Abstract
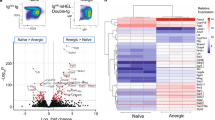
Apoptosis induced by B-cell receptor (BCR) signaling is critical for antigen-driven selection, a process critical to tolerance and immunity. Here, we examined the roles of microRNAs (miRNAs) in BCR signaling-induced apoptosis using the widely applied WEHI-231 model. Comparison of miRNA levels in BCR-stimulated and -unstimulated cells revealed that 39 miRNAs were differentially expressed upon stimulation of the BCR. Importantly, stimulation in the presence of anti-CD40 antibodies, which rescues cells from BCR-induced apoptosis, prevented most changes in miRNA expression. Ectopic expression of mir-150 and mir-181a1b1, miRNAs that were upregulated upon BCR stimulation, resulted in inhibition of cell growth. Finally, we showed that ectopic expression of mir-150, mir-181a1b1 and mir-17∼92 sensitized cells to anti-IgM stimulation-induced growth inhibition. Together, these results demonstrate that miRNAs are involved in BCR signaling, suggesting that they may have important roles in the regulation of B cell-mediated tolerance and immunity.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $19.83 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Niiro H, Clark EA . Regulation of B-cell fate by antigen-receptor signals. Nat Rev Immunol 2002; 2: 945–956.
Norvell A, Mandik L, Monroe JG . Engagement of the antigen-receptor on immature murine B lymphocytes results in death by apoptosis. J Immunol 1995; 154: 4404–4413.
Galibert L, Burdin N, Barthelemy C, Meffre G, Durand I, Garcia E et al. Negative selection of human germinal center B cells by prolonged BCR cross-linking. J Exp Med 1996; 183: 2075–2085.
O’Connell RM, Rao DS, Chaudhuri AA, Baltimore D . Physiological and pathological roles for microRNAs in the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol 2010; 10: 111–122.
Chen CZ, Li L, Lodish HF, Bartel DP . MicroRNAs modulate hematopoietic lineage differentiation. Science 2004; 303: 83–86.
Li QJ, Chau J, Ebert PJ, Sylvester G, Min H, Liu G et al. miR-181a is an intrinsic modulator of T cell sensitivity and selection. Cell 2007; 129: 147–161.
Xiao C, Calado DP, Galler G, Thai TH, Patterson HC, Wang J et al. MiR-150 controls B cell differentiation by targeting the transcription factor c-Myb. Cell 2007; 131: 146–159.
Zhou B, Wang S, Mayr C, Bartel DP, Lodish HF . miR-150, a microRNA expressed in mature B and T cells, blocks early B cell development when expressed prematurely. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2007; 104: 7080–7085.
Thai TH, Calado DP, Casola S, Ansel KM, Xiao C, Xue Y et al. Regulation of the germinal center response by microRNA-155. Science 2007; 316: 604–608.
van den Berg A, Kroesen BJ, Kooistra K, de Jong D, Briggs J, Blokzijl T et al. High expression of B-cell receptor inducible gene BIC in all subtypes of Hodgkin lymphoma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2003; 37: 20–28.
Belver L, de Yebenes VG, Ramiro AR . MicroRNAs prevent the generation of autoreactive antibodies. Immunity 2010; 33: 713–722.
Boyd AW, Schrader JW . The regulation of growth and differentiation of a murine B cell lymphoma. II. The inhibition of WEHI 231 by anti-immunoglobulin antibodies. J Immunol 1981; 126: 2466–2469.
Tsubata T, Wu J, Honjo T . B-cell apoptosis induced by antigen receptor crosslinking is blocked by a T-cell signal through CD40. Nature 1993; 364: 645–648.
Chen G, Zhu W, Shi D, Lv L, Zhang C, Liu P et al. MicroRNA-181a sensitizes human malignant glioma U87MG cells to radiation by targeting Bcl-2. Oncol Rep 2010; 23: 997–1003.
Zhu W, Shan X, Wang T, Shu Y, Liu P . miR-181b modulates multidrug resistance by targeting BCL2 in human cancer cell lines. Int J Cancer 2010; 127: 2520–2529.
Zimmerman EI, Dollins CM, Crawford M, Grant S, Nana-Sinkam SP, Richards KL et al. Lyn kinase-dependent regulation of miR181 and myeloid cell leukemia-1 expression: implications for drug resistance in myelogenous leukemia. Mol Pharmacol 2010; 78: 811–817.
He L, He X, Lim LP, de Stanchina E, Xuan Z, Liang Y et al. A microRNA component of the p53 tumour suppressor network. Nature 2007; 447: 1130–1134.
Wu M, Bellas RE, Shen J, Yang W, Sonenshein GE . Increased p27Kip1 cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor gene expression following anti-IgM treatment promotes apoptosis of WEHI 231 B cells. J Immunol 1999; 163: 6530–6535.
He L, Thomson JM, Hemann MT, Hernando-Monge E, Mu D, Goodson S et al. A microRNA polycistron as a potential human oncogene. Nature 2005; 435: 828–833.
Matsubara H, Takeuchi T, Nishikawa E, Yanagisawa K, Hayashita Y, Ebi H et al. Apoptosis induction by antisense oligonucleotides against miR-17-5p and miR-20a in lung cancers overexpressing miR-17-92. Oncogene 2007; 26: 6099–6105.
Arechiga AF, Habib T, He Y, Zhang X, Zhang ZY, Funk A et al. Cutting edge: the PTPN22 allelic variant associated with autoimmunity impairs B cell signaling. J Immunol 2009; 182: 3343–3347.
Rui L, Healy JI, Blasioli J, Goodnow CC . ERK signaling is a molecular switch integrating opposing inputs from B cell receptor and T cell cytokines to control TLR4-driven plasma cell differentiation. J Immunol 2006; 177: 5337–5346.
Spierings DC, McGoldrick D, Hamilton-Easton AM, Neale G, Murchison EP, Hannon GJ et al. Ordered progression of stage-specific miRNA profiles in the mouse B2 B-cell lineage. Blood 2011; 117: 5340–5349.
Mao TK, Chen CZ . Dissecting microRNA-mediated gene regulation and function in T-cell development. Methods Enzymol 2007; 427: 171–189.
Acknowledgements
We thank members of the Chen Lab and the van den Berg Lab for helpful discussions and advice, Dr David Hirschberg and Gergana Nestorova for their excellent advice and assistance with the miRNA microarray profiling, and Prof Dr Anke van den Berg and Dr Bart-Jan Kroesen for critical reading of the manuscript. This work was supported by an NWO Rubicon fellowship (825.06.027, JK) and NIH grants (1R01AI073724 and 1DP1 OD00643501, CZC) and a W.M. Keck young scholar award (CZC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Genes and Immunity website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kluiver, J., Chen, CZ. MicroRNAs regulate B-cell receptor signaling-induced apoptosis. Genes Immun 13, 239–244 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/gene.2012.1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/gene.2012.1
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Role of microRNA in chronic lymphocytic leukemia onset and progression
Journal of Hematology & Oncology (2015)
-
The role of microRNAs in B-cell development and function
Cellular & Molecular Immunology (2013)