Abstract
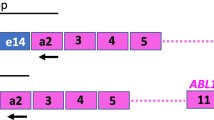
We took advantage of a recently developed system allowing performance of real-time quantitation of polymerase chain reaction to develop a quantitative method of measurement of PML-RARα transcripts which are hallmarks of acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) with t(15;17) translocation. Indeed, although quantitation of minimal residual disease has proved to be useful in predicting clinical outcome in other leukemias such as chronic myeloid leukemia or acute lymphoblastic leukemia, no quantitative data have been provided in the case of APL. We present here a method for quantitation of the most frequent subtypes of t(15;17) transcripts (namely bcr1 and bcr3). One specific forward primer is used for each subtype in order to keep amplicon length under 200 bp. The expression of PML-RARα transcripts is normalized using the housekeeping porphobilinogen deaminase (PBGD) gene. This technique allows detection of 10 copies of PML-RARα or PBGD plasmids, and quantitation was efficient up to 100 copies. One t(15;17)-positive NB4 cell could be detected among 106 HL60 cells, although quantitation was efficient up to one cell among 105. Repeatability and reproducibility of the method were satisfying as intra- and inter-assay variation coefficients were not higher than 15%. The efficiency of the method was finally tested in patient samples, showing a decrease of the PML-RARα copy number during therapy, and an increase at the time of relapse.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
De The H, Chomienne C, Lanotte M, Degos L, Dejean A . The t(15;17) translocation of acute promyelocytic leukaemia fuses the retinoic acid receptor alpha gene to a novel transcribed locus Nature 1990 347: 558–561
Pandolfi PP, Alcalay M, Fagioli M, Zangrilli D, Mencarelli A, Diverio D, Biondi A, Lo Coco F, Rambaldi A, Grignani F, Rochette-Egly C, Gaube MP, Chambon P, Pelicci PG . Genomic variability and alternative splicing generate multiple PML-RARα transcripts that encode aberrant PML proteins and PML-RARα isoforms in acute promyelocytic leukemia EMBO J 1992 11: 1397–1407
Geng JP, Tong JH, Dong S, Wang ZY, Chen SJ, Chen Z, Zelent A, Berger R, Larsen CJ . Localization of the chromosome 15 breakpoints and expression of multiple PML-RARa transcripts in acute promyelocytic leukemia: a study of 28 Chinese patients Leukemia 1996 7: 20–26
Fenaux P, Chastang C, Chevret S, Sanz M, Dombret H, Archimbaud E, Fey M, Rayon C, Huguet F, Sotto JJ, Cony Makhoul P, Travade P, Solary E, Fegueux N, Bordessoule D, San Miguel J, Link H, Desablens B, Stamatoulas A, Deconinck E, Maloisel F, Castaigne S, Preudhomme C, Degos L, European APL group . A randomized comparison of all trans retinoic acid followed by chemotherapy and ATRA plus chemotherapy, and the role of maintenance therapy in newly diagnosed acute promyelocytic leukemia Blood 1999 94: 1192–1200
Cave H, Van der Werff ten Bosch J, Suciu S, Guidal C, Waterkeyn C, Otten J, Bakkus M, Thielemans K, Grandchamp B, Vilmer E . Clinical significance of minimal residual disease in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia New Engl J Med 1998 339: 591–598
Lin F, van Rhee F, Goldman JM, Cross NCP . Kinetics of increasing Bcr-Abl transcripts numbers in chronic myeloid leukemia patients who relapse after bone marrow transplantation Blood 1996 87: 4473–4478
Seale JRC, Varma S, Swirsky DM, Pandolfi PP, Goldman JM, Cross NCP . Quantification of PML-RARα transcripts in acute promyelocytic leukemia: explanation for the lack of sensitivity of RT-PCR for the detection of minimal residual disease and induction of the leukaemia-specific mRNA by alpha interferon Br J Haematol 1996 95: 95–101
Gibson UEM, Heid CA, Williams PM . A novel method for real time quantitative RT-PCR Genome Res 1996 6: 995–1001
Mensink E, van de Locht A, Schattenberg A, Linders E, Schaap N, Geurts van Kessel A, de Witte T . Quantitation of minimal residual disease in Philadelphia chromosome positive chronic myeloid leukaemia patients using real-time quantitative RT-PCR Br J Haematol 1998 102: 768–774
Marcucci G, Livak KJ, Bi W, Strout MP, Bloomfield CD, Caliguri MA . Detection of minimal residual disease in patients with AML1/ETO-associated acute myeloid leukemia using a novel quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction assay Leukemia 1998 12: 1482–1489
Pongers-Willemse MJ, Verhagen OJHM, Tibbe GJM, Wijkhuijs AJM, de Haas V, Roovers E, van der Schoot CE, van Dongen JJM . Real-time quantitative PCR for the detection of minimal residual disease in acute lymphoblastic leukemia using junctional region specific TaqMan probes Leukemia 1998 12: 2006–2014
Castaigne S, Balitrand N, de The H, Dejean A, Degos L, Chomienne C . A PML/retinoic acid receptor alpha fusion transcript is constantly detected by RNA-based polymerase chain reaction in acute promyelocytic leukemia Blood 1992 79: 3110–3115
Holland PM, Abramson RD, Watson R, Gelfand GH . Detection of specific polymerase chain reaction products by utilizing the 5′ to 3′ exonuclease activity of Thermus aquaticus DNA polymerase Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1991 88: 7276–7280
Heid CA, Stevens J, Livak KJ, Williams PM . Real time quantitative PCR Genome Res 1996 6: 986–994
Chretien S, Dubart A, Beaupain D, Raich N, Grandchamp B, Rosa J, Goosens M, Romeo PH . Alternative transcription and splicing of the human porphobilinogen deaminase gene result either in tissue-specific or in housekeeping expression Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1988 85: 6–10
Fincke J, Fritzen R, Ternes P, Lange W, Dolken G . An improved strategy and a useful housekeeping gene for RNA analysis from formalin-embedded tissues by PCR Biotechniques 1993 14: 448–453
Lee LG, Connell CR, Bloch W . Allelic discrimination by nick-translation PCR with fluorogenic probes Nucleic Acids Res 1993 21: 3761–3766
Fink L, Seeger W, Ermert L, Hanze J, Stahl U, Grimminger F, Kummer W, Bohle RM . Real-time quantitative RT-PCR after laser-assisted cell picking Nature Med 1998 4: 1329–1333
Lo Coco F, Diverio D, Pandolfi PP, Biondi A, Rossi V, Avvisati G, Rambaldi A, Arcese W, Petti MC, Meloni G, Mandeli F, Grignani F, Macera G, Barbui T, Pelicci PG . Molecular evaluation of residual disease as a predictor of relapse in acute promyelocytic leukemia Lancet 1992 340: 1437–1438
Miller WH, Kakizuka A, Frankel SR, Warrel RP, DeBlasio A, Levine K, Evans RM, Dmitrovsky E . Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction for the rearranged retinoic acid receptor alpha clarifies diagnosis and detects minimal residual disease in acute promyelocytic leukemia Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1992 89: 2694–2698
Grimwade D, Howe K, Langabeer S, Burnett S, Goldstone A, Solomon E . Minimal residual disease detection in acute promyelocytic leukemia by reverse-transcriptase PCR: evaluation of PML-RAR alpha and RAR alpha-PML assessment in patients who ultimately relapse Leukemia 1996 10: 61–66
Chomienne C . RT-PCR in acute promyelocytic leukemia: second workshop of the European Retinoic Group Leukemia 1996 10: 368–371
Bolufer P, Barragan E, Sanz MA, Martin G, Bornstein R, Colomer D, Delgado MD, Gonzalez M, Marugan I, Roman J, Gomez MT, Anguita E, Diverio D, Chomienne C, Briz M . Preliminary experience in external quality control of RT-PCR PML-RAR alpha detection in promyelocytic leukemia Leukemia 1998 12: 2024–2028
Gerard CJ, Olsson K, Ramanathan R, Reading C, Hanania EG . Improved quantitation of minimal residual disease in multiple myeloma using real-time polymerase chain reaction and plasmid-DNA complementarity determining in region III standards Cancer Res 1998 58: 3957–3964
Henry JM, Sykes PJ, Brisco MJ, To LB, Juttner CA . Comparison of myeloma cell contamination of bone marrow and peripheral blood stem cell harvests Br J Haematol 1996 92: 614–619
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Ligue Contre le Cancer des Hauts de Seine and the Association pour la Recherche contre le Cancer.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cassinat, B., Zassadowski, F., Balitrand, N. et al. Quantitation of minimal residual disease in acute promyelocytic leukemia patients with t(15;17) translocation using real-time RT-PCR. Leukemia 14, 324–328 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2401652
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2401652
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Acute promyelocytic leukemia derived extracellular vesicles conserve PML-RARα transcript from storage-inflicted degradation: a stable diagnosis tool in APL patients
Annals of Hematology (2021)
-
Clinical implications of molecular genetic aberrations in acute myeloid leukemia
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology (2009)
-
Traitement des leucémies aiguës promyélocytaires de l’adulte
Oncologie (2008)
-
Epigenetic patterns of the retinoic acid receptor β2 promoter in retinoic acid-resistant thyroid cancer cells
Oncogene (2007)
-
Practical evaluation of universal conditions for four-plex quantitative PCR
Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry (2007)