Abstract
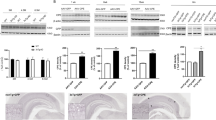
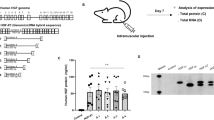
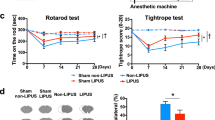
A new therapeutic approach to treat Alzheimer's disease (AD) is needed, and the use of growth factors is considered to be a candidate. Hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) is a unique multifunctional growth factor, which has the potential effect to exert neurotrophic action and induce angiogenesis. In this study, we examined the effects of overexpression of human HGF plasmid DNA using ultrasound-mediated gene transfer into the brain in an Aβ-infused cognitive dysfunction mouse model. We demonstrated that HGF gene transfer significantly alleviated Aβ-induced cognitive impairment in mice in behavioral tests. These beneficial effects of HGF might be due to (1) significant recovery of the vessel density in the dentate gyrus of the hippocampus, (2) upregulation of BDNF, (3) a significant decrease in oxidative stress and (4) synaptic enhancement. A pharmacological approach including gene therapy to increase the HGF level in combination with anti-Aβ therapy might be a new therapeutic option for the treatment of AD.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Glenner GG, Wong CW . Alzheimer's disease: initial report of the purification and characterization of a novel cerebrovascular amyloid protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1984; 120: 885–890.
Gandy S . The role of cerebral amyloid beta accumulation in common forms of Alzheimer disease. J Clin Invest 2005; 115: 1121–1129.
Naslund J, Haroutunian V, Mohs R, Davis KL, Davies P, Greengard P et al. Correlation between elevated levels of amyloid beta-peptide in the brain and cognitive decline. JAMA 2000; 283: 1571–1577.
Rosenberg RN . Translational research on the way to effective therapy for Alzheimer disease. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2005; 62: 1186–1192.
Bradbury J . Hope for AD with NGF gene-therapy trial. Lancet Neurol 2005; 4: 335.
Tuszynski MH, Thal L, Pay M, Salmon DPUHS, Bakay R, Patel P et al. A phase 1 clinical trial of nerve growth factor gene therapy for Alzheimer disease. Nat Med 2005; 11: 551–555.
Nakamura T, Nishizawa T, Hagiya M, Seki T, Shimonishi M, Sugimura A et al. Molecular cloning and expression of human hepatocyte growth factor. Nature 1989; 342: 440–443.
Korhonen L, Sjoholm U, Takei N, Kern MA, Schirmacher P, Castren E et al. Expression of c-Met in developing rat hippocampus: evidence for HGF as a neurotrophic factor for calbindin D-expressing neurons. Eur J Neurosci 2000; 12: 3453–3461.
Silvagno F, Follenzi A, Arese M, Prat M, Giraudo E, Gaudino G et al. In vivo activation of met tyrosine kinase by heterodimeric hepatocyte growth factor molecule promotes angiogenesis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 1995; 15: 1857–1865.
Akimoto M, Baba A, Ikeda-Matsuo Y, Yamada MK, Itamura R, Nishiyama N et al. Hepatocyte growth factor as an enhancer of nmda currents and synaptic plasticity in the hippocampus. Neuroscience 2004; 128: 155–162.
Shimamura M, Sato N, Waguri S, Uchiyama Y, Hayashi T, Iida H et al. Gene transfer of hepatocyte growth factor gene improves learning and memory in the chronic stage of cerebral infarction. Hypertension 2006; 47: 742–751.
Sun W, Funakoshi H, Nakamura T . Overexpression of HGF retards disease progression and prolongs life span in a transgenic mouse model of ALS. J Neurosci 2002; 22: 6537–6548.
Shimamura M, Sato N, Taniyama Y, Yamamoto S, Endoh M, Kurinami H et al. Development of efficient plasmid DNA transfer into adult rat central nervous system using microbubble-enhanced ultrasound. Gene Therapy 2004; 11: 1532–1539.
Morishita R, Aoki M, Hashiya N, Makino H, Yamasaki K, Azuma J et al. Safety evaluation of clinical gene therapy using hepatocyte growth factor to treat peripheral arterial disease. Hypertension 2004; 44: 203–209.
Shimamura M, Sato N, Oshima K, Aoki M, Kurinami H, Waguri S et al. Novel therapeutic strategy to treat brain ischemia: overexpression of hepatocyte growth factor gene reduced ischemic injury without cerebral edema in rat model. Circulation 2004; 109: 424–431.
Oshima K, Shimamura M, Mizuno S, Tamai K, Doi K, Morishita R et al. Intrathecal injection of HVJ-E containing HGF gene to cerebrospinal fluid can prevent and ameliorate hearing impairment in rats. FASEB J 2004; 18: 212–214.
Afford SC, Kakoullis T, Oates J, Crocker J, Strain AJ . Effects of hepatocyte growth factor on differentiation and cMET receptor expression in the promyelocytic HL60 cell line. Clin Mol Pathol 1995; 48: M23–M27.
Tajima H, Kawasumi M, Chiba T, Yamada M, Yamashita K, Nawa M et al. A humanin derivative, S14G-HN, prevents amyloid-beta-induced memory impairment in mice. J Neurosci Res 2005; 79: 714–723.
Cavaglia M, Dombrowski SM, Drazba J, Vasanji A, Bokesch PM, Janigro D . Regional variation in brain capillary density and vascular response to ischemia. Brain Res 2001; 910: 81–93.
Kuwabara Y, Ichiya Y, Otsuka M, Masuda K, Ichimiya A, Fujishima M . Cerebrovascular responsiveness to hypercapnia in Alzheimer's dementia and vascular dementia of the Binswanger type. Stroke 1992; 23: 594–598.
Frautschy SA, Hu W, Kim P, Miller SA, Chu T, Harris-White ME et al. Phenolic anti-inflammatory antioxidant reversal of Abeta-induced cognitive deficits and neuropathology. Neurobiol Aging 2001; 22: 993–1005.
Lim GP, Chu T, Yang F, Beech W, Frautschy SA, Cole GM . The curry spice curcumin reduces oxidative damage and amyloid pathology in an Alzheimer transgenic mouse. J Neurosci 2001; 21: 8370–8377.
Szocs K, Lassegue B, Sorescu D, Hilenski LL, Valppu L, Couse TL et al. Upregulation of Nox-based NAD(P)H oxidases in restenosis after carotid injury. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2002; 22: 21–27.
Hyman C, Hofer M, Barde YA, Juhasz M, Yancopoulos GD, Squinto SP et al. BDNF is a neurotrophic factor for dopaminergic neurons of the substantia nigra. Nature 1991; 350: 230–232.
Ferrer I, Marin C, Rey MJ, Ribalta T, Goutan E, Blanco R et al. BDNF and full-length and truncated TrkB expression in Alzheimer disease. Implications in therapeutic strategies. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 1999; 58: 729–739.
Niwa K, Younkin L, Ebeling C, Turner SK, Westaway D, Younkin S et al. Abeta 1–40-related reduction in functional hyperemia in mouse neocortex during somatosensory activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2000; 97: 9735–9740.
Beckmann N, Schuler A, Mueggler T, Meyer EP, Wiederhold KH, Staufenbiel M et al. Age-dependent cerebrovascular abnormalities and blood flow disturbances in APP23 mice modeling Alzheimer's disease. J Neurosci 2003; 23: 8453–8459.
Ratan RR, Baraban JM . Apoptotic death in an in vitro model of neuronal oxidative stress. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 1995; 22: 309–310.
Behl C, Davis JB, Lesley R, Schubert D . Hydrogen peroxide mediates amyloid beta protein toxicity. Cell 1994; 77: 817–827.
Zhu X, Raina AK, Lee HG, Casadesus G, Smith MA, Perry G . Oxidative stress signalling in Alzheimer's disease. Brain Res 2004; 1000: 32–39.
Thompson J, Dolcet X, Hilton M, Tolcos M, Davies AM . HGF promotes survival and growth of maturing sympathetic neurons by PI-3 kinase- and MAP kinase-dependent mechanisms. Mol Cell Neurosci 2004; 27: 441–452.
Niimura M, Takagi N, Takagi K, Mizutani R, Tanonaka K, Funakoshi H et al. The protective effect of hepatocyte growth factor against cell death in the hippocampus after transient forebrain ischemia is related to the improvement of apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease/redox factor-1 level and inhibition of NADPH oxidase activity. Neurosci Lett 2006; 407: 136–140.
Ozaki M, Haga S, Zhang HQ, Irani K, Suzuki S . Inhibition of hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced oxidative stress in HGF-stimulated antiapoptotic signaling: role of PI3-K and Akt kinase upon rac1. Cell Death Differ 2003; 10: 508–515.
Zou J, Crews F . CREB and NF-kappaB transcription factors regulate sensitivity to excitotoxic and oxidative stress induced neuronal cell death. Cell Mol Neurobiol 2006; 26: 383–403.
Du K, Montminy M . CREB is a regulatory target for the protein kinase Akt/PKB. J Biol Chem 1998; 273: 32377–32379.
Riccio A, Ahn S, Davenport CM, Blendy JA, Ginty DD . Mediation by a CREB family transcription factor of NGF-dependent survival of sympathetic neurons. Science 1999; 286: 2358–2361.
Calhoun ME, Jucker M, Martin LJ, Thinakaran G, Price DL, Mouton PR . Comparative evaluation of synaptophysin-based methods for quantification of synapses. J Neurocytol 1996; 25: 821–828.
Liu YY, Ju G . Quantitative evaluation of synaptophysin-like immunoreactive nerve terminals or varicosities in anterior pituitary of normal and adrenalectomized rats. J Neuroendocrinol 2001; 13: 967–974.
Laske C, Stransky E, Leyhe T, Eschweiler GW, Wittorf A, Richartz E et al. Stage-dependent BDNF serum concentrations in Alzheimer's disease. J Neural Transm 2006; 113: 1217–1224.
Egan MF, Kojima M, Callicott JH, Goldberg TE, Kolachana BS, Bertolino A et al. The BDNF val66met polymorphism affects activity-dependent secretion of BDNF and human memory and hippocampal function. Cell 2003; 112: 257–269.
Hansell NK, James MR, Duffy DL, Birley AJ, Luciano M, Geffen GM et al. Effect of the BDNF V166M polymorphism on working memory in healthy adolescents. Genes Brain Behav 2006; 6: 260–268.
Tao X, Finkbeiner S, Arnold DB, Shaywitz AJ, Greenberg ME . Ca2+ influx regulates BDNF transcription by a CREB family transcription factor-dependent mechanism. Neuron 1998; 20: 709–726.
Fenton H, Finch PW, Rubin JS, Rosenberg JM, Taylor WG, Kuo-Leblanc V et al. Hepatocyte growth factor (HGF/SF) in Alzheimer's disease. Brain Res 1998; 779: 262–270.
Machide M, Kamitori K, Kohsaka S . Hepatocyte growth factor-induced differential activation of phospholipase cgamma 1 and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase is regulated by tyrosine phosphatase SHP-1 in astrocytes. J Biol Chem 2000; 275: 31392–31398.
Bignami A . The role of astrocytes in CNS regeneration. J Neurosurg Sci 1984; 28: 127–132.
Yamada K, Tanaka T, Zou LB, Senzaki K, Yano K, Osada T et al. Long-term deprivation of oestrogens by ovariectomy potentiates beta-amyloid-induced working memory deficits in rats. Br J Pharmacol 1999; 128: 419–427.
Koike H, Morishita R, Iguchi S, Aoki M, Matsumoto K, Nakamura T et al. Enhanced angiogenesis and improvement of neuropathy by cotransfection of human hepatocyte growth factor and prostacyclin synthase gene. FASEB J 2003; 17: 779–781.
Nabeshima T, Noda Y, Mamiya T . The role of nociceptin in cognition. Brain Res 1999; 848: 167–173.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by a grant-in-aid for scientific research from the Organization for Pharmaceutical Safety and Research, a grant-in-aid from National Institute of Biomedical Innovation (to RM), The Ministry of Public Health and Welfare (to RM) and Takeda Science Foundation (to RM), and grants-in-aid from Japan Promotion of Science, the Japanese Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (to RM, NS), Novartis, Chiyoda and the Kanae Foundation (to NS). We thank Dr Hisae Sumi (Department of Neurology, Osaka University Graduate School of Medicine) for critical advice on immunostaining, and also thank Dr Yoshiaki Taniyama for critical advice on ultrasound-mediated gene transfer. We thank Drs Hironori Nakagami, Junya Azuma and Kaori Nagao for helpful discussion, and Ms Hizuki Hamada for technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Takeuchi, D., Sato, N., Shimamura, M. et al. Alleviation of Aβ-induced cognitive impairment by ultrasound-mediated gene transfer of HGF in a mouse model. Gene Ther 15, 561–571 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3303094
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3303094