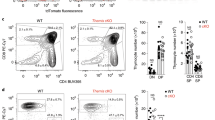
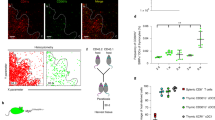
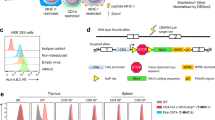
Abstract
The major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II transactivator (CIITA) is the 'master coactivator' of MHC class II genes. To identify new targets of CIITA, we analyzed cDNA microarrays of dendritic cells (DCs) from CIITA-deficient, MHC class II–deficient and control mice. We found the semaphorin receptor plexin-A1 was expressed in DCs, but not in other immune cells, and was strongly induced by CIITA. RNA interference by short hairpin RNA specific for plexin-A1, but not a single-nucleotide mutant, greatly reduced plexin-A1 expression and T cell stimulation by protein- or peptide-antigen–pulsed DCs.Plexin-A1 is not required for peptide binding to MHC. These data indicate involvement of plexin-A1 in T cell–DC interactions but not antigen processing or binding.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
Change history
22 August 2003
appended AOP PDF with erratum (will be corrected for print issue) and placed footnote in SGML
References
Cresswell, P. & Howard, J.C. Antigen recognition. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 9, 71–74 (1997).
van Der Merwe, P.A. & Davis, S.J. Immunology. The immunological synapse—a multitasking system. Science 295, 1479–1480 (2002).
Bromley, S.K. et al. The immunological synapse. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 19, 375–396 (2001).
Wulfing, C. & Rupp, F. Neuropilin-1: another neuronal molecule in the “immunological synapse”. Nat. Immunol. 3, 418–419 (2002).
Bismuth, G. & Boumsell, L. Controlling the immune system through semaphorins. Sci. STKE 2002, RE4 (2002).
Khan, A.A., Bose, C., Yam, L.S., Soloski, M.J. & Rupp, F. Physiological regulation of the immunological synapse by agrin. Science 292, 1681–1686 (2001).
Dickson, B.J. Molecular mechanisms of axon guidance. Science 298, 1959–1964 (2002).
Kumanogoh, A. et al. Class IV semaphorin Sema4A enhances T-cell activation and interacts with Tim-2. Nature 419, 629–633 (2002).
Shi, W. et al. The class IV semaphorin CD100 plays nonredundant roles in the immune system: defective B and T-cell activation in CD100-deficient mice. Immunity 13, 633–642 (2000).
Kikutani, H. & Kumanogoh, A. Semaphorins in interactions between T cells and antigen-presenting cells. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 3, 159–167 (2003).
Castellani, V. & Rougon, G. Control of semaphorin signaling. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 12, 532–541 (2002).
He, Z. & Tessier-Lavigne, M. Neuropilin is a receptor for the axonal chemorepellent semaphorin III. Cell 90, 739–751 (1997).
Kolodkin, A.L. et al. Neuropilin is a semaphorin III receptor. Cell 90, 753–762 (1997).
Tordjman, R. et al. A neuronal receptor, neuropilin-1, is essential for the initiation of the primary immune response. Nat. Immunol. 3, 477–482 (2002).
Ohta, K. et al. Plexin: a novel neuronal cell surface molecule that mediates cell adhesion via a homophilic binding mechanism in the presence of calcium ions. Neuron 14, 1189–1199 (1995).
Tamagnone, L. et al. Plexins are a large family of receptors for transmembrane, secreted, and GPI-anchored semaphorins in vertebrates. Cell 99, 71–80 (1999).
Tamagnone, L. & Comoglio, P.M. Signalling by semaphorin receptors: cell guidance and beyond. Trends Cell Biol. 10, 377–383 (2000).
Winberg, M.L. et al. Plexin A is a neuronal semaphorin receptor that controls axon guidance. Cell 95, 903–916 (1998).
Takahashi, T. et al. Plexin-neuropilin-1 complexes form functional semaphorin-3A receptors. Cell 99, 59–69 (1999).
Hu, H., Marton, T.F. & Goodman, C.S. Plexin B mediates axon guidance in Drosophila by simultaneously inhibiting active Rac and enhancing RhoA signaling. Neuron 32, 39–51 (2001).
Whitford, K.L. & Ghosh, A. Plexin signaling via off-track and rho family GTPases. Neuron 32, 1–3 (2001).
Comeau, M.R. et al. A poxvirus-encoded semaphorin induces cytokine production from monocytes and binds to a novel cellular semaphorin receptor, VESPR. Immunity 8, 473–482 (1998).
Granziero, L. et al. CD100/Plexin-B1 interactions sustain proliferation and survival of normal and leukemic CD5+ B lymphocytes. Blood 101, 1962–1969 (2003).
Ting, J.P. & Trowsdale, J. Genetic control of MHC class II expression. Cell 109, S21–33 (2002).
Reith, W. & Mach, B. The bare lymphocyte syndrome and the regulation of MHC expression. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 19, 331–373 (2001).
Taxman, D.J., Cressman, D.E. & Ting, J.P. Identification of class II transcriptional activator-induced genes by representational difference analysis: discoordinate regulation of the DNα/DOβ heterodimer. J. Immunol. 165, 1410–1416 (2000).
Guermonprez, P., Valladeau, J., Zitvogel, L., Thery, C. & Amigorena, S. Antigen presentation and T-cell stimulation by dendritic cells. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 20, 621–667 (2002).
Landmann, S. et al. Maturation of dendritic cells is accompanied by rapid transcriptional silencing of class II transactivator (CIITA) expression. J. Exp. Med. 194, 379–391. (2001).
Banchereau, J. et al. Immunobiology of dendritic cells. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 18, 767–811 (2000).
Mellman, I. & Steinman, R.M. Dendritic cells: specialized and regulated antigen processing machines. Cell 106, 255–258 (2001).
van Deventer, H.W. et al. Transfection of macrophage inflammatory protein 1α into B16 F10 melanoma cells inhibits growth of pulmonary metastases but not subcutaneous tumors. J. Immunol. 169, 1634–1639 (2002).
Grusby, M.J., Johnson, R.S., Papaioannou, V.E. & Glimcher, L.H. Depletion of CD4+ T cells in major histocompatibility complex class II-deficient mice. Science 253, 1417–1420 (1991).
Itoh-Lindstrom, Y. et al. Reduced IL-4-, lipopolysaccharide-, and IFN-γ-induced MHC class II expression in mice lacking class II transactivator due to targeted deletion of the GTP-binding domain. J. Immunol. 163, 2425–2431 (1999).
Gobin, S.J. et al. The RFX complex is crucial for the constitutive and CIITA-mediated transactivation of MHC class I and β2-microglobulin genes. Immunity 9, 531–541 (1998).
Gao, J.X. et al. Differentiation of monocytic cell clones into CD8α+ dendritic cells (DC) suggests that monocytes can be direct precursors for both CD8α+ and CD8α− DC in the mouse. J. Immunol. 170, 5927–5935 (2003).
Mallet-Designe, V.I. et al. Detection of low-avidity CD4+ T cells using recombinant artificial APC: following the antiovalbumin immune response. J. Immunol. 170, 123–131 (2003).
Yague, J. et al. The T-cell receptor: the α and β chains define idiotype, and antigen and MHC specificity. Cell 42, 81–87 (1985).
Rudensky, A.Y. et al. Intracellular assembly and transport of endogenous peptide-MHC class II complexes. Immunity 1, 585–594 (1994).
Nagarajan, U.M., Bushey, A. & Boss, J.M. Modulation of gene expression by the MHC class II transactivator. J. Immunol. 169, 5078–5088 (2002).
June Brickey, W. et al. Prolonged survival of class II transactivator-deficient cardiac allografts. Transplantation 74, 1341–138 (2002).
Martin, B.K. et al. Induction of MHC class I expression by the MHC class II transactivator CIITA. Immunity 6, 591–600 (1997).
Al-Alwan, M.M., Rowden, G., Lee, T.D. & West, K.A. Fascin is involved in the antigen presentation activity of mature dendritic cells. J. Immunol. 166, 338–345 (2001).
Swiercz, J.M., Kuner, R., Behrens, J. & Offermanns, S. Plexin-B1 directly interacts with PDZ-RhoGEF/LARG to regulate RhoA and growth cone morphology. Neuron 35, 51–63 (2002).
Driessens, M.H. et al. Plexin-B semaphorin receptors interact directly with active Rac and regulate the actin cytoskeleton by activating Rho. Curr. Biol. 11, 339–344 (2001).
Wong, A.W. et al. Regulation and specificity of MHC2TA promoter usage in human primary T lymphocytes and cell line. J. Immunol. 169, 3112–3119 (2002).
Brummelkamp, T.R., Bernards, R. & Agami, R. A system for stable expression of short interfering RNAs in mammalian cells. Science 296, 550–553 (2002).
Felix, N.J. et al. H2-DMα−/− mice show the importance of major histocompatibility complex-bound peptide in cardiac allograft rejection. J. Exp. Med. 192, 31–40 (2000).
Lich, J.D., Elliott, J.F. & Blum, J.S. Cytoplasmic processing is a prerequisite for presentation of an endogenous antigen by major histocompatibility complex class II proteins. J. Exp. Med. 191, 1513–1524 (2000).
Muhlethaler-Mottet, A., Otten, L.A., Steimle, V. & Mach, B. Expression of MHC class II molecules in different cellular and functional compartments is controlled by differential usage of multiple promoters of the transactivator CIITA. Embo J. 16, 2851–2860 (1997).
Acknowledgements
We thank S. Strittmatter for donation of the plexin-A1 antibody. This work was supported by grants AI29564, AI54309, NS34910 and DK38108 from the National Institutes of Health and grant RG1785 from the National Multiple Sclerosis Society to J.P.-Y.T. and National Institutes of Health grant A149589 to J.S.B.
*Note: In the version of this article originally published online, the ninth subheading in the Methods section was printed incorrectly. The correct subheading should read "Activation of T-cell hybridoma with 3B11 cells pulsed with OVA whole protein or peptide." This error has been corrected for the online and print versions of the article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wong, A., Brickey, W., Taxman, D. et al. CIITA-regulated plexin-A1 affects T-cell–dendritic cell interactions. Nat Immunol 4, 891–898 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/ni960
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ni960
This article is cited by
-
Development of potent class II transactivator gene delivery systems capable of inducing de novo MHC II expression in human cells, in vitro and ex vivo
Gene Therapy (2017)
-
Proteome dynamics during postnatal mouse corpus callosum development
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
Immunological functions of the neuropilins and plexins as receptors for semaphorins
Nature Reviews Immunology (2013)
-
Immune plexins and semaphorins: old proteins, new immune functions
Protein & Cell (2013)
-
Gene silencing of IL-12 in dendritic cells inhibits autoimmune arthritis
Journal of Translational Medicine (2012)