine oxide–trioctylphospine mixture. Nano Lett. 1, 207–211 (2001).
Yang, Y.A., Wu, H.M., Williams, K.R. & Cao, Y.C. Synthesis of CdSe and CdTe nanocrystals without precursor injection. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 44, 6712–6715 (2005).
Li, J.J. et al. Large-scale synthesis of nearly monodisperse CdSe/CdS core/shell nanocrystals using air-stable reagents via successive ion layer adsorption and reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 125, 12567–12575 (2003).
Xie, R.G., Kolb, U., Li, J.X., Basche, T. & Mews, A. Synthesis and characterization of highly luminescent CdSe-Core CdS/Zn0.5Cd0.5S/ZnS multishell nanocrystals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127, 7480–7488 (2005).
Dabbousi, B.O. et al. (CdSe)ZnS core-shell quantum dots: synthesis and characterization of a size series of highly luminescent nanocrystallites. J. Phys. Chem. B 101, 9463–9475 (1997).
Yu, Z.H., Guo, L., Du, H., Krauss, T. & Silcox, J. Shell distribution on colloidal CdSe/ZnS quantum dots. Nano Lett. 5, 565–570 (2005).
Jun, S., Jang, E. & Lim, J.E. Synthesis of multi-shell nanocrystals by a single step coating process. Nanotechnology 17, 3892–3896 (2006).
Talapin, D.V. et al. Highly emissive colloidal CdSe/CdS heterostructures of mixed dimensionality. Nano Lett. 3, 1677–1681 (2003).
Corbridge, D.E.C. The phosphorus world Chemistry, Biochemistry and Technology. CD-Rom (2005).
Liu, H.T., Owen, J.S. & Alivisatos, A.P. Mechanistic study of precursor evolution in colloidal group II–VI semiconductor nanocrystal synthesis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 129, 305–312 (2007).
Yang, Y.A., Chen, O., Angerhofer, A. & Cao, Y.C. Radial-position-controlled doping in CdS/ZnS core/shell nanocrystals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 128, 12428–12429 (2006).
Talapin, D.V. et al. CdSe/CdS/ZnS and CdSe/ZnSe/ZnS core-shell-shell nanocrystals. J. Phys. Chem. B 108, 18826–18831 (2004).
Bruchez, M., Moronne, M., Gin, P., Weiss, S. & Alivisatos, A.P. Semiconductor nanocrystals as fluorescent biological labels. Science 281, 2013–2016 (1998).
Jaiswal, J.K., Mattoussi, H., Mauro, J.M. & Simon, S.M. Long-term multiple color imaging of live cells using quantum dot bioconjugates. Nat. Biotechnol. 21, 47–51 (2003).
Harris, J.M. Poly(Ethylene Glycol) Chemistry: Biotechnical and Biomedical Applications (Plenum Press, New York and London, 1992).
Doose, S., Tsay, J.M., Pinaud, F. & Weiss, S. Comparison of photophysical and colloidal properties of biocompatible semiconductor nanocrystals using fluorescence correlation spectroscopy. Anal. Chem. 77, 2235–2242 (2005).
Pons, T., Uyeda, H.T., Medintz, I.L. & Mattoussi, H. Hydrodynamic dimensions, electrophoretic mobility, and stability of hydrophilic quantum dots. J. Phys. Chem. B 110, 20308–20316 (2006).
Hermanson, G.T. Bioconjugate Techniques (Academic Press, San Diego, California, 1996).
Leatherdale, C.A., Woo, W.K., Mikulec, F.V. & Bawendi, M.G. On the absorption cross section of CdSe nanocrystal quantum dots. J. Phys. Chem. B 106, 7619–7622 (2002).
Johnsson, M., Hansson, P. & Edwards, K. Spherical micelles and other self-assembled structures in dilute aqueous mixtures of poly(ethylene glycol) lipids. J. Phys. Chem. B 105, 8420–8430 (2001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carion, O., Mahler, B., Pons, T. et al. Synthesis, encapsulation, purification and coupling of single quantum dots in phospholipid micelles for their use in cellular and in vivo imaging. Nat Protoc 2, 2383–2390 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2007.351
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2007.351
This article is cited by
-
Direct nano-imaging of light-matter interactions in nanoscale excitonic emitters
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Monitoring cell membrane recycling dynamics of proteins using whole-cell fluorescence recovery after photobleaching of pH-sensitive genetic tags
Nature Protocols (2022)
-
A luminescent view of the clickable assembly of LnF3 nanoclusters
Nature Communications (2021)
-
Quantum dot-loaded monofunctionalized DNA icosahedra for single-particle tracking of endocytic pathways
Nature Nanotechnology (2016)
-
RGDS-conjugated CdSeTe/CdS quantum dots as near-infrared fluorescent probe: preparation, characterization and bioapplication
Journal of Nanoparticle Research (2016)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.