Abstract
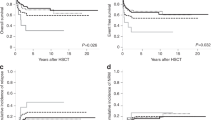
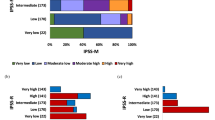
The International Prognostic Scoring System (IPSS) for myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) is based upon weighted data on bone marrow (BM) blast percentage, cytopenia, and cytogenetics, separating patients into four prognostic groups. We analyzed the value of the IPSS in 142 children with de novo MDS and 166 children with juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia (JMML) enrolled in retro- and prospective studies of the European Working Group on childhood MDS (EWOG-MDS). Survivals in MDS and JMML were analyzed separately. Among the criteria considered by the IPSS score, only BM blasts <5% and platelets >100 × 109/l were significantly associated with a superior survival in MDS. In JMML, better survival was associated with platelets >40 × 109/l, but not with any other IPSS factors including cytogenetics. In conclusion, the IPSS is of limited value in both pediatric MDS and JMML. The results reflect the differences between myelodysplastic and myeloproliferative diseases in children and adults.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Passmore SJ, Hann IM, Stiller CA, Ramani P, Swansbury GJ, Gibbons B et al. Pediatric myelodysplasia: a study of 68 children and a new prognostic scoring system. Blood 1995; 85: 1742–1750.
Hasle H, Kerndrup G, Jacobsen BB . Childhood myelodysplastic syndrome in Denmark: incidence and predisposing conditions. Leukemia 1995; 9: 1569–1572.
Bader-Meunier B, Mielot F, Tchernia G, Buisine J, Delsol G, Duchayne E et al. Myelodysplastic syndrome in childhood: report of 49 patients from a French multicenter study. Br J Haematol 1996; 92: 344–350.
Luna-Fineman S, Shannon KM, Atwater SK, Davis J, Masterson M, Ortega J et al. Myelodysplastic and myeloproliferative disorders of childhood: a study of 167 patients. Blood 1999; 93: 459–466.
Hasle H, Wadsworth LD, Massing BG, McBride M, Schultz KR . A population-based study of childhood myelodysplastic syndrome in British Columbia, Canada. Br J Haematol 1999; 106: 1027–1032.
Sasaki H, Manabe A, Kojima S, Tsuchida M, Hayashi Y, Ikuta K et al. Myelodysplastic syndrome in childhood: a retrospective study of 189 patients in Japan. Leukemia 2001; 15: 1713–1720.
Passmore SJ, Chessells JM, Kempski H, Hann IM, Brownbill PA, Stiller CA . Paediatric MDS and JMML in the UK: a population based study of incidence and survival. Br J Haematol 2003; 121: 758–767.
Anderson JE, Appelbaum FR, Schoch G, Gooley T, Anasetti C, Bensinger WI et al. Allogeneic marrow transplantation for refractory anemia: a comparison of two preparative regimens and analysis of prognostic factors. Blood 1996; 87: 51–58.
Kardos G, Baumann I, Passmore SJ, Locatelli F, Hasle H, Schultz KR et al. Refractory anemia in childhood: a retrospective analysis of 67 patients with particular reference to monosomy 7. Blood 2003; 102: 1997–2003.
Castro-Malaspina H, Schaison G, Passe S, Pasquier A, Berger R, Bayle-Weisgerber C et al. Subacute and chronic myelomonocytic leukemia in children (juvenile CML). Clinical and hematologic observations, and identification of prognostic factors. Cancer 1984; 54: 675–686.
Owen G, Lewis IJ, Morgan M, Robinson A, Stevens RF . Prognostic factors in juvenile chronic granulocytic leukaemia. Br J Cancer Suppl 1992; 18: S68–S71.
Niemeyer CM, Aricò M, Basso G, Cantù-Rajnoldi A, Creutzig U, Haas OA, et al., Members of the European Working Group on Myelodysplastic Syndromes in Childhood (EWOG-MDS). Chronic myelomonocytic leukemia in childhood: a retrospective analysis of 110 cases. Blood 1997; 89: 3534–3543.
Greenberg P, Cox C, Le Beau MM, Fenaux P, Morel P, Sanz G et al. International scoring system for evaluating prognosis in myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood 1997; 89: 2079–2088.
Hasle H, Niemeyer CM, Chessells JM, Baumann I, Bennett JM, Kerndrup G et al. A pediatric approach to the WHO classification of myelodysplastic and myeloproliferative diseases. Leukemia 2003; 17: 277–282.
Hasle H, Aricò M, Basso G, Biondi A, Cantù-Rajnoldi A, Creutzig U et al. Myelodysplastic syndrome, juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia, and acute myeloid leukemia associated with complete or partial monosomy 7. Leukemia 1999; 13: 376–385.
Kaplan EL, Meier P . Nonparametric estimation from incomplete observations. J Am Stat Assoc 1958; 53: 457–481.
Cox DR . Regression models and life tables. J R Stat Soc B 1972; 34: 187–220.
Hosmer DW, Lemeshow S . Applied Survival Analysis. Regression Modeling of Time to Event Data. New York: Wiley, 1999.
Chang KL, O'Donnell MR, Slovak ML, Dagis AC, Arber DA, Niland JC et al. Primary myelodysplasia occurring in adults under 50 years old: a clinicopathologic study of 52 patients. Leukemia 2002; 16: 623–631.
Woods WG, Barnard DR, Alonzo TA, Buckley JD, Kobrinsky N, Arthur DC et al. Prospective study of 90 children requiring treatment for juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia or myelodysplastic syndrome: a report from the Children's Cancer Group. J Clin Oncol 2002; 20: 434–440.
Nevill TJ, Fung HC, Shepherd JD, Horsman DE, Nantel SH, Klingemann HG et al. Cytogenetic abnormalities in primary myelodysplastic syndrome are highly predictive of outcome after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Blood 1998; 92: 1910–1917.
Manabe A, Okamura J, Yumura-Yagi K, Akiyama Y, Sako M, Uchiyama H et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for 27 children with juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia diagnosed based on the criteria of the International JMML Working Group. Leukemia 2002; 16: 645–649.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by grants from the Danish Childhood Cancer Foundation (Børnecancerfonden), the German José Carreras Leukemia Foundation, and the German BMBF Competence Network Pediatric Oncology (Project E: Preleukemic Bone Marrow Disorders).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hasle, H., Baumann, I., Bergsträsser, E. et al. The International Prognostic Scoring System (IPSS) for childhood myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) and juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia (JMML). Leukemia 18, 2008–2014 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2403489
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2403489
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Improved outcomes of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation including haploidentical transplantation for childhood myelodysplastic syndrome
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2020)
-
Cytogenetics and clinical features of pediatric myelodysplastic syndrome in Japan
International Journal of Hematology (2014)
-
Diagnosis of acquired aplastic anemia
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2013)
-
Analysis of risk factors influencing outcome in children with myelodysplastic syndrome after unrelated cord blood transplantation
Leukemia (2011)
-
Highly skewed T-cell receptor V-beta chain repertoire in the bone marrow is associated with response to immunosuppressive drug therapy in children with very severe aplastic anemia
Blood Cancer Journal (2011)