Abstract
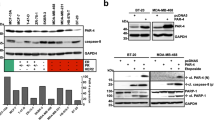
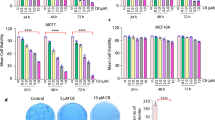
Antiapoptotic genes such as bcl-2 or xIAP may be responsible for resistance to apoptosis induced by cytotoxic drugs. The aim of this study was to investigate if downregulation of bcl-2 or xIAP by RNA interference (RNAi) would sensitize MCF-7 cells to etoposide and doxorubicin. FITC-siRNAs uptake was verified by fluorescence microscopy and downregulation of Bcl-2 or XIAP was confirmed by Western Blotting. Both siRNAs reduced the number of viable cells and increased cellular apoptosis. Treatment with siRNAs followed by treatment with etoposide or doxorubicin further reduced the number of viable cells, when compared to either of the treatments alone. Therefore, downregulation of bcl-2 or xIAP by RNAi enhances the effects of etoposide and doxorubicin.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Igney FH, Krammer PH . Death and anti-death: tumour resistance to apoptosis. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2:277–288.
Cory S, Adams JM . The Bcl2 family: regulators of the cellular life-or-death switch. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2:647–656.
Adams JM, Cory S . The Bcl-2 protein family: arbiters of cell survival. Science. 1998;281:1322–1326.
Salvesen GS, Duckett CS . IAP proteins: blocking the road to death's door. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2002;3:401–410.
Huang Z . Bcl-2 family proteins as targets for anticancer drug design. Oncogene. 2000;19:6627–6631.
Holcik M, Korneluk RG . XIAP, the guardian angel. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2001;2:550–556.
Verhagen AM, Coulson EJ, Vaux DL . Inhibitor of apoptosis proteins and their relatives: IAPs and other BIRPs. Genome Biol. 2001;2:3009.1–3009.10.
LaCasse EC, Baird S, Korneluk RG, et al. The inhibitors of apoptosis (IAPs) and their emerging role in cancer. Oncogene. 1998;17:3247–3259.
Wang J-L, Liu D, Zhang Z-J, et al. Structure-based discovery of an organic compound that binds Bcl-2 protein and induces apoptosis of tumor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2000;97:7124–7129.
Shangary S, Johnson DE . Recent advances in the development of anticancer agents targeting cell death inhibitors in the Bcl-2 protein family. Leukemia. 2003;17:1470–1481.
Pei XY, Dai Y, Grant S . The proteasome inhibitor bortezomib promotes mitochondrial injury and apoptosis induced by the small molecule Bcl-2 inhibitor HA14-1 in multiple myeloma cells. Leukemia. 2003;17:2036–2045.
Arnt CR, Chiorean MV, Heldebrant MP, et al. Synthetic Smac/DIABLO peptides enhance the effects of chemotherapeutic agents by binding XIAP and cIAP1 in situ. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:44236–44243.
Waterhouse PM, Wang MB, Lough T . Gene silencing as an adaptative defence against viruses. Nature. 2001;411:834–842.
Sharp PA . RNA interference-2001. Genes Dev. 2001;15:485–490.
Tuschl T . RNA interference and small interfering RNAs. Chembiochemistry. 2001;2:239–245.
Hammond SM, Caudy AA, Hannon GJ . Post-transcriptional gene silencing by double-stranded RNA. Nat Rev Genet. 2001;2:110–119.
Bosher JM, Labouesse M . RNA interference: genetic wand and genetic watchdog. Nat Cell Biol. 2000;2:E31–E36.
Bernstein E, Denli AM, Hannon GJ . The rest is silence. RNA. 2001;7:1509–1521.
Dykxhoorn DM, Novina CD, Sharp PA . Killing the messenger: short RNAs that silence gene expression. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2003;4:457–467.
Sullenger BA, Gilboa E . Emerging clinical applications of RNA. Nature. 2002;418:252–258.
Wilda M, Fuchs U, Wossmann W, et al. Killing of leukemic cells with BCR/ABL fusion gene by RNA interference (RNAi). Oncogene. 2002;21:5716–5724.
Scherr M, Battmer K, Winkler T, et al. Specific inhibition of bcr-abl gene expression by small interfering RNA. Blood. 2003;101:1566–1569.
Nieth C, Priebsch A, Stege A, et al. Modulation of the classical multidrug resistance (MDR) phenotype by RNA interference (RNAi). FEBS Lett. 2003;545:144–150.
Cioca DP, Aoki Y, Kiyosawa K . RNA interference is a functional pathway with therapeutic potential in human myeloid leukemia cell lines. Cancer Gene Ther. 2003;10:125–133.
Abdelrahim M, Samudio I, Smith III R, et al. Small inhibitory RNA duplexes for Sp1 mRNA block basal and estrogen-induced gene expression and cell cycle progression in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:28815–28822.
Abdelrahim M, Smith R, Safe S . Aryl hydrocarbon receptor gene silencing with small inhibitory RNA differentially modulates Ah-responsiveness in MCF-7 and HepG2 cancer cells. Mol Pharmacol. 2003;63:1373–1381.
Srinivasula SM, Gupta S, Datta P, et al. Inhibitor of apoptosis proteins are substrates for the mitochondrial serine protease Omi/HtrA2. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:31469–31472.
Friedrich K, Wieder T, Von Haefen C, et al. Overexpression of caspase-3 restores sensitivity for drug-induced apoptosis in breast cancer cell lines with acquired drug resistance. Oncogene. 2001;20:2749–2760.
Yang X-H, Sladek TL, Liu X, et al. Reconstitution of caspase 3 sensitizes MCF-7 breast cancer cells to doxorubicin- and etoposide-induced apoptosis. Cancer Res. 2001;61:348–354.
Vasconcelos MH, Beleza SS, Quirk C, et al. Limited synergistic effect of antisense oligonucleotides against bcr-abl and transferrin receptor mRNA in leukemic cells in culture. Cancer Lett. 2000;152:135–143.
Riedl SJ, Renatus M, Schwarzenbacher R, et al. Structural basis for the inhibition of caspase-3 by XIAP. Cell. 2001;104:791–800.
Srinivasula SM, Hegde R, Saleh A, et al. A conserved XIAP-interaction motif in caspase-9 and Smac/DIABLO regulates caspase activity and apoptosis. Nature. 2001;410:112–116.
Bilim V, Kasahara T, Hara N, et al. Role of XIAP in the malignant phenotype of transitional cell cancer (TCC) and the therapeutic activity of XIAP antisense oligonucleotides against multidrug-resistant TCC in vitro. Int J Cancer. 2003;103:29–37.
Sasaki H, Sheng Y, Kotsuji F, et al. Down-regulation of X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein induces apoptosis in chemoresistant human ovarian cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2000;60:5659–5666.
Harlin H, Reffey SB, Duckett CS, et al. Characterization of XIAP-deficient mice. Mol Cell Biol. 2001;21:3604–3608.
Nakayama K, Nakayama K-I, Negishi I, et al. Targeted disruption of Bcl-2αβ in mice: occurrence of gray hair, polycystic kidney disease, and lymphocytopenia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1994;91:3700–3704.
Borner C . Diminished cell proliferation associated with the death-protective activity of Bcl-2. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:12695–12698.
Konopleva M, Tari AM, Estrov Z, et al. Liposomal Bcl-2 antisense oligonucleotides enhance proliferation, sensitize acute myeloid leukemia to cytosine-arabinoside, and induce apoptosis independent of other antiapoptotic proteins. Blood. 2000;95:3929–3938.
Levkau B, Garton KJ, Ferri N, et al. xIAP induces cell-cycle arrest and activates nuclear factor-kB. Circul Res. 2001;88:282–290.
de Almodovar CR, Ruiz-Ruiz C, Munoz-Pinedo C, et al. The differential sensitivity of Bcl-2-overexpressing human breast tumor cells to TRAIL or doxorubicin-induced apoptosis is dependent on Bcl-2 protein levels. Oncogene. 2001;20:7128–7133.
Davis JM, Navolanic PM, Weinstein-Oppenheimer CR, et al. Raf-1 and bcl-2 induce distinct and common pathways that contribute to breast cancer drug resistance. Clin Cancer Res. 2003;9:1161–1170.
Piché A, Grim J, Rancourt C, et al. Modulation of Bcl-2 protein levels by an intracellular anti-Bcl-2 single-chain antibody increases drug-induced cytotoxicity in the breast cancer cell line MCF-7. Cancer Res. 1998;58:2134–2140.
Teixeira C, Reed JC, Pratt MAC . Estrogen promotes chemotherapeutic drug resistance by a mechanism involving Bcl-2 proto-oncogene expression in human breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 1995;55:3902–3907.
Del Bufalo D, Biroccio A, Trisciuoglio D, et al. Bcl-2 has differing effects on the sensitivity of breast cancer cells depending on the antineoplastic drug used. Eur J Cancer. 2002;38:2455–2462.
Holcik M, Yeh C, Korneluk RG, et al. Translational upregulation of X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis (XIAP) increases resistance to radiation induced cell death. Oncogene. 2000;19:4174–4177.
Acknowledgements
We thank Catarina A Silva (MD) for technical support in the initial experiments. This work was supported by FCT (Portugal), project POCTI/FCB/42754/2001 — Programa Operacional “Ciência, Tecnologia, Inovação” do Quadro Comunitário de Apoio (QCA) III, including FEDER funding. Raquel T Lima is a recipient of a young researcher grant from the referred project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lima, R., Martins, L., Guimarães, J. et al. Specific downregulation of bcl-2 and xIAP by RNAi enhances the effects of chemotherapeutic agents in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Cancer Gene Ther 11, 309–316 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cgt.7700706
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cgt.7700706
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Increased migration and motility in XIAP-null cells mediated by the C-RAF protein kinase
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
A small-molecule ARTS mimetic promotes apoptosis through degradation of both XIAP and Bcl-2
Cell Death & Disease (2020)
-
Pharmacological targets of breast cancer stem cells: a review
Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology (2018)
-
XIAP BIR domain suppresses miR-200a expression and subsequently promotes EGFR protein translation and anchorage-independent growth of bladder cancer cell
Journal of Hematology & Oncology (2017)
-
Time depended Bcl-2 inhibition might be useful for a targeted drug therapy
Cancer Cell International (2015)