Abstract
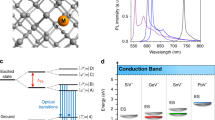
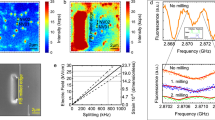
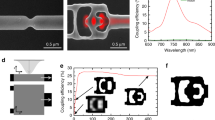
Diamond is an attractive material for photonic quantum technologies because its colour centres have a number of outstanding properties, including bright single photon emission and long spin coherence times. To take advantage of these properties it is favourable to directly fabricate optical microcavities in high-quality diamond samples. Such microcavities could be used to control the photons emitted by the colour centres or to couple widely separated spins. Here, we present a method for the fabrication of one- and two-dimensional photonic crystal microcavities with quality factors of up to 700 in single crystal diamond. Using a post-processing etching technique, we tune the cavity modes into resonance with the zero phonon line of an ensemble of silicon-vacancy colour centres, and we measure an intensity enhancement factor of 2.8. The controlled coupling of colour centres to photonic crystal microcavities could pave the way to larger-scale photonic quantum devices based on single crystal diamond.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ladd, T. et al. Quantum computers. Nature 464, 45–53, (2010).
Neumann, P. et al. Quantum register based on coupled electron spins in a room-temperature solid. Nature Phys. 6, 249–253 (2010).
Benjamin, S. C., Lovett, B. W. & Smith, J. M. Prospects for measurement-based quantum computing with solid state spins. Laser Photon. Rev. 3, 556–574 (2009).
Togan, E. et al. Quantum entanglement between an optical photon and a solid-state spin qubit. Nature 466, 730–734 (2010).
Noda, S., Fujita, M. & Asano, T. Spontaneous-emission control by photonic crystals and nanocavities. Nature Photon. 1, 449–458 (2007).
Su, C-H., Greentree, A. D. & Hollenberg, L. C. L. Towards a picosecond transform-limited nitrogen-vacancy based single photon source. Opt. Express 16, 6240–6250 (2008).
Kurtsiefer, C., Mayer, S., Zarda, P. & Weinfurter, H. Stable solid-state source of single photons. Phys. Rev. Lett. 85, 290–293 (2000).
Aharonovich, I. et al. Two-level ultrabright single photon emission from diamond nanocrystals. Nano Lett. 9, 3191–3195 (2009).
Neu, E. et al. Single photon emission from silicon-vacancy colour centres in chemical vapour deposition nano-diamonds on iridium. New J. Phys. 13, 025012 (2011).
Young, A. et al. Cavity enhanced spin measurement of the ground state spin of an NV center in diamond. New J. Phys. 11, 013007 (2009).
Childress, L., Taylor, J. M., Sørensen, A. S. & Lukin, M. D. Fault-tolerant quantum communication based on solid-state photon emitters. Phys. Rev. Lett. 96, 070504 (2006).
Greentree, A. D., Fairchild, B. A., Hossain, F. M. & Prawer, S. Diamond integrated quantum photonics. Mater. Today 11, 22–31 (September 2008).
Tomljenovic-Hanic, S., Steel, M. J., Sterke, C. M. & Salzman, J. Diamond based photonic crystal microcavities. Opt. Express 14, 3556–3562 (2006).
Kreuzer, C., Riedrich-Möller, J., Neu, E. & Becher, C. Design of photonic crystal microcavities in diamond films. Opt. Express 16, 1632–1644 (2008).
Riedrich-Möller, J., Neu, E. & Becher, C. Design of microcavities in diamond-based photonic crystals by Fourier- and real-space analysis of cavity fields. Photon. Nanostruct. Fund. Appl. 8, 150–162 (2010).
Bayn, I. & Salzman, J. High-Q photonic crystal nanocavities on diamond for quantum electrodynamics. Eur. Phys. J. Appl. Phys. 37, 19–24 (2007).
Tomljenovic-Hanic, S., Greentree, A. D., de Sterke, C. M. & Prawer, S. Flexible design of ultrahigh-Q microcavities in diamond-based photonic crystal slabs. Opt. Express 17, 6465–6475 (2009).
Babinec, T. M., Choy, J. T., Smith, K. J. M., Khan, M. & Lončar, M. Design and focused ion beam fabrication of single crystal diamond nanobeam cavities. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 29, 010601 (2011).
Park, Y-S., Cook, A. K. & Wang, H. Cavity QED with diamond nanocrystals and silica microspheres. Nano Lett. 6, 2075–2079 (2006).
Schietinger, S., Schröder, T. & Benson, O. One-by-one coupling of single defect centers in nanodiamonds to high-Q modes of an optical microresonator. Nano Lett. 8, 3911–3915 (2008).
Barclay, P. E., Santori, C., Fu, K-M., Beausoleil, R. G. & Painter, O. Coherent interference effects in a nano-assembled diamond NV center cavity–QED system. Opt. Express 17, 8081–8097 (2009).
Barclay, P. E., Fu, K-M. C., Santori, C. & Beausoleil, R. G. Chip-based microcavities coupled to NV centers in single crystal diamond. Appl. Phys. Lett. 95, 191115 (2009).
Fu, K-M., Barclay, P., Santori, C., Faraon, A. & Beausoleil, R. Low-temperature tapered-fiber probing of diamond NV ensembles coupled to GaP microcavities. New J. Phys. 13, 055023 (2011).
Wolters, J. et al. Enhancement of the zero phonon line emission from a single nitrogen vacancy center in a nanodiamond via coupling to a photonic crystal cavity. Appl. Phys. Lett. 97, 141108 (2010).
Englund, D. et al. Deterministic coupling of a single nitrogen vacancy center to a photonic crystal cavity. Nano Lett. 10, 3922–3926 (2010).
Van der Sar, T. et al. Deterministic nanoassembly of a coupled quantum emitter–photonic crystal cavity system. Appl. Phys. Lett. 98, 193103 (2011).
Shen, Y., Sweeney, T. M. & Wang, H. Zero-phonon linewidth of single nitrogen vacancy centers in diamond nanocrystals. Phys. Rev. B 77, 033201 (2008).
Santori, C. et al. Nanophotonics for quantum optics using nitrogen-vacancy centers in diamond. Nanotechnology 21, 274008 (2010).
Tamarat, P. et al. Stark shift control of single optical centers in diamond. Phys. Rev. Lett. 97, 083002 (2006).
Balasubramanian, G. et al. Ultralong spin coherence time in isotopically engineered diamond. Nature Mater. 8, 383–387 (2009).
Wang, C. F. et al. Observation of whispering gallery modes in nanocrystalline diamond microdisks. Appl. Phys. Lett. 90, 081110 (2007).
Wang, C. F. et al. Fabrication and characterization of two-dimensional photonic crystal microcavities in nanocrystalline diamond. Appl. Phys. Lett. 91, 201112 (2007).
Fairchild, B. A. et al. Fabrication of ultrathin single-crystal diamond membranes. Adv. Mater. 20, 1–6 (2008).
Bayn, I., Meyler, B., Salzman, J. & Kalish, R. Triangular nanobeam photonic cavities in single crystal diamond. New J. Phys. 13, 025018 (2011).
Bayn, I. et al. Processing of photonic crystal nanocavity for quantum information in diamond. Diamond Relat. Mater. 20, 937–943 (2011).
Faraon, A., Barclay, P. E., Santori, C., Fu, K-M. C. & Beausoleil, R. G. Resonant enhancement of the zero-phonon emission from a colour centre in a diamond cavity. Nature Photon. 5, 301–305 (2011).
Gsell, S., Bauer, T., Goldfuß, J., Schreck, M. & Stritzker, B. A route to diamond wafers by epitaxial deposition on silicon via iridium/yttria-stabilized zirconia buffer layers. Appl. Phys. Lett. 84, 4541–4543 (2004).
Meijer, J. et al. Towards the implanting of ions and positioning of nanoparticles with nm spatial resolution. Appl. Phys. A 91, 567–571 (2008).
Quan, Q., Deotare, P. B. & Lončar, M. Photonic crystal nanobeam cavity strongly coupled to the feeding waveguide. Appl. Phys. Lett. 96, 203102 (2010).
Akahane, Y., Asano, T., Song, B-S. & Noda, S. High-Q photonic nanocavity in a two-dimensional photonic crystal. Nature 425, 944–947 (2003).
Kim, S-H. et al. Characteristics of a stick waveguide resonator in a two-dimensional photonic crystal slab. J. Appl. Phys. 95, 411–416 (2004).
Hennessy, K. et al. Tuning photonic crystal nanocavity modes by wet chemical digital etching. Appl. Phys. Lett. 87, 021108 (2005).
Osswald, S., Yushin, G., Mochalin, V., Kucheyev, S. O. & Gogotsi, Y. Control of sp2/sp3 carbon ratio and surface chemistry of nanodiamond powders by selective oxidation in air. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 128, 11635–11642 (2006).
Kippenberg, T. J. & Vahala, K. J. Cavity optomechanics: back-action at the mesoscale. Science 321, 1172–1176 (2008).
Eichenfield, M., Chan, J., Camacho, R. M., Vahala, K. J. & Painter, O. Optomechanical crystals. Nature 462, 78–82 (2009).
Prawer, S. & Greentree, A. D. Diamond for quantum computing. Science 320, 1601–1602 (2008).
Schreck, M., Hörmann, F., Roll, H., Lindner, J. K. N. & Stritzker, B. Diamond nucleation on iridium buffer layers and subsequent textured growth: a route for the realization of single-crystal diamond films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 78, 192–194 (2001).
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge helpful discussions with D. Englund. The authors also thank J. Schmauch for SEM and TEM analysis, C. Zeitz for atomic force microscopy measurements, F. Soldera for assistance with FIB milling, T. Jung for fabrication tolerance analysis, K. Kretsch for assistance with wet chemical etching, S. Griesing for sputtering of metal layers, and S. Grandthyll for ellipsometry measurements. This work was financially supported by the BMBF (network EPHQAM, contract no. 01Bl0903).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J.R-M. and L.K. fabricated the photonic crystals, performed the experiments and carried out the numerical modelling of the structures. M.F., S.G. and M.S. developed the CVD growth process for the diamond films on iridium buffer layers. A.B. and M.W. prepared the diamond membrane. J.R-M. and S.W. thinned the diamond film. C.P., J.R-M., L.K. and F.M. performed FIB milling. C.H. and E.N. contributed experimental tools and helped with the photoluminescence measurements and interpretation of data. C.B. conceived and designed the experiments. J.R-M. and C.B. wrote the manuscript. All authors discussed the results and commented on the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information
Supplementary information (PDF 3963 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Riedrich-Möller, J., Kipfstuhl, L., Hepp, C. et al. One- and two-dimensional photonic crystal microcavities in single crystal diamond. Nature Nanotech 7, 69–74 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2011.190
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2011.190
This article is cited by
-
Recent advances in room temperature single-photon emitters
Quantum Information Processing (2023)
-
Dissipative generation of steady-state entanglement of two separated SiV\(^{-}\) centers coupled to photonic crystal cavities
Quantum Information Processing (2020)
-
Quantum nanophotonics with group IV defects in diamond
Nature Communications (2019)
-
Material platforms for spin-based photonic quantum technologies
Nature Reviews Materials (2018)
-
Photonic crystal cavities from hexagonal boron nitride
Nature Communications (2018)