Abstract
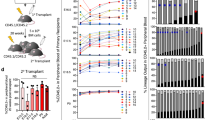
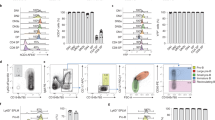
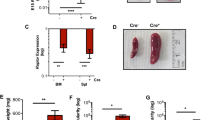
The mixed lineage leukemia (MLL) gene is disrupted by chromosomal translocations in acute leukemia, producing a fusion oncogene with altered properties relative to the wild-type gene. Murine loss-of-function studies have shown an essential role for Mll in developing the haematopoietic system, yet studies using different conditional knockout models have yielded conflicting results regarding the requirement for Mll during adult steady-state haematopoiesis. In this study, we used a loxP-flanked Mll allele (MllF) and a developmentally regulated, haematopoietic-specific VavCre transgene to reassess the consequences of Mll loss in the haematopoietic lineage, without the need for inducers of Cre recombinase. We show that VavCre;Mll mutants exhibit phenotypically normal fetal haematopoiesis, but rarely survive past 3 weeks of age. Surviving animals are anemic, thrombocytopenic and exhibit a significant reduction in bone marrow haematopoietic stem/progenitor populations, consistent with our previous findings using the inducible Mx1Cre transgene. Furthermore, the analysis of VavCre mutants revealed additional defects in B-lymphopoiesis that could not be assessed using Mx1Cre-mediated Mll deletion. Collectively, these data support the conclusion that Mll has an essential role in sustaining postnatal haematopoiesis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Behm FG, Raimondi SC, Frestedt JL, Liu Q, Crist WM, Downing JR et al. Rearrangement of the MLL gene confers a poor prognosis in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia, regardless of presenting age. Blood 1996; 87: 2870–2877.
Liedtke M, Cleary ML . Therapeutic targeting of MLL. Blood 2009; 113: 6061–6068.
Milne TA, Briggs SD, Brock HW, Martin ME, Gibbs D, Allis CD et al. MLL targets SET domain methyltransferase activity to Hox gene promoters. Mol Cell 2002; 10: 1107–1117.
Nakamura T, Mori T, Tada S, Krajewski W, Rozovskaia T, Wassell R et al. ALL-1 is a histone methyltransferase that assembles a supercomplex of proteins involved in transcriptional regulation. Mol Cell 2002; 10: 1119–1128.
Zeleznik-Le NJ, Harden AM, Rowley JD . 11q23 translocations split the ‘AT-hook’ cruciform DNA-binding region and the transcriptional repression domain from the activation domain of the mixed-lineage leukemia (MLL) gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1994; 91: 10610–10614.
Slany RK, Lavau C, Cleary ML . The oncogenic capacity of HRX-ENL requires the transcriptional transactivation activity of ENL and the DNA binding motifs of HRX. Mol Cell Biol 1998; 18: 122–129.
Ayton PM, Chen EH, Cleary ML . Binding to nonmethylated CpG DNA is essential for target recognition, transactivation, and myeloid transformation by an MLL oncoprotein. Mol Cell Biol 2004; 24: 10470–10478.
Yokoyama A, Cleary ML . Menin critically links MLL proteins with LEDGF on cancer-associated target genes. Cancer Cell 2008; 14: 36–46.
Bach C, Mueller D, Buhl S, Garcia-Cuellar MP, Slany RK . Alterations of the CxxC domain preclude oncogenic activation of mixed-lineage leukemia 2. Oncogene 2009; 28: 815–823.
Daser A, Rabbitts TH . Extending the repertoire of the mixed-lineage leukemia gene MLL in leukemogenesis. Genes Dev 2004; 18: 965–974.
Yu BD, Hess JL, Horning SE, Brown GA, Korsmeyer SJ . Altered Hox expression and segmental identity in Mll-mutant mice. Nature 1995; 378: 505–508.
Ayton P, Sneddon SF, Palmer DB, Rosewell IR, Owen MJ, Young B et al. Truncation of the Mll gene in exon 5 by gene targeting leads to early preimplantation lethality of homozygous embryos. Genesis 2001; 30: 201–212.
Ernst P, Fisher JK, Avery W, Wade S, Foy D, Korsmeyer SJ . Definitive hematopoiesis requires the mixed-lineage leukemia gene. Dev Cell 2004; 6: 437–443.
Terranova R, Agherbi H, Boned A, Meresse S, Djabali M . Histone and DNA methylation defects at Hox genes in mice expressing a SET domain-truncated form of Mll. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2006; 103: 6629–6634.
McMahon KA, Hiew SY, Hadjur S, Veiga-Fernandes H, Menzel U, Price AJ et al. Mll has a critical role in fetal and adult hematopoietic stem cell self-renewal. Cell Stem Cell 2007; 1: 338–345.
Jude CD, Climer L, Xu D, Artinger E, Fisher JK, Ernst P . Unique and independent roles for MLL in adult hematopoietic stem cells and progenitors. Cell Stem Cell 2007; 1: 324–337.
Yano T, Nakamura T, Blechman J, Sorio C, Dang CV, Geiger B et al. Nuclear punctate distribution of ALL-1 is conferred by distinct elements at the N terminus of the protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1997; 94: 7286–7291.
Kuhn R, Schwenk F, Aguet M, Rajewsky K . Inducible gene targeting in mice. Science 1995; 269: 1427–1429.
Jude CD, Gaudet JJ, Speck NA, Ernst P . Leukemia and hematopoietic stem cells: balancing proliferation and quiescence. Cell Cycle 2008; 7: 586–591.
Baron ML, Gauchat D, La Motte-Mohs R, Kettaf N, Abdallah A, Michiels T et al. TLR ligand-induced type I IFNs affect thymopoiesis. J Immunol 2008; 180: 7134–7146.
Demoulins T, Abdallah A, Kettaf N, Baron ML, Gerarduzzi C, Gauchat D et al. Reversible blockade of thymic output: an inherent part of TLR ligand-mediated immune response. J Immunol 2008; 181: 6757–6769.
Despres D, Goldschmitt J, Aulitzky WE, Huber C, Peschel C . Differential effect of type I interferons on hematopoietic progenitor cells: failure of interferons to inhibit IL-3-stimulated normal and CML myeloid progenitors. Exp Hematol 1995; 23: 1431–1438.
Mizutani T, Tsuji K, Ebihara Y, Taki S, Ohba Y, Taniguchi T et al. Homeostatic erythropoiesis by the transcription factor IRF2 through attenuation of type I interferon signaling. Exp Hematol 2008; 36: 255–264.
Essers MA, Offner S, Blanco-Bose WE, Waibler Z, Kalinke U, Duchosal MA et al. IFNalpha activates dormant haematopoietic stem cells in vivo. Nature 2009; 458: 904–908.
Sato T, Onai N, Yoshihara H, Arai F, Suda T, Ohteki T . Interferon regulatory factor-2 protects quiescent hematopoietic stem cells from type I interferon-dependent exhaustion. Nat Med 2009; 15: 696–700.
Ogilvy S, Metcalf D, Gibson L, Bath ML, Harris AW, Adams JM . Promoter elements of vav drive transgene expression in vivo throughout the hematopoietic compartment. Blood 1999; 94: 1855–1863.
de Boer J, Williams A, Skavdis G, Harker N, Coles M, Tolaini M et al. Transgenic mice with hematopoietic and lymphoid specific expression of Cre. Eur J Immunol 2003; 33: 314–325.
Georgiades P, Ogilvy S, Duval H, Licence DR, Charnock-Jones DS, Smith SK et al. VavCre transgenic mice: a tool for mutagenesis in hematopoietic and endothelial lineages. Genesis 2002; 34: 251–256.
Stadtfeld M, Graf T . Assessing the role of hematopoietic plasticity for endothelial and hepatocyte development by non-invasive lineage tracing. Development 2005; 132: 203–213.
Yagi H, Deguchi K, Aono A, Tani Y, Kishimoto T, Komori T . Growth disturbance in fetal liver hematopoiesis of Mll-mutant mice. Blood 1998; 92: 108–117.
Kim I, He S, Yilmaz OH, Kiel MJ, Morrison SJ . Enhanced purification of fetal liver hematopoietic stem cells using SLAM family receptors. Blood 2006; 108: 737–744.
Bhandoola A, Sambandam A . From stem cell to T cell: one route or many? Nat Rev Immunol 2006; 6: 117–126.
Chen MJ, Yokomizo T, Zeigler BM, Dzierzak E, Speck NA . Runx1 is required for the endothelial to haematopoietic cell transition but not thereafter. Nature 2009; 457: 887–891.
Abshire TC, Buchanan GR, Jackson JF, Shuster JJ, Brock B, Head D et al. Morphologic, immunologic and cytogenetic studies in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia at diagnosis and relapse: a Pediatric Oncology Group study. Leukemia 1992; 6: 357–362.
Huret JL, Brizard A, Slater R, Charrin C, Bertheas MF, Guilhot F et al. Cytogenetic heterogeneity in t(11;19) acute leukemia: clinical, hematological and cytogenetic analyses of 48 patients--updated published cases and 16 new observations. Leukemia 1993; 7: 152–160.
Pui CH, Chessells JM, Camitta B, Baruchel A, Biondi A, Boyett JM et al. Clinical heterogeneity in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia with 11q23 rearrangements. Leukemia 2003; 17: 700–706.
Acknowledgements
We thank our laboratory members, David Traver and Christopher Dant for insightful comments and suggestions, Dr Roderick Bronson, Dr Benjamin Lee and Dr Glen Raffel for histolology advice, and Dr Hanna Mikkola, Dr Matthias Stadtfeld and Dr Thomas Graf for VavCre mice and advice for breeding and analyzing this strain. We are grateful to Nancy Speck for advice and use of her microscopes. This work was supported by the NIH grant HL090036 to PE and NCRR COBRE grant P20RR016437 to William Green.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Leukemia website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gan, T., Jude, C., Zaffuto, K. et al. Developmentally induced Mll1 loss reveals defects in postnatal haematopoiesis. Leukemia 24, 1732–1741 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2010.171
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2010.171
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Wdr5 is essential for fetal erythropoiesis and hematopoiesis
Experimental Hematology & Oncology (2023)
-
Structure, function and inhibition of critical protein–protein interactions involving mixed lineage leukemia 1 and its fusion oncoproteins
Journal of Hematology & Oncology (2021)
-
Hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell proliferation and differentiation requires the trithorax protein Ash2l
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
CEBPA-mutated leukemia is sensitive to genetic and pharmacological targeting of the MLL1 complex
Leukemia (2019)
-
Why are so many MLL lysine methyltransferases required for normal mammalian development?
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2019)