Abstract
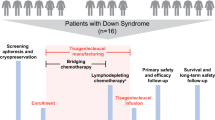
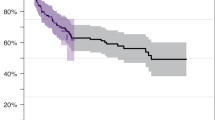
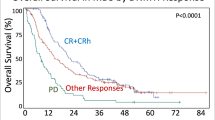
Despite improved prognosis in acute myelogenous leukaemia (AML) children with Down syndrome (DS), therapy-related toxicity remained a problem. We compared 67 DS patients from study AML-BFM 98 with 51 DS patients of the previous study AML-BFM 93, and the non-DS groups of both studies. Compared to non-DS patients, DS patients were treated with reduced anthracycline doses, without high-dose cytarabine/mitoxantrone and without cranial irradiation. AML-DS patients were in median 1.8 years old, and 102/118 (86%) showed the typical morphology of acute megakaryoblastic leukaemia. In study 93, seven DS patients did not receive AML-specific chemotherapy, and treatment modifications were more common. Results improved significantly for patients treated in study 98 with a 3-year survival of 91±4 vs 70±7% in study 93 (P=0.001). There were no differences in outcome concerning the age groups 0–⩽2 and 2–⩽4 years (event-free survival for treated patients 0–⩽2 years 83±4%, 2–⩽4 years 81±7%). The cumulative incidence of relapses was significantly lower in DS (7±3%) than in non-DS patients (28±7%). Therapy-related toxicity was generally lower in DS patients treated according to study 98. We conclude that a standardised and dose-reduced treatment schedule including the main components of AML treatment is advisable for AML children with DS.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Creutzig U, Ritter J, Vormoor J, Eschenbach C, Dickerhoff R, Burdach S et al. Transiente Myeloproliferation und akute myeloische Leukämie bei Säuglingen mit Morbus Down. Klin Pädiatr 1990; 202: 253–257.
Robison LL, Nesbit MEJ, Sather HN, Level C, Shahidi N, Kennedy A et al. Down syndrome and acute leukemia in children: a 10-year retrospective survey from Childrens Cancer Study Group. J Pediatr 1984; 105: 235–242.
Kojima S, Matsuyama T, Sato T, Horibe K, Konishi S, Tsuchida M, Okamura J et al. Down's syndrome and acute leukemia in children: an analysis of phenotype by use of monoclonal antibodies and electron microscopic platelet peroxidase reaction. Blood 1990; 76: 2348–2353.
Zipursky A, Thorner P, De Harven E, Christensen H, Doyle J . Myelodysplasia and acute megakaryoblastic leukemia in Down's syndrome. Leukemia Res 1994; 18: 163–171.
Zipursky A, Peeters M, Poon A . Megakaryoblastic leukemia and Down's syndrome: a review. Pediatr Hematol Oncol 1987; 4: 211–230.
Ravindranath Y, Abella E, Krischer JP, Wiley J, Inoue S, Harris M et al. Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) in Down's syndrome is highly responsive to chemotherapy: experience on Pediatric Oncology Group AML Study 8498. Blood 1992; 80: 2210–2214.
Creutzig U, Ritter J, Vormoor J, Ludwig WD, Niemeyer C, Reinisch I et al. Myelodysplasia and acute myelogenous leukemia in Down's syndrome. A report of 40 children of the AML-BFM Study Group. Leukemia 1996; 10: 1677–1686.
Bennett JM, Catovsky D, Daniel MT, Flandrin G, Galton DAG, Gralnick HR et al. Proposals for the classification of the myelodysplastic syndromes. Br J Haematol 1982; 51: 189–199.
Bennett JM, Catovsky D, Daniel MT, Flandrin G, Galton DAG, Gralnick HR et al. Criteria for the diagnosis of acute leukemia of megakaryocyte lineage (M7). A report of the French–American–British Cooperative Group. Ann Intern Med 1985; 103: 460–462.
Bennett JM, Catovsky D, Daniel MT, Flandrin G, Galton DAG, Gralnick HR et al. Proposed revised criteria for the classification of acute myeloid leukemia. Ann Intern Med 1985; 103: 626–629.
Creutzig U, Sperling CH, Harbott J, Ritter J, Zimmermann M, Löffler H et al. Clinical significance of surface antigen expression in children with acute myeloid leukemia: results of Study AML-BFM-87. Blood 1995; 86: 3097–3108.
Creutzig U, Ritter J, Zimmermann M, Reinhardt D, Hermann J, Berthold F et al. Improved treatment results in high-risk pediatric acute myeloid leukemia patients after intensification with high-dose cytarabine and mitoxantrone: results of Study Acute Myeloid Leukemia – Berlin–Frankfurt–Munster 93. J Clin Oncol 2001; 19: 2705–2713.
Craze JL, Harrison G, Wheatly K, Hann IM, Chessells JM . Improved outcome of acute myeloid leukaemia in Down's syndrome. Arch Dis Child 1999; 81: 32–37.
Kojima S, Kato K, Matsuyama T, Yoshikawa T, Horibe K . Favorable treatment outcome in children with acute myeloid leukemia and Down syndrome. Blood 1993; 81: 3164.
Lange BJ, Kobrinsky N, Barnard DR, Arthur DC, Buckley JD, Howells WB et al. Distinctive demography, biology, and outcome of acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome in children with Down syndrome: Children's Cancer Group Studies 2861 and 2891. Blood 1998; 91: 608–615.
Creutzig U, Ritter J, Niemeyer C, Reinisch I, Stollmann-Gibbels B, Zimmermann M et al. Akute myeloische Leukämie bei Kindern mit Down-Syndrom. Klin Pädiatr 1995; 207: 136–144.
Zubizarreta P, Felice MS, Alfaro E, Fraquelli L, Casak S, Quinteros R et al. Acute myelogenous leukemia in Down's syndrome: report of a single pediatric institution using a BFM treatment strategy. Leukemia Res 1998; 22: 465–472.
Lie SO, Jonmundsson G, Mellander L, Siimes MA, Yssing M, Gustafsson G . A population-based study of 272 children with acute myeloid leukaemia treated on two consecutive protocols with different intensity: best outcome in girls, infants, and children with Down's syndrome. Nordic Society of Paediatric Haematology and Oncology (NOPHO). Br J Haematol 1996; 94: 82–88.
Ravindranath Y . Down syndrome and leukemia: new insights into the epidemiology, pathogenesis, and treatment. Pediatr Blood Cancer 2005; 44: 1–7.
Frost BM, Gustafsson G, Larsson R, Nygren P, Lonnerholm G . Cellular cytotoxic drug sensitivity in children with acute leukemia and Down's syndrome: an explanation to differences in clinical outcome? Leukemia 2000; 14: 943–944.
Taub JW, Matherly LH, Stout ML, Buck SA, Gurney JG, Ravindranath Y . Enhanced metabolism of 1-beta-D-arabinofuranosylcytosine in Down syndrome cells: a contributing factor to the superior event free survival of Down syndrome children with acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 1996; 87: 3395–3403.
Taub JW, Stout ML, Buck SA, Huang X, Vega RA, Becton DL et al. Myeloblasts from Down syndrome children with acute myeloid leukemia have increased in vitro sensitivity to cytosine arabinoside and daunorubicin. Leukemia 1997; 11: 1594–1595.
Zwaan CM, Kaspers GJ, Pieters R, Hahlen K, Janka-Schaub GE, Van Zantwijk CH et al. Different drug sensitivity profiles of acute myeloid and lymphoblastic leukemia and normal peripheral blood mononuclear cells in children with and without Down syndrome. Blood 2002; 99: 245–251.
Athale UH, Razzouk BI, Raimondi SC, Tong X, Behm FG, Head DR et al. Biology and outcome of childhood acute megakaryoblastic leukemia: a single institution's experience. Blood 2001; 97: 3727–3732.
Gamis AS, Woods WG, Alonzo TA, Buxton A, Lange B, Barnard DR et al. Increased age at diagnosis has a significantly negative effect on outcome in children with Down syndrome and acute myeloid leukemia: a report from the Children's Cancer Group Study 2891. J Clin Oncol 2003; 21: 3415–3422.
Zeller B, Gustafsson G, Forestier E, Abrahamsson J, Clausen N, Heldrup J et al. Acute leukaemia in children with Down syndrome: a population-based Nordic Study. Br J Haematol 2005; 128: 797–804.
Ravindranath Y . Down syndrome and acute myeloid leukemia: the paradox of increased risk for leukemia and heightened sensitivity to chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol 2003; 21: 3385–3387.
Lipshultz SE, Colan SD, Gelber RD, Perez-Atayde AR, Sallan S, Sanders SP . Late cardiac effects of doxorubicin therapy for acute lymphoblastic leukemia in childhood. N Engl J Med 1991; 324: 808–815.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by the Deutsche Krebshilfe
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Information (‘Acknowledgements’) accompanies the paper on the Leukemia website (http://www.nature.com/leu).
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Creutzig, U., Reinhardt, D., Diekamp, S. et al. AML patients with Down syndrome have a high cure rate with AML-BFM therapy with reduced dose intensity. Leukemia 19, 1355–1360 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2403814
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2403814
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Clinical and biological aspects of myeloid leukemia in Down syndrome
Leukemia (2021)
-
The genomics of acute myeloid leukemia in children
Cancer and Metastasis Reviews (2020)
-
Down syndrome associated childhood myeloid leukemia with yet unreported acquired chromosomal abnormalities and a new potential adverse marker: dup(1)(q25q44)
Molecular Cytogenetics (2018)
-
AMKL chimeric transcription factors are potent inducers of leukemia
Leukemia (2017)
-
Pediatric non–Down syndrome acute megakaryoblastic leukemia is characterized by distinct genomic subsets with varying outcomes
Nature Genetics (2017)