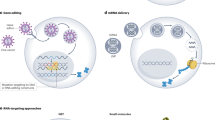
Abstract
At the post-transcriptional level, gene expression is largely regulated through a network of molecular machines that regulate pre-mRNA maturation integrity, transport, translation and degradation. These processes are based on the formation of nucleoprotein complexes and require the recognition of sequence motifs on the RNA. By masking these targets with complementary RNA sequences forming Watson–Crick base pairing, it is possible to efficiently and specifically impact on the cell phenotype, or to compensate the deleterious effect of mutations. Here we review how the adeno-associated virus technology is being exploited for expressing non-coding RNAs in tissues such as the brain, muscle or liver, in functional genomic studies as well as for the development of novel therapeutic strategies.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Conrad SE, Campbell JL . Role of plasmid-coded RNA and ribonuclease III in plasmid DNA replication. Cell 1979; 18: 61–71.
Izant JG, Weintraub H . Inhibition of thymidine kinase gene expression by anti-sense RNA: a molecular approach to genetic analysis. Cell 1984; 36: 1007–1015.
Kumar M, Carmichael GG . Nuclear antisense RNA induces extensive adenosine modifications and nuclear retention of target transcripts. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1997; 94: 3542–3547.
McManus MT, Sharp PA . Gene silencing in mammals by small interfering RNAs. Nat Rev Genet 2002; 3: 737–747.
Lewin AS, Hauswirth WW . Ribozyme gene therapy: applications for molecular medicine. Trends Mol Med 2001; 7: 221.
Tazi J, Durand S, Jeanteur P . The spliceosome: a novel multi-faceted target for therapy. Trends Biochem Sci 2005; 30: 469–478.
Sullenger BA, Cech TR . Ribozyme-mediated repair of defective mRNA by targeted trans-splicing. Nature 1994; 371: 619.
Puttaraju M, Jamison SF, Mansfield SG, Garcia-Blanco MA, Mitchell LG . Spliceosome-mediated RNA trans-splicing as a tool for gene therapy. Nat Biotechnol 1999; 17: 246–252.
Kim DH, Rossi JJ . Strategies for silencing human disease using RNA interference. Nat Rev Genet 2007; 8: 173–184.
Auricchio A, Kobinger G, Anand V, Hildinger M, O′Connor E, Maguire AM et al. Exchange of surface proteins impacts on viral vector cellular specificity and transduction characteristics: the retina as a model. Hum Mol Genet 2001; 10: 3075–3081.
Nakai H, Yant SR, Storm TA, Fuess S, Meuse L, Kay MA . Extrachromosomal recombinant adeno-associatedvirus vector genomes are primarily responsible for stable liver transduction in vivo. J Virol 2001; 75: 6969–6976.
Chang K, Elledge SJ, Hannon GJ . Lessons from Nature: microRNA-based shRNA libraries. Nat Methods 2006; 3: 707.
Poluri A, Sutton RE . Titers of HIV-based vectors encoding shRNAs are reduced by a dicer-dependent mechanism. Mol Ther 2007; 16: 378–386.
Fritz JJ, Lewin A, Hauswirth W, Agarwal A, Grant M, Shaw L . Development of hammerhead ribozymes to modulate endogenous gene expression for functional studies. Methods 2002; 28: 276–285.
Gorman L, Suter D, Emerick V, Schumperli D, Kole R . Stable alteration of pre-mRNA splicing patterns by modified U7 small nuclear RNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1998; 95: 4929–4934.
Denti MA, Rosa A, D′Antona G, Sthandier O, Angelis FGD, Nicoletti C et al. Chimeric adeno-associated virus/antisense U1 small nuclear RNA effectively rescues dystrophin synthesis and muscle function by local treatment of mdx mice. Hum Gene Ther 2006; 17: 565–574.
Millington-Ward S, O′Neill B, Tuohy G, Al-Jandal N, Kiang AS, Kenna PF et al. Strategems in vitro for gene therapies directed to dominant mutations. Hum Mol Genet 1997; 6: 1415–1426.
Grimm D, Streetz KL, Jopling CL, Storm TA, Pandey K, Davis CR et al. Fatality in mice due to oversaturation of cellular microRNA/short hairpin RNA pathways. Nature 2006; 441: 537.
Rendahl KG, Leff SE, Otten GR, Spratt SK, Bohl D, Van Roey M et al. Regulation of gene expression in vivo following transduction by two separate rAAV vectors. Nat Biotechnol 1998; 16: 757–761.
Henriksen JR, Lokke C, Hammero M, Geerts D, Versteeg R, Flaegstad T et al. Comparison of RNAi efficiency mediated by tetracycline-responsive H1 and U6 promoter variants in mammalian cell lines. Nucleic Acids Res 2007; 35: e67.
Bontempi B, Laurent-Demir C, Destrade C, Jaffard R . Time-dependent reorganization of brain circuitry underlying long-term memory storage. Nature 1999; 400: 671.
Burger C, Gorbatyuk OS, Velardo MJ, Peden CS, Williams P, Zolotukhin S et al. Recombinant AAV viral vectors pseudotyped with viral capsids from serotypes 1, 2, and 5 display differential efficiency and cell tropism after delivery to different regions of the central nervous system. Mol Ther 2004; 10: 302–317.
Kaemmerer WF, Reddy RG, Warlick CA, Hartung SD, McIvor RS, Low WC . In vivo transduction of cerebellar Purkinje cells using adeno-associated virus vectors. Mol Ther 2000; 2: 446–457.
Cao L, Jiao X, Zuzga DS, Liu Y, Fong DM, Young D et al. VEGF links hippocampal activity with neurogenesis, learning and memory. Nat Genet 2004; 36: 827–835.
Babcock AM, Standing D, Bullshields K, Schwartz E, Paden CM, Poulsen DJ . In vivo inhibition of hippocampal Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II by RNA interference. Mol Ther 2005; 11: 899.
Xia H, Mao Q, Eliason SL, Harper SQ, Martins IH, Orr HT et al. RNAi suppresses polyglutamine-induced neurodegeneration in a model of spinocerebellar ataxia. Nat Med 2004; 10: 816.
Harper SQ, Staber PD, He X, Eliason SL, Martins IH, Mao Q et al. RNA interference improves motor and neuropathological abnormalities in a Huntington's disease mouse model. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2005; 102: 5820–5825.
Machida Y, Okada T, Kurosawa M, Oyama F, Ozawa K, Nukina N . rAAV-mediated shRNA ameliorated neuropathology in Huntington disease model mouse. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2006; 343: 190.
Rodriguez-Lebron E, Denovan-Wright EM, Nash K, Lewin AS, Mandel RJ . Intrastriatal rAAV-mediated delivery of anti-huntingtin shRNAs induces partial reversal of disease progression in R6/1 Huntington's disease transgenic mice. Mol Ther 2005; 12: 618.
Hommel JD, Sears RM, Georgescu D, Simmons DL, DiLeone RJ . Local gene knockdown in the brain using viral-mediated RNA interference. Nat Med 2003; 9: 1539.
Hayashita-Kinoh H, Yamada M, Yokota T, Mizuno Y, Mochizuki H . Down-regulation of [alpha]-synuclein expression can rescue dopaminergic cells from cell death in the substantia nigra of Parkinson's disease rat model. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2006; 341: 1088.
Haberman R, Criswell H, Snowdy S, Ming Z, Breese G, Samulski R et al. Therapeutic liabilities of in vivo viral vector tropism: adeno-associated virus vectors, NMDAR1 antisense, and focal seizure sensitivity. Mol Ther 2002; 6: 495–500.
LaVail MM, Yasumura D, Matthes MT, Drenser KA, Flannery JG, Lewin AS et al. Ribozyme rescue of photoreceptor cells in P23 H transgenic rats: Long-term survival and late-stage therapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2000; 97: 11488–11493.
Lewin AS, Drenser KA, Hauswirth WW, Nishikawa S, Yasumura D, Flannery JG et al. Ribozyme rescue of photoreceptor cells in a transgenic rat model of autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa. Nat Med 1998; 4: 967–971.
Gorbatyuk M, Justilien V, Liu J, Hauswirth WW, Lewin AS . Preservation of photoreceptor morphology and function in P23 H rats using an allele independent ribozyme. Exp Eye Res 2007; 84: 44.
Tessitore A, Parisi F, Denti MA, Allocca M, Di Vicino U, Domenici L et al. Preferential silencing of a common dominant rhodopsin mutation does not inhibit retinal degeneration in a transgenic model. Mol Ther 2006; 14: 692.
O′Reilly M, Palfi A, Chadderton N, Millington-Ward S, Ader M, Cronin T et al. RNA interference-mediated suppression and replacement of human rhodopsin in vivo. Am J Hum Genet 2007; 81: 127–135.
Aarnisalo AA, Pietola L, Joensuu J, Isosomppi J, Aarnisalo P, Dinculescu A et al. Anti-clarin-1 AAV-delivered ribozyme induced apoptosis in the mouse cochlea. Hear Res 2007; 230: 9.
Liu J, Timmers AM, Lewin AS, Hauswirth WW . Ribozyme knockdown of the {gamma}-subunit of rod cGMP phosphodiesterase alters the ERG and retinal morphology in wild-type mice. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2005; 46: 3836–3844.
Qi X, Lewin AS, Sun L, Hauswirth WW, Guy J . Suppression of mitochondrial oxidative stress provides long-term neuroprotection in experimental optic neuritis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2007; 48: 681–691.
Justilien V, Pang J-J, Renganathan K, Zhan X, Crabb JW, Kim SR et al. SOD2 knockdown mouse model of early AMD. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2007; 48: 4407–4420.
Paskowitz DM, Greenberg KP, Yasumura D, Grimm D, Yang H, Duncan JL et al. Rapid and stable knockdown of an endogenous gene in retinal pigment epithelium. Hum Gene Ther 2007; 18: 871–880.
Andino LM, Takeda M, Kasahara H, Jakymiw A, Byrne BJ, Lewin AS . AAV-mediated knockdown of phospholamban leads to improved contractility and calcium handling in cardiomyocytes. J Gene Med 2008; 10: 132–142.
Magee TR, Artaza JG, Ferrini MG, Vernet D, Zuniga FI, Cantini L et al. Myostatin short interfering hairpin RNA gene transfer increases skeletal muscle mass. J Gene Med 2006; 8: 1171–1181.
Goyenvalle A, Vulin A, Fougerousse F, Leturcq F, Kaplan JC, Garcia L et al. Rescue of dystrophic muscle through U7 snRNA-mediated exon skipping. Science 2004; 306: 1796–1799.
t Hoen PA, van der Wees CG, Aartsma-Rus A, Turk R, Goyenvalle A, Danos O et al. Gene expression profiling to monitor therapeutic and adverse effects of antisense therapies for Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Pharmacogenomics 2006; 7: 281–297.
Denti MA, Rosa A, D′Antona G, Sthandier O, De Angelis FG, Nicoletti C et al. Body-wide gene therapy of Duchenne muscular dystrophy in the mdx mouse model. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2006; 103: 3758–3763.
van Deutekom JC, Janson AA, Ginjaar IB, Frankhuizen WS, Aartsma-Rus A, Bremmer-Bout M et al. Local dystrophin restoration with antisense oligonucleotide PRO051. N Engl J Med 2007; 357: 2677–2686.
Gardiner JV, Kong WM, Ward H, Murphy KG, Dhillo WS, Bloom SR . AAV mediated expression of anti-sense neuropeptide Y cRNA in the arcuate nucleus of rats results in decreased weight gain and food intake. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2005; 327: 1088–1093.
Hommel JD, Trinko R, Sears RM, Georgescu D, Liu Z-W, Gao X-B et al. Leptin receptor signaling in midbrain dopamine neurons regulates feeding. Neuron 2006; 51: 801.
Kimura B, Mohuczy D, Tang X, Phillips MI . Attenuation of hypertension and heart hypertrophy by adeno-associated virus delivering angiotensinogen antisense. Hypertension 2001; 37: 376–380.
Wang X, Skelley L, Cade R, Sun Z . AAV delivery of mineralocorticoid receptor shRNA prevents progression of cold-induced hypertension and attenuates renal damage. Gene Therapy 2006; 13: 1097–1103.
Sun Z, Roufai MB, Wang X . RNAi inhibition of mineralocorticoid receptors (MR) prevents the development of cold-induced hypertension. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 2008: (in press).
Shenouda SM, Johns C, Gavras I, Gavras H . Long-term inhibition of the central [alpha]2B-adrenergic receptor gene via recombinant AAV-delivered antisense in hypertensive rats[ast]. Am J Hypertens 2006; 19: 1135–1143.
Liu X, Luo M, Zhang LN, Yan Z, Zak R, Ding W et al. Spliceosome-mediated RNA trans-splicing with recombinant adeno-associated virus partially restores cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator function to polarized human cystic fibrosis airway epithelial cells. Hum Gene Ther 2005; 16: 1116–1123.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Danos, O. AAV vectors for RNA-based modulation of gene expression. Gene Ther 15, 864–869 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2008.69
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2008.69
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Assisted delivery of antisense therapeutics in animal models of heritable neurodegenerative and neuromuscular disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Scientific Reports (2018)
-
Replacement of huntingtin exon 1 by trans-splicing
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2012)
-
Multispecies-compatible antitumor effects of a cross-species small-interfering RNA against mammalian target of rapamycin
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2012)
-
Rescue of a Dystrophin-like Protein by Exon Skipping In Vivo Restores GABAA-receptor Clustering in the Hippocampus of the mdx Mouse
Molecular Therapy (2010)