Abstract
Objective:
Inflammation plays a pivotal role in the atherosclerotic process, and some chemokines seem to be crucial in the pathogenesis of vascular damage. High-serum homocysteine, recently recognized as an independent risk factor for vascular disease might increase cytokine and chemokine levels, thus amplifying endothelial damage; moreover, it might worse insulin resistance, thus further contributing to enhance cardiovascular risk. The effect of folic acid supplementation in improving in vivo endothelial function is still debated. In this study, we investigated the effect of folic acid supplementation on insulin sensitivity and peripheral markers of inflammation in overweight healthy subjects.
Design:
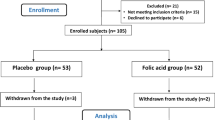
The study was performed as an unmasked randomized placebo-controlled trial of 12 weeks duration.
Subjects:
Sixty healthy volunteers with normal glucose tolerance and BMI between 25 and 29 kg/m2 were enrolled.
Measurements:
Biochemical parameters and plasma concentrations of homocysteine and of some inflammatory molecules were measured at baseline and at the end of the study, together with an estimation of insulin sensitivity.
Results:
Subjects receiving folic acid supplementation showed a decrement of homocysteine and an amelioration of insulin sensitivity; this treatment was also associated with a significant drop in the circulating concentration of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1, interleukin-8 and C-reactive protein, in the absence of any significant variation of BMI or fat mass.
Conclusions:
In healthy overweight subjects a short-term folic acid supplementation reduces the circulating level of some inflammatory mediators independently of weight change, thus suggesting a potential therapeutic role for folic acid in the protection from atherogenesis and cardiovascular diseases.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hackam DG, Anand SS . Emerging risk factors for atherosclerotic vascular disease: a critical review of the evidence. JAMA 2003; 290: 932–940.
Splaver A, Lamas GA, Hennekens CH . Homocysteine and cardiovascular disease: biological mechanisms, observational epidemiology, and the need for randomized trials. Am Heart J 2004; 148: 34–40.
Lawrence de Koning AB, Werstuck GH, Zhou J, Austin RC . Hyperhomocysteinemia and its role in the development of atherosclerosis. Clin Biochem 2003; 36: 431–441.
Gu L, Okada Y, Clinton SK, Gerard C, Sukhova GK, Libby P et al. Absence of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 reduces atherosclerosis in low density lipoprotein receptor-deficient mice. Mol Cell 1998; 2: 275–281.
Bruun JM, Pedersen SB, Richelsen B . Regulation of interleukin 8 production and gene expression in human adipose tissue in vitro. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2001; 86: 1267–1273.
Boekholdt M, Peters RJG, Hack CE, Day NE, Luben R, Bingham SA et al. IL-8 plasma concentrations and the risk of future coronary artery disease in apparently healthy men and women: the EPIC-Norfolk prospective population study. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2004; 24: 1503–1508.
Schieffer B, Selle T, Hilfiker A, Hilfiker-Kleiner D, Grote K, Tietge UJ et al. Impact of interleukin-6 on plaque development and morphology in experimental atherosclerosis. Circulation 2004; 110: 3493–3500.
Boisvert WA . Modulation of atherogenesis by chemokines. Trends Cardiovasc Med 2004; 14: 161–165.
Jialal I, Devaraj S, Venugopal SK . C-reactive protein: risk marker or mediator in atherothrombosis? Hypertension 2004; 44: 6–11.
Poddar R, Sivasubramanian N, DiBello PM, Robinson K, Jacobsen DW . Homocysteine induces expression and secretion of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 and interleukin-8 in human aortic endothelial cells: implications for vascular disease. Circulation 2001; 103: 2717–2723.
Cesari M, Zanchetta M, Burlina A, Pedon L, Maiolino G, Sticchi D et al. Hyperhomocysteinemia is inversely related with left ventricular ejection fraction and predicts cardiovascular mortality in high-risk coronary artery disease hypertensives. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2005; 25: 115–121.
Fruchart JC, Nierman MC, Stroes ES, Kastelein JJ, Duriez P . New risk factors for atherosclerosis and patient risk assessment. Circulation 2004; 109 (23 Suppl 1): III15–III19.
Bayraktar F, Dereli D, Ozgen AG, Yilmaz C . Plasma homocysteine levels in polycystic ovary syndrome and congenital adrenal hyperplasia. Endocr J 2004; 51: 601–608.
Seghieri G, Breschi MC, Anichini R, De Bellis A, Alviggi L, Maida I et al. Serum homocysteine levels are increased in women with gestational diabetes mellitus. Metabolism 2003; 52: 720–723.
Abbasi F, Facchini F, Humphreys MH, Reaven GM . Plasma homocysteine concentrations in healthy volunteers are not related to differences in insulin-mediated glucose disposal. Atherosclerosis 1999; 146: 175–178.
Pouwels MJ, Den Heijer M, Blom HJ, Tack CJ, Hermus AR . Improved insulin sensitivity and metabolic control in type 2 diabetes does not influence plasma homocysteine. Diabetes Care 2003; 26: 1637–1639.
Gallistl S, Sudi KM, Erwa W, Aigner R, Borkenstein M . Determinants of homocysteine during weight reduction in obese children and adolescents. Metabolism 2001; 50: 1220–1223.
Volek JS, Gomez AL, Love DM, Weyers AM, Hesslink Jr R, Wise JA et al. Effects of an 8-week weight-loss program on cardiovascular disease risk factors and regional body composition. Eur J Clin Nutr 2002; 56: 585–592.
Chrysohoou C, Panagiotakos DB, Pitsavos C, Das UN, Stefanadis C . Adherence to the Mediterranean diet attenuates inflammation and coagulation process in healthy adults: The ATTICA Study. J Am Coll Cardiol 2004; 44: 152–158.
Laimer M, Kaser S, Kranebitter M, Sandhofer A, Muhlmann G, Schwelberger H et al. Effect of pronounced weight loss on the nontraditional cardiovascular risk marker matrix metalloproteinase-9 in middle-aged morbidly obese women. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 2005; 29: 498–501.
Esposito K, Pontillo A, Di Palo C, Giugliano G, Masella M, Marfella R et al. Effect of weight loss and lifestyle changes on vascular inflammatory markers in obese women: a randomized trial. JAMA 2003; 289: 1799–1804.
Araki A, Sako Y . Determination of free and total homocysteine in human plasma by high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection. J Chromatogr 1987; 442: 43–52.
Kershaw EE, Flier JS . Adipose tissue as an endocrine organ. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2004; 89: 2548–2556.
Gerhardt CC, Romero IA, Cancello R, Camoin L, Strosberg AD . Chemokines control fat accumulation and leptin secretion by cultured human adipocytes. Mol Cell Endocrinol 2001; 175: 81–92.
Cottam DR, Mattar SG, Barinas-Mitchell E, Eid G, Kuller L, Kelley DE et al. The chronic inflammatory hypothesis for the morbidity associated with morbid obesity: implications and effects of weight loss. Obes Surg 2004; 14: 589–600.
Geisel J, Jodden V, Obeid R, Knapp JP, Bodis M, Herrmann W . Stimulatory effect of homocysteine on interleukin-8 expression in human endothelial cells. Clin Chem Lab Med 2003; 41: 1045–1048.
Setola E, Monti LD, Galluccio E, Palloshi A, Fragasso G, Paroni R et al. Insulin resistance and endothelial function are improved after folate and vitamin B12 therapy in patients with metabolic syndrome: relationship between homocysteine levels and hyperinsulinemia. Eur J Endocrinol 2004; 151: 483–489.
Kim WJ, Chereshnev I, Gazdoiu M, Fallon JT, Rollins BJ, Taubman MB . MCP-1 deficiency is associated with reduced intimal hyperplasia after arterial injury. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2003; 310: 936–942.
Srinivasan S, Yeh M, Danziger EC, Hatley ME, Riggan AE, Leitinger N et al. Glucose regulates monocyte adhesion through endothelial production of interleukin-8. Circ Res 2003; 92: 371–377.
Bronstrup A, Hages M, Prinz-Langenohl R, Pietrzik K . Effects of folic acid and combinations of folic acid and vitamin B-12 on plasma homocysteine concentrations in healthy, young women. Am J Clin Nutr 1998; 68: 1104–1110.
Bruun JM, Lihn AS, Pedersen SB, Richelsen B . Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 release is higher in visceral than subcutaneous human adipose tissue (AT): implication of macrophages resident in the AT. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2005; 90: 2282–2289.
Sjoholm A, Nystrom T . Endothelial inflammation in insulin resistance. Lancet 2005; 365 (9459): 610–612.
Hernandez R, Teruel T, de Alvaro C, Lorenzo M . Rosiglitazone ameliorates insulin resistance in brown adipocytes of Wistar rats by impairing TNF-alpha induction of p38 and p42/p44 mitogen-activated protein kinases. Diabetologia 2004; 47: 1615–1624.
Dandona P, Aljada A, Bandyopadhyay A . Inflammation: the link between insulin resistance, obesity and diabetes. Trends Immunol 2004; 25: 4–7.
Fonseca VA, Fink LM, Kern PA . Insulin sensitivity and plasma homocysteine concentrations in non-diabetic obese and normal weight subjects. Atherosclerosis 2003; 167: 105–109.
Bruun JM, Pedersen SB, Richelsen B . Interleukin-8 production in human adipose tissue. Inhibitory effects of anti-diabetic compounds, the thiazolidinedione ciglitazone and the biguanide metformin. Horm Metab Res 2000; 32: 537–541.
Das UN . Folic acid says NO to vascular diseases. Nutrition 2003; 19: 686–692.
Giltay EJ, Hoogeveen EK, Elbers JM, Gooren LJ, Asscheman H, Stehouwer CD . Insulin resistance is associated with elevated plasma total homocysteine levels in healthy, non-obese subjects. Atherosclerosis 1998; 139: 197–198.
Godsland IF, Rosankiewicz JR, Proudler AJ, Johnston DG . Plasma total homocysteine concentrations are unrelated to insulin sensitivity and components of the metabolic syndrome in healthy men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2001; 86: 719–723.
Shin WS, Szuba A, Rockson SG . The role of chemokines in human cardiovascular pathology: enhanced biological insights. Atherosclerosis 2002; 160: 91–102.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Solini, A., Santini, E. & Ferrannini, E. Effect of short-term folic acid supplementation on insulin sensitivity and inflammatory markers in overweight subjects. Int J Obes 30, 1197–1202 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0803265
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0803265
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Folic acid effect on homocysteine, sortilin levels and glycemic control in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients
Nutrition & Diabetes (2022)
-
Effects of folate supplementation on recurrence and metabolic status of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia grade 2/3 in overweight and obese women: a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (2022)
-
The Role of Nutrition on Meta-inflammation: Insights and Potential Targets in Communicable and Chronic Disease Management
Current Obesity Reports (2022)
-
Folate derivatives, 5-methyltetrahydrofolate and 10-formyltetrahydrofolate, protect BEAS-2B cells from high glucose–induced oxidative stress and inflammation
In Vitro Cellular & Developmental Biology - Animal (2022)
-
Unmetabolized folic acid is associated with TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-12 concentrations in a population exposed to mandatory food fortification with folic acid: a cross-sectional population-based study in Sao Paulo, Brazil
European Journal of Nutrition (2021)