Abstract
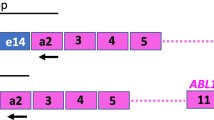
Quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (Q-RT-PCR) assessing the amount of transcripts of the BCR/ABL gene, the molecular marker of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), is the only method sensitive enough for monitoring of minimal residual disease (MRD) in CML patients after bone marrow transplantation (BMT). In this study we present a simple modification of competitive Q-RT-PCR using natural competitors from cell lines K562 and BV173. The competitors were used in the form of unpurified RNA in cell lysates which ensured their high stability. Mixing competitors and samples before RNA extraction eliminated problems with quantification of cDNA or RNA entering the competitive reaction and with checking for the RNA quality and reverse transcription (RT) efficiency. The bulk of the malignant clone was expressed as the number of leukemic cells in 106 leukocytes when the overproduction of the BCR/ABL mRNA in the cell lines we used as competitors was taken into account. It was found to be 82-fold and 14-fold in K562 and BV173, respectively, in comparison with 100% Ph-positive CML standard. The assay reliability was verified by comparison of results with the mathematical model of competitive PCR. The assay is highly reproducible and sensitive (10−5). Its accuracy was proved to be excellent in a wide range of malignant cell concentrations. The method is demonstrated on three CML patients suffering from MRD after BMT. In conclusion, this method fulfills all criteria of competitive Q-RT-PCR. Because of its simplicity it is suitable for clinical laboratories and due to the high stability of the lysates used it may serve in the standardization of results between different laboratories.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moravcová, J., Lukášová, M., Starý, J. et al. Simple competitive two-step RT-PCR assay to monitor minimal residual disease in CML patients after bone marrow transplantation. Leukemia 12, 1303–1312 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2401079
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2401079
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
t(5;6;12) associated with resistance to imatinib mesylate in chronic myeloid leukemia
International Journal of Hematology (2009)
-
Do transcriptionally silent BCR-ABL cells persist in CML patients in molecular remission after stem cell transplantation?
Leukemia (2001)