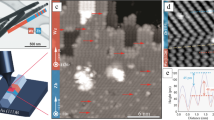
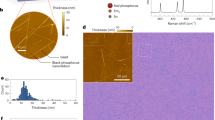
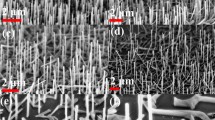
Abstract
Single-crystalline, one-dimensional semiconductor nanostructures are considered to be one of the critical building blocks for nanoscale optoelectronics1. Elucidation of the vapour–liquid–solid growth mechanism2 has already enabled precise control over nanowire position and size1,3,4,5,6,7,8, yet to date, no reports have demonstrated the ability to choose from different crystallographic growth directions of a nanowire array. Control over the nanowire growth direction is extremely desirable, in that anisotropic parameters such as thermal and electrical conductivity, index of refraction, piezoelectric polarization, and bandgap may be used to tune the physical properties of nanowires made from a given material. Here we demonstrate the use of metal–organic chemical vapour deposition (MOCVD) and appropriate substrate selection to control the crystallographic growth directions of high-density arrays of gallium nitride nanowires with distinct geometric and physical properties. Epitaxial growth of wurtzite gallium nitride on (100) γ-LiAlO2 and (111) MgO single-crystal substrates resulted in the selective growth of nanowires in the orthogonal [11̄0] and [001] directions, exhibiting triangular and hexagonal cross-sections and drastically different optical emission. The MOCVD process is entirely compatible with the current GaN thin-film technology, which would lead to easy scale-up and device integration.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Xia, Y. et al. One-dimensional nanostructures: Synthesis, characterization, and applications. Adv. Mater. 15, 353–389 (2003).
Wu, Y. & Yang, P. Direct observation of vapor-liquid-solid nanowire growth. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 123, 3165–3166 (2001).
Wu, Y., Yan, H. & Yang, P. Inorganic semiconductor nanowires: Rational growth, assembly, and novel properties. Chem. Eur. J. 8, 1261–1268 (2002).
Haraguchi, K. et al. Self-organized fabrication of planar GaAs nanowhisker arrays. Appl. Phys. Lett. 69, 386–387 (1996).
Han, S. et al. Controlled growth of gallium nitride single-crystal nanowires using a chemical vapor deposition method. J. Mater. Res. 18, 245–249 (2003).
Holmes, J.D. et al. Control of thickness and orientation of solution-grown silicon nanowires. Science 287, 1471–1473 (2000).
Ohlsson, B.J., Björk, M.T., Magnusson, M.H., Deppert, K. & Samuelson, L. Size-, shape-, and position-controlled GaAs nano-whiskers. Appl Phys. Lett. 79, 3335–3337 (2001).
Mårtensson, T. et al. Nanowire arrays defined by nanoimprint lithography. Nano Lett. 4, 699–702 (2004).
Johnson, J.C. et al. Single gallium nitride nanowire lasers. Nature Mater. 1, 106–109 (2002).
Goldberger, J. et al. Single-crystal gallium nitride nanotubes. Nature 422, 599–602 (2003).
Huang, Y., Duan, X., Cui, Y. & Lieber, C.M. Gallium nitride nanowire nanodevices. Nano Lett. 2, 101–104 (2002).
Choi, H. et al. Self-organized GaN quantum wire UV lasers. J. Phys. Chem. 107, 8721–8725 (2003).
Duan, X. & Lieber, C.M. Laser-assisted catalytic growth of single crystal GaN nanowires. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 122, 188–189 (2000).
Chen, C. et al. Catalytic growth and characterization of gallium nitride nanowires. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 123, 2791–2798 (2001).
Seo, H. et al. Strained gallium nitride nanowires. J. Chem. Phys. 116, 9492–9499 (2002).
Zhong, Z., Qian, F., Wang, D. & Lieber, C.M. Synthesis of p-type gallium nitride nanowires for electronic and photonic nanodevices. Nano Lett. 3, 343–345 (2003).
Kim, H., Kang, T. & Chung, K. Nanoscale ultraviolet-light-emitting diodes using wide-bandgap gallium nitride nanorods. Adv. Mater. 15, 567–569 (2003).
Ristic, J. et al. AlGaN nanocolumns grown by molecular beam epitaxy: optical and structural characterization. Phys. Status Solidi A 192, 60–66 (2002).
Ristic, J. et al. Characterization of GaN quantum discs embedded in AlxGa1-xN nanoclolumns grown by molecular beam epitaxy. Phys. Rev. B 68, 125305 (2003).
Stach, E., Pauzauskie, P., Kuykendall, T., Goldberger, J. & Yang, P. Watching GaN nanowires grow. Nano Lett. 3, 867–869 (2003).
Kuykendall, T., Pauzauskie, P., Lee, S.K., Zhang, Y. & Yang, P. Metalorganic chemical vapor deposition route to GaN nanowires with triangular cross sections. Nano Lett. 3, 1063–1066 (2003).
Huang, M. et al. Room-temperature ultraviolet nanowire nanolasers. Science 292, 1897–1899 (2001).
Park, W.I., Yi, G., Kim, M. & Pennucook, S. Quantum confinement observed in ZnO/ZnMgO nanorod heterojunctions. Adv. Mater. 15, 526–529 (2003).
Bir, G.L. & Pikus, G.E. Symmetry and Strain-induced Effects in Semiconductors (Wiley, New York, 1972).
Waltereit, P. et al. Nitride semiconductors free of electrostatic fields for efficient white light-emitting diodes. Nature 406, 865–868 (2000).
Domen, K., Horino, K., Kuramata, A. & Tanahashi, T. Analysis of polarization anisotropy along the c axis in the photoluminescence of wurtzite GaN. Appl. Phys. Lett. 71, 1996–1998 (1997).
Lawniczak-Jablonska, K. et al. Anisotropy of the nitrogen conduction states in the group III nitrides studied by polarized x-ray absorption spectroscopy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 70, 2711–2713, (1997).
Lawniczak-Jablonska, K. et al. Electronic states in valence and conduction bands of group-III nitrides: Experiment and theory. Phys. Rev. B 61, 16623–16632 (2000).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Camille and Henry Dreyfus Foundation, Beckman Foundation, the National Science Foundation (CAREER, NIRT) and Department of Energy. P. Y. is an Alfred P. Sloan Research Fellow. P. P. and J. G. thank the National Science Foundation for predoctoral fellowship support. Work at the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory was supported by the Office of Science, Basic Energy Sciences, Division of Materials Science of the US Department of Energy. We thank the National Center for Electron Microscopy for the use of their facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuykendall, T., Pauzauskie, P., Zhang, Y. et al. Crystallographic alignment of high-density gallium nitride nanowire arrays. Nature Mater 3, 524–528 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat1177
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat1177
This article is cited by
-
Low-dimensional wide-bandgap semiconductors for UV photodetectors
Nature Reviews Materials (2023)
-
Crystal orientation-dependent tensile mechanical behavior and deformation mechanisms of zinc-blende ZnSe nanowires
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Carrier Dynamics and Electro-Optical Characterization of High-Performance GaN/InGaN Core-Shell Nanowire Light-Emitting Diodes
Scientific Reports (2018)
-
Growth of magnetic nanowires along freely selectable 〈hkl〉 crystal directions
Nature Communications (2018)
-
A Tunable on-Chip Integrated Plasmonic Filter and Router Based on Metal/Dielectric Nanostructures
Plasmonics (2018)