Abstract
Objective: 1. To determine if resting energy expenditure (REE) adjusted for body composition is elevated in HIV-positive males when compared with healthy controls in the era of highly active antiretroviral therapy. 2. To examine the accuracy of prediction equations for estimating REE in people with HIV. 3. To determine if REE adjusting for body composition is significantly different between those HIV-positive subjects reporting lipodystrophy (LD) or weight loss (≥5%) and those who are weight stable when compared to controls.
Design: Cross-sectional study.
Setting: Tertiary referral hospital HIV unit and an outpatient clinic specializing in HIV care.
Subjects: HIV-positive males (n=70) and healthy male controls (n=16).
Methods: REE was measured using indirect calorimetry. Body composition was assessed using bioelectrical impedance analysis.
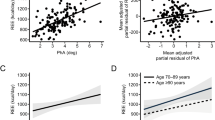
Results: 1. REE when adjusted for fat-free mass and fat mass using the general linear model (analysis of covariance) was greater in HIV-positive subjects than controls (7258±810 kJ, n=70 vs 6615±695 kJ, n=16, P<0.05). 2. The Harris and Benedict, Schofield, Cunningham and the two equations previously published by Melchior and colleagues in HIV-positive subjects all gave an estimate of REE significantly different from the measured REE in the HIV-positive subjects, therefore a new prediction equation was developed. The inability of the published equations to predict REE in the different HIV-positive subgroups reflected the heterogeneity in body composition. 3. REE adjusted for fat-free and fat mass was significantly greater in the both the HIV patients who were weight stable and those with lipodystrophy compared with the healthy controls.
Conclusion: REE is significantly higher in HIV-positive males when compared with healthy controls. Body composition abnormalities common in HIV render the use of standard prediction equations for estimating REE invalid. When measuring REE in HIV-positive males adjustment steps should include fat-free and fat mass.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bernstein, RS, Thornton, JC & Yang, MU (1983). Prediction of the resting metabolic rate in obese patients. Am. J. Clin. Nutr., 37, 595–602.
Bland, JM & Altman, DG (1986). Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet, 1, 307–310.
Bursztein, S, Saphar, P, Singer, P & Elwyn, DH (1989). A mathematical analysis of indirect calorimetry measurements in acutely ill patients. Am. J. Clin. Nutr., 50, 227–230.
Carbonnel, F, Maslo, C, Beaugerie, L, Carrat, F, Wirbel, E, Aussel, C, Gobert, JG, Girard, PM, Gendre, JP, Cosnes, J & Rozenbaum, W (1998). Effect of indinavir on HIV-related wasting. AIDS, 12, 1777–1784.
Carr, A, Samaras, K, Burton, S, Law, M, Freund, J, Chisholm, DJ & Cooper, DA (1998). A syndrome of peripheral lipodystrophy, hyperlipidaemia and insulin resistance in patients receiving HIV protease inhibitors. AIDS, 12, F51–F58.
Corcoran, C, Anderson, EJ, Burrows, B, Stanley, T, Walsh, M, Poulos, AM & Grinspoon, S (2000). Comparison of total body potassium with other techniques for measuring lean body mass in men and women with AIDS wasting. Am. J. Clin. Nutr., 72, 1053–1058.
Cunningham, JJ (1980). A reanalysis of the factors influencing basal metabolic rate in normal adults. Am. J. Clin. Nutr., 33, 2372–2374.
Cunningham, JJ (1991). Body composition as a determinant of energy expenditure: a synthetic review and a proposed general prediction equation. Am. J. Clin. Nutr., 54, 963–969.
Dallosso, HM & James, WP (1984). The role of smoking in the regulation of energy balance. Int. J. Obes., 8, 368–375.
Das, SK, Moriguti, JC, McCrory, MA, Saltzman, E, Mosunic, C, Greenberg, AS & Roberts, SB (2001). An underfeeding study in healthy men and women provides further evidence of impaired regulation of energy expenditure in old age. J. Nutr., 131, 1833–1838.
Datex Corporation (1995). Deltatrac TM II MBM-200 Metabolic Monitor, Operators Manual, (publication no. 882123-2) Helsinki: Datex Division, Instrumentarium Corp.
Department of Nutrition, Dietetics and Food Sciences (1996). Nutritional assessment. In:Dietitian's Pocket Book, pp36–47, Perth: School of Public Health, Curtin University of Technology
Deurenberg, P (1996). Limitation of the bioelectrical impedance method for the assessment of body fat in severe obesity. Am. J. Clin. Nutr., 64, (Suppl) 449S–452S.
Dionne, I, Despres, JP, Bouchard, C & Tremblay, A (1999). Gender differences in the effect of body composition on energy metabolism. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord., 23, 312–319.
Efron, B & Tibshirani, RJ (1993). An Introduction to the Bootstrap. Mongraphs on Statistics and Applied Probability, ed. DR Cox, DV Hinkley, N Reid, DB Rubin & BW Silverman, pp247–252, New York: Chapman & Hall
Ferraro, R & Ravussin, E (1992). Fat mass in predicting resting metabolic rate. Am. J. Clin. Nutr., 56, 460–461.
Garrow, JS & Webster, J (1985). Are pre-obese people energy thrifty?. Lancet, 1, 670–671.
Green, SB, Salkind, NJ & Akey, TM (2000). Univariate and multivariate analysis-of-variance techniques. In:Using SPSS for Windows: Analyzing and Understanding Data, 2nd edn, ed. CJ Owen, pp157–232, Upper Saddle River NJ: Prentice-Hall
Grunfeld, C, Pang, M, Shimizu, L, Shigenaga, JK, Jensen, P & Feingold, KR (1992). Resting energy expenditure, caloric intake, and short-term weight change in human immunodeficiency virus infection and the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Am. J. Clin. Nutr., 55, 455–460.
Harris, JA & Benedict, FG (1919). A Biometric Study of Basal Metabolism in Man, (publication no. 279), pp1–266, Washington, DC: Carnegie Institute of Washington
Heijligenberg, R, Romijn, JA, Westerterp, KR, Jonkers, CF, Prins, JM & Sauerwein, HP (1997). Total energy expenditure in juman immunodeficiency virus-infected men and healthy controls. Metabolism, 46, 1324–1326.
Hommes, MJ, Romijn, JA, Godfried, MH, Schattenkerk, JK, Buurman, WA, Endert, E & Sauerwein, HP (1990). Increased resting energy expenditure in human immunodeficiency virus-infected men. Metabolism, 39, 1186–1190.
Hommes, MJ, Romijn, JA, Endert, E & Sauerwein, HP (1991). Resting energy expenditure and substrate oxidation in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-infected asymptomatic men: HIV affects host metabolism in the early asymptomatic stage. Am. J. Clin. Nutr., 54, 311–315.
Jimenez-Exposito, MJ, Garcia-Lorda, P, Alonso-Villaverde, C, de Virgala, CM, Sola, R, Masana, L, Arija, V, Izquierdo, V & Salas-Salvado, J (1998). Effect of malabsorption on nutritional status and resting energy expenditure in HIV-infected patients. AIDS, 12, 1965–1972.
Kleinbaum, DG, Kupper, LL & Muller, KE (1988). Chapter 12 Regression diagnostics. In:Applied Regression Analysis and Other Multivariable Methods, 2nd edn, pp181–227, Boston: PWS-KENT
Kosmiski, LA, Kuritzkes, DR, Lichtenstein, KA, Glueck, DH, Gourley, PJ, Stamm, ER, Scherzinger, AL & Eckel, RH (2001). Fat distribution and metabolic changes are strongly correlated and energy expenditure is increased in the HIV lipodystrophy syndrome. AIDS, 15, 1993–2000.
Kotler, DP, Tierney, AR, Brenner, SK, Couture, S, Wang, J & Pierson-RN, J (1990). Preservation of short-term energy balance in clinically stable patients with AIDS. Am. J. Clin. Nutr., 51, 7–13.
Lukaski, HC & Bolonchuk, WW (1987). Theory and validation of the tetrapolar bioelectrical impedance method to assess human body composition. In:In Vivo Body Composition Studies, ed. KJ Ellis, S Yasamura & WD Morgan, pp410–414, London: Institute of Physical Medicine
Macallan, DC, Noble, C, Baldwin, C, Jebb, SA, Prentice, AM, Coward, WA, Sawyer, MB, McManus, TJ & Griffin, GE (1995). Energy expenditure and wasting in human immunodeficiency virus infection. New Engl. J. Med., 333, 83–88.
Melchior, JC, Salmon, D, Rigaud, D, Leport, C, Bouvet, E, Detruchis, P, Vilde, JL, Vachon, F, Coulaud, JP & Apfelbaum, M (1991). Resting energy expenditure is increased in stable, malnourished HIV-infected patients. Am. J. Clin. Nutr., 53, 437–441.
Melchior, JC, Raguin, G, Boulier, A, Bouvet, E, Rigaud, D, Matheron, S, Casalino, E, Vilde, JL, Vachon, F & Coulaud, JP (1993). Resting energy expenditure in human immunodeficiency virus-infected patients: comparison between patients with and without secondary infections. Am. J. Clin. Nutr., 57, 614–619.
Miao, YM, Bjarnason, I, Crane, R, Hayes, P & Gazard, B Normalization of intestinal permeability following antiretroviral therapy in HIV+ patients with diarrhoea. Sixth annual meeting of the British HIV association (BHIVA), 24–26 March 2000. Royal College of Physicians, Edinburgh, UK HIV Med., 1, 166–188, (Abstract 013)
Mifflin, MD, St-Jeor, ST, Hill, LA, Scott, BJ, Daugherty, SA & Koh, YO (1990). A new predictive equation for resting energy expenditure in healthy individuals. Am. J. Clin. Nutr., 51, 241–247.
Mulligan, K, Tai, VW & Schambelan, M (1997). Energy expenditure in human immunodeficiency virus infection. New Engl. J Med., 336, 70–71.
Nelson, KM, Weinsier, RL, Long, CL & Schutz, Y (1992). Prediction of resting energy expenditure from fat-free mass and fat mass. Am. J. Clin. Nutr., 56, 848–856.
Newsholme, EA & Leech, AR (1988). The integration of metabolism during starvation, refeeding and injury. In:Biochemistry for the Medical Sciences, pp356–561, Chicester: John Wiley
Nielsen, S, Hensrud, DD, Romanski, S, Levine, JA, Burguera, B & Jensen, MD (2000). Body composition and resting energy expenditure in humans: role of fat, fat-free mass and extracellular fluid. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord., 24, 1153–1157.
Poizot-Martin, I, Benourine, K, Philibert, P, Boulet, JM, Badetti, C, Tramier, M, Vollot, F, Dalmas, AM, Manelli, JC & Gastaut, JA (1994). Diet-induced thermogenesis in HIV infection. AIDS, 8, 501–504.
Ravussin, E & Bogardus, C (1989). Relationships of genetics, age, and physical fitness to daily energy expenditure and fuel utilization. Am. J. Clin. Nutr., 49, 968–975.
Ravussin, E, Lillioja, S, Anderson, TE, Christin, L & Bogardus, C (1986). Determinants of 24-hour energy expenditure in man. J. Clin. Invest., 78, 1568–1578.
Renard, E, Fabre, J, Paris, F, Reynes, J & Bringer, J (1999). A syndrome of body fat redistribution in HIV-1-infected patients: relationships to cortisol and catecholamines. Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf.), 51, 223–230.
Schofield, WN (1985). Predicting basal metabolic rate, new standards and review of previous work. Hum. Nutr. Clin. Nutr., 39, (Suppl) S5–S41.
Schwenk, A, Höffer-Belitz, E, Jung, B, Kremer, G, Burger, B, Salzberger, B, Diehl, V & Schrappe, M (1996). Resting energy expenditure, weight loss, and altered body composition in HIV infection. Nutrition, 12, 595–601.
Schwenk, A, Beisenherz, A, Kremer, G, Diehl, V, Salzberger, B & Fätkenheuer, G (1999). Bioelectrical impedance analysis in HIV-infected patients treated with triple antiretroviral treatment. Am. J. Clin. Nutr., 70, 867–873.
Sharpstone, DR, Murray, CP, Ross, HM, Hancock, MR, Phelan, MS, Crane, RC, Menzies, IS, Reaveley, DA, Lepri, AC, Nelson, MR & Gazzard, BG (1996a). Energy balance in asymptomatic HIV infection. AIDS, 10, 1377–1384.
Sharpstone, DR, Ross, HM & Gazzard, BG (1996b). The metabolic response to opportunistic infections in AIDS. AIDS, 10, 1529–1533.
Shevitz, AH, Knox, TA, Spiegelman, D, Roubenoff, R, Gorbach, SL & Skolnik, PR (1999). Elevated resting energy expenditure among HIV-seropositive persons receiving highly active antiretroviral therapy. AIDS, 13, 1351–1357.
Suttmann, U, Ockenga, J, Hoogestraat, L, Selberg, O, Schedel, I, Deicher, H & Muller, MJ (1993). Resting energy expenditure and weight loss in human immunodeficiency virus-infected patients. Metabolism, 42, 1173–1179.
Wadden, TA, Vogt, RA, Anderson, RE, Bartlett, SJ, Foster, GD, Kuehnel, RH, Wilk, J, Weinstock, R, Buckenmeyer, P, Berkowitz, RI & Steen, SN (1997). Exercise in the treatment of obesity: effects of four interventions on body composition, resting energy expenditure, appetite, and mood. J. Consult. Clin. Psychol., 65, 269–277.
Weir, JB (1949). New methods for calculating metabolic rate with special reference to protein metabolism. J. Physiol., 109, 1–9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Batterham, M., Morgan-Jones, J., Greenop, P. et al. Calculating energy requirements for men with HIV/AIDS in the era of highly active antiretroviral therapy. Eur J Clin Nutr 57, 209–217 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1601536
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1601536
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Food Security in the Context of HIV: Towards Harmonized Definitions and Indicators
AIDS and Behavior (2014)
-
Dietary intakes of HIV-infected adults in urban UK
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (2013)