Abstract
Background:
Tissue factor (TF) is the main in vivo initiator of the blood coagulation cascade. Active circulating TF was detected on small, negatively charged membrane vesicles, the so-called microvesicles (MVs), which are released upon cell activation and apoptosis from a variety of cells. Increased coagulation activation was found in morbidly obese patients, and elevated levels of TF-bearing MVs may contribute to the prothrombotic state in these patients.
Aim:
To determine MV-associated TF activity levels in morbidly obese patients before and after weight loss due to bariatric surgery.
Methods:
MV-TF activity was measured with a factor Xa generation assay in morbidly obese patients before and 2 years after bariatric surgery. In addition, clinical parameters were determined.
Results:
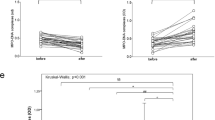
Seventy-four morbidly obese patients (mean age: 42 (±11) years; 61 females) were included in this study. After bariatric surgery, the body mass index decreased from (median, 25–75th percentile) 45.5 (42.3–50.2) to 30.5 (28.0–34.4 kg m−2; P<0.001), and a significant improvement in metabolic parameters was observed. Preoperative MV-TF activity correlated with C-reactive protein levels (r=0.3; P=0.02). Postoperatively, the mean MV-TF activity decreased significantly from 0.20 pg ml−1 (0.18–0.47) to 0.02 (0.00–0.28; P<0.01).
Conclusion:
We could demonstrate a significant decrease in MV-TF activity after weight loss in morbidly obese patients. Decreased MV-TF activity might contribute to an improved coagulation profile in these patients after weight loss.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams KF, Schatzkin A, Harris TB, Kipnis V, Mouw T, Ballard-Barbash R et al. Overweight, obesity, and mortality in a large prospective cohort of persons 50 to 71 years old. N Engl J Med 2006; 355: 763–778.
Goldhaber SZ, Savage DD, Garrison RJ, Castelli WP, Kannel WB, McNamara PM et al. Risk factors for pulmonary embolism. The Framingham Study. Am J Med 1983; 74: 1023–1028.
Stevens J, Cai J, Pamuk ER, Williamson DF, Thun MJ, Wood JL . The effect of age on the association between body-mass index and mortality. N Engl J Med 1998; 338: 1–7.
Calle EE, Thun MJ, Petrelli JM, Rodriguez C, Heath CW Jr . Body-mass index and mortality in a prospective cohort of US adults. N Engl J Med 1999; 341: 1097–1105.
Pontiroli AE, Folli F, Paganelli M, Micheletto G, Pizzocri P, Vedani P et al. Laparoscopic gastric banding prevents type 2 diabetes and arterial hypertension and induces their remission in morbid obesity: a 4-year case-controlled study. Diabetes Care 2005; 28: 2703–2709.
Kopp HP, Kopp CW, Festa A, Krzyzanowska K, Kriwanek S, Minar E et al. Impact of weight loss on inflammatory proteins and their association with the insulin resistance syndrome in morbidly obese patients. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2003; 23: 1042–1047.
Sjostrom L, Narbro K, Sjostrom CD, Karason K, Larsson B, Wedel H et al. Effects of bariatric surgery on mortality in Swedish obese subjects. N Engl J Med 2007; 357: 741–752.
Darvall KA, Sam RC, Silverman SH, Bradbury AW, Adam DJ . Obesity and thrombosis. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 2007; 33: 223–233.
Ay C, Tengler T, Vormittag R, Simanek R, Dorda W, Vukovich T et al. Venous thromboembolism—a manifestation of the metabolic syndrome. Haematologica 2007; 92: 374–380.
Ageno W, Prandoni P, Romualdi E, Ghirarduzzi A, Dentali F, Pesavento R et al. The metabolic syndrome and the risk of venous thrombosis: a case-control study. J Thromb Haemost 2006; 4: 1914–1918.
Samad F, Ruf W . Inflammation, obesity, and thrombosis. Blood 2013; 122: 3415–3422.
Goichot B, Grunebaum L, Desprez D, Vinzio S, Meyer L, Schlienger JL et al. Circulating procoagulant microparticles in obesity. Diabetes Metab 2006; 32: 82–85.
Tesselaar ME, Romijn FP, Van Der Linden IK, Prins FA, Bertina RM, Osanto S . Microparticle-associated tissue factor activity: a link between cancer and thrombosis? J Thromb Haemost 2007; 5: 520–527.
Manly DA, Wang J, Glover SL, Kasthuri R, Liebman HA, Key NS et al. Increased microparticle tissue factor activity in cancer patients with Venous Thromboembolism. Thromb Res 2010; 125: 511–512.
Langer F, Spath B, Haubold K, Holstein K, Marx G, Wierecky J et al. Tissue factor procoagulant activity of plasma microparticles in patients with cancer-associated disseminated intravascular coagulation. Ann Hematol 2008; 87: 451–457.
Thaler J, Pabinger I, Sperr WR, Ay C . Clinical evidence for a link between microparticle-associated tissue factor activity and overt disseminated intravascular coagulation in patients with acute myelocytic leukemia. Thromb Res 2014; 133: 303–305.
Thaler J, Koppensteiner R, Pabinger I, Ay C, Gremmel T . Microparticle-associated tissue factor activity in patients with acute unprovoked deep vein thrombosis and during the course of one year. Thromb Res 2014; 134: 1093–1096.
National Institutes of Health Consensus Development Conference Statement. Gastrointestinal surgery for severe obesity. Am J Clin Nutr 1992; 55 (Suppl): 615S–619S.
Kriwanek S, Tuchmann A . Gastric bypass in the management of morbid obesity. Wien Klin Wochenschr 1989; 101: 617–621.
Mason EE, Doherty C, Cullen JJ, Scott D, Rodriguez EM, Maher JW . Vertical gastroplasty: evolution of vertical banded gastroplasty. World J Surg 1998; 22: 919–924.
American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetes—2014. Diabetes Care Jan 2014; 37 (Suppl 1): S14–S80.
Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, Naylor BA, Treacher DF, Turner RC . Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 1985; 28: 412–419.
Khorana AA, Francis CW, Menzies KE, Wang JG, Hyrien O, Hathcock J et al. Plasma tissue factor may be predictive of venous thromboembolism in pancreatic cancer. J Thromb Haemost 2008; 6: 1983–1985.
Lee RD, Barcel DA, Williams JC, Wang JG, Boles JC, Manly DA et al. Pre-analytical and analytical variables affecting the measurement of plasma-derived microparticle tissue factor activity. Thromb Res 2012; 129: 80–85.
Adams M . Assessment of thrombin generation: useful or hype? Semin Thromb Hemost 2009; 35: 104–110.
Samad F, Pandey M, Loskutoff DJ . Tissue factor gene expression in the adipose tissues of obese mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1998; 95: 7591–7596.
Samad F, Pandey M, Loskutoff DJ . Regulation of tissue factor gene expression in obesity. Blood 2001; 98: 3353–3358.
Badeanlou L, Furlan-Freguia C, Yang G, Ruf W, Samad F . Tissue factor-protease-activated receptor 2 signaling promotes diet-induced obesity and adipose inflammation. Nat Med 2011; 17: 1490–1497.
Diamant M, Nieuwland R, Pablo RF, Sturk A, Smit JW, Radder JK . Elevated numbers of tissue-factor exposing microparticles correlate with components of the metabolic syndrome in uncomplicated type 2 diabetes mellitus. Circulation 2002; 106: 2442–2447.
Ayer JG, Song C, Steinbeck K, Celermajer DS, Ben Freedman S . Increased tissue factor activity in monocytes from obese young adults. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 2010; 37: 1049–1054.
Kopp CW, Kopp HP, Steiner S, Kriwanek S, Krzyzanowska K, Bartok A et al. Weight loss reduces tissue factor in morbidly obese patients. Obes Res 2003; 11: 950–956.
Geddings JE, Mackman N . Comment on 'tissue factor expressed by microparticles is associated with mortality but not with thrombosis in cancer patients'. Thromb Haemost 2013; 111: 180–181.
Acknowledgements
We thank Tanja Altreiter (Clinical Division of Haematology and Haemostaseology, Department of Medicine I, Medical University of Vienna) for proofreading this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ay, L., Thaler, J., Brix, JM. et al. Decrease in microvesicle-associated tissue factor activity in morbidly obese patients after bariatric surgery. Int J Obes 40, 768–772 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2015.246
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2015.246
This article is cited by
-
Bariatric surgery in morbidly obese individuals affects plasma levels of protein C and thrombomodulin
Journal of Thrombosis and Thrombolysis (2019)
-
Pathogenic roles of microvesicles in diabetic retinopathy
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica (2018)
-
Body Weight Reduction and Biochemical Parameters of the Patients After RYGB and SG Bariatric Procedures in 12-Month Observation
Obesity Surgery (2017)